What Are The Recommended Targets For Blood Glucose Levels
Many people with diabetes aim to keep their blood glucose at these normal levels:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- About 2 hours after a meal starts: less than 180 mg/dL
Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. Be sure to tell your health care professional if your glucose levels often go above or below your target range.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patients diagnosed with diabetes need comprehensive care in the first few months of the diagnosis as management can be overwhelming and time-consuming. Patients and family members need to be educated about testing blood sugar, taking medications especially insulin, going to their medical appointments, and lifestyle modifications which include diet and exercise. Patients need to be given information for diabetes classes.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
Normal blood glucose levels are from between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol per litre of blood when fasting, and up to 7.8 mmol per litre of blood two hours after a meal.
If you’re having your blood sugar levels tested, your doctor will perform something called a ‘glucose tolerance test‘ which involves two blood tests, one after fasting, and one after the consumption of a sugary drink.
Manage your blood sugar levels with GlucoBalance
You can also help manage your blood sugar levels with GlucoBalance, an advanced plant-based formula to protect against highs and lows of blood sugar, manage blood glucose and your blood sugar metabolism. Find out more here.
You May Like: Blood Sugar Level After Eating Chart
How Can I Prevent Hyperglycaemia
To reduce your risk of severe or prolonged hyperglycaemia:
- monitor your blood glucose level regularly
- be careful with what you eat be particularly aware of how snacking and eating sugary foods or carbohydrates can affect your blood glucose levels
- stick to your management plan take diabetes medicines as and when directed
- be as active as possible getting regular exercise can help stop your blood glucose level rising, but you should check with your doctor first if you’re taking diabetes medication, as some medicines can lead to hypoglycaemia if you exercise too much.
- take extra care when you’re ill see our page on having a diabetes sick day plan.
Can Drinking A Lot Of Water Lower Your Blood Sugar Levels
Although feeling very thirsty is a symptom of a hyper, drinking a lot of water will not bring your blood sugar levels down. It will only help to reduce your risk of dehydration.
Its important that you take your diabetes medication to bring your blood sugar levels down. If you have consistently high blood sugar levels, you will need to follow the advice below and speak to your diabetes healthcare team.
Also Check: What Is Blood Sugar Test Called
How Can I Treat And Manage Hyperglycemia
People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
If you dont have diabetes and have any of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, call your healthcare provider. Together you can work to manage your hyperglycemia.
Pearls And Other Issues
Patients with severe hyperglycemia should be assessed for clinical stability including mentation and hydration. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state are acute, severe disorders related to hyperglycemia.
Patients confirmed with type 2 diabetes are faced with a life-long challenge to maintain euglycemia. This is not an easy undertaking and is also prohibitively expensive. Patients must be educated that making changes in their lifestyle can markedly improve their prognosis.
Also Check: Target Blood Sugar Levels For Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes And Blood Glucose Levels
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition. This means that your blood glucose levels are likely to increase over time. Regular monitoring is needed. Again, illness may cause an increase in your blood glucose levels. If you have acute elevations over 15mmol/L for 8-12 hours, or are unwell, follow your sick day plan.
