A Few More Things Related To Blood Sugars
Remember that there is no healthy number, per se. You are shooting for your blood sugars to be in a target range, so you have a little leeway. It is important to get your blood sugars into your target range. This is due to the target ranges for blood sugars coincide with the blood sugar target range that prevents the long-term complications of diabetes.
For blood sugar, over 250 mg/dl for two readings, or for low blood sugar that is not over 80 mg/dl after several attempts to correct the low blood sugar with quick acting carbohydrates, assistance may be needed. For the high blood sugar, a patient should call their primary care provider, or the provider on call if it is on the weekend. If a low blood sugar will not come up after two attempts, a 911 call may be warranted. Remember to post your comments down below.
TheDiabetesCouncil Article | Reviewed by Dr. Christine Traxler MD on May 21, 2020
References
You May Like: Low Carb Meal Plan For Diabetics Type 2
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
How To Do A Finger
Your healthcare team will show you how to do it the first time, but these are the key steps:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water. Dont use wet wipes as the glycerine in them can affect the test result. Make sure your hands are warm so its easier to get blood and wont hurt as much.
- Take a test strip and slot it into the meter to turn it on. Some meters will have tests strips built in.
- Remove the cap from your finger prick device and put in a new lancet. Then put the cap back on and set the device by pulling or clicking the plunger.
- Choose which finger to prick but avoid your thumb or index finger . And dont prick the middle, or too close to a nail. Place the device against the side of your finger and press the plunger. Use a different finger each time and a different area.
- Take your meter with the test strip and hold it against the drop of blood. Itll tell you if the test strip is filled, usually by beeping.
- Before you look at your reading, check your finger. Use a tissue to stop bleeding, then use it to take out the lancet and throw it away in your sharps bin.
- You can use the same tissue to take out the test strip and throw that away too. Taking out the strip will usually turn the meter off.
Don’t Miss: Best Coffee Creamer For Diabetics
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluids between your bodys cells every few minutes and can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
Tips For Tracking Your Blood Sugar Patterns And Using Your Results
Here are some great tips:
Have a blood sugar chart on your phone or a written notebook nearby to compare your numbers
For my patients during the class entitled, Monitoring your Blood Glucose, I pass out individual notebooks, and packs of different colored highlighter pens for pattern management. Inside, there are copies of an enhanced blood sugar log.
Patients log their blood sugars at different times of the day, and color-code them with highlighters. This helps patients to pick out their blood sugar patterns, and to do different things to adjust their blood sugars to get them in a target range.
Patients may either take a walk following a high carbohydrate meal, take more insulin if they are correcting blood sugar with insulin, decrease the amount of carbohydrates at the next meal, etc. By seeing what their blood sugars are at different times of the day, they can work their blood sugars into their target ranges. Once blood sugars are in the target range, their A1C should also be on target.
I have included a copy of the enhanced blood sugar log that I use to make a pattern notebook for my patients. Readers here at TheDiabetesCouncil are welcome to copy the form for their own use in self-managing their diabetes. You can also download our comprehensive log book here.
Phone Apps
Also Check: Why Are Diabetic Supplies So Expensive
Make A Note Of Your Readings
It may sound obvious, but you must record your readings. Note them down in a diary, a notebook or in your phone calendar. Some meters have software that lets you do this. You could try a diabetes app too.
You and your healthcare team can then look back over your results to see if you need to adjust your treatment.
Healthy Normal Sugar Levels In Diabetic Adults
Summary
Healthy diabetic adults should maintain a normal sugar level of 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after 2 hours of meals. Pregnant women should maintain a blood glucose level of 95-140 mg/dL to avoid complications. This can be done with the right habits in place that help you maintain your sugar level without getting stressed about it.
Also Check: Diabetes Leading To Kidney Disease
Do You Think You Can’t Afford Healthy Food
The No. 1 thing I often hear is its just too costly to eat healthy with diabetes, Nunlee-Bland says. But she says there are ways to follow a balanced diet on a budget.
For example:
- Eat dried beans for protein and fiber
- Choose frozen or canned fruits and vegetables
- Buy in-season produce
- Plan your meals ahead of time
Prep meals on the weekends, Nunlee-Brand suggests. That helps keep you on track for the week ahead.
You dont have to give up all your favorite foods. Ask a dietitian for tips. They can help you plan your meals so you can enjoy some of the things that you like to eat, she says.
