If You’re Considering Surgery
Speak to your GP if you think bariatric surgery might be an option for you. If you qualify for NHS treatment, you will be referred for an assessment to check whether surgery is suitable.
The NHS guidelines are broadly similar to a set of international clinical guidelines published in 2016 by a group of leading international diabetes organisations, including Diabetes UK. These guidelines also recommend a lower BMI threshold for people from a South Asian background with type 2 diabetes.
Bariatric Surgery For Diabetes
Bariatric surgery refers to a group of surgical procedures that help a person lose weight by changing their digestive system.
These procedures typically make the stomach much smaller, which helps a person feel full sooner and eat less food overall. They also usually limit the ability of the small intestine to absorb calories from food.
Bariatric surgery can also affect certain hormones to reduce a persons appetite and improve how their body metabolizes fat and uses insulin.
Because the bodies of people with type 2 diabetes become resistant to insulin, bariatric surgery may be helpful for treating diabetes.
Some research suggests that bariatric surgery can help people with type 2 diabetes better control their blood sugar levels in addition to improving weight loss, cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and kidney function.
Healthcare professionals are increasingly recommending it for people with obesity and comorbid conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Several types of bariatric surgery can decrease the amount of food a person can eat at one time. Some procedures also reduce the absorption of nutrients.
The following sections will look at the different types of bariatric surgery in more detail.
Determinants And Mechanisms Of Diabetes Remission
Overall, BS leads to remarkable type 2 diabetes remission in 40% to 80% of cases at 1 year . The determinants of early remission include clinical markers of good islet cell function at the time of surgery in addition to the amount of weight loss and the type of surgery . The greater effect of BPD and RYGB on remission of type 2 diabetes is confounded by the greater weight loss observed after these 2 surgeries compared to VSG and AGB . The predictors of long-term type 2 diabetes remission of up to 15 years in the SOS included greater amount of weight loss and shorter duration of type 2 diabetes .
BS results in great, often sustained weight loss, which leads to improvements in blood glucose as well as blood pressure and lipid levels . The rate of type 2 diabetes remission tracks the amount of weight loss. Acute caloric restriction leads to improvement in hepatic insulin sensitivity, estimated by homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance as early as 1 week after RYGB . Greater weight loss months after RYGB results in improvement in peripheral insulin sensitivity, best measured by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp . However, improvements in glycemia after RYGB occurs before significant weight loss , suggesting that there may be other contributing factors.
Also Check: Different Types Of Insulin Pumps
Bariatric Surgery For Type 2 Diabetes Reversal: The Risks
Diabetes Care
Andrei Keidar Bariatric Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Reversal: The Risks. Diabetes Care 1 May 2011 34 : S361S266.
It has been over 10 years since the resolution of type 2 diabetes was observed as an additional outcome of surgical treatment of morbid obesity. Moreover, it has been shown unequivocally that diabetes-related morbidity and mortality have declined significantly postoperatively, and this improvement in diabetes control is long lasting. Bypass procedures, the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and the biliopancreatic diversion , are more effective treatments for diabetes than other procedures and are followed by normalization of concentrations of plasma glucose, insulin, and HbA1c in 80100% of morbidly obese patients. Studies have shown that return to euglycemia and normal insulin levels occurs within days after surgery, long before any significant weight loss takes place. This fact suggests that weight loss alone is not a sufficient explanation for this improvement. Other possible mechanisms effective in this phenomenon are decreased food intake, partial malabsorption of nutrients, and anatomical alteration of the gastrointestinal tract, which incites changes in the incretin system, affecting, in turn, glucose balance. Better understanding of those mechanisms may bring about a discovery of new treatment modalities for diabetes and obesity.