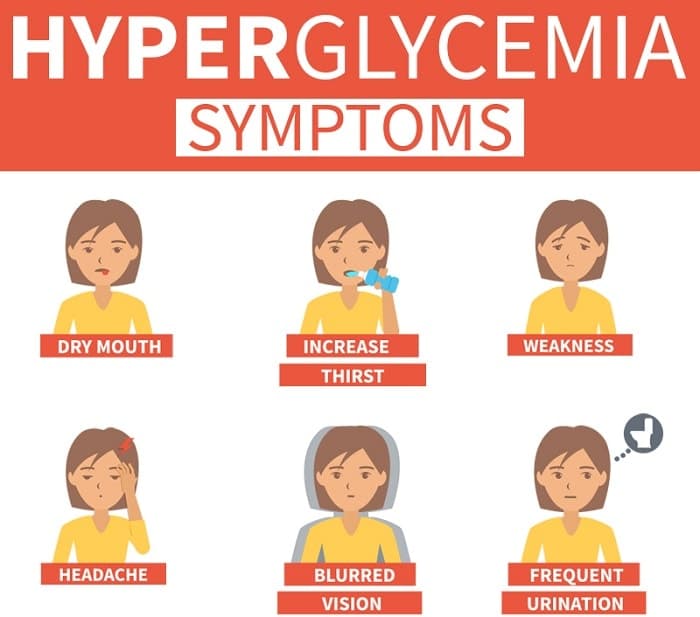
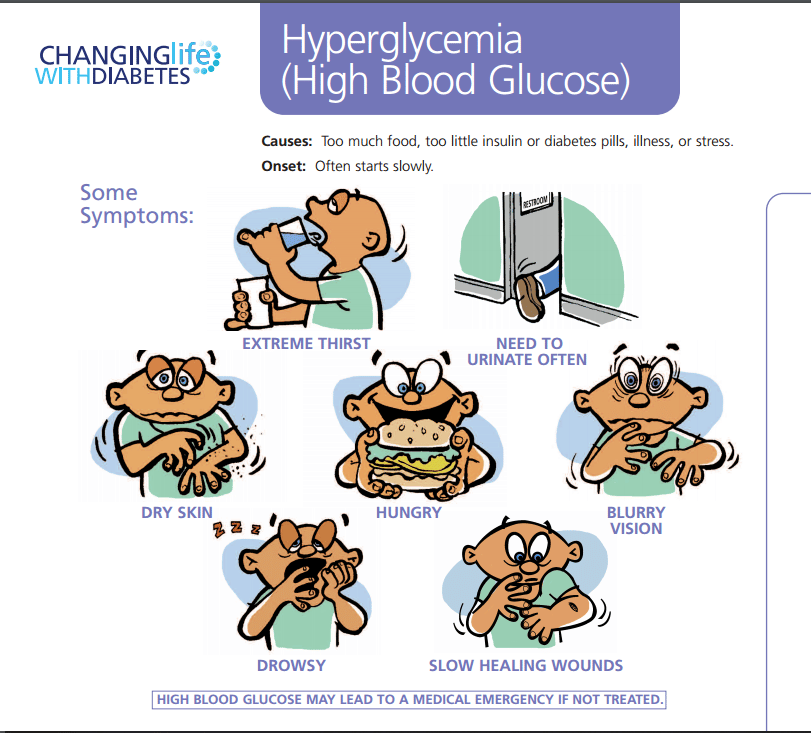
Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar
Learning to recognize the symptoms of hyperglycemia can help you successfully manage your diabetes.
Some people with diabetes immediately feel the symptoms of high blood sugar. Others dont because their symptoms are mild or vague.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia typically begin when your blood glucose goes above per deciliter . Symptoms can worsen the longer its untreated.
Symptoms of a blood sugar spike may include:
- frequent urination
Don’t Miss: Is Type 1 Diabetes Genetic
Tingling Hands And Feet
Over the years, hyperglycemia can begin to impact nerve function and eventually cause nerve damage, called neuropathy, Dr. Hatipoglu says. The most common kind of neuropathy is peripheral, according to the NIDDK, which affects the extremities. You might start noticing feelings of tingling, numbness, or burning in your hands, feet, arms, and legs, per the Mayo Clinic.
Postprandial Or Reactive Hyperglycemia
This type of hyperglycemia occurs after eating .
During this type of hyperglycemia, your liver doesn’t stop sugar production, as it normally would directly after a meal, and stores glucose as glycogen.
If your blood glucose level 1-2 hours after eating is above 180mg/dL, that signals postprandial or reactive hyperglycemia.
However, it’s not just people with diabetes who can develop hyperglycemia. Certain medications and illnesses can cause it, including beta blockers, steroids, and bulimia. This article will focus on hyperglycemia caused by diabetes.
Also Check: Why Does Diabetes Make You Thirsty
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Lack Of Physical Activity
A lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can lead to an increase in your blood glucose levels. Your skeletal muscle uses the glycogen in the muscle cells to produce energy during physical activity.
In the absence of physical movement, the glycogen remains stored and the excess glucose remains in the bloodstream, causing elevated blood glucose levels.