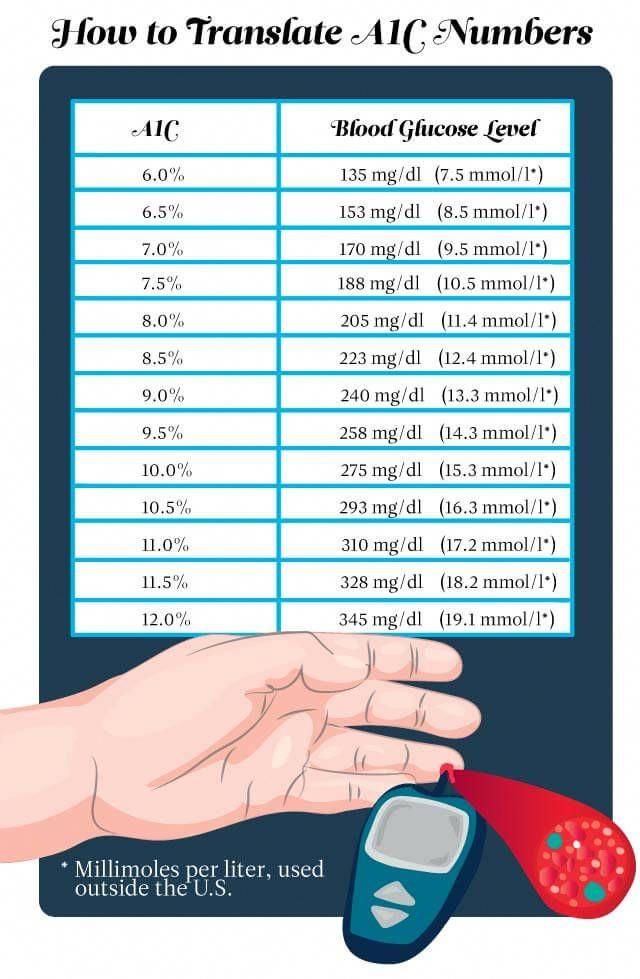
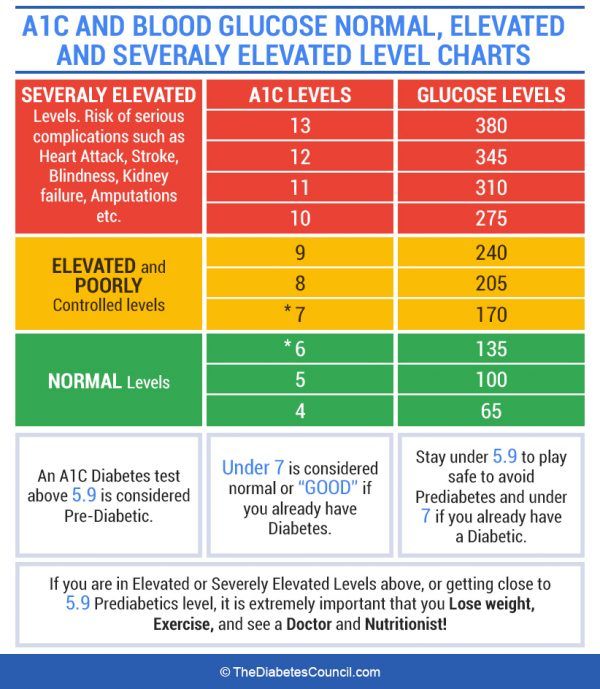
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their health care provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
You May Like: Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Caution: Birth Control Pills
Types that have estrogen can affect the way your body handles insulin. Still, oral contraceptives are safe for women with diabetes. The American Diabetes Association suggests a combination pill with norgestimate and synthetic estrogen. The group also says birth control shots and implants are safe for women with the condition, though they can affect your blood sugar levels.
12
Read Also: Contour Next One Blood Glucose Meter
Causes Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst the liver and muscles produce some glucose, most comes from the foods we eat. Food and drinks that are high in carbohydrates are most impactful on blood sugar level. What we eat provides us most of the nutrients our body needs and sometimes, does not need. That is not to say that food is a major cause of blood sugar level increasing or decreasing too dramatically.
Typically, if a person has health conditions or poor nutrition, this will lead to a spike or decline in blood sugar level. The causes differ from high to low blood sugar levels and are as follows:
Know Your Body Mass Index
Being overweight or obese puts you at risk for developing type 2 diabetes. BMI is an easy way to estimate excess fat. Even a small change in body weight can reduce your risk of diabetes.
