Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
Learn To Manage Your Stress
We all have stress. However, some people can manage it better than others. Personally, Im a Type-A, and Ive had to work hard and learn ways to manage stress.
Chronic stress takes a toll on your immune system. It makes you more likely to contract a cold or flu, or even develop a chronic autoimmune disease. Stress also raises your cortisol levels, which in turn raises your blood sugar. Its a major cause of high fasting blood sugars.
To manage stress, try any or all of these things:
- Yoga or tai chi
- Keep a gratitude journal
- Use adaptogenic herbs like Tulsi or one of my favorites Ashwagandha
Adaptogens are a class of herbs that help your body adapt to various types of stressors. They have long been used in Ayurvedic medicine. Tulsi is one of my favorites and it happens to be another ingredient in Herbaly Wellness Collection tea. Tulsi been shown to enhance your immune system, reduce cortisol levels, and improve blood sugar.
What Happens If My Blood Glucose Level Becomes Too Low
Sometimes blood glucose levels drop below where they should be, which is called hypoglycemia. For most people with diabetes, the blood glucose level is too low when it is below 70 mg/dL.
Hypoglycemia can be life threatening and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia.
Recommended Reading: Weight Loss Supplements For Diabetics
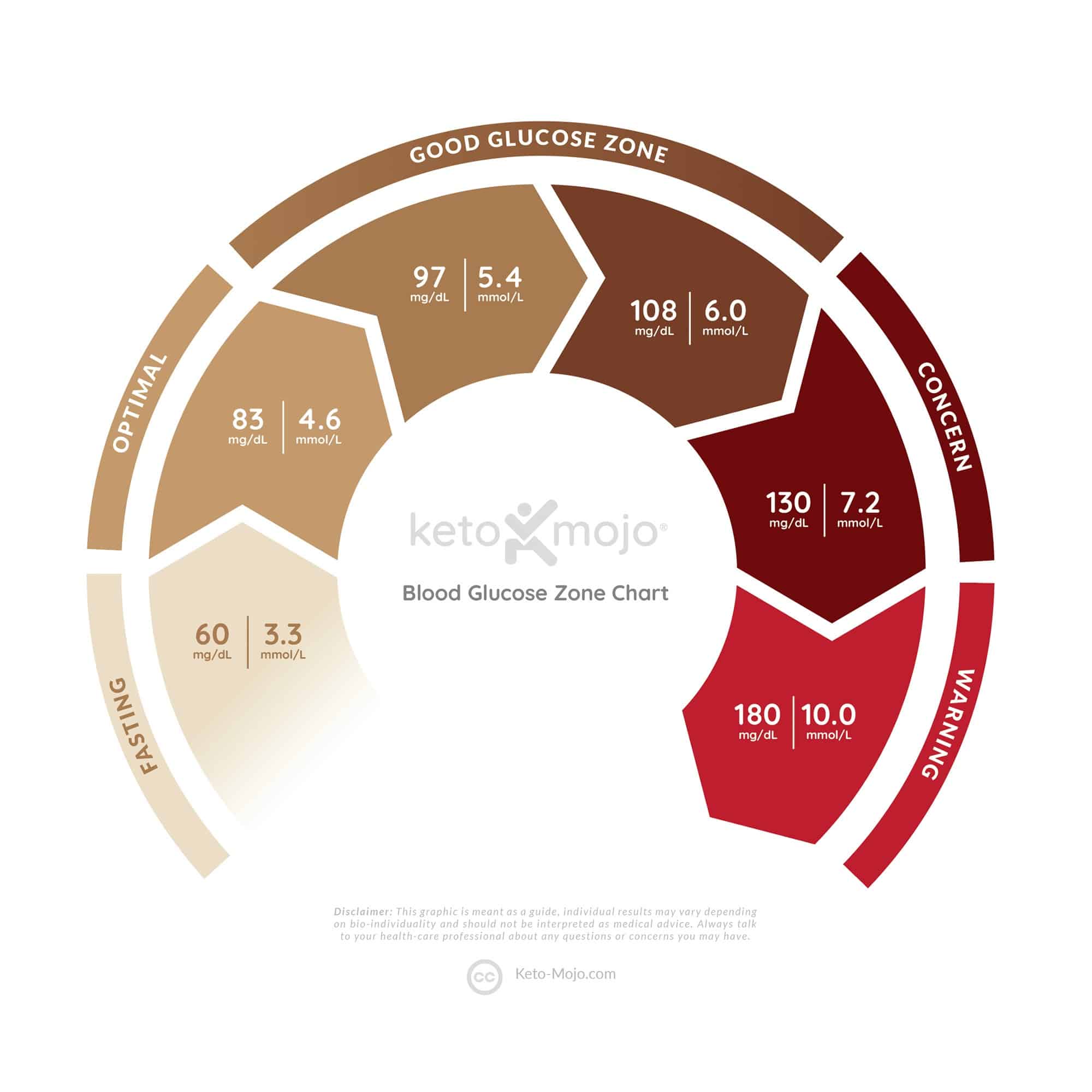
What Should I Aim For
Effective management of diabetes is all about aiming for a careful balance between the foods you eat, how active you are and the medication you take for your diabetes. Because this is a delicate balance, it can be quite difficult to achieve the best possible blood glucose management all the time.