Why Does The Diabetes Come Back After Gastric Bypass Surgery
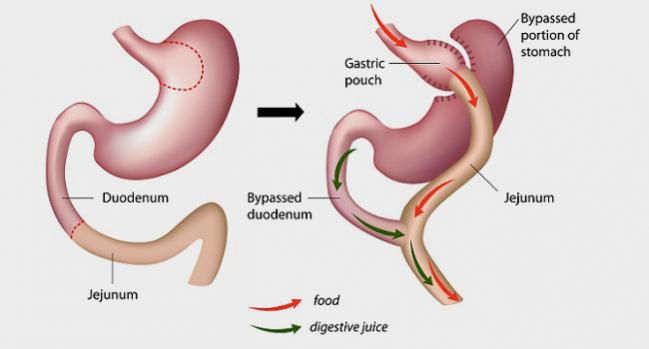
The researchers are not sure why the diabetes eventually relapses. It could be due to gradual weight gain, or some underlying progression of the disease. They found that there was not a close link between patients weight before and after surgery and diabetes remission or relapse.
Researchers from the University of Massachusetts Medical Center found that 67% of diabetes patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery achieved complete remission.
Also Check: Is Cassava Flour Good For Diabetics
Bariatric Procedures And Their Effect On Diabetes Control
After bariatric surgery, patients lose more weight than with traditional weight-loss methodsâup to 25% of their total body weight. Furthermore, of those with type 2 diabetes, 87% achieve at least better glucose control and need fewer antidiabetic medications,12 and an average of 78% achieve normal glycemic control without taking any antidiabetic medications at all.12,13
But not all bariatric procedures have the same effect on weight and diabetes: certain procedures have a greater effect.
The two major types are classified as gastric restrictive procedures and intestinal bypass procedures. The classification was initially based on the presumed mechanism of weight loss.
Gastric restrictive procedures limit gastric volume and, hence, restrict the intake of calories by inducing satiety. Afterward, patients lose approximately 10% to 20% of their total body weight.
Furthermore, multiple studies, including a randomized controlled trial14 , have shown remission of type 2 diabetes with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding but not with conventional medical therapy. The effect is primarily mediated by weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity, both of which occur several months following surgery. Of note, however: in this trial,14 all the patients had diabetes of short duration, less than 2 years.
What Is The Relationship Between Diabetes And Obesity
Being overweight is an indicator that allows patients and doctors to know if someone may develop diabetes. Obesity and diabetes are very closely linked since 80% of type 2 diabetics also have obesity problems or have a high BMI. Unfortunately, such a condition is the most common disease that affects all ages and races globally.
We all depend on our bodys ability to use insulin to control blood sugar levels. Thus, obesity leads to insulin resistance, which puts these patients at a higher risk of developing diabetes and other serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, depression, and kidney failure.
On the other hand, when a person lives with diabetes and has excess fat, the amount of adipokines tends to increase excessively, directly affecting his organs.
Consequently, it has been proven that weight loss can improve insulin secretion and reduce the effects of diabetes considerably. Likewise, it has been recognized that bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for that purpose since extensive research has shown that after a bariatric procedure, patients benefit from glycemic control thanks to enforced caloric restriction, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and increased insulin production.
Also Check: Va Disability Rating For Diabetes
Complications Of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery procedures are generally considered safe. The average perioperative mortality is < 0.3%, comparable to this of appendicectomy or cholecystectomy. The 1-year complication rate varies among different procedures, being 4.6, 10.8, 14.9, and 25.7% for AGB, VSG, RYGB, and BPD, respectively . The factors that negatively affect the incidence of adverse events after surgery include male sex, the presence of co-morbidities, high pre-operative BMI, old age, and the lack of adequate experience of the surgical team. Among patients with T1DM, no excess in mortality has been reported . Apart from the common complications of bariatric surgery, however, an increased prevalence of diabetic ketoacidosis and hypoglycemia has been observed .
Table 3. Incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis and hypoglycemia after bariatric surgery in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and obesity.
Risks And Benefits Of Bariatric Surgery
Although BS can have numerous benefits, all surgical procedures and medical treatments are associated with risks. The rigorous preparation of patients, the development of centres of excellence and the elective nature of BS, now performed almost laparascopically, have reduced mortality and complications. Short-term 30-day postoperative mortality and longer term mortality associated with the surgical procedure is very low, less than 1% for all procedures and a bit higher for RYGB than for VSG or LAGB . The frequency of acute surgical complications differ with each procedure: AGB, 7.8% VSG, 8.9% RYGB, 12% .
