Canine Diabetes Type Ii
Cats are more likely to develop Type II diabetes, but obesity as well as some diseases and medications can cause Type II diabetes in dogs.
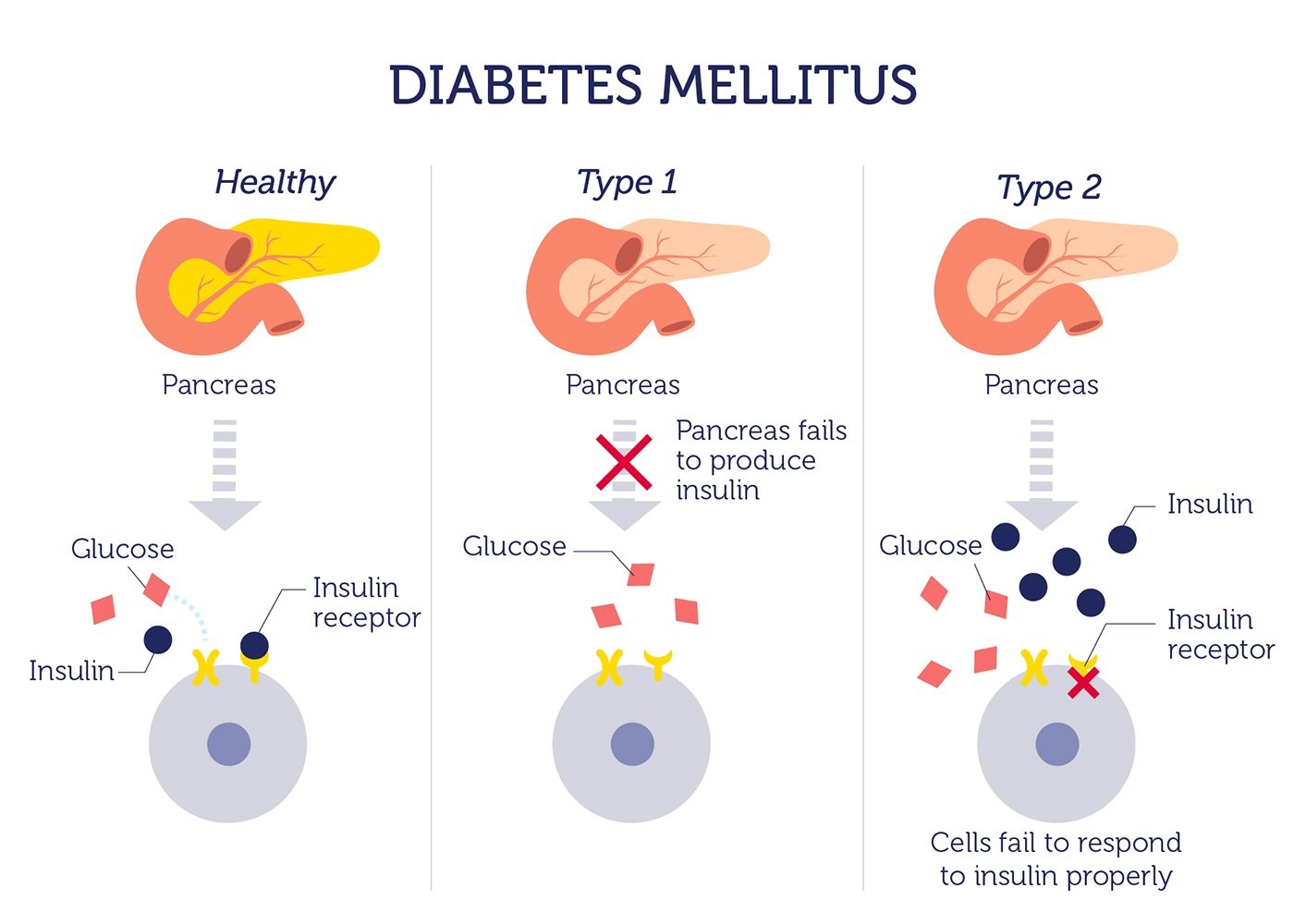
Type II diabetes is known as insulin-resistant diabetes. It happens when the pancreas makes insulin, but the body’s cells do not respond to the insulin. Sometimes Type II diabetes can be reversed through weight loss and improvements in diet and exercise.
