How The Eye Is Affected
The structure of the eye is like a camera. Light passes through the transparent front lenses, as if through the lenses of a camera, until it reaches the back wall of the eye. This wall contains a very thin piece of light-sensitive tissue: the retina.
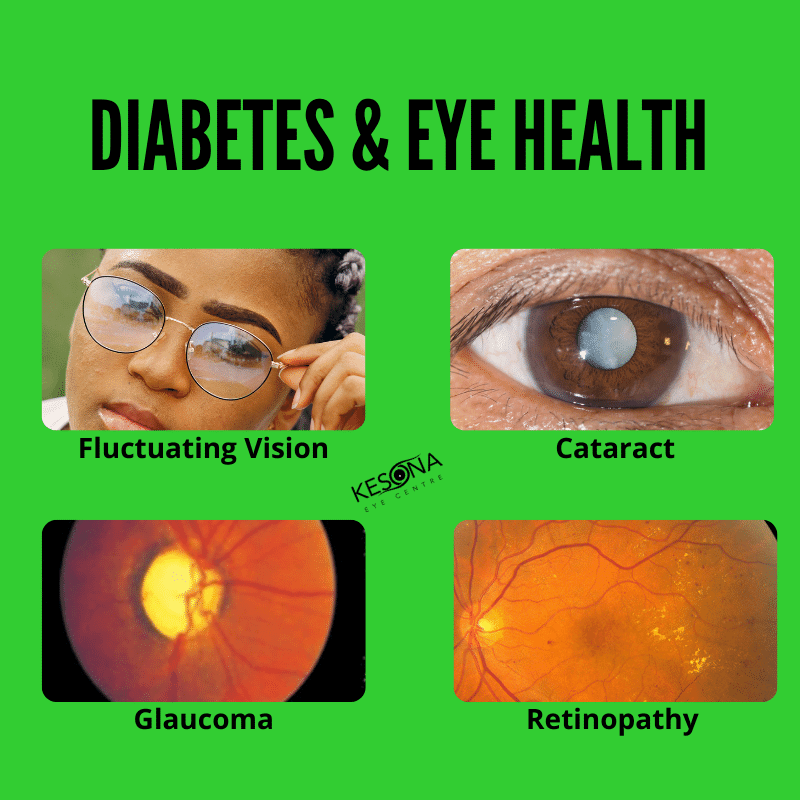
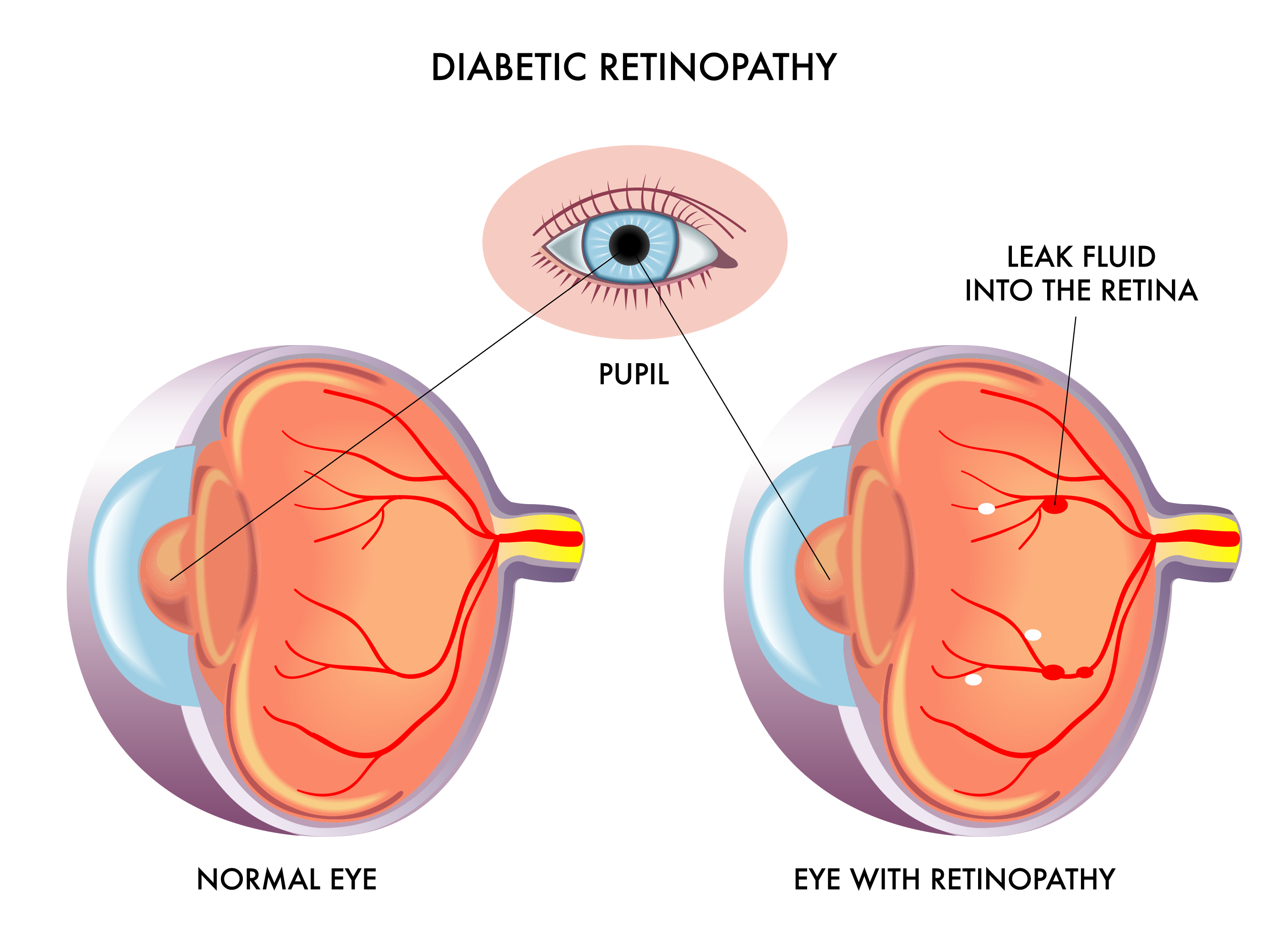
The tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina can be damaged by diabetes. The damage can cause the blood vessels to become leaky, like a water hose with holes in it. This is called non-proliferative retinopathy. Fluid leaks out of the blood vessels and into the retinal tissue which can cause vision problems. This causes the retina to thicken, creating blurred vision. The swelling associated with diabetes in the macula, the central part of the eye responsible for staring straight ahead, called diabetic macular edema.
In another process, blood vessels damaged by hyperglycemia close, and a series of events begin. Starving retinal tissue produces growth causing new blood vessels to form on the surface of the retina. When the new blood vessels form, its called proliferative retinopathy.
These new blood vessels are weak and can easily break and bleed. This leads to scar tissue, which can build up on the back wall of the eye and stretch the retina, eventually separating it from the back of the eye. This condition is known as retinal detachment, and it can happen suddenly or slowly over time.
You can have 20/20 vision and still have diabetic retinopathy. Some of the early signs include:
Glaucoma Laser Treatments And Surgical Options
Depending on the type of glaucoma associated with diabetes, different treatment options are available. Primary open-angle glaucoma patients are treated the same as non-diabetic patients with medications, lasers, and surgery, as needed. For neovascular glaucoma, lasers and injections can be used to treat the diabetic retinopathy, but the angle-closure glaucoma usually needs to be treated with a shunt to help restore drainage. A combination of these glaucoma treatments might be required to treat steroid-induced glaucoma, which can be a side-effect of steroid injections used to treat diabetic macular edema.
