How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
Every day we make choices that affect our health. Take these important five steps to make your lifestyle healthier and to start to prevent or reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and pre-diabetes:
Make Changes Part Of Your Everyday
Changing too many things at the same time can make them difficult to stick to in the long run. Start with small things you can change about your everyday routine and build up to more.
We know it can be hard to stay motivated, but remember you’re in this for the long run. Your risk of developing diabetes is serious and you can’t reduce your risk by eating better or moving more for just a couple of weeks.
First The Risks You Cant Avoid
Before you tackle the things that can lower your risk of developing diabetes, consider that there are some risk factors beyond your control. For example:
- Race: certain ethnic groups carry a higher risk of developing diabetes, especially those of African, Indian, Asian, and Hispanic/Latino decent.
- Family history: having a close relative with diabetes will increase your risk for the disease.
- Age: most people have an increased risk for diabetes after the age of 40.
- Gestational diabetes: women who develop diabetes while they are pregnant have a higher risk of developing it again later in life.
Also Check: Blue Cross Blue Shield Diabetic Supplies
The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study
The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study included 522 overweight Finnish adults with impaired glucose tolerance, who were divided into two groups: these were given standard intervention or intensive therapy. The median follow-up for participants was 7 years . In the intensive therapy group, the strategy consisted of weight reduction, limited total and saturated fat intake, and the consumption of fiber, whole-grain products, vegetables, fruit, low-fat milk, soft margarines, and vegetable oils rich in monounsaturated fat, combined with an increase in exercise . After 3.2 years of follow-up, WC was reduced by 4.4 cm in the intensive therapy group compared to 1.3 cm in the control group, and blood pressure was reduced by 5/5 mmHg in the intensive group compared to 1/3 mmHg in the intervention group for systolic/diastolic blood pressure .
Maryann N. Mugo, … James R. Sowers, in, 2007
Dietary Strategies To Improve Blood Sugar Management

A major goal in diabetes prevention and control is blood sugar management. Normal blood pressure and cholesterol are also essential. Many of these strategies will improve all three risk factors of diabetes:
- 1.
-
Eat enough calories for optimal weight. Eat fewer calories to lose weight and the right amount of calories to maintain weight. Specific guidelines for determining ideal body weight and healthy weight loss can be found in Chapter 10. Here are some guidelines:
-
Choose foods that are naturally lower in calories, such as some fruits, lean meats, legumes, low-fat dairy products, vegetables and whole grains, and control the portion sizes of these foods.
-
Replace higher-calorie side dishes, such as french fries, with lower-calorie vegetables, such as side salads. As recommended by the USDA MyPlate Guidelines, fill half the plate with vegetables and fruits. The extra fiber is not only filling, but it also helps to stabilize to blood sugar.
-
Increase water consumption because soluble fiber depends on it, and water assists in fat metabolism. But other sweetened liquid calories, including fruit drinks, soft drinks, and coffee and tea beverages. Even pure fruit juice should be consumed in moderation.
Jennifer Miller, … Desmond A. Schatz, in, 2004
Also Check: Is Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Or Type 2
Reducing The Risk Of Developing Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by destruction of pancreatic beta cells. The causes are multi-factorial, with both genetic and environmental factors. The exact nature of causative environmental factors continues to be debated. There is a long preclinical period before the onset of overt symptoms, which may be amenable to therapeutic intervention to prevent disease. Immunotherapeutic interventions continue to be the main focus of type 1 diabetes prevention.
A second strategy is to try to halt, at the time of diagnosis, the immune-mediated destruction of beta cells to preserve any residual capacity to produce insulin. Progress in the field has been slow due to safety considerations namely, side effects from immunosuppression/modulation must be minimized before consideration can be given for clinical use, especially because of the reasonable life expectancy of people with type 1 diabetes and technological advancements with insulin replacement therapy.
As safe and effective preventive therapies for type 1 diabetes have not yet been identified, any attempts to prevent type 1 diabetes should be undertaken only within the confines of formal research protocols.
Prevention Tips For Parents
Not long ago, it was almost unheard of for young children or teens to get type 2 diabetes. Now, about one-third of American youth are overweight, which is directly related to the increase in kids who have type 2 diabetes, some as young as 10 years old.
