What Does The Research Say About Pcos And Diabetes
Researchers in Australia collected data from over 8,000 women and found that those who had PCOS were 4 to 8.8 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than women who didnt have PCOS. Obesity was an important risk factor.
According to older research, up to approximately 27 percent of premenopausal women with type 2 diabetes also have PCOS.
A 2017 study of Danish women found that those with PCOS were four times as likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Women with PCOS also tended to be diagnosed with diabetes 4 years earlier than women without PCOS.
With this recognized connection, experts recommend that women with PCOS get routinely screened for type 2 diabetes earlier and more often than women without PCOS.
According to the Australian study, pregnant women with PCOS are nearly three times as likely as women without it to develop gestational diabetes. As a pregnant women, should pregnant women undergo regular screening for gestational diabetes?
Multiple studies have shown that PCOS and its symptoms are also frequently found in women with type 1 diabetes.
Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is extremely common in the U.S. According to the CDCs National Diabetes Statistics Report, 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes, and 1 in 3 Americans have prediabetes, or high blood sugar.
Anyone can get type 1 diabetes, but the condition is generally diagnosed around ages 13 to 14, the CDC says. In fact, type 1 diabetes used to be referred to as Juvenile Onset Diabetes because it is often diagnosed in young children. But adults over the age of 40 can develop type 1 diabetes, too, its just typically more rare.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is often seen in individuals who are middle-aged or older. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of the disease, or are overweight or obese. Although its generally seen in individuals aged 45 or older, more and more children and teens are developing type 2 diabetes, the CDC says.
Typically, type 1 diabetes is confirmed with antibody screening, Dr. Block says. This is a blood test that looks for islet antibodies or GAD antibodies. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can also be diagnosed with the A1C test, or a blood test that examines your average blood sugar levels over the course of several months. An A1C level of 6.5 or higher indicates diabetesbut more tests are typically required to determine the type of diabetes you have.
Causes of type 1 diabetes
Causes of type 2 diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Complications
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
- Damage to macrovascular and microvascular blood vessels
- Type 3 diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
- Damage to macrovascular and microvascular blood vessels
- Type 3 diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Sweetener For Type 2 Diabetes
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Rick Factors: Who Is Affected
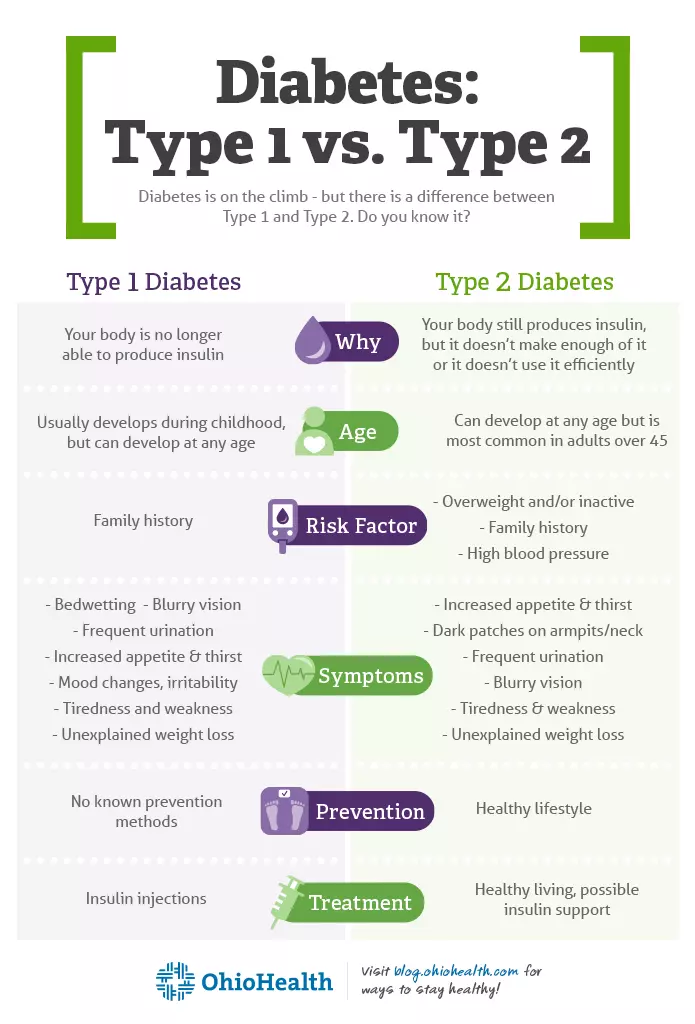
Only about 5% to 10% of diagnosed diabetes cases are type 1. The disease is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can technically strike at any age. Scientists do not know yet exactly what causes type 1 diabetes but suspect the disease involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors.
