Type 1 Diabetes Complications
Type 1 diabetes is complicatedand if you dont manage it properly, there are complications, both short-term and long-term. If you dont manage it properly is an important if statement: by carefully managing your blood glucose levels, you can stave off or prevent the short- and long-term complications. And if youve already developed diabetes complications, controlling your blood glucose levels can help you manage the symptoms and prevent further damage.
Short-term Diabetes Complications
- Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is low blood glucose . It develops when theres too much insulinmeaning that youve taken too much insulin or that you havent properly planned insulin around meals or exercise. Other possible causes of hypoglycemia include certain medications and alcohol .
- Rapid heartbeat
- Numbness in fingers, toes, and lips
- Sleepiness
- Headache
- Slurred speech
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Diabetic ketoacidosis is sometimes the first indication that a person has type 1 diabetes, and can be a serious complication of lack of insulin.
Heres how diabetes ketoacidosis develops:ketones
- Frequent urination
- Confusion
- Weakness
Long-term Diabetes Complicationsmicrovascular complicationsmacrovascular complicationsMicrovascular Complications: Eye, Kidney, and Nerve DiseaseMacrovascular Complications: The Heart
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes2009. Diabetes Care. 2009 32:S13-61.
Are There Other Ways To Manage Type 1 Diabetes
People with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar closely. Maintaining a healthy blood sugar range is the best way to avoid health complications. You can monitor your blood sugar in the following ways:
- Blood glucose meter: You prick your finger and put a small drop of blood on the meters test strip. Your blood glucose level appears on the meter. A blood glucose meter is usually the least expensive home testing option, but it only reports your blood sugar at the time of the check.
- Continuous glucose monitoring : There are different types of CGMs. Most CGMs require you to insert a small sensor under your skin at home every seven to 14 days. Some CGMs are implanted by a healthcare provider. The sensor continuously records your blood glucose levels. People using a CGM require fewer finger sticks. CGM systems can be more expensive than fingerstick blood glucose meters, but they provide much more information about your glucose levels, including where they have been and where they are going.
How Will I Know If My Blood Sugar Is Too High
Even with treatment, people with type 1 diabetes sometimes have blood sugar levels that are too high. The best way to check your blood sugar level and to see how sensitive you are to insulin is to test your blood sugar level at least three times each day, including at bedtime. If it’s too high, take some extra short-acting insulin. If your level is too low, eat some food.
Read Also: Best Fruit Drinks For Diabetics
Search Strategy And Selection Criteria
We searched MEDLINE for publications in English published between Jan 1, 2014, and March 1, 2018, using the term type 1 diabetes and MEDLINE subheadings and selected papers on the basis of our opinion of their scientific importance. Research published since the 2014 Lancet Seminar on this topic was given particular attention. We provide an overview of type 1 diabetes focusing on updating the reader on recent advances and controversies.
Risks For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that occurs during pregnancy. Three to 20 per cent of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes, depending on their risk factors.
All pregnant women should be screened for gestational diabetes between 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. Women who are at high risk for type 2 diabetes should be screened before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
You’re more likely to develop gestational diabetes if you:
- are 35 years of age or older
- are from a high-risk group
- use corticosteroid medication
Don’t Miss: Does Diabetes Cause Red Eyes
Sensory And Autonomic Neuropathy
Sensory and autonomic neuropathy in people with diabetes are caused by axonal degeneration and segmental demyelination. Many factors are involved, including the accumulation of sorbitol in peripheral sensory nerves from sustained hyperglycemia. Motor neuropathy and cranial mononeuropathy result from vascular disease in blood vessels supplying nerves.
Getting Your Heart Checked
You should have your blood cholesterol and blood pressure checked at least once a year.
If you smoke, you should stop. Diabetes makes the effects of smoking on your heart worse.
Diabetes can damage your nerves , causing:
- numbness
- problems with sex
- constipation or diarrhoea
Let your GP or diabetes nurse know if you notice any changes like these. Early treatment can prevent nerve damage getting worse.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes Emergency Kit
> > > Discover The 1 Green Veggie That Worsens Diabetes Type 2 Symptoms
Diabetes can be managed through oral medications. In addition to insulin, metformin, which is a sugar-reducing agent, is also a common treatment for diabetes. It is considered a first-line therapy for diabetes treatment and is often added to insulin. It is important to know the risks of taking diabetes medications. Some drugs can be addictive, so you must consult your doctor before taking any medication. Your physician can prescribe you an appropriate treatment plan based on your medical history.
