How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
If your doctor suspects you have diabetes, you will probably need to have a blood test to assess your glucose level. It is important for diabetes to be diagnosed early, whether its type 1 or type 2 diabetes. That way, it can be better controlled and complications can be avoided or minimised.
During a test, blood is taken from a vein and sent to a pathology lab. The tests that can be done include:
- a fasting blood glucose test fasting is required for at least 8 hours, which may mean not eating or drinking overnight
- an oral glucose tolerance test after fasting for 8 hours, you have a blood glucose test, then you drink a sugary drink and then have another blood test done 1 and then 2 hours later
- HbA1c this blood test shows your average blood glucose levels over a period of time it does not involve fasting beforehand
Watch the first video below to learn why its important to detect undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. The second video tells you all about the HbA1c test.
Video provided by Lab Tests Online
How Can I Manage My Type 2 Diabetes
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking if you smoke, are important ways to manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes that include planning healthy meals, limiting calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes. So is taking any prescribed medicines. Work with your health care team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
What’s The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Although both type 1 and type 2 diabetes involve involve too-high levels of sugar in the bloodstream, they have different causes and treatments, according to Harvard Health Publishing. Type 2 is linked to genetics as well as lifestyle factors, such as having overweight or obesity, while type 1 is usually caused by an autoimmune reaction.
“The body just stops making insulin,” Sheth says of type 1. “That usually happens pretty rapidly.”
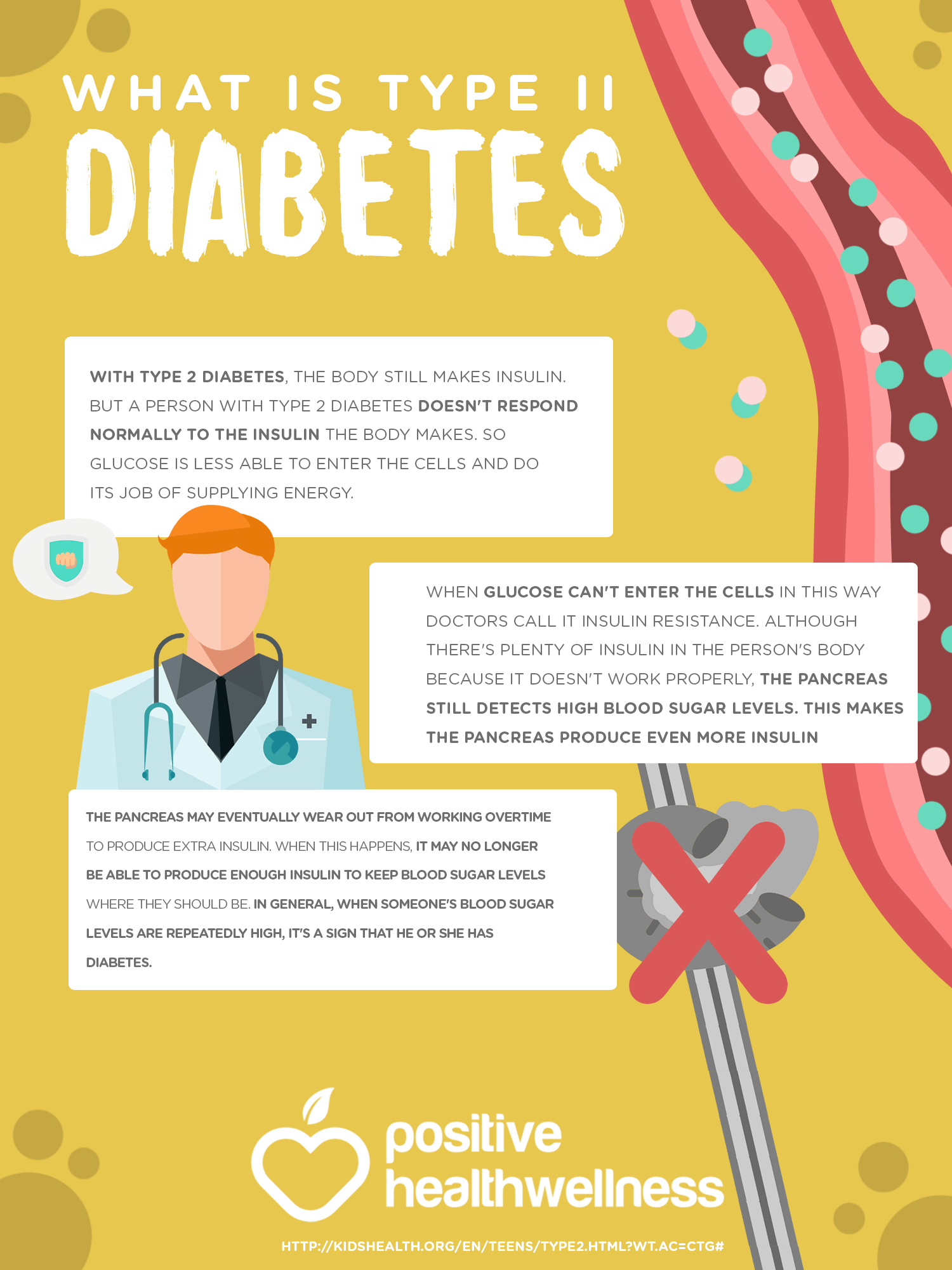
People with type 2, on the other hand, still produce some insulin, but their bodies aren’t able to use it properly.
Type 2 is more common by far: According to the CDC, about 90 to 95 percent of people with diabetes in the U.S. have this type.
Type 1 is more often diagnosed in children, teens or young adults, whereas type 2 is more often diagnosed in adults, with about one-third of people over the age of 65 having the condition, Dr. Buse says.
