When To See A Doctor
So when should you make an appointment with your doctor to discuss one or more of the three Ps?
If youre experiencing an abnormal increase in thirst, urination, or appetite that lasts over a period of several days, you should see your doctor. This is particularly important if youre experiencing more than one of the three Ps.
Also keep in mind that each of the three Ps can occur individually as a symptom of conditions other than diabetes. If youre experiencing symptoms that are new, persistent, or concerning, you should always make an appointment with your doctor so that they can evaluate you.
If Symptoms Of Diabetes In Children Are Missed
Too many children and young people are not diagnosed with type 1 diabetes until they are in diabetic ketoacidosis a life-threatening condition that requires urgent medical attention.
If a child has type 2 diabetes and it isnt diagnosed for a long time or they also become unwell with an infection, they may be at risk of something called hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state or DKA. And high blood sugar can start to damage parts of their body. If your child is diagnosed with diabetes, were here to support you. We have lots of information and if you have any questions, you can speak to one of our trained advisors on our helpline.
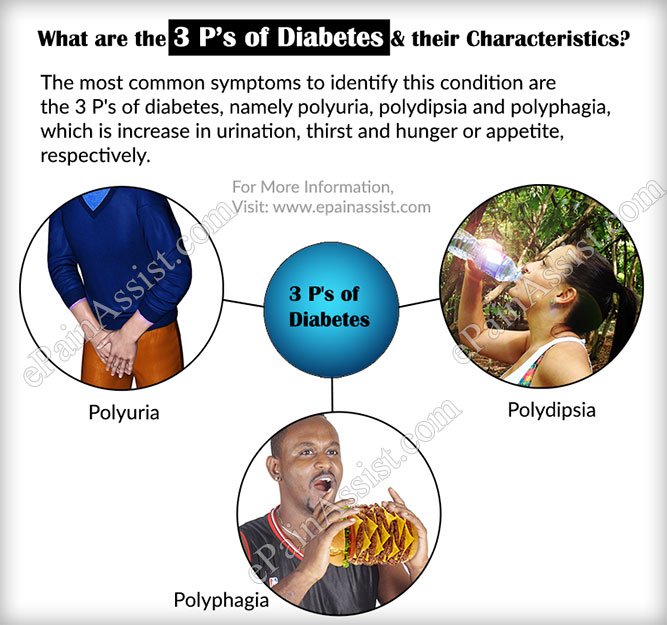
/5common Signs Of Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition characterised by high blood sugar levels that can only be managed by taking medications. A person is diagnosed with diabetes when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or if the cells are not able to utilise it to turn the glucose produced from food into energy. Due to this glucose remain in the blood affecting different functioning of the body. The signs and symptoms of diabetes start to appear slowly and vary from person to person. However, there are some signs which are common and can be witnessed in most cases of diabetes. Together they are referred to as the three P’s of diabetes -polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Kidney Failure
Toxicity And Side Effect Management
One of the most common adverse effects of insulin is hypoglycemia. Gastrointestinal upset is the most common side effect of many of the T2DM medications. Metformin can lead to lactic acidosis and should be used with caution in patients with renal disease and discontinued if the estimated glomerular filtration rate is under 30 mL/min. Sulfonylureas can lead to hypoglycemia and may promote cardiovascular death in patients with diabetes. Thiazolidinediones have fallen out of favor in clinical practice due to their adverse effects, specifically resulting in fluid retention, worsening heart failure, and fractures. DPP-4 may increase the risk for upper respiratory tract infections but may have less nausea and diarrhea compared to other drugs such as metformin. SGLT-2 inhibitors can lead to increased urinary tract infections due to increased urinary glucose excretion. Both SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor agonists reduce ASCVD events and are now considered the second line to metformin in such patients.