Diabetes & The Eyes Educational Toolkit
The Diabetes & the Eyes Educational Toolkit offers educational materials on diabetes and the impact of diabetes on eye health in both English and Spanish. These educational resources are intended for healthcare professionals, community health educators, diabetes educators, and anyone in a caregiving or diabetes education role.
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes A1c Numbers
Keep On Top Of Your Cholesterol And Blood Pressure
High blood pressure and a lot of fat in your blood will increase your chances of getting eye problems. This is because your blood vessels can get damaged or blocked, so the blood cant move around your eye properly.
We have advice and information to help you manage your blood pressure and cholesterol. Your healthcare team will also be able to support you with this.
Diabetes Treatment And Blurriness
For people who take medication to increase insulin in the body, changing the timing of food or a change in activity levels can result in low blood sugar levels.
Blurriness from low blood sugar does not result from changes in the eye. Instead, it is due to the way hypoglycemia affects the brain.
Vision that changes in this way will return to normal after glucose levels return to normal.
Don’t Miss: Does Chromium Picolinate Help With Diabetes
Is Diabetes Affecting Your Eyes 7 Signs Of Diabetic Eyes
Diabetes is becoming an increasingly alarming problem in the US. The estimated number of people over the age of 18 with diabetes, both diagnosed and undiagnosed, is 30.2 million-or roughly 30% of the population. The effects of diabetes can be disastrous, especially on the eyes, known as diabetic eyes. At Southside Medical Center in Atlanta, Georgia, our vision is to set the standard in affordable, quality healthcare, including diabetic eye exams.
What Does Diabetes Do To Your Eyes
Any type of eye problem that affects people with diabetes falls under the umbrella term of diabetic eye disease. Diabetic eye disease can include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma.
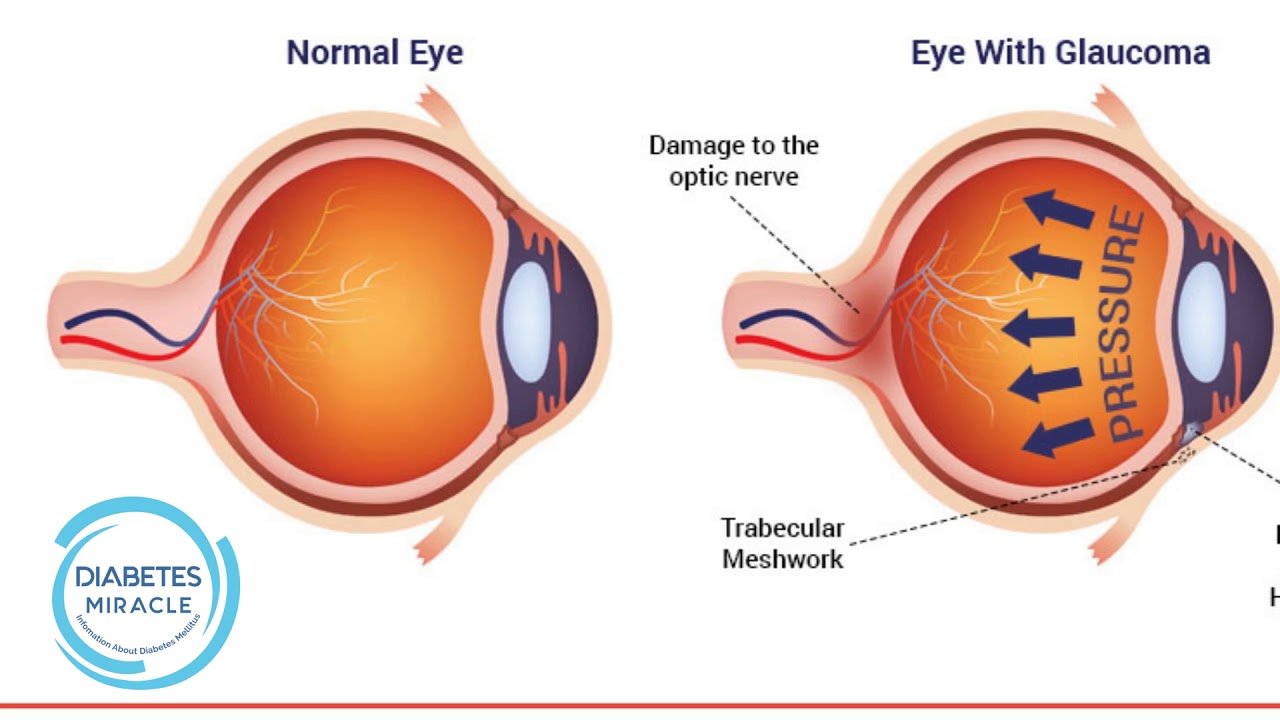
The increased blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can impact your eyes in a number of ways. The most common impact is weakened blood vessels that leak into your eye causing swelling that can damage the sensitive structures in your eye. Diabetes can also cloud the lens of your eye, and is associated with an increased risk of elevated eye pressure that can damage your optic nerve and lead to vision loss.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Yourself From Getting Diabetes
How Retinopathy Is Treated
If a doctor diagnoses you with retinopathy at your diabetic eye exam, all is not lost! Tremendous strides have been made in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. These treatments can prevent blindness in most people, but as always, the earlier diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed, the better your chances will be.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by high blood sugar due to diabetes. Over time, having too much sugar in your blood can damage your retina the part of your eye that detects light and sends signals to your brain through a nerve in the back of your eye .
