Type 2 Diabetes Blood Sugar Levels
Consistently testing and tracking the blood sugar levels that you and your doctor have agreed on can tell you how well your type 2 diabetes plan is working. Your doctor will work with you to determine the target levels that are best suited for you. What Do My Blood Sugars Tell Me? Checking your blood sugar levels is important, but keeping track of them in a written logbook or software will help you spot trends of blood sugar levels that are too high or too low. If you see a trend like this, be sure to discuss it with your doctor. Keep in mind that if you have recently started a new type 2 diabetes therapy, it may take some time to see the results. Be sure to discuss with your doctor how long it should take before you see an improvement in your blood sugar levels. If your doctor recommends blood sugar guidelines for you, he or she may ask you to check your blood sugar levels every day. Self-monitoring measures blood sugar levels at the time of the test, so its important that your doctor also tests your A1C to see how well your blood sugar is being managed over time The A1C test measures your average blood sugar level over the previous 2 to 3 months, and results are given as a percentage, called your A1C level. The higher your A1C level, the more sugar you have in your blood Whether youre making changes to your treatment or wondering about what might come next, were here to listen. Learn more Continue reading > >
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Read Also: How To Lower Insulin Resistance
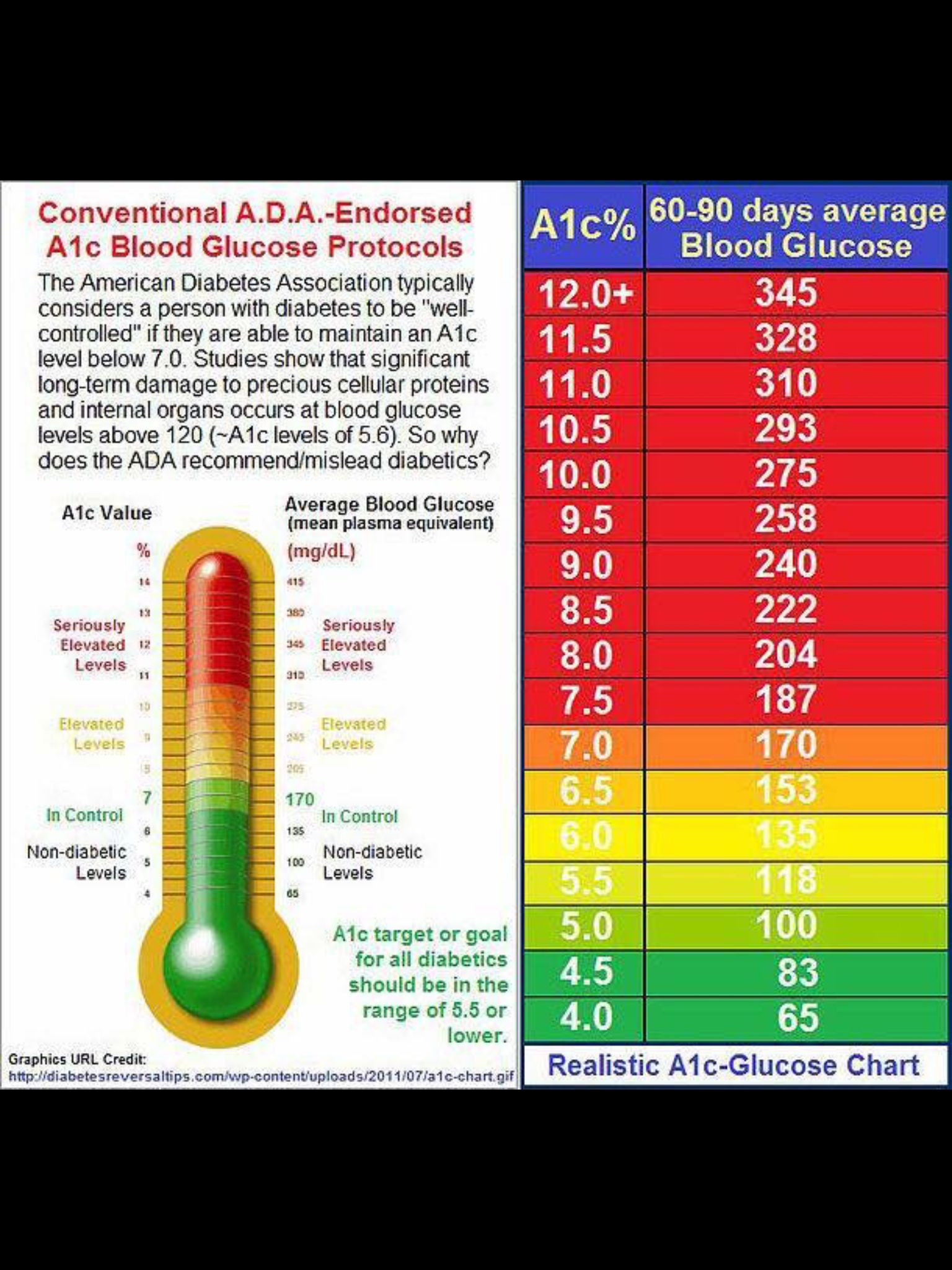
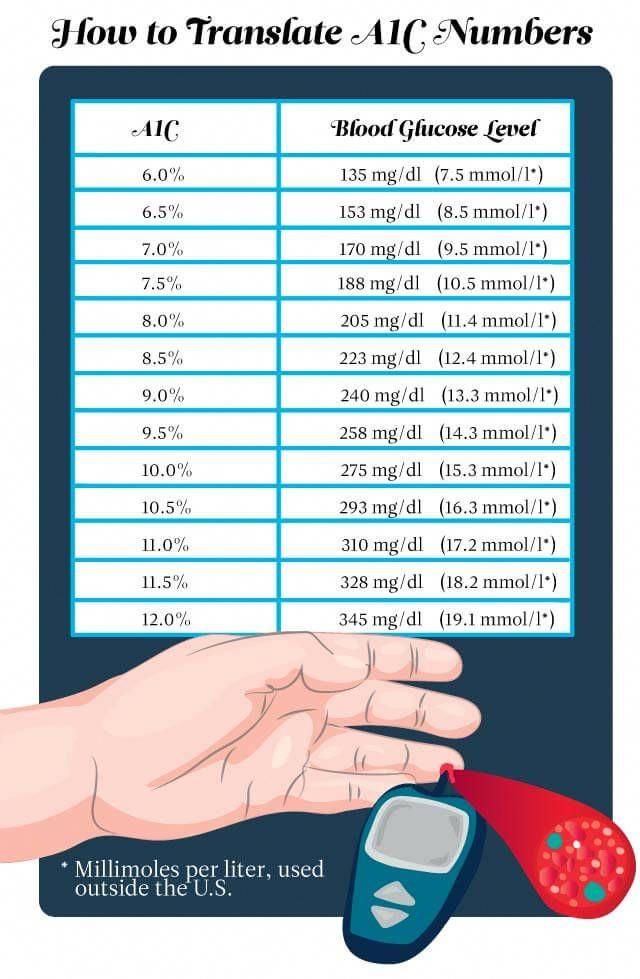
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
What Is Blood Glucose

Blood glucose is the main sugar content in your blood. It comes from the food you eat, and it’s your body’s main source of energy. Blood glucose levels are a measure of how much sugar is in your blood. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate during the day and night because of various reasons. What we eat, how active we are, and even stress can all affect our blood sugar levels.
You May Like: What Size Syringe For Insulin
What Causes A Low Blood Sugar Level
In people with diabetes, the main causes of a low blood sugar level are:
- the effects of medicine especially taking too much insulin, medicines called sulfonylureas , medicines called glinides , or some antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C
- skipping or delaying a meal
- not eating enough carbohydrate foods in your last meal, such as bread, cereals, pasta, potatoes and fruit
- exercise, especially if it’s intense or unplanned
- drinking alcohol
Sometimes there’s no obvious reason why a low blood sugar level happens.
Very occasionally, it can happen in people who do not have diabetes.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children
