Determining The Right A1c Goal For You
Just because a normal blood sugar range of 70 to 130 mg/dL is considered the healthiest doesnt necessarily mean thats the appropriate goal range for you especially if you have type 1 diabetes, or take insulin as a person with type 2 diabetes.
The reason this may not be the right goal for you is that extremely tight blood sugar management in people taking insulin can potentially lead to frequent low blood sugars which can be dangerous.
Achieving extremely tight blood sugar management, like a range of 70 to 130 mg/dL, also often requires a strict nutrition plan, more frequent than usual blood sugar monitoring, precise medication management, and most importantly, years of experience studying your blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Targets In People With Diabetes
In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels are too high, either because the individual isn’t making any insulin , or isn’t able to make or use insulin efficiently . As a result, glucose levels then remain elevated in the blood and fuel can’t enter cells.
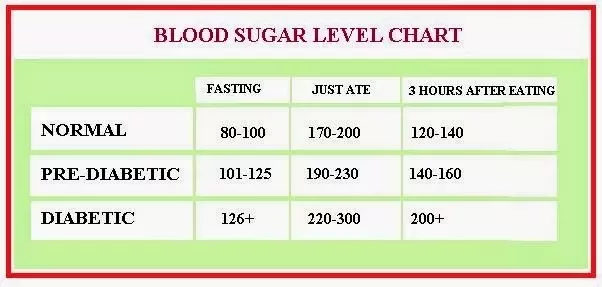
But generally, according to the ADA , for most non-pregnant adults with diabetes the fasting blood sugar target range should be in the range of between 80 and 130 mg/DL. Meanwhile, the ADA suggests the after-meal goal about two hours after eating for the same subset of patients should be less than 180 mg/DL.
Overall, eating plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity alongside medication can all help stabilize and maintain normal blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
For pregnant women who have pre-existing diabetes or develop diabetes during pregnancy, ADA guidelines are generally lower. Fasting glucose targets for this population should be less than 95 mg/DL, while they suggest that the after-meal goal about two hours after eating should be below 120 mg/DL.
Does A Blood Sugar Spike Mean You Have Diabetes
Occasional high spikes donât mean you have diabetes. Itâs normal for your blood sugar to go up after eating a meal high in carbohydrates or even due to lifestyle habits and events. Besides food, your blood sugar can be affected by stress, lack of sleep, age, menstrual cycle, physical activity, and even being sick.
What affects one person’s blood sugar may also affect yours differently. We can all have different responses to food, so monitoring the overall trend of your blood sugar gives you the most insight into your overall health.
However, while infrequent spikes aren’t a problem, if they happen more regularly, it’s time to take a closer look at what’s contributing.
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/mitigate-high-glucose-spikes”> how to mitigate glucose spikes to avoid fat storage< /a> < /p>
Don’t Miss: How To Get Diabetic Shoes Through Medicare
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieve closer to normal blood sugar levels.
If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
Read Also: How To Use Insulin Flexpen
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Your blood sugar, or glucose, level is found in your blood and serves as your main source of energy. During digestion, carbohydrates, which are sugars, starches, and fiber, are changed into glucose. Your body then uses this as energy, or stores whatever isn’t used in your cells for later use.
Your blood sugar is influenced by the food you eat, your age, stress, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol use. It is also impacted by heart issues or diabetes, a group of conditions where too much glucose builds up in the bloodstream.
Danie Drankwalter / Verywell
This article explores the range of glucose levels an individual may experience after eating. It will also cover how different types of food impact blood sugar, as well as how to manage glucose levels.
Why They Happen And How To Try And Reduce Them If You Live With Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes requires you to regularly check your blood sugar levels before you eat. However, we may not always consider what happens to our sugar levels immediately after we eat where it is very normal for people who dont have diabetes, let alone those who do, to temporarily have high sugar levels. Given that having high sugar levels can give you symptoms like thirst, tiredness and needing to go to the toilet a lot, learning about ways to try and reduce spikes in your sugar levels after meals may make a difference to your overall health and wellbeing.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Diabetes Insulin Cost
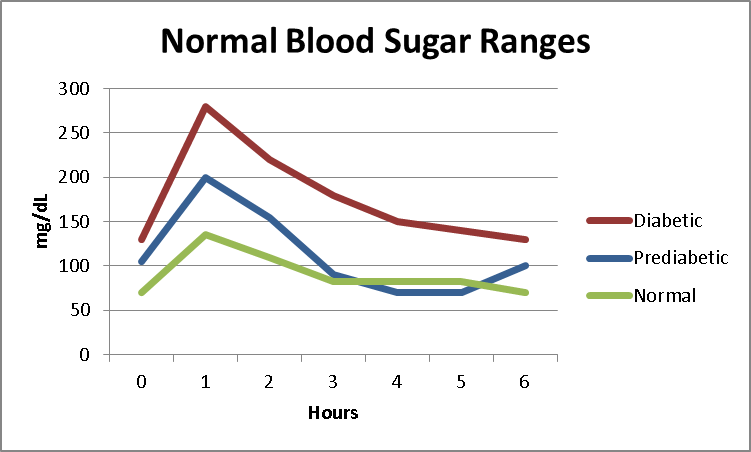
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal.
Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : Less than 100 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after a meal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- 2-3 hours after eating: Less than 100 mg/dL
Blood Sugar Levels 2 Hours After Youve Eaten
Many foods have types of carbohydrates called starches and sugars. When you eat foods with these types of carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is a type of simple sugar, and releases the glucose into your bloodstream. Aside from glucose produced by your liver, food is the main source of plasma glucose.
Two hours after eating, your blood sugar levels rise. They rise more when you eat more carbohydrates, when you do not eat fiber, fat, or protein with your carbs, and when you eat certain types of carbohydrates, such as refined sugars and starches.