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individuals circumstances. While it is important to keep your blood glucose levels as close to the target range of target range between 4 to 6 mmol/L as possible to prevent complications, it is equally important to check with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator for the range of blood glucose levels that are right and safe for you. Therefore the following information should be treated only as a general guide.
High Calorie Foods May Or May Not Cause The Blood Sugar Level To Rise
Many people think that all high-calorie foods raise blood sugar level, but this is not always the case.
In general, foods that cause blood sugar level to rise the most are those that are high in carbohydrates, which are quickly converted into energy, such as rice, bread, fruits and sugar. Next are foods high in protein, such as meats, fish eggs, milk and dairy products, and oily foods. However, even though carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels, if you dont eat them your diet will be unbalanced and you wont feel satisfied after your meal, which can lead to excessive consumption of foods rich in protein and fat.
Food containing three major nutrients
| Carbohydrates |
|---|
Also Check: What Happens When You Take Insulin
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly.
The following blood sugar and A1c results are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note:Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly that they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in ourDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Does A Blood Sugar Spike Mean You Have Diabetes
Occasional high spikes donât mean you have diabetes. Itâs normal for your blood sugar to go up after eating a meal high in carbohydrates or even due to lifestyle habits and events. Besides food, your blood sugar can be affected by stress, lack of sleep, age, menstrual cycle, physical activity, and even being sick.
What affects one person’s blood sugar may also affect yours differently. We can all have different responses to food, so monitoring the overall trend of your blood sugar gives you the most insight into your overall health.
However, while infrequent spikes aren’t a problem, if they happen more regularly, it’s time to take a closer look at what’s contributing.
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/mitigate-high-glucose-spikes”> how to mitigate glucose spikes to avoid fat storage< /a> < /p>
You May Like: Can You Get A Tummy Tuck If You Have Diabetes
What Is Normal Blood Sugar
Maintaining a healthy blood glucose range is important, but what is normal blood sugar?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main source of fuel for our bodies. It powers up our internal organs, muscles and nervous system. Keeping your blood sugar in check is essential to our physical health, wellbeing and energy levels. But what is considered a normal blood glucose level? And what happens when it rises above the normal threshold?
Our blood sugar levels are directly related to the food we eat. We obtain glucose mostly from carbohydrate-rich foods like bread, pasta, potatoes or fruit, but many different food groups play a role in regulating glucose metabolism. How we absorb, use and store this important sugar is dependent on multiple complex processes that take place in our digestive systems.
There is no single universal value that would describe a healthy blood sugar level. What constitutes normal blood glucose varies for an individual depending on a range of factors, including age, any underlying medical conditions, and the medications they take. It will also be heavily linked to when you consumed your last meal. Hence when we refer to ‘normal blood sugar levels’, we refer to a range of values that are considered healthy.
Here, we will discuss everything you need to know about a healthy blood sugar range.
Why You Should Care About Your A1c
Multiple studies have shown that high average blood sugars increase the risk of diabetes-related complications. Lowering your A1c to the recommended range will reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications significantly:
- Eye disease risk is reduced by 76%
- Kidney disease risk is reduced by 50%
- Nerve disease risk is reduced by 60%
- Any cardiovascular disease event risk is reduced by 42%
- Nonfatal heart attack, stroke, or risk of death from cardiovascular causes is reduced by 57%
Achieving an A1c in the recommended range is, therefore, one of the most important things you can do to improve your long-term health when you live with diabetes.
However, the closer you get to the recommended A1c target, the less benefit you will get from lowering your A1c further. Taking your A1c from 12% to 11% makes a big difference while lowering your A1c from 7% to 6% provides a much smaller benefit. In fact, lowering your A1c too much may not be a good idea if it means that you increase how often you experience hypoglycemia .
I will explain why time-in-range is just as important as a low A1c later in this guide.
Also Check: Can Diabetes Cause Low Blood Pressure
Can I Check My Own Blood Sugar
You can do blood sugar level check by doing a finger-prick test, or by using an electronic blood sugar monitor called a flash glucose monitor or CGM. You can do this several times a day helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take. Find out your ideal target range.
