How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
What Vegetables Are Good For People With Diabetes And Which Arent
Vegetables are an important food group to include in any healthy diet, and a diabetes diet is no exception. Veggies are full of fiber and nutrients, and nonstarchy varieties are low in carbohydrates a win for people with diabetes who want to gain control over their blood sugar level, Massey says.
As for packaging, frozen veggies without sauce are just as nutritious as fresh, and even low-sodium canned veggies can be a good choice if youre in a pinch. Just be sure to watch your sodium intake to avoid high blood pressure, and consider draining and rinsing salted canned veggies before eating, per the ADA. If possible, opt for low-sodium or sodium-free canned veggies if going that route.
Follow this general rule: Aim to fill one-half your plate with nonstarchy veggies, as recommended by the NIDDK. And if youre craving mashed white potatoes, try mashed cauliflower, Massey suggests.
Best veggie options, according to the ADA:
- Greens, like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard
- Cruciferous veggies, like broccoli and cauliflower
- Cucumbers
Aim to fill one-quarter your plate with starchy veggies, which count toward your daily carb goal.
Veggies to enjoy in moderation, as the ADA notes:
RELATED: Sweet Potatoes vs. White Potatoes: How Do They Compare?
Types Of Diabetes: Which Are You
Chances are, youve heard people talk about diabetes as if its a diagnosis where everyone living with diabetes shares the same symptoms, traits, and complications. In casual conversation, thats understandable since each type of diabetes is related to problems with blood glucose. However, if youre living with diabetes, you might need more information to work with even talking about diabetes as a disease with two types is an oversimplification.
Are you wondering where you can learn more about the different types of diabetes? Youre in luck: in this article, the pros at ADS will help you learn more about all four types of diabetes and their defining factors.
Also Check: What To Do If You Think Your Diabetic
Conditions Linked With Type 1 Diabetes
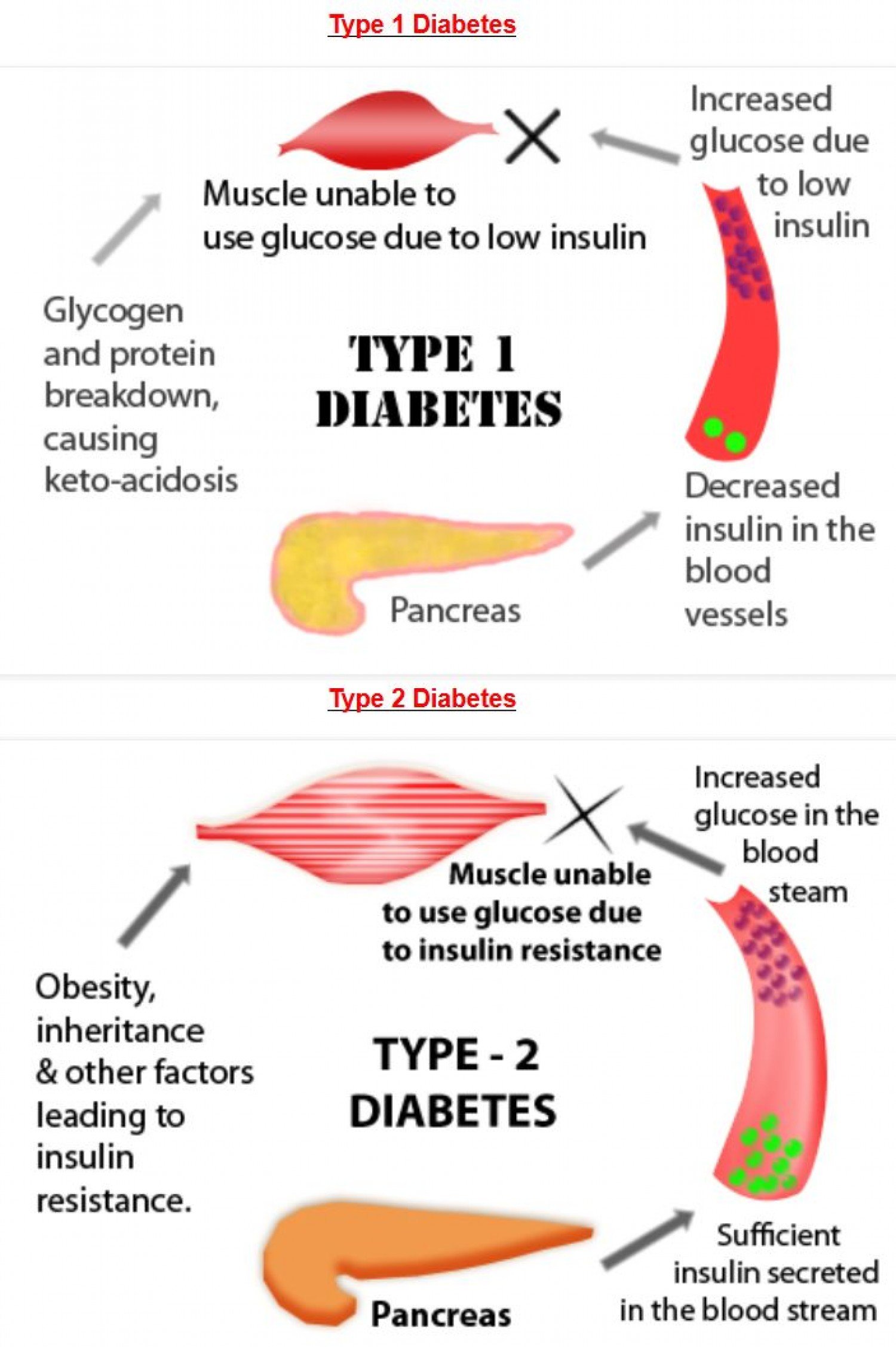
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, meaning that the bodys immune system mistakes its own cells for invading pathogens that need to be destroyed.