Your doctor will prescribe medication and check your blood glucose levels on a regular basis. Your A1c level will be checked every six months and your cholesterol levels will be tested regularly. Your doctor will also look for any signs of retinopathy, which is damage to the nerves in the eye caused by diabetes. You will also be examined for any foot problems. It is important to see a foot specialist regularly. Your feet should be thoroughly inspected for damage to the nerves.
While the first two types of insulin are the most common treatments, diabetes can be treated in a variety of ways. Your doctor may prescribe medications to control high blood pressure, which can protect the kidneys. Other types of medication include aspirin and other types of anti-platelet drugs. If your doctor is concerned about your blood sugar level, you may need to try a different medication. Some medications can cause side effects. Your treatment will depend on what type of insulin you need.
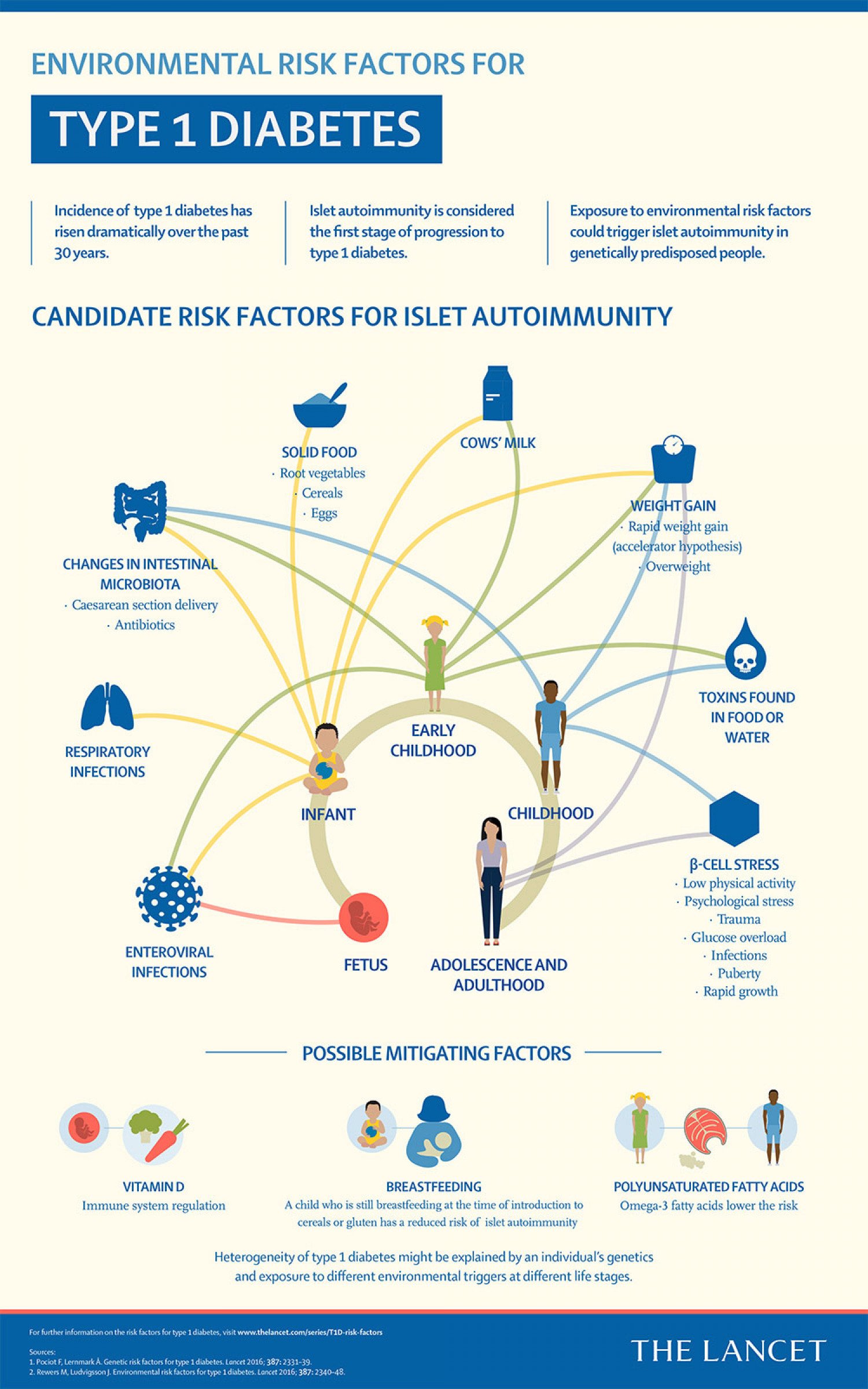
Is Type 1 Diabetes A Genetic Disease
There is a strong genetic link with type 1 diabetes. This can be tested for by looking at the human leukocyte antigen genotype. First-degree relatives are at higher risk. However, with any genetic condition, it is important to remember that gene expression changes in response to the epigenetic environment, and risk factors can be addressed with a health care professional or nutrition/functional/naturopathic practitioner knowledgeable about epigenetics.
