Does Gestational Diabetes Affect Future Pregnancies
Two out of three women diagnosed with gestational diabetes will be diagnosed again in future pregnancies the more pregnancies a woman has with elevated blood sugar levels, the more likely future pregnancies will bring about similar blood glucose trends. This risk can be reduced through healthy eating habits and regular exercise as well as weight loss if recommended by a healthcare professional.
Importance Of A Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for the control of blood glucose levels and for a healthy pregnancy. When there is gestational diabetes, certain modifications need to be made to the mothers diet, including to the amount of carbohydrates in each meal. A carbohydrate-controlled diet is the foundation of the treatment. It is essential not to eliminate carbohydrates completely but rather to distribute them throughout the day.
Duration Of Gestational Diabetes
Diabetes that appears during pregnancy typically goes away right after delivery, but that is not always the case.
For true gestational diabetes it should resolve immediately after birth, since the insulin resistance is driven by the metabolic and hormonal changes in pregnancy, says Emily Fay, MD, a maternal-fetal-medicine specialist at UW Medicine, who helps run the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program there. However, sometimes when we diagnose a woman with gestational diabetes in pregnancy, it is actually that she has pre-gestational diabetes that we diagnosed during pregnancy.
Pre-gestational diabetes is any diabetes arising prior to pregnancy, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as well as other more rare types of diabetes like medication-induced diabetes or Cystic Fibrosis-related diabetes. Pre-gestational diabetes will not resolve after delivery.
The way to tell whether the patient had gestational diabetes or pre-gestational diabetes, Dr. Fay explains, is by doing a glucose test at the postpartum visit. This allows your doctor to screen for pre-gestational diabetes and insulin resistance.
If you have pre-gestational diabetes that was diagnosed during pregnancy, your doctor will discuss a treatment plan with you. This may include diet and lifestyle modifications, and use of insulin or oral medications.
Recommended Reading: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Diabetic Polyneuropathy
Diabetic Eye Screening In Pregnancy
You will be offered regular diabetic eye screening during your pregnancy. This is to check for signs of diabetic eye disease .
Checking your eyes during pregnancy is important. The risk of diabetic retinopathy increases in pregnancy.
Diabetic retinopathy is treatable, especially if it is caught early.
If you decide not to have the test, you should tell the doctor looking after your diabetes care.
- ophthalmologists
- other health care professionals
The obstetricians and midwives will have training in diabetes in pregnancy. They will work with you to provide your antenatal care. They will organise visits and ultrasounds to check on your babys development and growth.
What Are The Benefits Of This Routine Test

The benefits of this routine screening test havent yet been looked at in comparative studies. So it isnt exactly clear what advantages and disadvantages it may have. If the made it possible to treat the diabetes early enough, and that was shown to lower the risk of complications at birth, for instance, then that would be an advantage.
The research so far has shown the following:
- Treating gestational diabetes reduces the likelihood that the child will weigh more than 4,000 grams at birth.
- Treatment reduces the risk of one of the childs shoulders getting stuck in the mothers pelvis during the birth , which also reduces the risk of injury to the mother and child.
- Many women who are diagnosed with gestational diabetes dont have any related problems during pregnancy or childbirth.
Although the pros and cons of the test havent been thoroughly researched, it is thought that the advantages outweigh the disadvantages and that screening for gestational diabetes can somewhat lower the risk of complications in childbirth.
Recommended Reading: When You Have Type 2 Diabetes
Blood Glucose Target Levels
You and your care team should agree ideal blood glucose levels that are right for you and are manageable without causing problems with hypoglycaemia.
If you are taking metformin, or you are on insulin, you should be advised to aim for the following target blood glucose levels, unless this leads to difficulties with hypoglycaemia:
-
fasting: below 5.3 mmol/litreand
-
1 hour after meals: below 7.8 mmol/litre.
If you are not able to test until 2 hours after a meal, the target glucose level at that time should be below 6.4 mmol/litre.
If you are on insulin, you should also be advised to keep your blood glucose above 4 mmol/litre, because of the risk of hypoglycaemia.
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
Women who have gestational diabetes have a high chance of developing type 2 diabetes at some point later in their lives. However, type 2 diabetes can be prevented. The following steps can reduce your risk:
- maintain a healthy eating plan
- maintain a healthy weight for your height
- do regular physical activity
- have regular follow-up blood tests every one to 3 years to check your blood glucose levels, especially if you have further pregnancies.
Talk to your doctor about follow-up blood tests to check for diabetes. The frequency of the tests will depend on your risk for developing diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Can Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Its not possible to prevent gestational diabetes entirely. However, adopting health-promoting habits can help reduce your chances of developing the condition.