Also Check: How To Use Glucose Meter
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
What Happens If My Blood Glucose Level Becomes Too Low
Sometimes blood glucose levels drop below where they should be, which is called hypoglycemia. For most people with diabetes, the blood glucose level is too low when it is below 70 mg/dL.
Hypoglycemia can be life threatening and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia.
Also Check: Continuous Glucose Monitor Cpt Code
How To Effectively Manage High Blood Sugar
While diabetes is a dangerous disease, it is often possible to manage it and control blood sugar levels.
Recognizing the symptoms of high blood sugar is critical. When blood glucose levels are high, a person must take appropriate action. This is the case with both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
The patient should start by discussing the high blood sugar level with their doctor. The doctor will be able to perform a few tests to give them a better view of the patients diabetes.
It also helps the doctor determine what type of diabetes the patient has. This may be type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes in some cases. Patients also need to be aware that insulin resistance can develop into diabetes. Thus, if the patient is insulin resistant, they need to take action.
There are medications that can help. Some drugs help to ensure there is enough insulin in the body. Others rather have a direct effect on blood sugar levels. This can help to reduce the risk of a blood sugar spike. Failure to manage high blood sugar levels can lead to dangerous problems, such as diabetic coma.
A healthy diet is also critical for a person with diabetes. Carbohydrate counting is important, and you should learn what an appropriate portion size is for you. Meals should be balanced to avoid low blood sugar levels and a spike in blood glucose. It is also important that you take your medication with food.
Why Do These Symptoms Matter For Diabetics
These symptoms are essential for diabetics to understand, because they may encounter high or low blood sugar levels from time to time.
A cold or virus can cause sudden high blood sugar levels, and understand the symptoms means knowing how to deal with hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
People with diabetes who can recognise the symptoms can avoid levels that lead to medical emergencies such as diabetic ketoacidosis
Recommended Reading: How To Lower Insulin Resistance
What Are High Blood Sugar Levels
It is essential to address glucose levels in general. In persons without type 1 or type 2 diabetes, blood sugar levels generally range between 70 to 130 mg/dl.
It depends on the last time they ate a meal and the time of day. Normal blood glucose ranges in persons without any type of diabetes are:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning before eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
- One hour after a meal 90 to 130 mg/dl
- Two hours after a meal 90 to 110 mg/dl
- Five or more hours after eating 70 to 90 mg/dl
In pregnant women, blood sugar levels tend to be lower. Harvard Health also confirms that a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 mg/dl after an eight-hour fast. Also, a person has diabetes if their blood sugar is 126 mg/dl or higher.
When it comes to hyperglycemia or high blood sugar, there are two kinds of problems. The first kind is fasting hyperglycemia, which is blood sugar higher than 130 mg/dl after not eating or drinking for eight hours.
The other kind is postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia, which happens when your blood sugar is higher than 180 mg/dl two hours after a meal. People without diabetes rarely have blood sugar higher than 140 mg/dl after a meal unless its a big one.
When To See A Healthcare Professional
Hyperglycemia can happen suddenly after injury or illness. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms call 911 or have someone else call for you:
- Trouble breathing or talking
- Weakness or confusion
The aforementioned signs and symptoms can be a signal of diabetic ketoacidosis or worse, and if left untreated can be life-threatening. Fortunately, immediate recognition and treatment of these symptoms can lead to a rapid amelioration of your high blood sugar levels.
Although more research needs to be done to elucidate the long-term impacts of hyperglycemia on nondiabetic patientsespecially after acute injuryone thing is clear: living a healthy lifestyle that includes eating a balanced diet and routine exercise is the best way to avoid hyperglycemia and acute complications.
To prevent hyperglycemia:
Recommended Reading: Best Cookbook For Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetic Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome
Diabetic hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome, or HHS, is a complication from very high blood sugars in people with type 2 diabetes.
It doesnt occur in people with type 1 diabetes, who experience a different complication called diabetic ketoacidosis when blood sugar levels are dangerously high.
HHS is a condition of:
- Extremely high blood sugar level
- Extreme lack of water
- In many cases, decreased alertness or consciousness
Normally, the kidneys help to filter out extra blood glucose by increasing the amount of urine removed from the body. This is why one of the symptoms of diabetes is increased urination.