Parents have the power to make healthy changes that give kids the best chance to prevent type 2 diabetes. And when the whole family makes changes together, its easier to create healthy habits that stick. Get started with these simple but effective tips for healthy eating and being active family style.
You May Like: How To Treat Hypoglycemia In Type 2 Diabetes
Can Type 1 Diabetes Be Prevented
Type 1 diabetes can’t be prevented. Doctors can’t even tell who will get it and who won’t.
No one knows for sure what causes type 1 diabetes, but scientists think it has something to do with genes. But just getting the genes for diabetes isn’t usually enough. In most cases, a child has to be exposed to something else like a virus to get type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes isn’t contagious, so kids and teens can’t catch it from another person or pass it along to friends or family members. And eating too much sugar doesn’t cause type 1 diabetes, either.
There’s no reliable way to predict who will get type 1 diabetes, but blood tests can find early signs of it. These tests aren’t done routinely, however, because doctors don’t have any way to stop a child from developing the disease, even if the tests are positive.
The Cause Of Diabetes
Diabetes is an illness related to elevated blood sugar levels. When you stop releasing and responding to normal amounts of insulin after eating foods with carbohydrates, sugar and fats, you have diabetes. Insulin, a hormone thats broken down and transported to cells to be used as energy, is released by the pancreas to help with the storage of sugar and fats. But people with diabetes dont respond to insulin properly, which causes high blood sugar levels and diabetes symptoms.
Its important to note that theres a difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Heres an explanation of the two types of diabetes and what causes these conditions:
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is commonly called juvenile diabetes because it tends to develop at a younger age, typically before a person turns 20 years old. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
The damage to the pancreatic cells leads to a reduced ability or complete inability to create insulin. Some of the common causes that trigger this autoimmune response may include a virus, genetically modified organisms, heavy metals, or foods like wheat, cows milk and soy.
The reason foods like wheat and cows milk have been linked to diabetes is because they contain the proteins gluten and A1 casein. These proteins can cause leaky gut, which in turn causes systemic inflammation throughout the body and over time can lead to autoimmune disease.
Don’t Miss: Body Wash For Diabetic Skin
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 and type 2 are often referred to simply as diabetes, but while they share symptoms, there are some distinct differences. For example, type 2 diabetes symptoms can develop much slower and it can be more difficult to recognise. Other differences include:
- Prevalence: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, making up about 90% of diabetic cases.
- Cause: Type 1 diabetes is considered an autoimmune disease when the human body incorrectly attacks its own healthy cells of the pancreas, mistaking them for a foreign invader in the body. These cells are responsible for producing the hormone insulin. Whereas, type 2 diabetes is linked to lifestyle factors.
- Role of insulin: Type 1 diabetes affects the bodys ability to produce insulin, so it must be injected instead. Type 2 diabetics can still produce insulin, but the bodys cells become resistant to the effects this can be managed with medication, diet and exercise, as well as insulin.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis : Those with type 1 are more at risk of DKA a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Due to low levels of insulin, the body cannot get glucose into the cells to use for fuel. The body uses fat as an energy source instead and produces an excess of ketones. Symptoms include vomiting, dehydration, high heart rate, confusion and a distinctive smell on the breath, sometimes compared to nail varnish remover or pear drops.
How Can I Prevent Or Delay Getting Type 2 Diabetes
If you are at risk for diabetes, you may be able to prevent or delay getting it. Most of the things that you need to do involve having a healthier lifestyle. So if you make these changes, you will get other health benefits as well. You may lower your risk of other diseases, and you will probably feel better and have more energy. The changes are:
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Dry Mouth
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented
Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes can sometimes be prevented. Excessive weight gain, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are all things that put a person at risk for type 2 diabetes.
In the past, type 2 diabetes usually happened only in adults. But now, more kids and teens are being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, due to the rapidly increasing number of overweight kids.
Although kids and teens might be able to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes by managing their weight and increasing physical activity, other risk factors for type 2 diabetes can’t be changed. Kids with one or more family members with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk for the disease, and some ethnic and racial groups are more likely to developing it.