Understanding Diabetes From Other Causes
In addition to type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, a small minority of people develop specific types of diabetes due to other causes. This includes:
- Monogenic diabetes syndromes, such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Diseases of the exocrine pancreas, such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis
- Drug or chemical-induced diabetes, such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS or after organ transplantation
Because these types of diabetes are rare, they are often misdiagnosed as other types of diabetes. You can learn more about these types of diabetes in the Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes section in the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. If you think you might have one of these types, be sure to talk with your doctor.
Read Also: Insulin Dosing Guidelines Type 1 Diabetes
How Many Canadians Live With Diabetes
According to the most recent data , about 3.0 million Canadians were living with diagnosed diabetes in 20132014, representing 1 in 300 children and youth , and 1 in 10 adults . The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes generally increases with age and is higher among males than among females , both overall and in most age groups .
Figure 1: Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes , by age group and sex, Canada, 20132014
| 8.7 | 7.6 |
Note: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
What Are The Effects Of Consuming Sugars On The Risk Of Developing Diabetes
Numerous clinical trials, cohort studies, and meta-analyses have been performed to describe the impact of consumption of sugars on weight gain, as well as risk for and development of diabetes . Te Morenga et al. recently performed a systematic review and meta-analysis for the WHO and estimated that adults who reduced intake of dietary sugars decreased 0.80 kg body weight among randomized controlled trials . The same systematic review and meta-analysis, however, did not show a body weight decrease in the randomized controlled trials of children. Conversely, an increase intake of sugars was associated with an increase of 0.75 kg of body weight in both adults and children. A reduced intake of free sugars was associated with weight loss and increased intake of sugars was associated with weight gain in European adults in the EPIC-InterAct cohort study . Other researchers have performed systematic reviews and meta-analyses and calculated pooled estimates showing a statistically significant positive relationship between increased consumption of calories in the form of sugars and weight gain. In the absence of weight gain seen in calorie matched trial comparisons, the relationship between weight gain and consumption of sugars appear to be mediated through an increase in calorie consumption .
Moderate amounts of sugars can safely be consumed by people with diabetes and those at risk.
Read Also: Diet For Insulin Resistance To Lose Weight
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Primary care clinicians are often the first to identify diabetes in their patients. Since DM is a complex disease, it requires an interprofessional team approach to management. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants can be critical to ensuring proper patient follow-ups and monitoring the efficacy of treatments. Nutritionists and diabetes educators can also provide consultations to help educate patients on appropriate lifestyle modifications and at-home glucose management.
Ophthalmologists, neurologists, podiatrists, and nephrologists may also be part of the healthcare team to ensure that patients with DM have adequate screenings to prevent devastating microvascular complications. Endocrinologists may be consulted when patients have a complex presentation or are unresponsive to initial treatments. Of course, pharmacists play a crucial role in evaluating proper medication administration and preventing polypharmacy in DM patients who are often taking multiple medications for the frank disease and its complications they can ensure optimal dosing and recommend the most efficient regimens to achieve glycemic control, and also educate the patient on the medications and disease process.
A Note About Prediabetes
What about the three Ps and prediabetes? Prediabetes is when your blood glucose levels are higher than they should be, but not high enough to diagnose type 2 diabetes.
If you have prediabetes, you likely wont experience clear signs or symptoms like the three Ps. Because prediabetes can go undetected, its important to get your blood glucose levels tested regularly if youre at risk for type 2 diabetes.
In diabetes, the cause of the three Ps is higher than normal blood glucose. As such, keeping blood glucose levels managed can help to stop the three Ps.
Some examples of ways to do this include:
- being more physically active
Following a diagnosis, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan thats appropriate for your condition. In order to keep your diabetes symptoms managed, stick to this plan as much as possible.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Diabetes 2 In Adults
The Importance Of An Early Diagnosis
As we mentioned above, identifying diabetes in all its forms early can be crucial to preventing complications like hyperglycemia , hypoglycemia , diabetic ketoacidosis , high blood pressure, and other dangerous complications.
Also, quickly seeking out medical advice can be incredibly valuable to treatment for these conditions.