Does Eating Sugary Foods Cause Diabetes
Sugar itself doesn’t directly cause diabetes. Eating foods high in sugar content can lead to weight gain, which is a risk factor for developing diabetes. Eating more sugar than recommended American Heart Association recommends no more than six teaspoons a day for women and nine teaspoons for men leads to all kinds of health harms in addition to weight gain.
These health harms are all risk factors for the development of diabetes or can worsen complications. Weight gain can:
- Raise blood pressure, cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Cause fat buildup in your liver.
- Cause tooth decay.
What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
Don’t Miss: Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
What Are The Acute Complications Of Diabetes
Acute complications of type 2 diabetes
In patients with type 2 diabetes, stress, infection, and medications can also lead to severely elevated blood sugar levels. Accompanied by dehydration, severe blood sugar elevation in patients with type 2 diabetes can lead to an increase in blood osmolality . This condition can worsen and lead to coma . A hyperosmolar coma usually occurs in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Like diabetic ketoacidosis, a hyperosmolar coma is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment with intravenous fluid and insulin is important in reversing the hyperosmolar state. Unlike patients with type 1 diabetes, patients with type 2 diabetes do not generally develop ketoacidosis solely on the basis of their diabetes. Since in general, type 2 diabetes occurs in an older population, concomitant medical conditions are more likely to be present, and these patients may actually be sicker overall. The complication and death rates from hyperosmolar coma is thus higher than in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Blood glucose is essential for the proper functioning of brain cells. Therefore, low blood sugar can lead to central nervous system symptoms such as:
Combination With Other Antidiabetic Drugs
A combination therapy of insulin and other appears to be most beneficial in people who are diabetic, who still have residual insulin secretory capacity. A combination of insulin therapy and is more effective than insulin alone in treating people with type 2 diabetes after secondary failure to oral drugs, leading to better glucose profiles and/or decreased insulin needs.
Recommended Reading: Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
Monitoring Your Dogs Blood Sugar
Your veterinarian will monitor your dog’s blood glucose, performing a blood-glucose curve where they take measurements every one to two hours over the course of 12-24 hours.
Your veterinarian is looking to see how high your dog’s blood sugar gets, and then how low it drops. This indicates how well the body is responding to insulin and will be periodically reevaluated throughout your dog’s life.
Don’t Miss: Does Viagra Work For Diabetics
Symptoms Of Diabetes In Dogs
Canine diabetes usually has a slow onset. Dogs start drinking more water and urinating more frequently and in larger amounts. They may even have accidents in the house. Dogs may also eat more while losing or maintaining weight.
These symptoms are not specific to diabetes, but they are big indicators that your dog should be examined by your veterinarian.
In diabetic dogs, excess sugar in the blood is excreted in their urine. When there is sugar in urine, bacteria can grow and cause urinary tract infections and even bladder infections. Symptoms of these conditions include frequent urgent urination, painful urination, urine that is bloody or smells bad, and excessive licking of the genitals.
Your veterinarian will prescribe antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections.
Diabetes in dogs can also cause high pressure within the eye, known as glaucoma. In humans, glaucoma is painful, often described as a bad headache that won’t go away. Dogs can lose vision or even need to have one or both eyes removed due to severe glaucoma that results from diabetes.
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Feet Tingling At Night
When To Call A Professional
If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly.
People with high blood sugar levels have a higher risk of dehydration. Contact your doctor immediately if you develop vomiting or diarrhea and are not able to drink enough fluids.
Monitor your blood sugar as advised by your health care team. Report any significant deviations in blood sugar levels.