How To Reduce Your Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
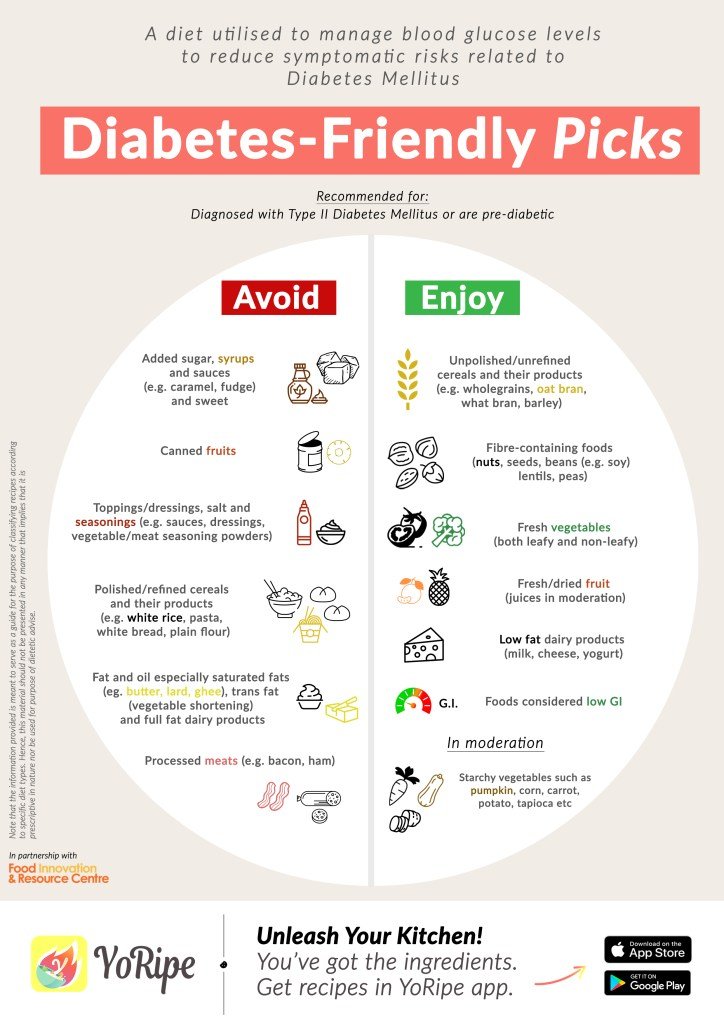
today April 13, 2021 Commentslocal_offerLifestyle
Did you know that about 11 million Canadians are living with prediabetes or diabetes? And of the 11 million, 90% of them are cases of Type 2 diabetes. While Type 2 diabetes typically appears in those over the age of 40, it is increasingly becoming a concern amongst children and adolescents with a link to obesity. Type 2 diabetes is also common with those who have a family history of Type 2 diabetes. However, Type 2 diabetes is preventable – and there are a few things that you can do to reduce your risk of developing prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when either your bodycannot produce enough insulin or your body is unable to properly use the insulin that it makes. Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas. Its job is to help regulate and control the amount of glucose in your blood.
Who is at risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is linked to many other health concerns and risks and there are a variety of factors that can increase your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. The risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes are:
What Are the Long Term Side Effects of Type 2 Diabetes?
Developing Type 2 Diabetes can pose long term risks and can lead to serious health complications, if it is not properly managed.Type 2 Diabetes can lead to:
What Can You Do to Reduce Your Risk of Type 2 Diabetes?
Here are 10 ways you can prevent Type 2 Diabetes:
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Eyeglasses For Diabetics
Diabetes Prevention In High
Certain ethnic groups, including African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous and South Asian peoples, are at very high risk for and have a high prevalence of type 2 diabetes . The reasons for this are multifactorial and include genetic susceptibility, altered fat distribution and higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Many of them develop diabetes at a younger age and often have complications at the time of diagnosis due to long-standing, pre-existing diabetes. As a result, there may be a benefit of delaying the onset of diabetes in this population. The Indian Diabetes Prevention Programme randomized 531 people with IGT diabetes in Chennai, India to 4 groups: healthy behaviour interventions metformin healthy behaviour interventions and metformin and control with a median follow up of 30 months. Progression to diabetes in the control group was high over 3 years . The relative risk reduction was 28.5% with healthy behaviour interventions, 26.4% with metformin and 28.2% with healthy behaviour interventions and metformin compared with the control group.
