Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Each time you test your blood sugar, log it in a notebook or online tool or with an app. Note the date, time, results, and any recent activities: What medication and dosage you took What you ate How much and what kind of exercise you were doing That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working. Well-managed diabetes can delay or prevent complications that affect your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes doubles your risk for heart disease and stroke, too. Fortunately, controlling your blood sugar will also make these problems less likely. Tight blood sugar control, however, means a greater chance of low blood sugar levels, so your doctor may suggest higher targets.Continue reading > >
Complementary And Integrative Health Approaches
Apart from these conventional medication treatment options, effective diabetes management means taking a well-rounded approach: Youll need to eat well, exercise, manage stress, and sleep enough, because all these factors can affect your blood sugar levels.
Certain complementary approaches may help support your conventional diabetes care, including certain botanical therapies, supplements, traditional Chinese medicine, mind-body therapies, and special diets like keto, research shows.
Measuring Sugar In Your Urine Yourself
You can also measure the blood sugar levels in your urine on your own. Having sugar in your urine is usually a sign of very high blood sugar levels. The extra sugar in the bloodstream is usually only removed via the kidneys at blood sugar concentrations of about 10 mmol/l and above. In order to measure the amount of sugar in your urine, you need a urine test strip and a container for collecting urine.
Its important to talk with your doctor about the best time of day to do the urine test, and whether to do it before or after eating. When measuring sugar in your urine yourself, you need a sample of urine that hasnt been in your bladder for long. So you wouldn’t use morning urine which has collected overnight. Instead, its more typical to urinate and collect a sample about an hour after the last time you went to the toilet. The test strip is then dipped into the sample. After about two minutes, the color pads on the test strip show the results.
Also Check: Type 2 Adult Onset Diabetes
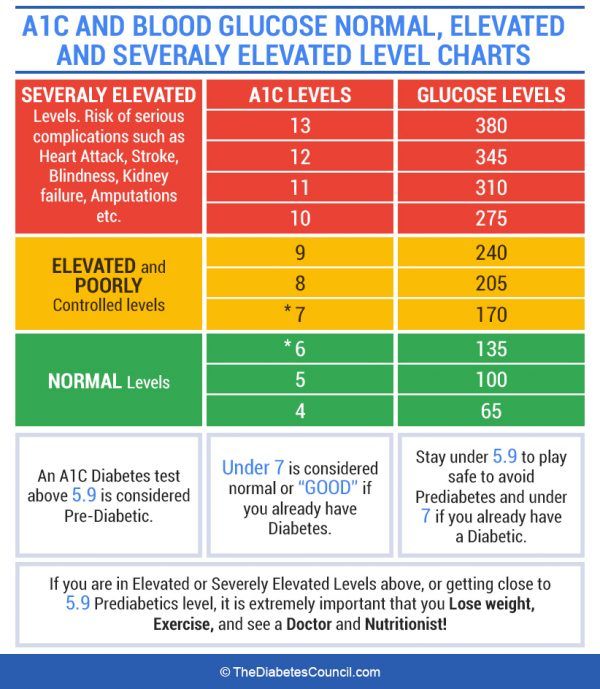
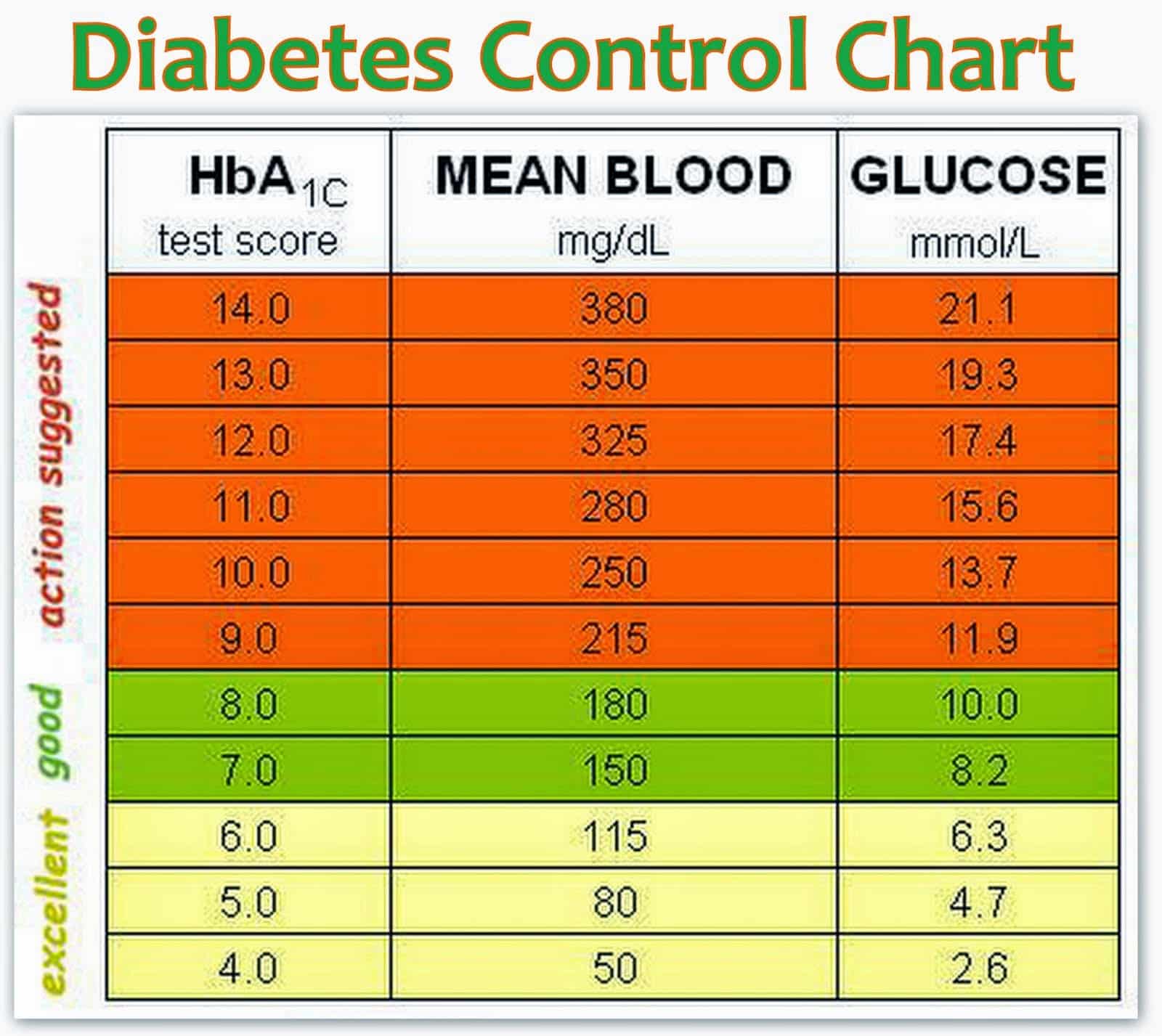
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every three years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every one to two years.
Tips For Tracking Your Blood Sugar Patterns And Using Your Results
Here are some great tips:
Have a blood sugar chart on your phone or a written notebook nearby to compare your numbers