Not everyone with diabetes needs to check their levels like this. Youll need to if you take certain diabetes medication. Always talk to your healthcare team if youre not sure whether thats you theyll give you advice on whether to check them yourself and how often.
And theres also something called an HbA1c, which is a blood test to measure your average blood sugar level over the last three months. Everyone with diabetes is entitled to this check.
High blood sugar levels increase your risk of developing serious complications. However you manage your diabetes, stay in the know about your blood sugar levels
How To Prevent Low Blood Sugar
Small changes to your diet and physical activity habits can help prevent blood sugar spikes and decreases.
- Take smaller portions of high-carb foods, such as bread, pasta, potatoes, desserts, soft drinks and other sugar-sweetened beverages, and rice.
- Include a source of protein, fat, and/or dietary fiber when you eat carbohydrates.
- Choose less-processed versions of foods, such as whole fruit instead of juice, whole grains instead of refined, and pasta al dente instead of very well-cooked pasta.
- Instead of exercising on an empty stomach, have a small snack an hour or two before you start, or a larger snack or small meal three hours before.
- Have a snack or your next scheduled meal as soon as possible after exercising.
These changes can help prevent blood sugar swings.
| Instead of |
|---|
Dont Miss: What Is Too Low Of Blood Sugar
Recommended Reading: Pain Medicine For Diabetic Neuropathy
Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
The NIDDK states that gestational diabetes is high blood sugar that occurs during pregnancy if you were not diabetic before getting pregnant. Healthy blood sugar during pregnancy can help lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. It can also lower the risk of your baby being born prematurely, at a high birth weight, and having respiratory problems.
Blood sugar and insulin levels during the first trimester of pregnancy tend to be lower than usual, but they rise during the late second and early third trimesters. You can be diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test .
These are the steps for the 2-step strategy.
- Drink a solution with 50 grams of glucose about the amount in 1 16-oz. bottle of a soft drink
- Get your blood drawn after 1 hour. Ig the value is high, retest
- Drink a solution with 100 grams of glucose about the amount in 12 peanut butter cups
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1, 2, and 3 hours
Or, your doctor might use the 1-step strategy with a 2-hour OGTT:
- Drink a solution with 75 grams of glucose
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1 and 2 hours
These are some values to know from NIDKK related to gestational diabetes and healthy blood sugar in pregnancy.
Blood sugar can vary greatly depending on when you take it. For example, after 1 hour, a reading of at least 180mg/dl can indicate signs of gestational diabetes, while a blood sugar reading after 3 hours would need to be 140 mg/dl would be cause for concern.
Normal Blood Sugar Values
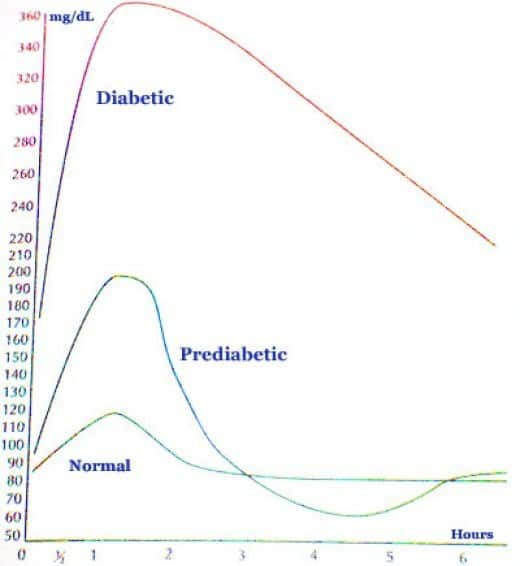
The closer your blood sugar stays in the normal range throughout the day, the easier it is for your immune system to do its job. Heres what to aim for:
- If you have prediabetes, try to keep your fasting sugar below 100 mg/dL, and your A1c below 5.7%. Those numbers are considered normal no diabetes.
- If you have diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends working to keep your fasting or premeal blood sugar under 130 mg/dL, and your A1c under 7.0%.
- If you check your glucose during the day, youll see that it goes up after you eat. Thats called a postprandial glucose. Ideally, it shouldnt go over 140 mg/dL 2 hours after you eat. Thats still considered normal.
Luckily, there are a few natural ways to improve your blood sugar and support your immune system at the same time. And hey, anything that kills two birds with one stone is good in my book!
You May Like: Is Olive Oil Good For Type 2 Diabetes
Problems Caused By High Blood Sugar
It’s not usually a serious problem if your blood sugar is sometimes slightly high for a short time.
But high blood sugar can cause serious problems if it stays high for a long time or gets to a very high level.