- Prenatal exposures include maternal preeclampsia or metabolic syndrome .
- Environmental exposures include chemicals, especially those found in plastics and foods, specifically introduction of gluten, casein or fruit before 4 months of age or late introduction to grains and casein.
- Viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus or EBV , Coxsackie, CMV, and other infections can also be risk factors for developing type 1 diabetes.
- Living in a northern climate is a risk factor that has not been fully explained.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat Diabetic Retinopathy
Definition Symptoms Causes & Treatment
The goal of type 1 diabetes treatment is to normalize blood sugar levels. For most people, this means keeping blood sugar between 80 and 130 mg/dL. There are other targets, including after-meal blood sugar levels and HbA1C levels. HbA1C is a test that shows long-term blood sugar control over the last 2 to 3 months. In most cases, the goal result is 7%. Your doctor may have different target levels for you, depending on your specific situation.
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Don’t Miss: How To Treat A Corn When Diabetic
How To Stay Safe
Everyone should focus on staying safe from the virus. There are steps you can take to lower your risk of getting COVID-19. You may be able to avoid going to the pharmacy or hospital unless it is an emergency. You may also be able to receive your diabetes supplies at home by ordering them.
Stay safe by:
- Not going out unless it is necessary
- Not staying in big crowds
- Avoiding people who are sick
- Staying 6 feet apart from other people
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
Signs are often subtle, but they can become severe. They include:
- Extreme thirst
- Heavy, labored breathing
- Frequent infections of your skin, urinary tract, or vagina
- Crankiness or mood changes
- Bedwetting in a child whoâs been dry at night
Signs of an emergency with type 1 diabetes include:
- Shaking and confusion
- Loss of consciousness
You May Like: Dexcom And Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes Can It Be Cured
Currently, type 1 diabetes cannot be cured. People with type 1 diabetes require injectable insulin because their pancreas does not produce enough on its own. There are different types of insulin and different routes of administration. Most people with type 1 diabetes use both a long-acting insulin , and inject additional insulin before or after meals to match the carbohydrate content of the meal. An insulin pump may also be used to optimize insulin delivery to the body’s needs.
- Unfortunately, one of the major side effects of insulin is weight gain. People with type 1 diabetes can reduce weight gain by:
- Eating a healthy low-carbohydrate diet,
- Getting plenty of exercise, and
- Learning to use insulin correctly in order to use just the right amount
- Diet and level of activity.
Type 1 Diabetes In Children
Type 1 diabetes was once known as juvenile diabetes. That is because its frequently diagnosed in children and young adults. By comparison, type 2 diabetes is typically diagnosed in older adults. However, both types can be diagnosed at almost any age.
According to a
The ketogenic diet has shown some benefits for people with type 2 diabetes.
The high fat, low carb diet may help manage blood sugar levels, according to 2018 research . It can even lead to weight loss, a goal for many people with type 2.
For type 1 diabetes, however, the keto diet hasnt been well-studied. To date, the general dietary recommendation for this type of diabetes is a low carb diet. However, researchers are looking at the possible benefits and safety of a diet that restricts carbs even more for people with type 1 diabetes.
One small study found that people with type 1 diabetes who followed the keto diet for more than 2 years showed better A1C results and glycemic control. However, these individuals also had higher blood lipids and more low blood sugar episodes. Long-term safety is unknown.
If youre interested in trying the keto diet and you have type 1 diabetes, start by talking with your doctor. They may refer you to a registered dietitian or nutritionist to help you find a plan that is right for you.
Also Check: How Can I Know If I Am Diabetic
Complications Of Type 1 Diabetes And Covid
Your risk of having complications from COVID-19 might be higher because of type 1 diabetes. You may have worse symptoms and outcomes because of your underlying medical condition.