An overweight person who does not exercise, is over 30, and/or has close relatives who have type 2 diabetes, runs a very high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Higher-risk ethnic groups include African Americans, Latinos and Hispanics, Native Americans, Alaskan Natives, Asians, and those with Pacific Islander American heritage.
People are more likely to get diabetes if they smoke, have high blood pressure or cholesterol, or, in women, if they had gestational diabetes or gave birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds. A free diabetes risk test is provided by Diabetes.org and only takes a few minutes to complete.
Also Check: What Types Of Diabetes Are There
Main Difference Between Type 1 And 2 Diabetes
Why Is Type 1 Worse Than Type 2 In Covid
Generally a Type 1 sufferer is likely to have had Diabetes for much longer than a person with Type 2. The longer youve had Diabetes, the more likely you would be prone to complications, including damage to the heart and kidneys.
With Type 1, the cells that make insulin are being destroyed by the immune system. This is different from Type 2, which is not a disease of the immune system. And compromised immune systems are already known to be at great risk from Covid-19.
Blood sugar levels are, on average, higher in people with Type 1 than with Type 2 Diabetes.
People with Diabetes who contract COVID-19 are clearly at a greater risk of worse outcomes, including death. In light of the vast numbers of Diabetes sufferers worldwide, they represent a worryingly large and vulnerable proportion of the COVID-19 population.
For people with Diabetes, poorer prognosis is the consequence of hyperglycaemia and comorbidities in particular, hypertension, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
Read Also: How To Use Diabetes Monitor
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
Also Check: Does Cialis Work For Diabetics
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy.
When you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose and sends that to your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells, which use it for energy.
When you have diabetes and donât get treatment, your body doesnât use insulin like it should. Too much glucose stays in your blood, a condition usually called high blood sugar. This can cause health problems that may be serious or even life-threatening.
Thereâs no cure for diabetes. But with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can live a long, healthy life.
Diabetes comes in different forms, depending on the cause.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision and extreme tiredness.
Type 2 symptoms appear gradually and are more subtle than those seen with type 1. This makes catching the onset of type 2 diabetes harder to recognize for early treatment. Symptoms include unexpected weight loss, blurred vision, feeling tired or sick more frequently, more frequent urination . Higher levels of thirst, frequent infections and slower healing of cuts and scrapes.
Read Also: What Is The Best Thing For Diabetes
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
Check Your Diabetes Risk:
By understanding your own personal risk, you can access support to help take steps to reduce your chances of developing type 2 diabetes. Firstly, head to the free online Know Your Risk tool. Once completed, the tool advises you on your risk and suggests next steps. Those in England who are advised to be at moderate or high risk may then directly sign up to the Healthier You: NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme .
Also Check: Psoriasis And Diabetes Type 1
Is Diagnosing Diabetes Types 1 And 2 Similar
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
“The blood sugar testing we do to diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes is very similar to the testing we do for type 2 diabetes,” says Drincic. “We can do a blood test that looks for antibodies. That tells us if it is type 1 or 2.” In type 1 diabetes, the immune system makes antibodies that act against the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, and these antibodies can be detected in a blood test. Your doctor may suspect type 2 diabetes based on your symptoms and risk factors, such as obesity and family history.
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes
To diagnose type 1 diabetes youll need to get blood tests done, one of which is called an A1C screening. A1C screenings measure your blood sugar levels from the past two to three months and can be used to diagnose type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Life Line Screening also offers an A1C screening from the privacy of you own home through our home tests. You can learn more here.
You May Like: Reversing Type 2 Diabetes With Ketogenic Diet
What Does Diabetes Do To The Body
People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin, and as a result sugar builds up in the blood instead of going into the cells, where it’s needed for energy. In type 1 diabetes, high blood sugar causes symptoms like thirst, hunger, and fatigue and can cause devastating consequences, including damage to the nerves, blood vessels, and internal organs. The same scary complications of diabetes appear in type 2 as well. The difference is that people with type 2 diabetes still produce insulin their bodies just become less sensitive to it over time, which is what causes the complications.
The Difference Between Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus
There are several differences between type1 and type2 diabetes mellitus. First, type 1 diabetes most often develops in young children while type2 diabetes can occur at any age. Additionally, type1 patients are dependent on insulin because their pancreas does not produce any. Those with type2 may produce some insulin in their pancreas, but they do not produce enough, or it is not used efficiently in their bodies.
Another difference between the two types is that those with type one can experience episodes of low blood sugar as well as high levels while those with type2 rarely do. Moreover, type1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but, in many cases, type2 can be avoided. Finally, there are many more cases of type2 diabetes are documented.