It can lead to:
- life-threatening conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis
If you have high blood sugar, your doctor or care team may ask you to test your blood or pee to check for ketones. A high level of ketones is a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Times To Check More Often
There will be times when you need to check more often, however you should first discuss this with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator. Example of these times include when you are:
- Being more physically active or less physically active
- Sick or stressed
- Experiencing changes in routine or eating habits, e.g. travelling
- Changing or adjusting your insulin or medication
- Experiencing symptoms of hypoglycaemia
- Experiencing night sweats or morning headaches
- A female planning pregnancy or are pregnant.
- Pre/post minor surgical day procedures
- Post dental procedures
Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator can help you work out self-monitoring approach especially for you.
You May Like: Why Do Diabetes Pee A Lot
What Should My Bgl Be
For a person without diabetes, throughout the day blood glucose levels will generally range between 4.0 7.8 millimoles of glucose per litre of blood regardless of how they eat or exercise, or what stress theyre under.
When youre living with diabetes your body cannot, or finds it hard to, keep your BGLs within a healthy range.
Because each person living with diabetes is different, your GP or specialist will set target BGLs that are right for you. However, here is some information you can use as a general guide. The information below is a general guide for target blood glucose levels before meals and after eating.
Diabetes & Ketones: Everything You Need To Know
These days, understanding what ketones are can be confusing, because even mainstream society and non-diabetics are talking about ketones.
What has always been something people with diabetes feared, has now become something that low-carb and ketogenic dieters strive for: ketosis.
In this article, well talk about the crucial differences between diabetic ketones , starvation ketones, and nutritional ketosis. Well also cover what to do if youve developed diabetic ketones and how to manage ketones and diabetes during an illness.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If Your Child Has Type 1 Diabetes
What To Know About High Blood Sugar When Living With Diabetes:
What is hyperglycemia?
After eating a meal, the body signals the release of insulin. Insulin is like a key that unlocks the cells in order to store glucose for later use. This process reduces the amount of glucose in your blood stream. In people with diabetes, this process does not work as well because either there isnt enough insulin being produced, or because the body is resistant to the effects of the insulin. As a result, levels of glucose in the blood stream can reach high levels, causing hyperglycemia or high blood sugar.
Scale of normal blood sugar range
- Hyperglycemia occurs when the blood sugar is above 130 mg/dL while fasting, or greater than 180 mg/dL after eating a meal.
- American Diabetes Association Glucose Goals for people with Diabetes:
- Before meals or fasting: 70 to 130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL
Hb A1CIf blood glucose is regularly higher than the normal ranges, then this will reflect in the Hemoglobin A1C test that your doctor will run. The Hemoglobin A1C gives your care team an idea of what your blood sugar typically is at.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
- Illness, colds, infections, injuries, surgeries
- Emotional stress
- Not enough Diabetes Medication, or skipped doses of medication
- Too little exercise
How to treat hyperglycemia
When to call your doctor or seek emergency treatment:
REMEMBER: DO NOT DRIVE yourself if you think you may have very high blood Sugars or Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Types Of Replacement Insulin
Supplemental insulin comes in different types, and some are designed to replace bolus insulin, while others replace basal insulin.
The different types of insulin are differentiated based on three characteristics:
- Onset: The time between the insulin injection and when it starts to affect blood sugar levels.
- Duration: How long insulin continues to work after taking effect.
- Peak: The point at which insulin is working at maximum capacity.
The ADA lists five types of supplemental insulin: rapid-acting, short-acting , intermediate-acting, long-acting, and ultra long-acting.
Also Check: Contour Next One Blood Glucose Monitoring System
Blood Sugar And Diabetes
To better understand what’s considered normal for blood sugar levels, it helps to know what happens when blood sugar is out of range and why it happens.
Diabetes occurs when your pancreas can’t make enough insulin to move sugar out of your blood, or your cells become less responsive to insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that tells your body to move glucose out of the blood and into your cells. Once inside your cells, glucose can be used for energy or stored as fat. People with diabetes aren’t able to lower blood sugar effectively, so it remains higher than what’s considered normal.
Abnormal blood sugar occurs when too much or too little sugar is in the blood.
- Hypoglycemia is 70 mg/dL or less.
- Hyperglycemia is 180 mg/dL or more.
There are four tests used to test blood sugar levels. Blood glucose, aka blood sugar, is measured in milligrams per deciliter :
- Hemoglobin A1c: A1c measures long-term blood sugar averages over two to three months. Anything about 6.5% is considered a diagnosis of diabetes. This plus fasting are most commonly used.
- Fasting blood sugar: Fasting blood sugar looks at glucose levels before you’ve eaten anything. Fasting glucose above 126 mg/dL is also considered diabetes.
- Casual or random plasma glucose test. As the name suggests, this test randomly tests your blood sugar at any time and doesn’t require fasting. Anything higher than 200 mg/dL is considered diabetes.