Dumping syndrome, with or without reactive hypoglycemia, self-reported in about 10% of patients 4 to 5 years after RYGB and/or gastroesophogeal reflux after VSG can be invalidating. BS increases the risk for long-term vitamin , mineral or protein deficiencies, which can lead to new comorbidities, such as iron deficiency anemia or secondary hyperparathyroidism, and require lifelong monitoring, prevention and treatment . Restrictive procedures, such as AGB and VSG, lead to fewer nutritional deficiencies than malabsorptive procedures such as RYGB . Laboratory testing for these deficiencies should be performed at regular intervals and at least annually for life .
Don’t Miss: Best Diet For Type One Diabetes
Bariatric And Other Gi Operations In Type 2 Diabetic Patients With Bmi < 35 Kg/m2
The remarkable control of diabetes in severely obese patients, along with experimental studies showing that GI operations can improve diabetes in both obese and nonobese animals , suggests that surgery may be beneficial for moderately obese or nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Recent data on the existent clinical results of bariatric operations in type 2 diabetic patients with BMI < 35 kg/m2 were reviewed by Fried et al. . Most of the data were reported from countries outside of the U.S., and included were 343 patients who underwent one of eight procedures with 6- to 216-month follow-up. Most of the procedures were conventional bariatric operations, but there were also two experimental proceduresileal interposition with SG or diverted SG. Patients lost a clinically meaningful but not excessive amount of weight , moving from the overweight into the normal weight category. Of the patients, 85.3% were off type 2 diabetes medications with fasting plasma glucose approaching normal , and normal HbA1c, . Operative mortality was at 0.29%. The improvement was better in the malabsorptive operations than the restrictive ones, and interestingly, the the higher BMI subgroup resolved their type 2 diabetes at a significantly higher rate than the lower BMI subgroup .
How Does Gastric Bypass Surgery Affect Diabetes
Gastric bypass surgery can result in rapid improvements to blood sugar and lead to complete diabetes remission, but why does this happen?
Weight loss is a clear component, but blood sugar can improve quickly after surgery, even before much weight is lost. Scientists are still working to figure this out, but there are a number of suspected causes:
- Improved sensitivity to insulin.
- Changes in blood sugar hormones.
- Changes in hunger and fullness hormones.
- Changes in gut bacteria.
Essentially, it is thought that after surgery there is a sharp drop in food consumed. Food that is consumed hits the small intestine quicker, and body hormones are able to respond better to balance blood sugar. As more weight is lost, the body is no longer resistant to insulin which further helps blood sugars stay controlled.
Recommended Reading: What Diet Plan Is Best For Type 2 Diabetes
Possible Mechanisms Not Related To
Ghrelin suppresses insulin secretion, opposes its action, and stimulates counterregulatory hormones. Its secretion is decreased after gastric bypass surgery, which may contribute to hypoglycemia.
In sum, it is unclear why severe hypoglycemia occurs in a small proportion of patients who have had a gastric bypass. In addition to the above offenders, other potential contributors include sustained weight loss, complex anatomical changes including bypass of the duodenum, and increased levels of circulating bile acids. This hypoglycemia is most likely a combination of the above-noted anatomic, hormonal, and metabolic changes. Finally, it also remains to be seen whether this is an extreme physiological response or is a result of an unrecognized genetic predisposition.
Bariatric Surgery To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Dr. David Arterburn discusses how bariatric surgery can be safe and effective in improving health for people who have obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Using medical records data, researchers with the National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network Bariatric Study analyzed the five-year outcomes for more than 46,000 adults who underwent bariatric surgery . A subset of these adults had type 2 diabetes, and a was conducted to determine the effectiveness of two types of surgery, sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, for this group. Here, David Arterburn, MD, MPH, describes the study findings and discusses bariatric surgery guidelines for patients with type 2 diabetes.
Q: What were the PCORnet Bariatric Studys findings for people who have type2 diabetes?