Read Also: Grocery Shopping List For Type 2 Diabetes
Diagnosis Is The Same
Diagnosing type 1 and type 2 diabetes is based on tests to determine how high your blood sugar is. There are several different types of tests, including the A1C test, a blood test which looks at your average blood-sugar levels over the past two to three months, and a fasting plasma glucose test, a blood test which measures levels after you’ve been fasting for at least eight hours.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, he or she may also order certain antibody tests.
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
The majority of people who develop Type 1 diabetes will be on the thinner side. It is extremely rare to meet a Type 1 diabetic who is overweight. On the other hand, the majority of people with Type 2 diabetes will be overweight. The high-fat content in the body also plays a major role in developing insulin resistance.
Type 1 diabetes usually presents with symptoms much earlier in life. In most cases, the diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes will be made between ages two and fifteen. Whereas the majority of Type 2 diabetes cases present when the individual is over 50 years of age.The symptoms in Type 1 diabetes generally present suddenly. The individual may present with a sudden fever, severe dehydration, frequent urination, ketones in the urine, or even be in a coma, and medical tests will reveal a lack of insulin in the body.
However, with Type 2 diabetes, the symptoms may be vague, and the diagnosis can be delayed for a few months. Some individuals may develop a milder form of diabetes, called prediabetes, a few months or years before developing the full onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: Does Diabetes Affect Your Stomach
Type 1 And Type 2 Differences
Below is a guide to some of the main differences between type 1 and type 2.
|
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to make enough insulin or the insulin you do make doesnt work properly. |
|
|
We dont currently know what causes type 1 diabetes. |
We know some things can put you at risk of having type 2 like weight and ethnicity. |
|
|
The symptoms for type 1 appear more quickly. |
Type 2 symptoms can be easier to miss because they appear more slowly. |
|
|
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin. |
|
|
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but there is evidence to say in many cases it can be prevented and put into remission. |
Treatment For Type 1 And Type 2
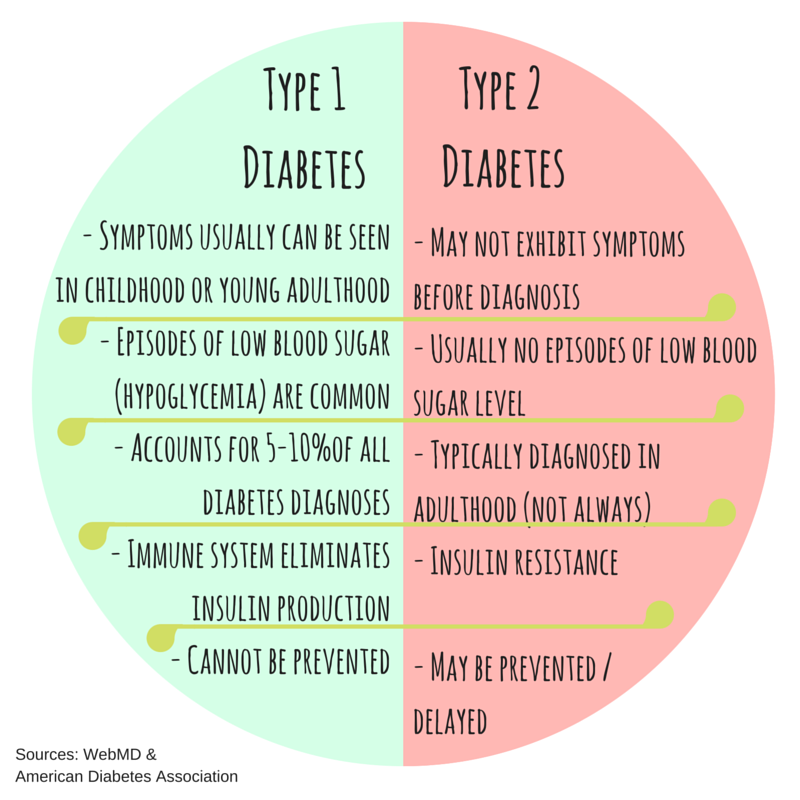
Type I is primarily cured through regular insulin therapy. Since your pancreas is unable to produce insulin on its own, you can inject insulin into your body via insulin injections. Whereas, in the case of Type 2, other treatments such as regular medication, healthy eating, and regular exercises are applicable. That said, Treatment for both Type 1 and Type 2 involved lowering the blood sugar level. Therefore, most treatments for Type II are also effective in treating Type 1 as well.
Also Check: Where Is The Best Place To Inject Insulin