Diabetes damages blood vessels all over the body. The damage to your eyes starts when sugar blocks the tiny blood vessels that go to your retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed. To make up for these blocked blood vessels, your eyes then grow new blood vessels that dont work well. These new blood vessels can leak or bleed easily.
You May Like: How To Deal With Gestational Diabetes
Progression Of Diabetic Retinopathy
Retinopathy can worsen over time. Broadly, there are two stages.
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Also known as background retinopathy, this is the early stage, with mild or no symptoms.
At this stage, the retinas tiny blood vessels may become weak and blocked. There may be bulges in them, or fluid can leak out. This can cause swelling in the central part of the retina.
NPDR can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on how serious the blood vessel problem is.
Swelling in the retinaor macula edemacan cause vision problems. This is because it is the central part in the back of the eye that allows people to see fine details clearly.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
This is an advanced stage of eye complications. Blood vessels cannot deliver blood to the retina effectively, because they have closed up. New vessels start to grow to compensate for this. This stage only develops in some people with diabetes. It takes several years to develop.
The growth of new blood vessels does not provide normal blood flow to the retina, however, and it can lead to scarring and wrinkling. In severe cases, it can distort a persons vision. The retina can even become detached, causing a loss of vision.
The fragile new vessels can also bleed out. Symptoms include floating spots in the vision. If a bleed from the retina into the central fluid of the eye is big, a person can sometimes lose sight in that eye. After this, they will only be able to tell light from dark.
How Can I Protect My Vision
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , 90% of diabetes-related vision loss is preventable. If you have diabetes, then you are at risk of developing a diabetic eye disease.
Follow these top 5 tips for how you can protect your eyesight from diabetic eye disease:
Also Check: Medtronic Closed Loop Insulin Pump
Other Types Of Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of vision loss for people with diabetes. But diabetes can also make you more likely to develop several other eye conditions:
- Cataracts. Having diabetes makes you 2 to 5 times more likely to develop cataracts. It also makes you more likely to get them at a younger age. Learn more about cataracts.
- Open-angle glaucoma. Having diabetes nearly doubles your risk of developing a type of glaucoma called open-angle glaucoma. Learn more about glaucoma.
Diabetes And Eye Exams
Q: I have type 2 diabetes that is under control . Is it still necessary to have the dilated eye exam annually? M.G.