People with type 1 diabetes tend to have a higher risk of having other autoimmune diseases than the rest of the population.
Other autoimmune diseases include:
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
Why Was This Classification Developed
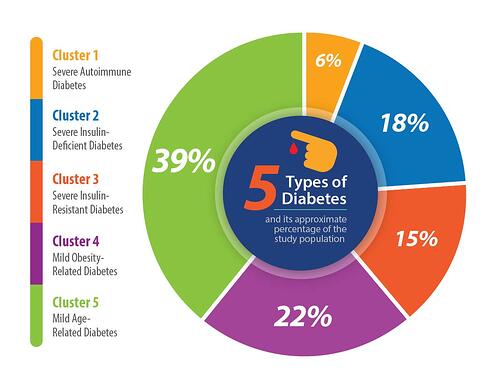
Dr. Groop and his team analyzed data from a number of diabetes patient registries to do their research. The number of patients involved in the analysis was more than 13,000. For all of the patients, the researchers isolated measurements of a number of variables, including insulin resistance, insulin secretion, blood sugar levels, age and onset of illness.
The results of their data analysis suggested that there should be five classifications of diabetes two mild types and three severe types.
Also Check: Who Buys Diabetic Testing Supplies
Idf Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition 2021
Get the latest national, regional and global diabetes data
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas is no longer able to make insulin, or when the body cannot make good use of the insulin it produces.
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas, that acts like a key to let glucose from the food we eat pass from the blood stream into the cells in the body to produce energy. All carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose in the blood. Insulin helps glucose get into the cells.
Not being able to produce insulin or use it effectively leads to raised glucose levels in the blood . Over the long-term high glucose levels are associated with damage to the body and failure of various organs and tissues.
Types of diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes type 1, type 2 and gestational.
Gestational Diabetes Insipidus Can Be Cured
This form of DI is the only version that can actually be cured. It also targets one specific population demographic: pregnant women. Thats because gestational diabetes insipidus can only occur when placental enzymes interact with the ADH that a mothers body produces. The enzymes interfere with the communication systems between the kidneys and the hormone and will even counteract the hormone to reduce the amount there is within the body.