Having a viral infection can make it more difficult to manage your blood glucose level, so it may be higher than normal. This increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis . During DKA, your body cannot get glucose to your cells and burns fat for energy, which leads to the creation of ketones.
Diabetic ketoacidosis can be life-threatening. You should seek immediate medical care if you suspect you have DKA.
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Recommended Reading: When To Take Basal Insulin
What Should I Eat
The best diet for you is low in fat, low in salt and low in added sugars. It has lots of complex carbohydrates , fruits and vegetables. This diet will help you control your blood pressure and cholesterol levels too. It’s important not to eat too much, so you don’t gain weight. You can eat something sweet once in a while but, when you do, take enough insulin to keep your blood sugar level in the normal range.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. They have similar symptoms and over time, they can lead to many of the same complications. However, they are very different diseases.
Type 1 diabetes is the result of a persons body not producing insulin on its own. Taking insulin is necessary for survival, to move glucose from the bloodstream into the bodys cells.
For people with type 2 diabetes, the cells have stopped responding well to insulin. The body struggles to move glucose from the blood into the cells, despite having adequate levels of the hormone. Eventually, their bodies may stop making adequate insulin entirely.
Type 1 diabetes develops very quickly and symptoms are obvious. For people with type 2 diabetes, the condition can develop over many years. In fact, a person with type 2 diabetes may not know they have it until they have a complication.
The two types of diabetes are caused by different things. They also have unique risk factors.
Read Also: Can You Control Diabetes With Diet And Exercise
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
People with Type 1 diabetes need to replenish their insulin each day. There are different types of insulin. Some insulin starts acting as soon as you take the medicine other insulins take several hours to work. The various types of insulin also last in your body for different lengths of time. Some are more expensive than others. Work with your doctor to find the right type of insulin for your needs.
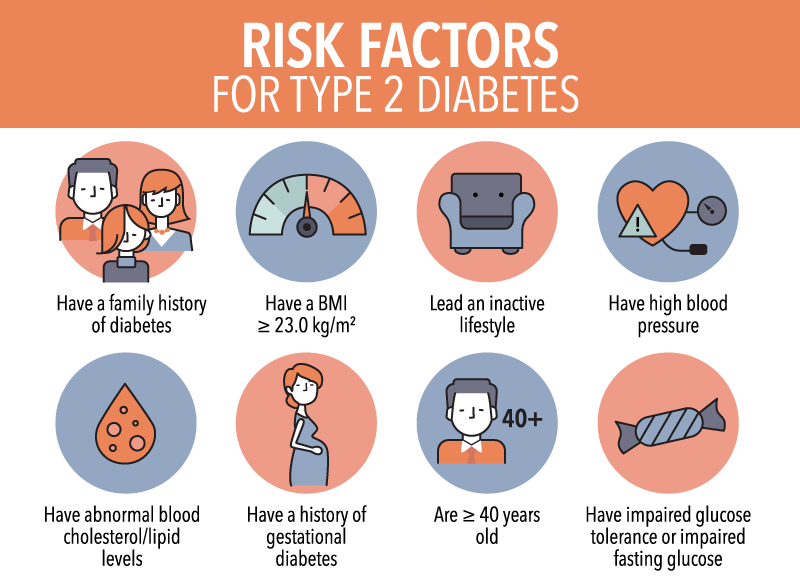
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
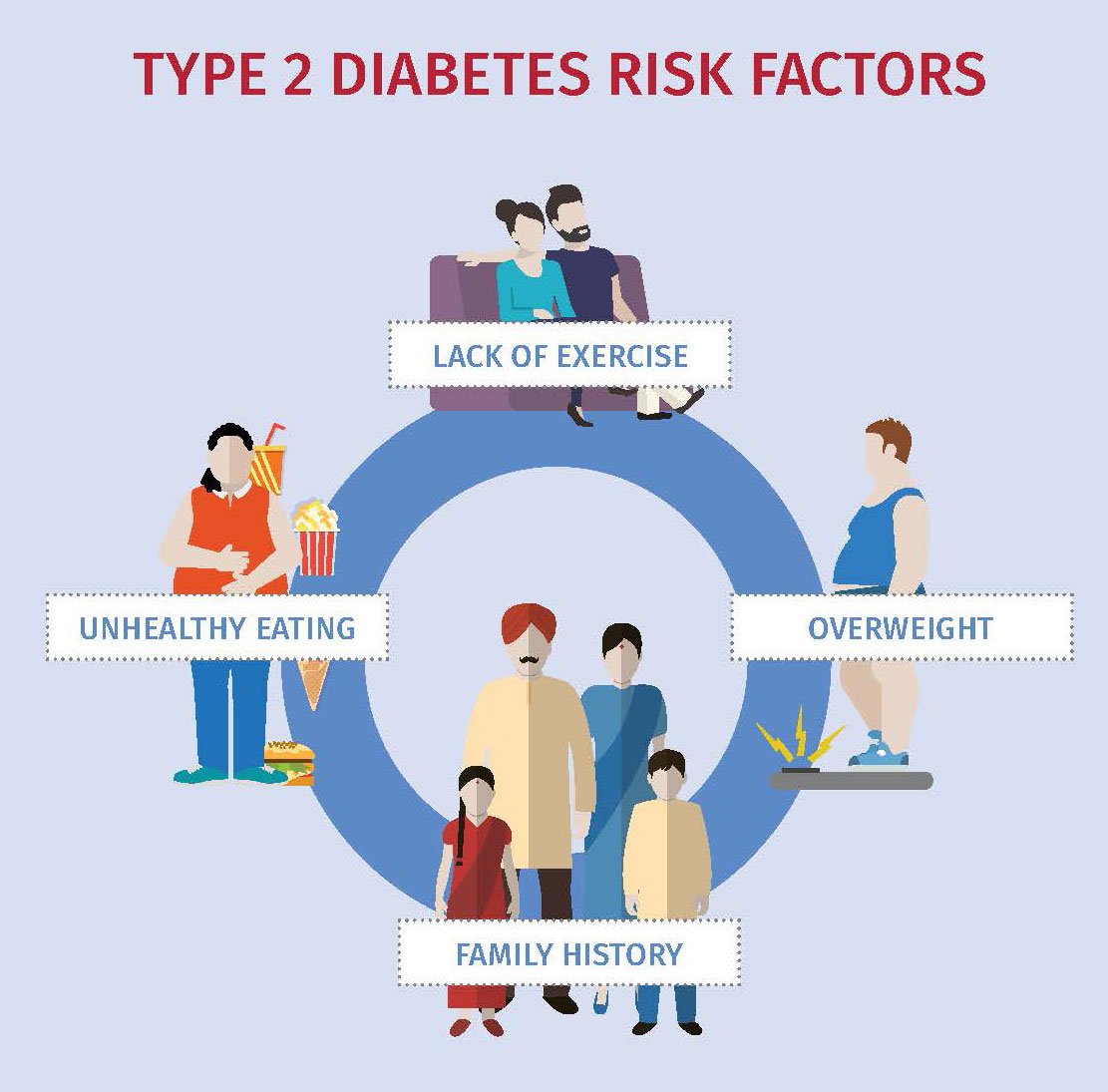