If youre pregnant and have one of the risk factors for gestational diabetes, try to eat a nutritious diet and get regular exercise. Even light activity, such as walking, may be beneficial.
If youre planning to become pregnant in the near future and youre overweight, consider preparing for your pregnancy by talking with a healthcare professional about ways to safely lose excess weight.
They can help you create a plan to reach and maintain a moderate weight. Even losing a small amount of weight can help you reduce your risk of gestational diabetes.
Furthermore, its important for pregnant people to seek prenatal care and follow all doctor-recommended visits to receive the appropriate screenings and evaluations during their pregnancies.
Pregnancy If You Have Diabetes
On this page:
If you have diabetes and plan to have a baby, you should try to get your blood glucose levels close to your target range before you get pregnant.
Staying in your target range during pregnancy, which may be different than when you arent pregnant, is also important. High blood glucose, also called blood sugar, can harm your baby during the first weeks of pregnancy, even before you know you are pregnant. If you have diabetes and are already pregnant, see your doctor as soon as possible to make a plan to manage your diabetes. Working with your health care team and following your diabetes management plan can help you have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
If you develop diabetes for the first time while you are pregnant, you have gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar Too High Symptoms
Risks And Possible Complications
There are numerous risks when gestational diabetes is not properly controlled and blood glucose levels remain high.
For the mother:
- Excess amniotic fluid, increases the risk of premature birth
- Risk of caesarean section or a more difficult vaginal birth
- Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia
- Higher risk of staying diabetic after the birth or of developing type 2 diabetes in the future .
For the baby:
- Bigger than normal at birth
- Hypoglycemia at birth
- Risk of the babys shoulders getting stuck in the birth canal during the birth
- Risk of obesity and glucose intolerance in early adulthood
Slight risk of:
- Jaundice, especially if the baby is premature
- Lack of calcium in the blood
- Breathing problems
Proper diabetes control considerably reduces the risks of complications.
How Is Diabetes During Pregnancy Managed
Special testing and monitoring of the baby may be needed for pregnant diabetics, especially those who are taking insulin. This is because of the increased risk for stillbirth. These tests may include:
-
Fetal movement counting. This means counting the number of movements or kicks in a certain period of time, and watching for a change in activity.
-
Ultrasound. This is an imaging test that uses sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasounds are used to view internal organs as they function, and to look at blood flow through blood vessels.
-
Nonstress testing. This is a test that measured the babys heart rate in response to movements.
-
Biophysical profile. This is a measure that combines tests such as the nonstress test and ultrasound to check the baby’s movements, heart rate, and amniotic fluid.
-
Doppler flow studies. This is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to measure blood flow.
Read Also: Glucose Meters Covered By Medicare
Risks Of Diabetes And Pregnancy
This information is for women who were diagnosed with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes before they got pregnant. It does not cover gestational diabetes.
Most pregnant women with diabetes will go on to have a healthy baby. But there are some possible complications you should be aware of.
Risks to the baby can include:
- the baby having low blood glucose levels, low calcium or jaundice after delivery – this is common
- having a larger baby – which can cause problems during labour
- having a smaller baby than expected – who might need care in a neonatal unit
- malformation incorrect development of the baby – this is rare
- being stillborn – baby dies before it is delivered – this is also rare
Risks to the mother can include:
- more frequent low blood glucose
- poor hypo awareness of a low glucose
- developing a blood pressure problem
- worsening of existing diabetes kidney or eye problems
Is Low Blood Sugar Level Normal During Pregnancy

It is a known fact that the body produces more insulin for the growth of the baby but what about the sugar levels, even these change during pregnancy. When the question of the low presence of glucose in blood during pregnancy is concerned, it isnt normal however, high blood glucose level is normal.
The sugar levels come down too low in these following conditions
You are not eating enough frequently or having the wrong diet in a worry to normalize sugar level. So when this happens the baby absorbs more glucose from your body and at times may lead to low glucose in the body.
Too much exercising which leads to consumption of glucose present in the body.
At times even few medicines can drop the blood sugar quantity in the body. In such cases ask for a change of drugs so that youre saved from the low presence of sugar.
Read Also: Best Essential Oils For Diabetes
How Does The Screening Work
Your doctor will ask you to take a test called the oral glucose tolerance test. Heres what happens:
When youre screened early, if that screening is normal, you should get screened again around 24 to 28 weeks when insulin resistance from the placental hormones is at its peak, he says.