A: The good news is that the cumulative rates of diabetes remission during the five years after surgery are quite similar between the two procedures. The difference was 86.1 percent of patients achieving remission within 5 years of gastric bypass, compared with 83.5 percent for sleeve gastrectomy. We define diabetes remission as hemoglobin A1C that is less than 6.5 percent, the standard cut point for diagnosing diabetes, after being off diabetes medications for at least three months.
Weight loss may factor into the equation for some patients. In the full study, at five years, gastric bypass was associated with a greater average weight loss than sleeve gastrectomy .
Read Also: What Is The A1c Range For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are The Benefits Of Weight
A majority of patients lose 50 to 80% of the excess weight during the 18-24 months after surgery. However, the effects on blood sugar are immediate after surgery. People who have this surgery are able to reduce or eliminate diabetes medications.
In particular, Roux-en-Y surgery is effective at diabetes control. About 33% of these patients do not need diabetes drugs after surgery. Within 2 years of surgery, a total of 85% of patients do not require medication. Their diabetes is in remission.
Complete resolution of diabetes is more common among people who have a form of diabetes that does not require medication and who have had diabetes less than five years. Resolution is also more common among people who have more weight loss after surgery. The benefits extend to high blood pressure and high cholesterol. These factors, which increase the risk of strokes and heart attacks, are also improved and/or resolved after surgery.
Observational Studies Of The Effect Of Roux
Several observational studies have evaluated the benefit of Roux-en-Y surgery for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Pories et al15 followed 608 severely obese patients, of whom 165 had type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance.
At a mean follow-up of 7.6 years after surgery, 83% of the diabetic patients were off their antidiabetic drugs, and 99% of those with impaired glucose tolerance were normoglycemic, with normal fasting glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels. Marked improvements in hyperlipidemia, hypertension, fertility, osteoarthritis, and obstructive sleep apnea were also noted.
Schauer et al17 observed similar results in 1,160 morbidly obese patients, of whom 240 had type 2 diabetes or impaired fasting glucose.
After laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, fasting glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels returned to normal levels in 83% of cases and were markedly improved in the remaining 17%. Significantly fewer patients needed oral antidiabetic agents or insulin . Patients most likely to achieve complete remission of diabetes were those with the shortest duration of diabetes , the mildest severity of diabetes , and the greatest weight loss after surgery. The rate of diabetes remission in patients who had been diabetic for 5 years or less was 95%, compared with 75% in those who had been diabetic for 6 to 10 years and 54% in those who had been diabetic for more than 10 years .
Read Also: High Blood Sugar And Insulin
Effect Of Bariatric Surgery On Type 2 Diabetic Subjects With Bmi > 35 Kg/m: The Evidence
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the English literature reported complete resolution of type 2 diabetes in 78.1% of cases. This percentage increased to 86.6% when counting patients reporting improvement of glycemic control, and diabetes resolution occurred in concomitance with an average weight loss of 38.5 kg ).
Two large case-series studies, by Pories et al. and Schauer et al. , focused principally on diabetes outcomes after RYGBP. In the former study, mean fasting blood glucose decreased from clearly diabetic values to near normal levels , and HbA1c fell to normal levels without diabetes medicines in 89% of patients. In the latest study by Schauer et al., researchers provided the in-depth evaluation of the clinical outcome in 240 diabetic morbidly obese bariatric patients with a follow-up rate of 80%. The authors noted that after surgery, weight and BMI decreased from 308 lbs and 50.1 kg/m2 to 211 lbs and 34 kg/m2 for a mean weight loss of 97 lbs and mean excess weight loss of 60%. Fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c concentrations returned to normal levels or markedly improved in all patients. A significant reduction in use of oral antidiabetic agents and insulin followed surgical treatment. Patients with the shortest duration , the mildest form of type 2 diabetes , and the greatest weight loss after surgery were most likely to achieve complete resolution of type 2 diabetes.
To Summarize Gastric Bypass Surgery Can Create Diabetes Remission
Type 2 diabetes is a complication of obesity and is often a reason to pursue gastric bypass surgery. Gastric bypass surgery leads to complete and sustained diabetes remission in a majority of cases. It accomplishes this through a variety of complex means that involve helping the body to use its own insulin.
Also Check: Purpose Of Insulin In The Body