In terms of treatment, people with type 1 diabetes have to take insulin every day, otherwise they’ll die. Those with type 2 may be able to manage their condition through lifestyle changes but may eventually need insulin if they’re unable to keep their blood sugar levels well controlled.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Kidney Failure
Approximately 10 Percent Of Type 2 Diabetes Has Autoantibodies
If you are, the one diagnosed as type 2 diabetes, and later told to have, type 1 diabetes or LADA. You are not alone, a European study, published in Medscape Medical News nearly 10 percent of patients with adult-onset diabetes were found to have associated with autoantibodies.
Many of those with autoimmune diabetes did not require insulin during diagnosis, although they are young and lean structure. About 90 percent of the patients with positive antibodies had GADA, and they need insulin very shortly. Everyone to undergo GAD antibodies test for people with type 2 diabetes who is not responding to the treatment or for thinner people who have diagnosed as having diabetes type 2.
Healthy Eating For Type 2 Diabetes
A dietitian or your doctor will be able to advise you on what to eat to meet your nutritional needs and control your blood sugar. Your doctor should be able to refer you to a registered dietitian for personalised advice.
Eating healthy foods with a low glycaemic index can help to optimise your blood sugar levels. This includes wholegrain breads, minimally processed breakfast cereals like rolled or steel cut oats, legumes, fruit, pasta and dairy products.
Avoid high-carbohydrate, low-nutrient foods such as cakes, lollies and soft drinks, and eat a diet low in saturated fat.
You should eat at regular times of the day and may also need snacks. Try to match the amount of food you eat with the amount of activity you do, so that you dont put on weight.
If you are overweight or obese, losing even 5-10 per cent of your body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
You May Like: What’s The Normal Diabetes Level
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Cured
Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but people with the condition may be able to manage their type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and, if needed, diabetes medications to control blood sugar levels.