A: Yes! Your eye doctor is an important part of a medical team managing your diabetes.
Damage from diabetes usually shows up first in what are called the “end organs” of the body, meaning the fingers, toes, kidneys and eyes. They can suffer the most from a lack of oxygen caused by too much sugar in the blood.
And damage can happen even with tight glucose control. Retinal damage, particularly leaky blood vessels in the retina, can be treated to avoid major vision loss.
The eyes are the only body organs that have windows to see inside and find out what’s going on. A dilated eye exam can help pick up minor changes that can help your doctors know if your diabetes is stable or not. It’s truly a peek inside your body a small price to pay for good health! Dr. Dubow
Q: I have diabetes. How often should I be checked to make sure my eyes are okay? E.B., Pennsylvania
A: Diabetes is the number one cause of blindness in the United States. Although diabetics have elevated blood sugar levels, the real damage is done by lack of oxygen. Because the eyes have such tiny blood vessels and yet need a lot of blood , diabetes can cause a great deal of damage.
Diabetes also can cause leaking of blood vessels in the eyes, which leads to scarring and loss of vision.
There are other changes as well:
More Diabetic Retinopathy Articles
Schedule an exam
Also Check: Best Type 2 Diabetes App
Treatments For Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is only necessary if screening detects significant problems that mean your vision is at risk.
If the condition has not reached this stage, the above advice on managing your diabetes is recommended.
The main treatments for more advanced diabetic retinopathy are:
- laser treatment
- injections of medication into your eyes
- an operation to remove blood or scar tissue from your eyes
Prevent Or Delay Eye Diseases
You can protect your vision and lower your chance for vision loss with these steps:
- Get a dilated eye exam at least once a year so your eye doctor can spot any problems early when theyre most treatable.
- Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Over time, high blood sugar not only damages blood vessels in your eyes, it can also affect the shape of your lenses and make your vision blurry.
- Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels in your target range to lower your risk for eye diseases and vision loss. Also good for your health in general!
- Quit smoking. Quitting lowers your risk for diabetes-related eye diseases and improves your health in many other ways too.
- Get active. Physical activity protects your eyes and helps you manage diabetes.
- Ask your doctor for a referral to diabetes self-management education and support services. People who receive less diabetes education are twice as likely to get diabetic retinopathy as people who receive more education.
Also Check: How Long Do Insulin Pens Last
How Diabetes Affects Your Eyes
Many things affect your eyes that you wouldnt necessarily expect would. The list is practically endless.
The fact is, your eyes dont exist on their own. They are part of a complex system consisting of various nerves, neurons, and organs including the brain.
Thankfully, you dont need to know how it all works in order to see.
One thing we do need to do for our eyes is manage systemic and external factors and conditions many of which may seem unrelated or insignificant.
One of these conditions that affects your eyes is diabetes. Diabetes, a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas is no longer able to produce insulin, can affect the health of your eyes and the quality of your vision in numerous ways.
The main reason for this is that, because of the bodys inability to produce insulin, high levels of glucose can build-up in the blood. In consequence, blood vessels all over the body can be affected. Since the eyes have some of the smallest vessels in the body, they are one of the first things to be affected.
In the short-term, high blood sugar levels can change your vision so you may experience fluctuating vision when the blood sugar is not under control or when you are changing medications.
Over the long-term, however, diabetes can lead to significant vision loss and permanent damage to your eyes.
The most serious diabetic eye diseases begin with blood vessel problems. Lets dive into the four biggest threats to sight.
Why Does Diabetes Affect Your Eyes
There are three types of diabetes . All involve ones body improperly handling insulin, a hormone that delivers glucose to the cells in your body. If an individual has too much glucose in their bloodstream because insulin is not carrying it to the cells, then this can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves.