For my patients during the class entitled, Monitoring your Blood Glucose, I pass out individual notebooks, and packs of different colored highlighter pens for pattern management. Inside, there are copies of an enhanced blood sugar log.
Patients log their blood sugars at different times of the day, and color-code them with highlighters. This helps patients to pick out their blood sugar patterns, and to do different things to adjust their blood sugars to get them in a target range.
Patients may either take a walk following a high carbohydrate meal, take more insulin if they are correcting blood sugar with insulin, decrease the amount of carbohydrates at the next meal, etc. By seeing what their blood sugars are at different times of the day, they can work their blood sugars into their target ranges. Once blood sugars are in the target range, their A1C should also be on target.
I have included a copy of the enhanced blood sugar log that I use to make a pattern notebook for my patients. Readers here at TheDiabetesCouncil are welcome to copy the form for their own use in self-managing their diabetes. You can also download our comprehensive log book here.
Phone Apps
Also Check: Managing Your Type 2 Diabetes
Your Guide To Diabetes
- Diabetes affects roughly two and a half million Canadians. Left untreated, diabetes can lead to many serious complications, including: heart disease, kidney disease, vision loss, and lower limb amputation.
- The Public Health Agency of Canada estimates that 5 million Canadians over the age of 20 are currently pre-diabetic. An additional 1 million new cases of pre-diabetes are expected by 2016. Pre-diabetes is a key risk factor for type 2 diabetes, and if left untreated more than half of the people with pre-diabetes will develop type 2 diabetes within 8 to 10 years.
- Although diabetes can lead to serious complications and premature death, there are steps that can be taken to prevent or control the disease and lower the risk of complications. This guide is intended to help you understand diabetes, how certain types can be prevented or managed, and how to live with the condition.
Did You Know?
You may be pre-diabetic and not know it. Pre-diabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are high, but not high enough to diagnose diabetes. Talk to your health care provider to learn more.
Also Check: What Does Black Seed Oil Do For Diabetics
Check Your Blood Glucose Levels
For many people with diabetes, checking their blood glucose level each day is an important way to manage their diabetes. Monitoring your blood glucose level is most important if you take insulin. The results of blood glucose monitoring can help you make decisions about food, physical activity, and medicines.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. You get a drop of blood by pricking the side of your fingertip with a lancet. Then you apply the blood to a test strip. The meter will show you how much glucose is in your blood at the moment.