Its also emerging that some people who are overweight or obese can put their type 2 diabetes into remission by losing a substantial amount of weight, especially early in their diagnosis. Their blood sugar measurements return to healthy levels below the diabetes range. Its not a permanent solution, and diabetes could come back, so it needs to be maintained. However, many people were still in remission 2 years later. This should only be tried under the supervision of your doctor.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
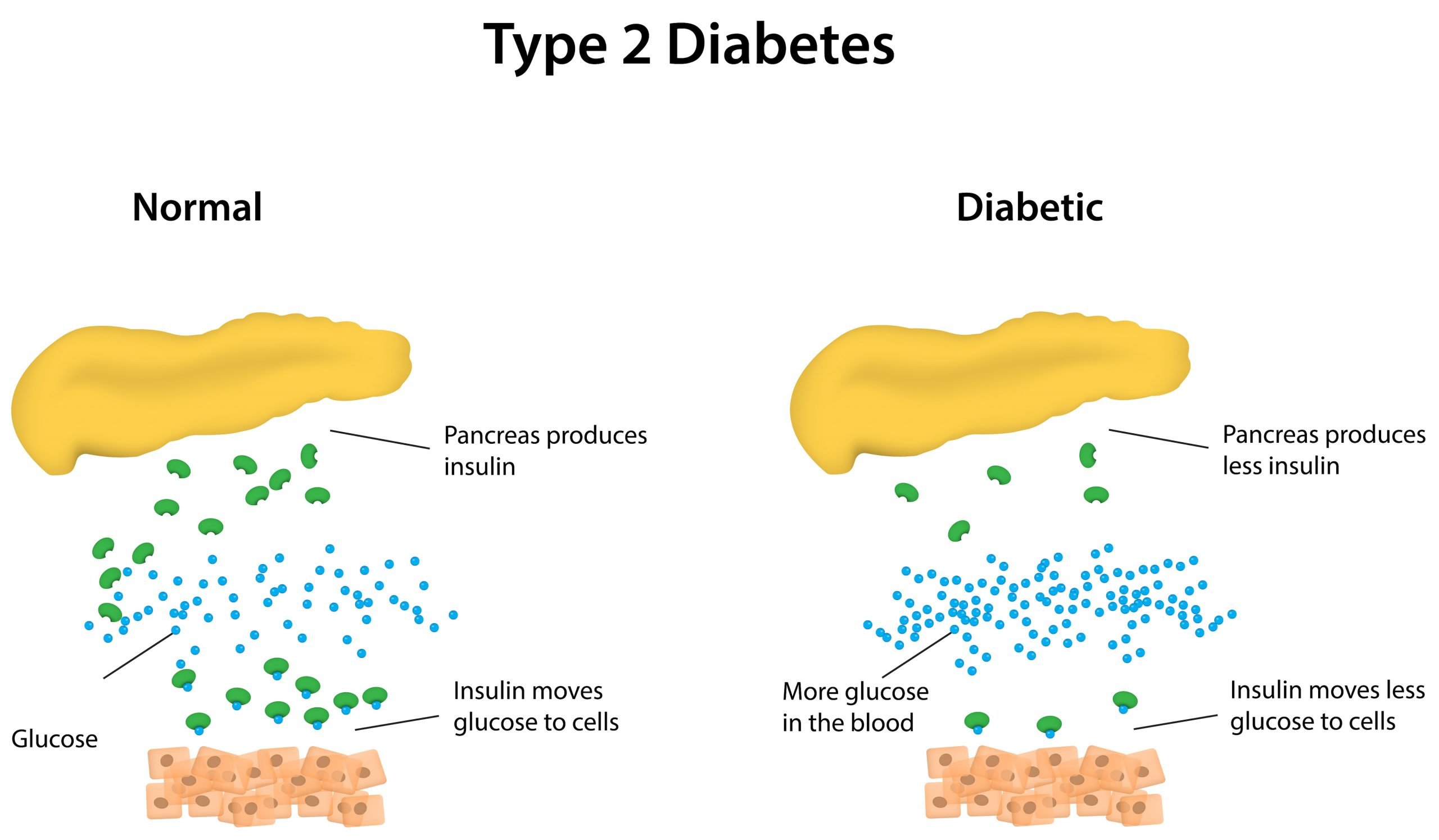
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. If you have type 2 diabetes, cells dont respond normally to insulin this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas cant keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
You May Like: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
Risk Factors For Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a complex disease, and the diagnosis of T2D is never the patients fault. Though there isnt a single cause for this form of diabetes, there are various risk factors associated with it:
- History of prediabetes or gestational diabetes
- History of PCOS
- Age The risk of Type 2 diabetes increases as you age.