For example, if caught early enough, type 2 diabetes and prediabetes can be effectively reversed by reversing the underlying insulin resistance that causes them.
And in the case of type 1 diabetes, quickly intervening and making sure that you get enough insulin can be the key to controlling your high blood glucose, and beginning to build the habits and dietary decisions that will help you return to a normal, healthy life.
You can learn more about the early indicators and risk factors of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes by clicking on each link.
And if youre already living with any form of diabetes, but still struggling to prevent it from taking over your life, we have a number of resources throughout this website that can help you take back control.
Stop Guessing What to Eat
Get Delicious Recipes Sent to Your Inbox Every Week!
Discover the custom-designed Weekly Meal Plan that gives you clarity on what to eat and how to shop to simplify your journey to lower blood sugar, weight loss, and your best A1c
Diagnostic Tests For Diabetes
Diabetes may be diagnosed based on A1C criteria or plasma glucose criteria, either the fasting plasma glucose or the 2-h plasma glucose value after a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test .
Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes
| A1C 6.5%. The test should be performed in a laboratory using a method that is NGSP certified and standardized to the DCCT assay. |
| OR |
| FPG 126 mg/dL . Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 h. |
| OR |
| 2-h PG 200 mg/dL during an OGTT. The test should be performed as described by the WHO, using a glucose load containing the equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. |
| OR |
| In a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, a random plasma glucose 200 mg/dL . |
| A1C 6.5%. The test should be performed in a laboratory using a method that is NGSP certified and standardized to the DCCT assay. |
| OR |
| FPG 126 mg/dL . Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 h. |
| OR |
| 2-h PG 200 mg/dL during an OGTT. The test should be performed as described by the WHO, using a glucose load containing the equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water. |
| OR |
| In a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, a random plasma glucose 200 mg/dL . |
Also Check: Keto Diet Good For Type 2 Diabetes
World Health Organization Sugars Intake Guideline
In 2015 the WHO released guidelines on the intake of free sugars for adults and children . These guidelines recommend:
- Reduced intake of free sugars throughout the life-course
- In both adults and children, intake of free sugars not exceed 10% of total energy
- Further reduction to below 5% of total energy
The WHO states that the first two recommendations are based on the health risks of free sugars consumption in predisposing those who consume them to overweight and obesity, and dental caries. WHOs third recommendation states that a further reduction of free sugars to below 5% of total energy intake per day would provide additional benefits. The limits would apply to all sugars added to food, as well as sugars naturally present in honey, syrups, fruit juices and fruit concentrates.
Diabetes Canada supports these recommendations for Canadians and acknowledges the importance of the outcomes described by the WHO. Diabetes Canada recommends reducing free sugars consumption by the general population to promote dental health and decrease the risk overweight and obesity and subsequent illnesses. Furthermore, for people living with diabetes, limiting sucrose intake to 10% or less of total daily energy is recommended by the 2013 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Intake of sucrose > 10% of total daily energy may increase blood glucose and triglyceride concentrations in some individuals with type 2 diabetes .
Cules Son Las 3 P De La Diabetes

Bueno, todas las 3 P de la diabetes generalmente se disparan desde niveles altos de glucosa en sangre. La glucosa en sangre generalmente es filtrada por los riñones y luego es absorbida nuevamente a la sangre.
Si el nivel de glucosa en sangre es más alto, los riñones no pueden funcionar de manera eficiente para reabsorber todo el azúcar y por lo tanto termina en la orina .
- Poliuria Si hay un alto contenido de azúcar en la orina, el exceso de agua del cuerpo se pierde por la orina y por lo tanto se desarrolla poliuria.
- Polidipsia La pérdida de agua en exceso causa deshidratación y esto aumenta la sed, así se desarrolla la polidipsia.