The placenta is the organ that connects you to your baby to nourish it as it grows. Some hormones that the placenta makes work against the action of the insulin your body makes. As the placenta grows, so does this insulin resistance. In some people, this change is enough to cause the blood sugar level to be increased as it is in people with diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring your blood glucose levels is essential. It gives you a guide as to whether the changes you have made to your lifestyle are effective or whether further treatment is required.
A diabetes nurse educator can teach you how and when to measure your blood glucose levels. They will discuss the recommended blood glucose levels to aim for.
Your doctor or diabetes educator can help you register with the National Diabetes Services Scheme for discounted blood glucose strips. Regular contact with your diabetes educator or doctor is recommended.
Also Check: How To Reduce Risk Of Diabetes
How Does Gestational Diabetes Affect Pregnancy
If left untreated, the high blood sugar levels associated with gestational diabetes can lead to various issues during pregnancy, such as:
-
Giving birth to a large baby , increasing the risk of injury during birth for both the baby and the mother. The chances of requiring a Caesarean section also increase at high birth weights.
-
Increased risk of miscarriage, birth defects, and stillbirths.
-
High blood pressure, which can harm both long-term and short-term health.
-
Preeclampsia, a rare complication characterized by high blood pressure with possible kidney or liver damage.
Adjustment Of Glycemic Targets Based Upon Fetal Abdominal Circumference On Third
Despite reduced perinatal morbidity with interventions to achieve euglycemia in women with GDM, increased prevalence of macrosomia persists in this population. To improve outcomes, 4 randomized controlled trials have examined the use of fetal abdominal circumference as measured sonographically and regularly in the third trimester to guide medical management of GDM. This approach involves using stricter maternal BG targets , and an increased use of insulin, if needed, when the fetal AC measures 75th percentile or 70th percentile and conversely relaxed glycemic objectives when risk of LGA was considered low. A recent meta-analysis has shown that this approach can result in a significant 50% reduction in LGA rate compared to standard care, without an increase in SGA rate , but caution should be used before extrapolation of these results to routine clinical practice. Indeed, it may be difficult to apply this flexible approach given the extreme glycemic targets that were used, the fact that routine determination of AC is not done or sufficiently reliable, and frequent ultrasounds may not be accessible to most centres. Further analyses are needed to establish safe stricter and relaxed glycemic targets that should be recommended for women with GDM to limit LGA and SGA rates.
Also Check: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Quickly
What Is A Glucose Test In Pregnancy
There are two glucose tests that are typically offered during pregnancy as part of your prenatal care. Both the glucose challenge test and the glucose tolerance test measure how your body responds to glucose and help determine if you have gestational diabetes, which may develop during your pregnancy.These glucose tests are routinely done during pregnancy and are recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists for all pregnant women.
Key Points About Diabetes During Pregnancy
-
Diabetes is a condition in which the body can’t produce enough insulin, or it can’t use it normally.
-
There are 3 types of diabetes: Type 1, tType 2, and gestational diabetes.
-
Nearly all pregnant women without diabetes are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
-
Treatment for diabetes focuses on keeping blood sugar levels in the normal range.
-
Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes in later life. Follow-up testing is important.
Recommended Reading: Dr Earl Hutchins Diabetes Seminar
How To Avoid High Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Avoiding high blood sugar during pregnancy involves keeping the mothers blood levels within the normal range as follows: Less than 120 mg/dl two hours after meals 70 100 mg/dl before eating 100- 140 mg/dl just before bedtime snack
The normal ranges can be maintained through:
Eating a healthy diet. This involves seeking the advice of a dietician who will help in crafting a healthy eating plan. Although the mother should eat a balanced diet, the diet should include a reduced amount of carbohydrates to avoid raising the blood sugar levels.
Physical exercises. These work by helping the body insulin to work effectively in regulating the sugar levels in the blood. However, physical exercises should be done on a regular basis for better results. Two and a half hours each week is healthy. However, the exercise should be moderate enough not to overstrain the pregnant mother as this may result in other pregnancy complications. Ideal physical exercises for pregnant women may include swimming and walking. It is advisable to consult with the doctor about the physical exercise plan.
Insulin shots and diabetes medications. This is applicable, especially, where other methods such as regular exercises and balanced diet fail to work. Diabetes medicine and insulin shots help keep the blood sugar levels within normal ranges.