These are target values from The Joslin Diabetes Center, which include levels for people with diabetes:
| When Measured |
|---|
You May Like: Freestyle Libre With Insulin Pump
How Do I Detect Spikes In My Sugar Levels
The exact timing of blood sugar spikes can vary from person to person and meal to meal. However, on average, the post-meal peaks tend to be about one hour and 15 minutes after starting a meal.
The best way to measure post-meal patterns is by using a continuous glucose monitor or Flash monitors. These devices can give you a clear view, including graphs, of what happens with the glucose levels after meals without the need for finger pricking . You can ask your diabetes health team if they are available for you as they are not available to everybody.
If you are not using a CGM, then please speak to your healthcare team about the best way to do this for you with finger prick testing.
How do I know it is a spike?
There is no universal answer or specific guidelines on when a sugar level is too high after meals. However, if post-meal readings are consistently above your target range , then you should discuss whether it would be beneficial for you to address these spikes and how to do this, with your healthcare team .
If you are reviewing your post-breakfast sugar levels, you should also be aware of changes in your hormones in the morning, which cause increases in sugar levels . This Digibete video may help.
Some ways to reduce blood sugar spikes after meals
1. Choose low glycaemic index foods
When blood sugar levels are low or hypoglycaemic we need high glycaemic index foods , such as dextrose tablets or juice, that are absorbed quickly to raise our levels and to treat the hypo.
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Corn On The Cob
Causes Of High Blood Sugar
Common causes of high blood sugar in people with diabetes include:
- being unwell
- eating too much sugary or starchy food
- being less active than usual
- missing doses of diabetes medicine
You can also get high blood sugar if your diabetes medicine is not working well, you’re taking certain medicines or you recently had an operation.
What Is A Normal A1c
A person’s A1C is a measure of their average blood glucose levels over the previous 2 or 3 months, and it is measured through a blood test. A normal result for someone without diabetes or prediabetes would be below 5.7% an A1C between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes and if your A1C is above 6.4% you would be diagnosed as having diabetes, according to the CDC .
Specifically, the A1C test is a measure of the percent of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated hemoglobin attached to them. The glucose that enters your bloodstream gets stuck to hemoglobin molecules on red blood cells. And the more glucose in your bloodstream , the more of your blood’s hemoglobin will be “sugar-coated,” and the higher your A1C will be, according to the CDC. As such, for people with diabetes , the number can give you and your doctors a sense of how well your sugars are being controlled.
The ADA recommends that most adults with diabetes should keep their A1C below 7% to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications the goal is the generally the same for many children with diabetes Targets for the elderly with diabetes are slightly less stringent for the otherwise healthy with few coexisting chronic illnesses and intact cognitive function, the ADA recommends less than 7.5%, while those who don’t meet these requirements have a more lenient goal of below 8.0% to 8.5%.
This article is for informational purposes only, and is not meant to offer medical advice.
Don’t Miss: How Much Do Diabetic Strips Cost
Interested In Learning More Read About Normal Blood Glucose Numbers Getting Tested For Type 2 Diabetes And Using Blood Sugar Monitoring To Manage Diabetes
Want to keep track of your blood glucose readings to help you better manage your condition? With our free printable diabetes logbook sheets, youll be able to monitor the effects of food, exercise, medicines and more. One sheet tracks levels for a week. Download your free blood sugar logbook today to start analyzing your patterns!
Who Should Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, tracking your blood sugar regularly will help you understand how medication, food, and physical activity affect it. It also allows you to catch rising blood sugar levels early.
This is the most important thing you can do to prevent complications from diabetes. These may include blindness, heart attacks, amputation, and kidney disease, which is a decline in the kidney’s functioning. Other complications may include a stroke, which is a medical emergency where blood flow to the brain is blocked.
Others who may want to track their blood glucose regularly include those:
- Taking insulin
You May Like: What Is Early Onset Diabetes
How To Test Blood Sugar
People with diabetes usually check their blood sugar levels themselves. However, its a good idea to have a roommate, friend, or family member also know how to do it if you are sick and cant do it yourself.
To use a blood sugar meter, follow these steps:
If you are interested in CGM, you should talk to your healthcare provider since these are prescription devices. To use CGM, follow these steps:
You will also need to change the sensors on the CGM regularly, usually every one to two weeks.
How To Measure Your Spikes
The American Diabetes Association recommends you check your blood sugar levels right before mealtime with a blood sample from a finger stick. Then do it again 1 to 2 hours after that first bite of food.
Keep this up for a week or so. Write down the time and the blood sugar number. Make a note about anything you think might affect your levels, like medicine or exercise. And don’t forget to log exactly what you ate, along with portion sizes and the amount of carbs.What levels are too high after a meal? Experts vary on what the number should be, but the ADA says a general goal is a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dL, 1 to 2 hours after a meal. Talk to your doctor about what you should aim for, and don’t adjust your medicine without speaking to them first.
You May Like: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Diabetes
Why Test Blood Sugar Levels
If you take certain medication, like insulin or sulphonylureas, checking your blood sugars is a vital part of living with diabetes. It can help you work out when you need to take more medication, when you need to eat something or for when you want to get up and move around more.
Routine checks can help you know when you might be starting to go too low or too high . Its a way of getting to know your body and how it works. It can help you and your healthcare team spot patterns too. Do you write your results down? You might find that helpful.
But importantly, it will help you stay healthy and prevent serious diabetes complications now and in the future. By complications, we mean serious problems in places like your feet and your eyes. This happens because too much sugar in the blood damages your blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow around your body. This can lead to very serious problems like sight loss and needing an amputation.
The higher your blood sugar levels are and the longer theyre high for, the more at risk you are.