If your score is:
25.029.9 = Overweight/Pre-obese 30.0 and over = Obese
To calculate your BMI, you can use the BMI chart or the formulas at the bottom of this page or complete the Canadian diabetes risk questionnaire.
Don’t Miss: I Am Type 2 Diabetes
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Below chart displays possible blood sugar levels . Units are expressed in mg/dL and mmol/L respectively. Additional topics: What is diabetes? How do you know if you have diabetes? How to test for diabetes? Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently? Diet for people with diabetes You can also download or print this chart by clicking here. Reference: American Diabetes Association, Additional topics: What is diabetes? How do you know if you have diabetes? How to test for diabetes? What is normal blood sugar level? Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently? Diet for people with diabetesContinue reading > >
Make Physical Activity Part Of Your Daily Routine
Set a goal to be more physically active. Try to work up to 30 minutes or more of physical activity on most days of the week.
Brisk walking and swimming are good ways to move more. If you are not active now, ask your health care team about the types and amounts of physical activity that are right for you. Learn more about being physically active with diabetes.
Following your meal plan and being more active can help you stay at or get to a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan that is right for you.
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Skin Problems
Is Sugar Bad For You
If you love sweets, don’t despair. You don’t have to give them up forever. Sugar will raise your blood sugar levels more quickly than other carbs, but diabetes experts now say the total amount of carbs is most important. So keep your serving sizes small and take into account the total carbs and calories.
22
To Check Or Not To Check
Ultimately, while the researchers mentioned here found that blood sugar monitoring had no effect on the A1Cs of those with type 2 who did not take insulin, they hope that their findings will inspire both adults with diabetes and providers to regularly engage in conversations about the question.
If you currently monitor, you shouldnt stop doing so without first consulting your physician.
And while its the rare person who would choose to monitor if a doctor deemed it unnecessary, its ultimately very individual. In the end, patient-centric care matters most.
Also Check: Patient Teaching On Diabetic Diet
Read Also: How Can An Ophthalmologist Help A Diabetic
Is Diabetes Diagnosed The Same Way In Every Country
There are four methods of diagnosing diabetes, which are used around the world. They are:
Target Levels In People With Diabetes
A doctor will set a persons target A1C level based on many factors. The right target varies from person to person.
For someone with diabetes, the target A1C level may depend on:
- the persons age
- how long they have had diabetes
- their prescribed treatment plan
- any history of adverse effects from the treatment, including episodes of low blood glucose, or hypoglycemia
- any complications from diabetes
- the persons preferences and treatment priorities
In general, a doctor might recommend aiming for A1C levels under 6.5% if a person:
- is young and has a long life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a short period
- is effectively managing their diabetes with lifestyle changes or metformin alone
- is otherwise in good health
A doctor might recommend A1C targets of 7.08.5% if a person:
- is older and has a shorter life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a longer period
- has diabetes that is hard to manage, even with multiple medications
- has a history of severe hypoglycemia or other adverse effects of treatment
- has experienced complications of diabetes
- has other chronic health conditions
A person should work with their doctor to reassess and adjust their A1C targets over time. The condition and treatment goals may change.
To screen for diabetes, a doctor may order an A1C test for someone older than 45. They may also do this for younger people who have other risk factors.
After diagnosing diabetes, a doctor determines how often to test A1C levels.
Symptoms of high blood glucose levels include:
You May Like: Whats A Good A1c For A Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The Test To Check Blood Sugar Levels For Type 2 Diabetes
You can check your blood sugar levels several times a day at home with a blood glucose monitor, which uses a drop of blood from your finger. A better measure of how well your diabetes is being managed, however, is a blood test called the A1C.
The A1C test involves a blood test that measures the percentage of hemoglobin proteins in your blood that are bound to sugar. In a more practical sense, these tests show how well your blood sugar levels have been managed in the last two to three months.
Instead of relying on occasional blood glucose tests that can spike or drop for many reasons, A1C tests provide a more accurate picture of how well your diabetes has been managed on average across the preceding three months.
Some people are diagnosed with diabetes using the A1C test, and doctors often recommend that those with prediabetes should get a yearly A1C test. Those with diabetes who don’t use insulin may only need two of these tests per year. People who use insulin, or struggle to keep blood sugar levels within their target range, may get four A1C tests per year.
A1C tests don’t require any preparation for fasting beforehand, so you can have this blood test any time of the day, even after eating and drinking normally.