You can have type 2 diabetes without any obvious warning signs or symptoms. If you think you might be at risk for developing diabetes, don’t ignore these risk factors. The earlier you’re diagnosed, the sooner you can take action to stay wellnow and in the future.
Some diabetes risk factors can be managed or reduced, while other factors may be beyond your control. For example, you have a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you are over the age of 40 or if you have a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes. Your ethnic background is also a factor: being of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous, or South Asian descent can increase your risk of living with type 2 diabetes.
Having any of the following conditions increases your chances of developing diabetes:
- high blood pressure
- high levels of cholesterol or other fats in the blood
- a high BMIor are overweight
- prediabetes (impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- psychiatric disorders
- obstructive sleep apnea
- darkened patches of skin called acanthosis nigricans
Lastly, if you have been prescribed a glucocorticoid medication by a doctor, you will also have an increased risk.
You May Like: List Of Insulins For Diabetes
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system, the bodys system for fighting infection, attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Scientists think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and environmental factors, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease. Studies such as TrialNet are working to pinpoint causes of type 1 diabetes and possible ways to prevent or slow the disease.
Understanding Diabetes From Other Causes
In addition to type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, a small minority of people develop specific types of diabetes due to other causes. This includes:
- Monogenic diabetes syndromes, such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Diseases of the exocrine pancreas, such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis
- Drug or chemical-induced diabetes, such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS or after organ transplantation
Because these types of diabetes are rare, they are often misdiagnosed as other types of diabetes. You can learn more about these types of diabetes in the Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes section in the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. If you think you might have one of these types, be sure to talk with your doctor.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Insulin Pens Last