Ask your health care team how often you should check your blood glucose levels. Make sure to keep a record of your blood glucose self-checks. You can print copies of this glucose self-check chart. Take these records with you when you visit your health care team.
Recommended Reading: What Is The First Sign Of Type 1 Diabetes
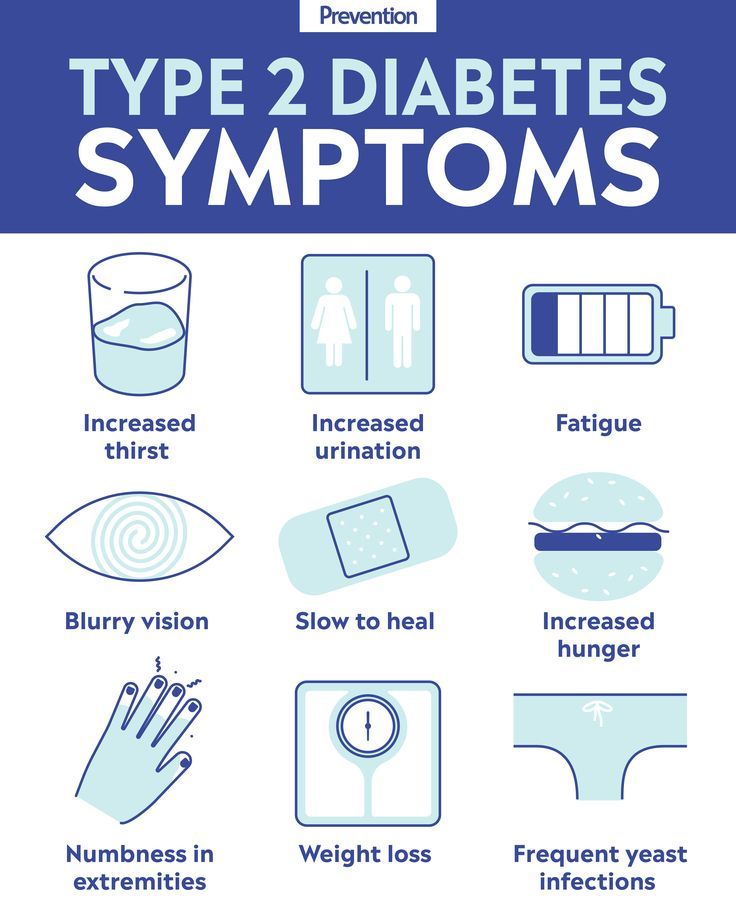
You Feel Tiredness And Fatigue Constantly
Fatigue and extreme tiredness are symptoms of uncontrolled blood sugar, the ADA says. Simply put, when your body is not processing insulin properly or it doesnt have sufficient amounts of insulin, the sugar is staying in our blood rather than getting into our cells to be used for energy, Zanini says. Also, frequent urination can lead to dehydration, which Bandukwala identifies as another contributing factor to fatigue.
Also Check: Can You Eat After Taking Insulin
Newly Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
Knowing where to get started following a type 2 diagnosis can be a challenge. You may feel overwhelmed, but its important to know there isnt a one-size fits all approach to managing the condition.
As well as using the information on this page to understand your condition, you can meet other people with type 2 diabetes in our Learning Zone. Youll hear advice from others in your position, and get practical tools to help you feel more confident managing your condition.
You May Like: What Does High Blood Sugar Feel Like
Testing Your Own Blood Glucose
Usually, blood glucose testing is done by your doctor or nurse. But some people might be able to do this at home with a continuous glucose monitor or finger prick hometesting kit. If your doctor or nurse thinks CGM or finger prick testing would be suitable for you:
-
they will give you training and support so you know what to do
-
they will assess your blood glucose testing skills and needs regularly, as part of the reviews of your diabetes care plan.
Not everyone needs to monitor their blood glucose at home. You should only do this if your doctor or nurse advises it.
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
Also Check: Is Bio X4 Safe For Diabetics
Don’t Miss: Fresh Figs And Diabetes 2
Roller Coaster: Female Hormones
When a womans hormones change, so does their blood sugar. Keep a monthly record of your levels to get a better idea of how your menstrual cycle affects you. Hormone changes during menopause may make blood sugar even harder to control. Talk to your doctor about whether hormone replacement therapy is a good idea.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Age Range
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluids between your bodys cells every few minutes and can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
Don’t Miss: Purpose Of Insulin In The Body
Favorite Resource For Diet Advice
Giving up some of the foods you once loved is arguably the biggest bummer about receiving a diabetes diagnosis. But with this Harvard-affiliated organizations expert diet guidance, you dont have to.