When To See A Doctor
Visit your GP as soon as possible if you experience the main symptoms of diabetes, which include:
- weight loss and loss of muscle bulk
- itching around the penis or vagina, or frequent episodes of thrush
- cuts or wounds that heal slowly
- blurred vision
Type 1 diabetes can develop quickly over weeks or even days.
Many people have type 2 diabetes for years without realising because the early symptoms tend to be general.
Read Also: Best Frozen Yogurt For Diabetics
What Types Of Diabetes Require Insulin
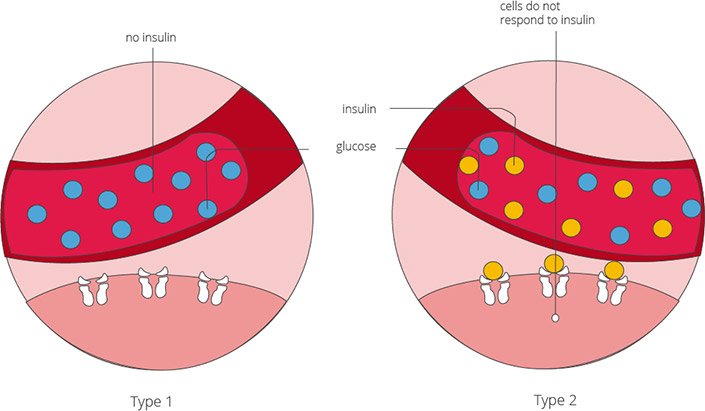
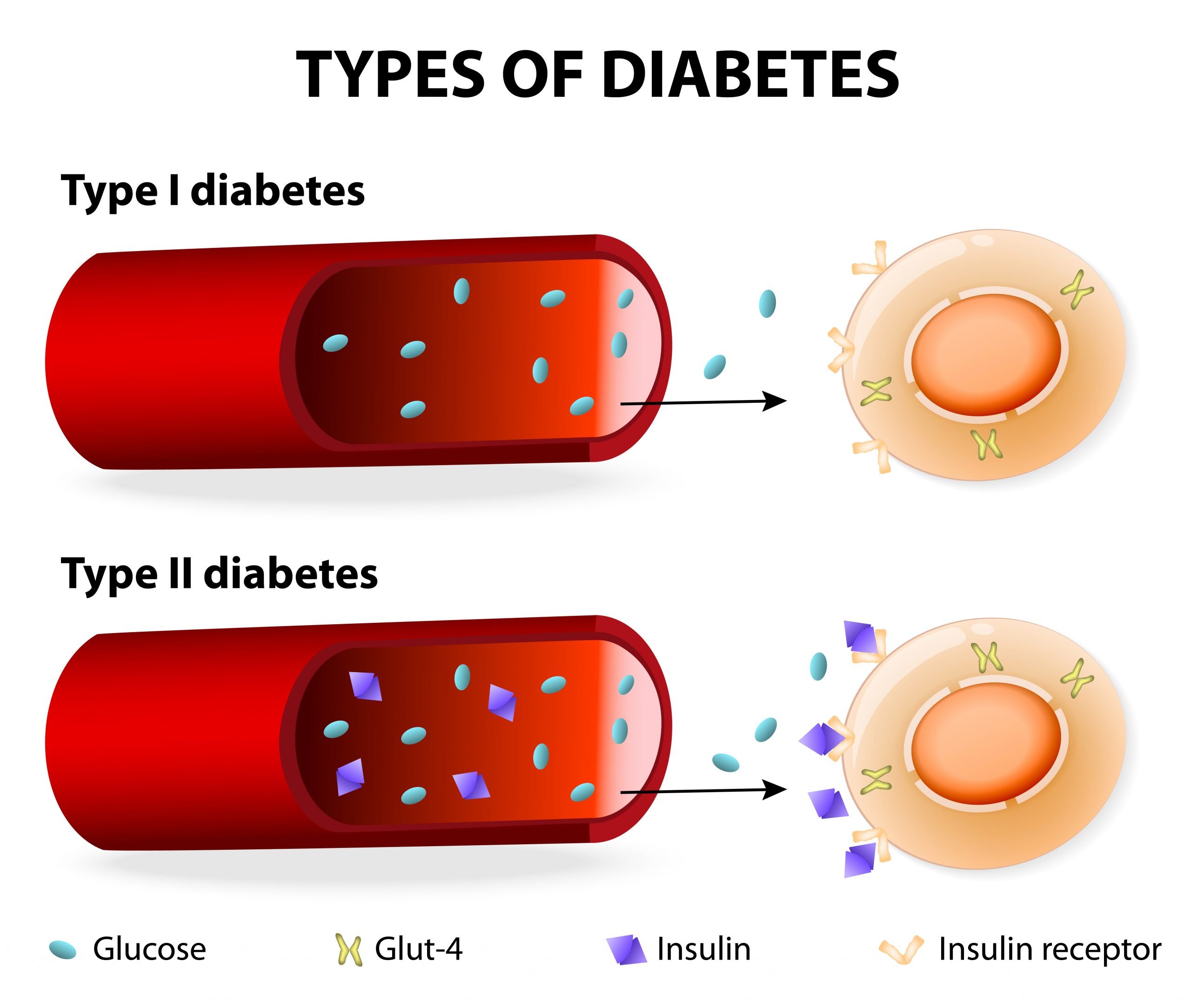
People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin to live. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your body has attacked your pancreas, destroying the cells that make insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, your pancreas makes insulin, but it doesnt work as it should. In some people with Type 2 diabetes, insulin may be needed to help glucose move from your bloodstream to your bodys cells where its needed for energy. You may or may not need insulin if you have gestational diabetes. If you are pregnant or have Type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider will check your blood glucose level, assess other risk factors and determine a treatment approach which may include a combination of lifestyle changes, oral medications and insulin. Each person is unique and so is your treatment plan.
General Treatment Of Diabetes
People with diabetes benefit greatly from learning about the disorder, understanding how diet and exercise affect their blood glucose levels, and knowing how to avoid complications. A nurse trained in diabetes education can provide information about managing diet, exercising, monitoring blood glucose levels, and taking drugs.
|
|
Don’t Miss: Type 1 2 3 Diabetes
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Types Of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous clinical disorder with numerous causes. Two main classifications of diabetes mellitus exist, idiopathic and secondary.
Idiopathic diabetes is divided into two main types insulin dependent and non-insulin-dependent. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, IDDM is defined by the development of ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. See the Diabetic Ketoacidosis diagnosis and treatment page. Type 1 diabetes most often manifests in childhood and is the result of an autoimmune destruction of the -cells of the pancreas. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, NIDDM is characterized by persistent hyperglycemia but rarely leads to ketoacidosis. Type 2 diabetes generally manifests after age 40 and therefore has the obsolete name of adult onset-type diabetes. However, due to the rising rates of adolescent obesity in industrialized countries there is an increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes in pre- and postpubescent children. Type 2 diabetes can also result from genetics defects that cause both insulin resistance and insulin deficiency. There are two main forms of type 2 diabetes:
You May Like: Is Glaucoma Related To Diabetes
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The primary test used to diagnose both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is known as the A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, test.
This blood test determines your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Your doctor may draw your blood or give you a small finger prick.
The higher your blood sugar levels have been over the past few months, the higher your A1C level will be. Test results are expressed as a percentage. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher indicates diabetes.
The A1C test isnt accurate for people with sickle cell anemia or the sickle cell trait. If you have this condition or trait, then your doctor will have to use a different test.
What Are The Other Types Of Diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Diabetes can occur temporarily during pregnancy, and reports suggest that it occurs in 2% to 10% of all pregnancies. Significant hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to blood sugar elevation in genetically predisposed individuals. Blood sugar elevation during pregnancy is called gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually resolves once the baby is born. However, 35% to 60% of women with gestational diabetes will eventually develop type 2 diabetes over the next 10 to 20 years, especially in those who require insulin during pregnancy and those who remain overweight after their delivery. Women with gestational diabetes are usually asked to undergo an oral glucose tolerance test about six weeks after giving birth to determine if their diabetes has persisted beyond the pregnancy, or if any evidence is present that may be a clue to a risk for developing diabetes.