How To Reduce Your Risk Of Getting Diabetes
Learn how to prevent type 2 diabetes through weight loss, regular exercise, and lowering your intake of fat and calories.
If you want to lower your risk of getting type 2 diabetes, you’ll have to make some changes. Making big changes in your life is hard, especially if you are faced with more than one change. You can make it easier by taking these steps:
- Take seriously a diagnosis of prediabetes.
- Make a plan to change behavior.
- Plan what you need to get ready.
- Think about what might prevent you from reaching your goals.
- Find family and friends who will support and encourage you.
Your doctor, a dietitian, or a counselor can help you make a plan. Consider making changes to lower your risk of diabetes.
Also Check: What Happens When You Take Insulin
What Are The Causes Of Diabetes
As mentioned previously, obesity plays a large role in causing diabetes. There are different causes for the different types of diabetes. According to Diabetes UK, type 1 diabetics have inherited genes that have increased their chances of developing diabetes.12 This means that it could have been inherited by parents or in the family history. Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed at a young age. In England and Wales alone, 96% of children with diabetes have type 1.8 Other causes include geographical location and environmental factors.8
Type 2 diabetes is caused more often by lifestyle factors.5 A person can develop type 2 diabetes when they consume too much sugar and no longer respond to insulin or do not produce any insulin. This means that blood sugar levels remain high, meaning that it could end up in urine and increase the risk of heart attacks and cardiovascular diseases. As mentioned previously, inactivity and obesity are leading contributors to type 2 diabetes as blood sugar levels remain high. Other factors include age, blood pressure, and race and ethnicity, with black and minority ethnic people being more prone to the disease.5
How To Reduce Risk Factors Associated With Diabetes According To A Nutritionist
With men more at risk than women to develop type 2 diabetes, its never been more important to equip yourself with these nutritionist-approved tips to minimize your chances of developing this increasingly ubiquitous disease.
With Mens Health Week coming up , theres never been a more important time to raise awareness of widespread health problems faced by a multitude of men. Type 2 diabetes, in particular, has become more prevalent amongst men than women, and the risk of development has also been shown to increase with age.
In fact, one in ten Brits over the age of 40 now has type 2 diabetes. The number of people living with diabetes in the UK has reached 4.7 million, and is expected to reach 5.5 million by 2030.1
Nutriburst is working together with leading nutritionist Jenny Tschiesche, to offer advice on how to address this common health condition, encouraging men to incorporate vital vitamins into their diets to minimize the predisposing risk factors.
Jenny comments: Detecting diabetic risk factors earlier is crucial, to help ensure that men of all ages are treated more quickly and feel supported in engaging in healthier lifestyle choices and activities.
Low zinc levels are also found in those with prediabetes, as zinc is significantly associated with beta cell function and insulin resistance2. Supplementing with zinc daily is also advisable.
Jenny offers her advice on how to reduce the risk factors associated with diabetes, as part of a healthy lifestyle:
Also Check: What Is A Smart Insulin Pen
What Types Of Diabetes Are There
As previously mentioned, there are three main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.2
Type 1 is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas is attacked, meaning it does not produce insulin.3 A person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes produces very little or no insulin in the pancreas, meaning that blood sugar levels are left highly unregulated. This can be fatal if left undiagnosed or untreated.
Type 2 can occur when the insulin made by the pancreas does not work or when the pancreas does not make enough.4 Type 2 diabetes is mainly caused by diet and too much intake of sugary foods. This means that the insulin in the body becomes immune and resistant to the glucose and stops working. The majority of type 2 diabetics are obese and have a higher body-fat percentage.5
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy mostly in overweight mothers or during high-risk pregnancies.6 This means that the hormones produced by the body to sustain the placenta become immune to insulin. Therefore, pregnant women need to be careful of their diets during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can be reversible whilst type 1 and type 2 are irreversible.