Over time, the bodys mismanagement of glucose causes the blood vessels around the retina to weaken. If signs of pathology in the retina are undetected and therefore left untreated, the vessels can rupture and leak blood into the eye. This can eventually lead to more severe consequences, including blindness.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Diabetic Sores
The Role Of Insulin In Diabetes
To understand why insulin is important in diabetes, it helps to know more about how the body uses food for energy. Your body is made up of millions of cells. To make energy, these cells need food in a very simple form. When you eat or drink, much of your food is broken down into a simple sugar called “glucose.” Then, glucose is transported through the bloodstream to the cells of your body where it can be used to provide some of the energy your body needs for daily activities.
The amount of glucose in your bloodstream is tightly regulated by the hormone insulin. Insulin is always being released in small amounts by the pancreas. When the amount of glucose in your blood rises to a certain level, the pancreas will release more insulin to push more glucose into the cells. This causes the glucose levels in your blood to drop.
To keep your blood glucose levels from getting too low , your body signals you to eat and releases some glucose from storage kept in the liver.
People with diabetes either don’t make insulin or their body’s cells are resistant to insulin, leading to high levels of sugar circulating in the blood, called simply high blood sugar. By definition, diabetes is having a blood glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter or more after an overnight fast .
What Can I Do To Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
Managing your diabetes is the best way to lower your risk of diabetic retinopathy. That means keeping your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. You can do this by getting regular physical activity, eating healthy, and carefully following your doctors instructions for your insulin or other diabetes medicines.
To make sure your diabetes treatment plan is working, youll need a special lab test called an A1C test. This test shows your average blood sugar level over the past 3 months. You can work with your doctor to set a personal A1C goal. Meeting your A1C goal can help prevent or manage diabetic retinopathy.
Having high blood pressure or high cholesterol along with diabetes increases your risk for diabetic retinopathy. So controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol can also help lower your risk for vision loss.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Immunosuppression
What Can Be Done For Me If I Have Eye Damage From Diabetes
Your ophthalmologist can perform laser procedures to stop progression of the disease and reduce swelling. Medications may also be injected straight into the eye to help reduce swelling. Surgery is a later resort to clear out blood and remove scar tissue that may be causing the retina to swell or detach.
What Are The Treatments For Diabetic Eye Problems
Treatment for diabetic eye problems depends on the problem and how serious it is. Some of the treatments include:
- Lasers to stop blood vessels from leaking
- Injections in the eye to stop new, leaky blood vessels from growing
- Surgery to remove blood and scar tissue or replace a cloudy lens
- Eye drops to lower fluid pressure in the eye
But these treatments aren’t cures. Eye problems can come back. That’s why your best defense against serious vision loss is to take control of your diabetes and get regular eye exams. It’s also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol in a healthy range.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
You May Like: Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
Four Facts You Should Know About Diabetes And Eye Health
1. At first, the eye damage from diabetes may not be noticeable
Often, Rosenthal explains, there arent clear early warning signs that you have diabetic eye disease, that its developing, or even progressing.
And the longer you have diabetes, the greater the risk you have of it affecting your eyes.
Early changes can include bleeding within the retina, which may not affect your vision at first. At any stage, you can develop swelling in the macula, which often leads to blurred central vision, known as macular edema, said Rosenthal. The macula is where you have your sweet spot of vision. It’s what helps you recognize faces, read and see objects up close.
As your diabetes advances to the later stages, the blood flow to the retina can decrease, depriving your retina of oxygen and nutrition, recruiting new blood vessels, called neovascularization, one of the hallmarks of a condition called diabetic retinopathy.
While those new blood vessels sound like a really great solution to not getting enough nutrients and oxygen, they’re not good blood vessels, said Rosenthal. And, if left untreated, they can lead to vision loss.”
2. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy could cause irreversible vision loss
Diabetic retinopathy has two stages:
Macular edema can happen at either of these stages.
3. Luckily, there are treatment options available for diabetic retinopathy
According to Rosenthal, the gold standard for PDR is a laser treatment.