Younger than 6 years old mg/dL
| Bedtime | 100-140 |
Adults who are 20 years or older will have blood sugar levels that range between less than 100-180 mg/dL over the course of a day. When you wake up in the morning, your fasting blood sugar should be at its lowest because you havent consumed food for about eight hours. If youre an adult and struggling with glucose control, your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage your blood sugar better.
Blood glucose levels outside the ranges listed above are categorized as either high or low blood sugar. Blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher. The highest blood sugar level thats considered safe will depend on the person and whether they have diabetes, but will typically be between 160 to 240 mg/dL.
You May Like: How Can I Tell I Have Diabetes
What Blood Sugar Goals Should I Be Aiming For
The American Diabetes Association recommends that most people with diabetes aim for the following blood sugar goals:
- Preprandial : 80-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dL
Your doctor will likely set different goals for you based on many factors including your age, how long you’ve had diabetes, other health problems you have.
A Low Blood Sugar Level And Driving
You may still be allowed to drive if you have diabetes or you’re at risk of a low blood sugar level for another reason, but you’ll need to do things to reduce the chance of this happening while you’re driving.
You also need to tell the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency and your car insurance company about your condition.
For more information, see:
You May Like: Does Insurance Cover Cgm For Type 2 Diabetes
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous
Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
Possible Driving Factors Behind Health Disparities
Annals of EpidemiologyPopulation Research and Policy ReviewJournal of General Internal Medicine PLoS MedicineJournal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities
Taking the ADAs 60-Second Type 2 Diabetes Risk Test can help you determine whether youre at a higher risk for diabetes based on a number of factors, including your race or ethnicity.
Also Check: What Does Diabetic Retinopathy Feel Like
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level For Teens
Teenagers are recommended to have a blood sugar range between 70-150 mg/dL. It’s not easy for a teenager to maintain a tight range, therefore it’s important to aim for these numbers to give them a bit more flexibility.
- Fasting: 70-150 mg/dL
- Preprandial : 90-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial : Less than 140 mg/dL
- Bedtime: 90-150 mg/dL
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
According to the American Diabetes Association, a normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL.