When excess urine is removed from the body, it can lead to dehydration. When the body is dehydrated, it cant make enough urine to flush out the extra sugar.
This leads to hyperosmolality, where the blood has higher concentrations of glucose , salt, and other substances. This can cause water to be drawn away from other sources of fluid, such as the brain, which is why it can cause an altered level of consciousness.
What Is The Treatment For High Blood Sugar
Mild or transient hyperglycemia may not need medical treatment, depending upon the cause. People with mildly elevated glucose or prediabetes can often lower their glucose levels by incorporating diet and lifestyle changes. Discuss any dietary or lifestyle changes with your healthcare team to assure or use reliable resources such as the American Diabetes Association.
Insulin is the treatment of choice for people with type 1 diabetes and life-threatening increases in glucose levels. People with type 2 diabetes may be managed with a combination of different oral and injectable medications. Some people with type 2 diabetes also take insulin.
High blood sugar due to medical conditions other than diabetes is generally treated by addressing the underlying condition responsible for elevated glucose. In some cases, insulin may be needed to stabilize glucose levels during this treatment.
You May Like: Insulin Pump For Type 2 Diabetes
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
What To Think About When Your Blood Sugar Is High
High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down. If you have diabetes, here are some questions to ask yourself when your blood sugar is high:
- Are you eating right?
- Are you eating too much?
- Have you been following your diabetes meal plan?
- Did you have a meal or a snack with a lot of carbohydrates, starches, or simple sugars?
Are you taking your diabetes medicines correctly?
- Has your doctor changed your medicines?
- If you take insulin, have you been taking the correct dose? Is the insulin expired? Or has it been stored in a hot or cold place?
- Are you afraid of having low blood sugar? Is that causing you to eat too much or take too little insulin or other diabetes medicine?
- Have you injected insulin into a scar or overused area? Have you been rotating sites? Was the injection into a lump or numb spot under the skin?
What else has changed?
To prevent high blood sugar, you will need to:
- Follow your meal plan
- Take your diabetes medicines as instructed
You and your doctor will:
- Set a target goal for your blood sugar levels for different times during the day. This helps you manage your blood sugar.
If your blood sugar is higher than your goals over 3 days and you don’t know why, check your urine for ketones. Then call your health care provider.
Read Also: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
American Heart Association / World Cancer Research Fund / American Institute For Cancer Research
The , , and recommend a diet that consists mostly of unprocessed plant foods, with emphasis on a wide range of whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables and fruits. This healthy diet includes a wide range of non-starchy vegetables and fruits which provide different colors including red, green, yellow, white, purple, and orange. The recommendations note that tomato cooked with oil, allium vegetables like garlic, and like cauliflower, provide some protection against cancer. This healthy diet is low in energy density, which may protect against weight gain and associated diseases. Finally, limiting consumption of sugary drinks, limiting energy rich foods, including “fast foods” and red meat, and avoiding processed meats improves health and longevity. Overall, researchers and medical policy conclude that this healthy diet can reduce the risk of chronic disease and cancer.
It is recommended that children consume less than 25 grams of added sugar per day. Other recommendations include no extra sugars in those under 2 years old and less than one soft drink per week. As of 2017, decreasing total fat is no longer recommended, but instead, the recommendation to lower risk of is to increase consumption of and , while decreasing consumption of .
What Causes Hyperglycemia In People With Diabetes
- The dose of insulin or oral diabetes medication that you are taking is not the most helpful dose for your needs.
- Your body isnt using your natural insulin effectively .
- The amount of carbohydrates you are eating or drinking is not balanced with the amount of insulin your body is able to make or the amount of insulin you inject.
- You are less active than usual.
- Physical stress is affecting you.
- Emotional stress is affecting you.
- You are taking steroids for another condition.
- The dawn phenomenon is affecting you.
Other possible causes
- Pancreatic diseases such as pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and cystic fibrosis.
- Certain medications .
- Gestational diabetes, which happens in 4% of pregnancies, and is due to decreased insulin sensitivity.
- Surgery or trauma.
Also Check: Diabetes Secondary To Sleep Apnea