For more on “bad” foods you can eat in a diabetes diet, check out our article “5 ‘Bad’ Diabetes Foods You Can Enjoy in Moderation.”
Want to get involved? The IDF, which reaches 168 countries, makes it easy with their advocacy network page. Youll find different organizations that you can work with to help propel diabetes research, legislation, and awareness.
Follow Your Diabetes Meal Plan
Make a diabetes meal plan with help from your health care team. Following a meal plan will help you manage your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Choose fruits and vegetables, beans, whole grains, chicken or turkey without the skin, fish, lean meats, and nonfat or low-fat milk and cheese. Drink water instead of sugar-sweetened beverages. Choose foods that are lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt. Learn more about eating, diet, and nutrition with diabetes.
Also Check: Glucose Test For Pregnant Women
Do You Have Insulin Resistance
How do you find out if youre insulin resistant? No one test will tell you, but if you have high blood sugar levels, high triglycerides , high LDL cholesterol, and low HDL cholesterol, your health care provider may determine you have insulin resistance.
Important note: Type 1 diabetes is different its thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction . People with type 1 diabetes dont make enough insulin and need to take it to survive.
Make Physical Activity Part Of Your Daily Routine
Set a goal to be more physically active. Try to work up to 30 minutes or more of physical activity on most days of the week.
Brisk walking and swimming are good ways to move more. If you are not active now, ask your health care team about the types and amounts of physical activity that are right for you. Learn more about being physically active with diabetes.
Following your meal plan and being more active can help you stay at or get to a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan that is right for you.
Read Also: How Many Carbs Should A Pre Diabetic Eat Per Day
After You Have Low Blood Sugar
If your low blood sugar was mild , you can return to your normal activities once your blood sugar is back in its target range.
After you have low blood sugar, your early symptoms for low blood sugar are less noticeable for 48 to 72 hours. Be sure to check your blood sugar more often to keep it from getting too low again, especially before eating, physical activity, or driving a car.
If you used glucagon because of a severe low , immediately call your doctor for emergency medical treatment. If you have had lows several times close together , you should also tell you doctor. They may want to change your diabetes plan.
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a persons needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
Read Also: Best Essential Oils For Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Diabetes How To Control Blood Sugar
Diabetes By The Numbers
Staying healthy with type 2 diabetes is a numbers game. Get the scoop on the health indicators you should be measuring and why.
Thinkstock
When you have type 2 diabetes, youve got to know your numbers. Its not just about blood sugar. To successfully manage diabetes, there are several measurements that you should take, or have taken, on a regular basis. Keeping track of the following numbers can help you live well with type 2 diabetes and lower your risk of complications.
Blood sugar levels. This is probably the type 2 diabetes measure youre most familiar with. Testing your blood sugar regularly allows you to see how certain foods, exercise, and other activities affect your blood sugar levels on a day-to-day basis. Many people with type 2 diabetes need to test once or twice a day to make sure blood sugar levels are in target range. If your blood sugar is very well controlled, you may only need to check a few times a week, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for a blood sugar level between 70 to 130 mg/dl before meals and less than 180 mg/dl one to two hours after a meal. To keep your blood sugar within this range, follow a healthy, well-rounded diet and eat meals and snacks on a consistent schedule. If your blood sugar is not well controlled, talk to your doctor about adjusting your diabetes management plan.
Warning Signs Of Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia can cause both short- and long-term complications. Know the signs so that you can treat the condition as soon as youre aware of it.
As a person living with diabetes, you know how important it is to reduce blood sugar when it is too high, a phenomenon called hyperglycemia. But blood sugar that is too low, or hypoglycemia, is equally critical to avoid.
Hypoglycemia happens when the amount of blood glucose drops to a level thats too low to sustain normal functioning, says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, who is based in Sparta, New Jersey. In most people, this is defined as a blood sugar level at or below 70 milligrams per deciliter .
Hypoglycemia is common among people with type 2 diabetes, according to a review published in June 2015 in the journal PLoS One. Individuals with the condition had an average of 19 mild or moderate episodes of hypoglycemia per year and nearly one severe episode per year on average, according to the researchers. Low blood sugar was particularly common among those taking insulin.
RELATED: What to Know Before You Use OTC Insulin
This decrease in blood sugar levels can cause both short-term complications, like confusion and dizziness, as well as more serious issues, including seizures, coma, and, rarely, death, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Hypoglycemia is usually the result of a too-high dose of insulin or a change in diet or exercise habits, according to Harvard Health Publishing.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Diabetes 2 In Adults
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 35. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every three years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner and repeat testing may be recommended more often.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 or the onset of puberty and then every three years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.