A fasting blood sugar reading of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and a reading above 125 indicates diabetes.
| Fasting Blood Sugar | |
| 100 mg/dl to 125 mg/dl | Prediabetes |
| 126 mg/dl or higher | Diabetes |
If you test your blood sugar two hours after eating or drinking something containing sugar instead , the numbers to look for are:
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | Prediabetes |
You can learn more in the in-depth article: What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Read Also: How Fast Can Diabetes Develop
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes tend to develop slowly over time. They can include:
- Urinary tract infections and bladder infections.
Rarely, Type 2 diabetes leads to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis . DKA is a life-threatening condition that causes your blood to become acidic. People with Type 1 diabetes are more likely to have DKA.
High Blood Glucose: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If your insulin level is too low, your blood glucose could become so high that it is unsafe. You might develop a serious problem called diabetic ketoacidosis . This usually happens in people with Type 1 diabetes and those with glucose levels over 500.
If you have DKA, chemicals called ketones start to make a lot of acid in your body. The acid and high blood glucose can make you very sick. You might also become dehydrated . You can prevent DKA by carefully giving yourself the correct insulin dose every day.
If you have any of the following symptoms of DKA, get to your local emergency department right away. You need to be treated with insulin and fluids that are given to you through an IV :
- Blurry vision
- Dry mouth, eyes or skin
- Fast breathing
- Feeling very weak or tired
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Stomach pain, nausea or vomiting
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Kidney Failure In Diabetics
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
Nighttime Low Blood Sugar
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think youre at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldnt rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while youre sleeping.
Also Check: Normal A1c Range For Diabetics
Low Blood Sugar Levels Symptoms
Low blood sugar levels or also known as hypoglycemia can happen to anyone but is more common in people with diabetes. Low blood sugar levels can occur if you miss a meal, exercise too hard, or take too much insulin.
Signs and symptoms that your blood sugar might be on the low side include:
- Feeling shaky
- Headache
- Anxiety or feeling of nervousness
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to check your blood sugar levels right away. You can use a home glucose meter to test your blood sugar levels. The ADA recommends that people with diabetes keep a fast-acting source of sugar like glucose tablets with them at all times in case they experience low blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes And Blood Sugar Levels
Type 2 diabetes prevents glucose sugar from entering your body’s cells to properly use for energy. Insulin is a hormone released by your pancreas , which helps glucose get into your cells to carry out body functions.
However, in those with type 2 diabetes, the cells become resistant to insulin. This makes it more difficult for the glucose in your bloodstream to get into the cells to provide your body with the energy it needs for many of its functions. This can lead to high levels of sugar in your blood that can’t get into your cells, which over time may result in dangerous health consequences.
Read Also: Are Protein Bars Good For Diabetics
Are Some Canadians At Higher Risk For Elevated Blood Sugar Levels Than Others
You may have a higher risk for elevated blood sugars and type 2 diabetes if you:
- Are 40 or years of age or older
- Have a close relative with diabetes
- Are of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous or South Asian descent
- Are overweight
- Have been diagnosed with prediabetes
Some medical conditions can also increase your risk of type 2 diabetes, such as:
- High blood pressure or cholesterol levels
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Psychiatric disorders
- Sleep apnea
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar, or âblood glucose,â gets high — after a meal, for example. That signals your body to absorb glucose until levels get back to normal.
But if you have diabetes, your body doesnât make insulin or doesnât respond to it normally . That can leave your blood sugar too high for too long. Over time, that can damage nerves and blood vessels and lead to heart disease and other problems.
If you have diabetes, your doctor may ask you to keep track of your blood sugar by testing it at home with a special device called a blood glucose monitor or home blood sugar meter. It takes a small sample of blood, usually from the tip of your finger, and measures the amount of glucose in it.
Follow your doctorâs instructions about the best way to use your device.
Your doctor will tell you when and how to test your blood sugar. Each time you do it, log it in a notebook or online tool or in an app. The time of day, recent activity, your last meal, and other things can all affect whether a reading will be of concern to your doctor. So try to log relevant information like:
- What medication and dosage you took
- What you ate, when you ate, or whether you were fasting
- How much, how intense, and what kind of exercise you were doing, if any
That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working.
Tight blood sugar control, however, means a greater chance of low blood sugar levels, so your doctor may suggest higher targets.
Read Also: Advanced Diabetes Supply Freestyle Libre
Type 2 And Blood Sugar Checks
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, checks are a routine part of diabetes self-management, but for the nearly 75% of Americans with diabetes who dont take insulin, research suggests those checks might not be necessary.
But dont toss out your blood glucose meter and your test strips just yet. The question of whether routine self-monitoring of blood glucose , also known as blood sugar, has value remains unsettled. And it leads to other questions. For example: Even if self-monitoring does prove to be unnecessary for many adults with type 2 diabetes not on insulin, might there still be people in this group who would benefit or circumstances that would require self-monitoring?
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Before a meal.
- Two hours after a meal.
- At bedtime.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Don’t Miss: How To Use Insulin Glargine Injection
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.