- Polifagia Cuando hay falta de insulina producción en el cuerpo, que ocurre en la diabetes, conduce a la absorción deficiente de azúcar en la sangre en el tejido corporal y, por tanto, se desarrolla polifagia. Cuando hay falta de azúcar en el cuerpo, se reduce la producción de energía y esto aumenta el apetito y el hambre, lo que resulta en polifagia.
El principal factor que gira en torno a las 3 P de diabetes es el nivel alto de azúcar en la sangre, que es caso en diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Best Way To Eat For Diabetes
What Is The Cause Of Polydipsia
An increase in thirst is caused by the excessive loss of water in the body secondary to frequent urination. To quench thirst, a diabetic patient drinks a lot of water.
However, the result is only temporary as the water being drunk will then be excreted in the urine. If you feel thirsty most of the time and at the same time urinate too often, then you need to start suspecting diabetes, especially if diabetes runs in your family.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy.
When you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose and sends that to your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells, which use it for energy.
When you have diabetes and donât get treatment, your body doesnât use insulin like it should. Too much glucose stays in your blood, a condition usually called high blood sugar. This can cause health problems that may be serious or even life-threatening.
Thereâs no cure for diabetes. But with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can live a long, healthy life.
Diabetes comes in different forms, depending on the cause.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes And High Eye Pressure
Categories Of Increased Risk For Diabetes
Recommendations
-
Testing to assess risk for future diabetes in asymptomatic people should be considered in adults of any age who are overweight or obese and who have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes. For all patients, particularly those who are overweight or obese, testing should begin at age 45 years. B
-
If tests are normal, repeat testing carried out at a minimum of 3-year intervals is reasonable. C
-
To test for prediabetes, the A1C, FPG, and 2-h PG after 75-g OGTT are appropriate. B
-
In patients with prediabetes, identify and, if appropriate, treat other cardiovascular disease risk factors. B
-
Testing to detect prediabetes should be considered in children and adolescents who are overweight or obese and who have two or more additional risk factors for diabetes. E
Criteria for testing for diabetes or prediabetes in asymptomatic adults
| 1. Testing should be considered in all adults who are overweight and have additional risk factors: |
| physical inactivity |
What Is The Trend Of Diagnosed Diabetes Over Time
Between 20032004 and 20132014, there was a relative increase of 37.3%Footnote i in the age-standardized prevalence of diagnosed diabetes, from 5.6% to 7.8%. During the same period, the age-standardized incidence rate fluctuated. It increased until 20062007, from 6.7 to 7.6 per 1,000 population, but then it decreased to 6.3 per 1,000 population by 20132014, slightly below its original level . This implies that factors other than an increase in new diabetes diagnoses contributed to this rise in prevalence, including the fact that Canadians with diabetes now live longer. With the growth and aging of the Canadian population, the number of Canadians living with diabetes is also expected to increase in the coming years.
Figure 3: Age-standardized prevalence and incidence of diagnosed diabetes among Canadians aged 1 year and older, 20032004 to 20132014
| Fiscal year | |
|---|---|
| 7.8 | 6.3 |
Notes: Age-standardized estimates to the 2011 Canadian population. The 95% confidence intervals are not shown as they were too small to be illustrated.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
Don’t Miss: Fastest Way To Get Rid Of Diabetes
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a condition resulting from high blood sugar and acid buildup, primarily affecting people with type 1 diabetes.
Despite significant improvement in diagnosis and treatment, DKA is still the number one cause of death in children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes, according to Dr. Umpierrez. Overall, mortality is low, but its occurrence is common, and the number of diabetics with DKA has increased with the cost of insulin, which has risen 1200 percent since its initial price of $21 per vial in 1996. As of 2019, that same vial cost $275.
Though diabetic ketoacidosis is most common and serious with type 1 diabetes, it can also strike people with type 2 diabetes who are skipping or cant afford insulin, have prolonged uncontrolled blood sugar, or are very sick with a co-occurring illness or infection, according to Dr. Umpierrez.
Infographic by Lauren Hunter