The good news for expectant mothers is this: virtually all cases of gestational DI will resolve themselves in 6 weeks or less after the pregnancy. The bad news is that the extreme thirst and frequent need to urinate is probably not going to go away. Gestational diabetes mellitus is also a threat, which is why when the symptoms of DI are experienced, an immediate examination should be scheduled.
Treatment options may include the addition of Desmopressin, but many doctors will only prescribe the synthetic hormone if the symptoms are very bothersome. Many women simply increase their water intake to prevent dehydration and are monitored by their doctors to prevent disease development.
Also Check: How Long Do Insulin Pens Last
Maturity Onset Diabetes Of The Young
MODY is a rare form of diabetes which is different from both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and runs strongly in families. MODY is caused by a mutation in a single gene. If a parent has this gene mutation, any child they have, has a 50 per cent chance of inheriting it from them. If a child does inherit the mutation they will generally go on to develop MODY before theyre 25, whatever their weight, lifestyle, ethnic group etc.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition. It happens when your liver breaks down fat to use as energy because theres not enough insulin and therefore glucose isnt being used as an energy source. Fat is broken down by the liver into a fuel called ketones. The formation and use of ketones is a normal process if it has been a long time since your last meal and your body needs fuel. Ketones are a problem when your fat is broken down too fast for your body to process and they build up in your blood. This makes your blood acidic, which is a condition called ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis can be the result of uncontrolled Type 1 diabetes and less commonly, Type 2 diabetes.Diabetic ketoacidosis is diagnosed by the presence of ketones in your urine or blood and a basic metabolic panel. The condition develops over several hours and can cause coma and possibly even death.
Recommended Reading: How To Give Insulin Injection
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Also Check: Gestational Diabetes Test At Home
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
People who have type 2 diabetes may not know it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Some people don’t have any symptoms at all.
But when a person gets type 2 diabetes, he or she may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- feel tired all the time because the body can’t use sugar for energy properly
Also, people whose bodies are having problems using insulin or who are overweight may notice something called acanthosis nigricans. This can cause a dark ring around the neck that doesn’t wash off, as well as thick, dark, velvety skin under the arms, in between fingers and toes, between the legs, or on elbows and knees. This skin darkening can lighten over time with improvement in insulin resistance.
In addition, girls with insulin resistance may have polycystic ovary syndrome . In PCOS, the ovaries get bigger and develop fluid-filled sacs called cysts. Girls with this condition often have irregular periods or may stop having periods, and they might have excess facial and body hair.
How Many Types Of Diabetes Are There Two Five Or Eleven
More specific classifications for the disease could lead to more personalized treatments in the future. Is it time?
Diabetes is normally split into two categories: type 1 and type 2. But a group of scientists from Sweden and Finland say diabetes is actually five separate diseases. More specific classifications for the disease could lead to more personalized treatments in the future. Knowing which of these 5 categories of diabetes your patients have can be a benefit in choosing the treatment.
We know that each of the five proposed categories are genetically distinct. Their signs and symptoms can vary by age, weight, insulin resistance, how much insulin they can produce, or if the diabetes is caused by an autoimmune disorder.
This new classification of diabetes can be the first step toward personalized treatment of diabetes. Existing treatment guidelines are limited by the fact they respond to poor metabolic control when it has developed, but do not have the means to predict which patients will need intensified treatment.
This study moves us toward a more clinically useful diagnosis, and represents an important step toward personalized treatment of diabetes as our current diagnostics and classification of diabetes are unable to predict future complications or choice of treatments. We know that diabetes is a progressive disease and the type of diabetes changes as a person gets older, which means that the patient will need probably need new drugs that work differently.
Read Also: Medicare Requirements For Diabetic Shoes
Understanding Diabetes From Other Causes
In addition to type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, a small minority of people develop specific types of diabetes due to other causes. This includes:
- Monogenic diabetes syndromes, such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Diseases of the exocrine pancreas, such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis
- Drug or chemical-induced diabetes, such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS or after organ transplantation
Because these types of diabetes are rare, they are often misdiagnosed as other types of diabetes. You can learn more about these types of diabetes in the Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes section in the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. If you think you might have one of these types, be sure to talk with your doctor.