-
Pregnancy is a wonderful time, but everyone knows it is packed with challenges. Being with
How Gestational Diabetes Can Affect You
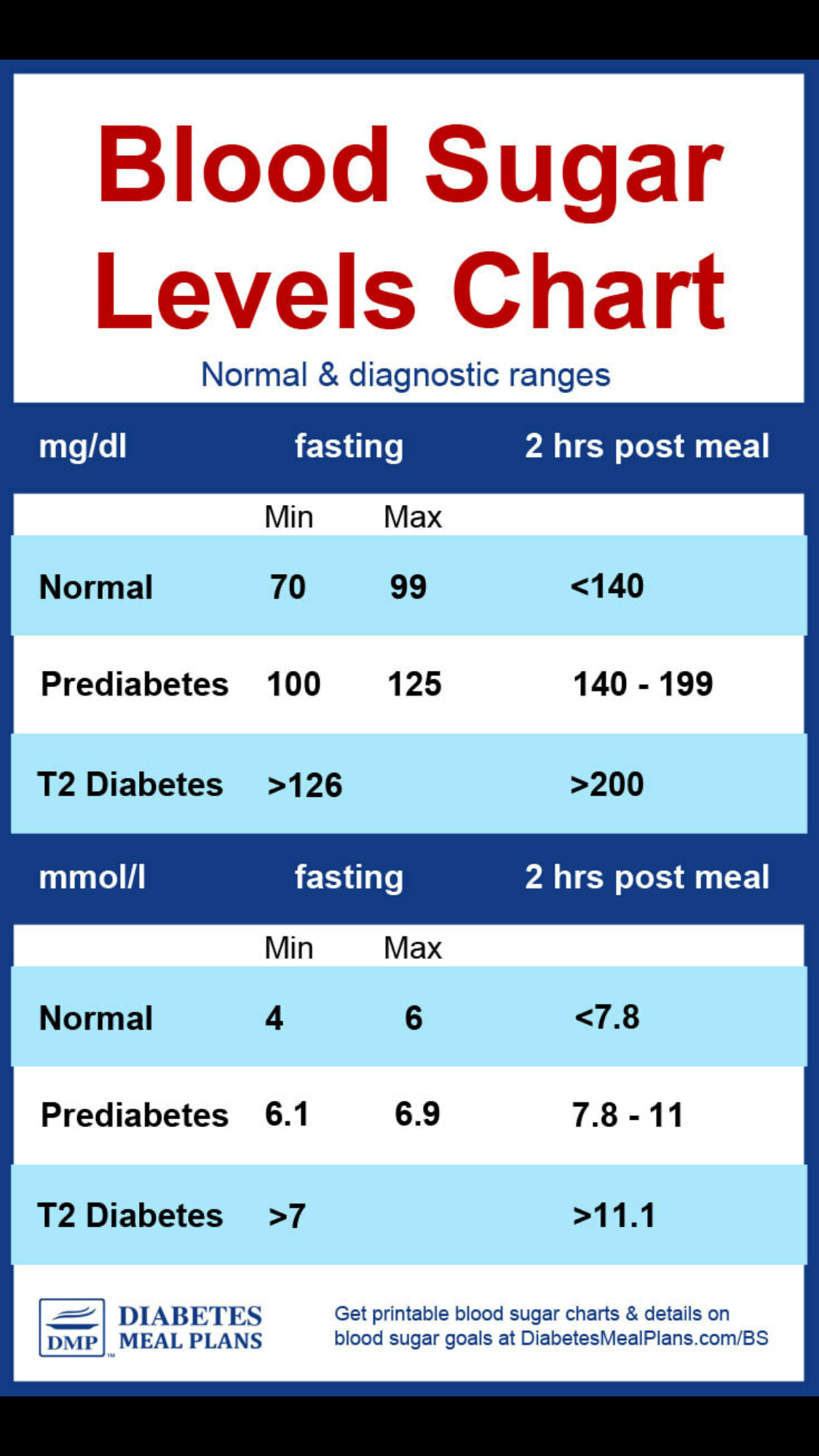
As mentioned above, gestational diabetes often comes with no symptoms, so you probably wont know that you have it until the doctor diagnoses it. However, gestational diabetes can still have an effect on you.
Gestational diabetes can increase your risk of high blood pressure while youre pregnant. Also, you may have a larger baby, which can make delivery difficult or require a C-section.
Gestational diabetes can also put you more at risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Also Check: American Association Of Diabetes Educators Conference
Who Is At Risk Of Developing Gestational Diabetes
Risk factors for developing gestational diabetes include:
-
Having obesity or excess weight
-
Being physically inactive
-
A history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy, or a family history of type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
-
Previously giving birth to a baby nine pounds or heavier
-
High blood pressure, polycystic ovary syndrome , or a history of heart disease
-
Ethnic background: African-American, Asian American, Hispanic, Native American or Pacific Island
-
Are older than 25
It is possible to have none of these risk factors and still develop gestational diabetes . The condition results from a combination of factors, many of which are beyond any individuals control. If you are pregnant, speak with your healthcare professional about screening and healthy pregnancy behaviors.