Secondary diabetes
“Secondary” diabetes refers to elevated blood sugar levels from another medical condition. Secondary diabetes may develop when the pancreatic tissue responsible for the production of insulin is destroyed by disease, such as chronic pancreatitis , trauma, or surgical removal of the pancreas.
Hormonal disturbances
Medications
Certain medications may worsen diabetes control, or “unmask” latent diabetes. This is seen most commonly when steroid medications are taken and also with medications used in the treatment of HIV infection .
You May Like: Best Diet For Diabetes And Kidney Disease
Causes Of Canine Diabetes
In dogs, Type I diabetes is caused by the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. These cells die as a result of inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis. Some dog breeds are predisposed to chronic pancreatitis and diabetes, including Keeshonds and Samoyeds.
Like humans and cats, obese dogs are at risk for developing Type II diabetes. So are dogs with Cushing’s disease , intact female dogs and those on glucocorticoid medications.
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
Diabetes is diagnosed and managed by checking your glucose level in a blood test. There are three tests that can measure your blood glucose level: fasting glucose test, random glucose test and A1c test.
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test is best done in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- A1c test: This test, also called HbA1C or glycated hemoglobin test, provides your average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. This test measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen. You dont need to fast before this test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: In this test, blood glucose level is first measured after an overnight fast. Then you drink a sugary drink. Your blood glucose level is then checked at hours one, two and three.
| Type of test |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Does One High A1c Mean Diabetes
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that impacts 1.25 million American children and adults. For type 1, the immune system destroys the cells that release insulin, eventually leading to the complete inability to produce insulin in the body. Type 1 generally manifests at a young age and lasts a lifetime.
Type 2 diabetes has multiple contributing factors including genetics and lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The disease generally arises during adulthood and oftentimes can be reversed or controlled through diet and exercise. 90-95% of those diagnosed with diabetes have type 2.
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share common symptoms. They are:
- going to the toilet a lot, especially at night
- being really thirsty
- feeling more tired than usual
- losing weight without trying to
- genital itching or thrush
- cuts and wounds take longer to heal
- blurred vision.
But where type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different in symptom is how they appear. Type 1 can often appear quite quickly. That makes them harder to ignore. This is important because symptoms that are ignored can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis .
But type 2 diabetes can be easier to miss. This is because it develops more slowly, especially in the early stages. That makes it harder to spot the symptoms. That is why it is important to know your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some people have diabetes and dont know it. They can have it for up to 10 years without knowing.
Don’t Miss: Non Insulin Drugs For Diabetes
Glucose Homeostasis And The Role Of Insulin
Glucose homeostasis is the bodys functions and processes that maintain a balance of glucose in the blood and in cells and tissues. Glycemic control is an indicator of how well this mechanism is working. It is also a measuring stick of how effective treatment of diabetes is. Glycemic means pertaining to the level of glucose in the blood. Therefore, glycemic control denotes the degree to which the level of glucose in the blood is within the normal range.
Proper regulation of the pendulum keeps glucose in blood from being too high or too low. The balance is important because glucose is the main source of energy for all cells yet it must be in the blood for delivery to appropriate cells at the right time. Critical to this balance is the role of insulin.
The source of blood sugar is directly from the diet or from the conversion of more complex compounds by means of chemical reactions within the body. Glucose can be absorbed directly into the bloodstream via the small intestine or following digestion of more complex sugars or starches. In the fasting state the liver produces glucose from protein and fat subunits. Those subunits are amino acids and glycerol respectively. Gluconeogenesis is the name of this process. Additionally, in the fasting state, the liver produces glucose from the breakdown of glycogen a storage form of carbohydrate in liver and muscle tissue. The name for this process is glycogenolysis. The glucose is then absorbed into the blood.