Which Type Of Diabetes Do I Have
In some cases, it may not be clear which type of diabetes you have. If your doctor cannot be sure which type of diabetes you have, they may run one or more tests to help determine your diabetes type
Learn about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
There are a number of different types of diabetes. In this video we look at 5 of the most common types of diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes amongst adults about 85% of people with diabetes in the UK have type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the second most common approximately 15% of people with diabetes in the UK have type 1. There are also other less common types of diabetes including gestational diabetes, LADA and MODY.
The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, meaning that most people who develop type 2 diabetes are usually middle aged or older. However, type 2 diabetes can develop earlier in adulthood or even childhood. Diabetes UK reports that obesity accounts for over 80% of the overall risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Other risk factors include having a close family member with type 2 diabetes, being of African/Caribbea, South Asian or Middle Eastern descent, or having high blood pressure and/or cholesterol. Type 2 diabetes can be treated with diet and exercise alone, or with tablets, insulin or other injectable medication.
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes come on slowly and may take months or years to appear.
You May Like: Cerave Moisturizing Cream For Diabetics Dry Skin
Conditions Which Can Lead To Diabetes
Some conditions, including genetic syndromes and surgery, can lead to high blood glucose levels and therefore diabetes.
Such types of diabetes account for around 1 to 2% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes.
Examples of such conditions include:
- Glucagonoma a condition in which the body produces too much of the hormone glucagon
- Chronic pancreatitis a condition which causes inflammation of the pancreas
- Cystic fibrosis a genetic condition that causes mucus to build up in the lungs and digestive system
- Pancreatectomy surgical removal of the pancreas
How To Lower Your Risk Of Diabetes
You can control some but not all of the risk factors of the four types of diabetes. However, if you have any of these risk factors, discuss your diabetes risk with your healthcare provider. The earlier you can intervene, the better, explains Nilem Patel, MD, an endocrinologist in Los Angeles, California, who is affiliated with Adventist Health-White Memorial. In general, youre trying to fend off the complications of diabetes as long as you can, she says.
Along with glucose management, these steps can help:
Today, a wide range of computerized diabetes devices are available to help people better manage their blood sugar levels while research toward a cure for diabetes marches forward, Saenz says. Advances in technology include continuous glucose monitors, smart insulin pens, combination CGM-insulin pumps, and even mobile apps.
RELATED: How to get free diabetic supplies
But its still important to use the technology correctly and remain compliant with the diabetes care plan that your healthcare team helps you develop. The complications from diabetes are very real, but tight management of your blood sugar levels can help you avoid them longer.
Read Also: How To Cure Early Signs Of Diabetes
When Should I Call My Doctor
If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
Then Why Do People Think Covid
A common phrase in the research community is correlation does not equal causation. This is a common error in many media headlines taking two things that happen to exist at the same time and assuming that one is causing the other.
In this case, it is understandable that people who recently experienced a COVID-19 infection and were later diagnosed with T1D think that the COVID caused the T1D. But as we know from our understanding of autoantibodies, these people were most likely already developing T1D.
Again, the CDCs January 2022 report on risk for newly diagnosed diabetes in children who have had COVID-19 did not adequately explain this science, leading to a severe misunderstanding in media coverage. And most media reports also do not differentiate between types of diabetes.
Heres where more questions get raised, though. There is very early-stage research that COVID-19 may have some sort of impact on beta cells the cells within the pancreas that produce insulin. This does not equate to an immediate T1D diagnosis, but it does raise questions that further research will need to answer in the coming years about the impact of COVID-19 on our bodies.
Two specific studies have come out looking at what happens to the beta cells in someone who has had COVID-19. However, neither study was done on people who have been diagnosed with T1D after having COVID.
Read Also: How Much Does It Cost To Make Insulin
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.