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Inactivity
- Obesity
- Environmental Factors
- Smoking
- Genetics is also a strong factor in developing Type 2 diabetes. If you have an immediate family member with Type 2, youre more likely to develop the disease.
Of the 415 million diabetes cases globally, 90% are estimated to be Type 2. There currently is no cure for it, but it can often be managed with lifestyle changes, diet, exercise, stress management, and medication. Everyones management technique differs. To learn whats right for you, explore our resources on our website and discuss with your healthcare team strategies to try. It may take some trial and error, however, we believe every person with Type 2 can live a healthy life with it.
The Health Risks Of Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a lifelong condition. High blood glucose levels over a long period of time can cause:
- blindness
- reduced blood supply to the limbs, leading to amputation
- nerve damage
- erectile dysfunction and
- stroke.
Although there is no cure for diabetes, the condition can be managed by medication and/or insulin, and by making healthy lifestyle choices.
Read Also: Pain Medicine For Diabetic Neuropathy
Medicines For Type 2 Diabetes
There are many types of diabetes medications and they work in different ways to control blood glucose. If you have diabetes, over time it can change, meaning your medications may need to change too. For example, you may need more than one medication to control your blood glucose levels. Some people with type 2 diabetes may eventually need insulin to manage their condition.
If you are living with type 2 diabetes, you can join the National Diabetes Services Scheme to access support services, including free or subsidised products. Visit Diabetes Australia for information and resources.
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 diabetes differs from Type 2 in that Type 1 is an auto-immune condition that occurs when the bodys own immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. People with Type 1 are insulin-dependent for life and there currently is no cure. Unless detected early, at diagnosis, people have too much sugar built up in their blood and exhibit symptoms such as extreme thirst, frequent urination, blurry vision, weight gain or loss, recurrent infections, and headaches.
While Type 2 and Type 1 differ in nature, where they often meet is in complications. Prolonged levels of high blood sugar in anyone with diabetes can lead to long-term complications ranging from heart disease, kidney failure, foot, eye and nerve damage to skin disorders.
To learn more about Type 1 diabetes, visit our sister site, Beyond Type 1.
Don’t Miss: The Effects Of Diabetes On Your Body
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, people produce little or no insulin, as the insulin-producing cells have been destroyed by the bodys immune system. Type 1 diabetes is an auto-immune disease.
In type 2 diabetes, the body may make enough insulin early in the disease, but doesnt respond to it effectively. As type 2 diabetes progresses, the pancreas gradually loses the ability to produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is associated with inherited factors and lifestyle risk factors such as being overweight or obese, poor diet, and insufficient physical activity.
Wounds That Do Not Heal Easily
Wounds or sores that tend to heal slowly can be a sign of undiagnosed diabetes. Abnormally high blood glucose levels cause blood vessel damage, nerve damage, chronic inflammation and poor immunity.
All these factors impair thebody’s ability to heal wounds and injuries, putting people with diabetes at a very high risk for complications such as bacterial and fungal infections, which may require emergency care. Wounds, if left untreated, can even become gangrenous, requiring surgical removal of the affected area or perhaps a limb in severe cases.
High glucose level in the blood causes premature narrowing and hardening of the arteries. This causes poor blood circulation, reducing the supply of oxygen and nutrients reaching the damaged tissue for healthy wound healing. As a result, wounds take a long time to heal.
Neuropathy plays a threatening role in the growth of wounds in diabetes. Nerve damage that causes numbness in the periphery further complicates the wound healing in people with diabetes as they don’t feel the pain from a cut or injury due to loss of sensation, particularly in their limbs.
Wounds often go unnoticed, increasing the risk of infections without timely treatment. People with diabetes need to closely monitor their feet for cuts, calluses and minor wounds to prevent diabetic foot ulcers that can quickly progress into other complications like gangrene and sepsis.
Also Check: Is Keto Good For Type 1 Diabetes
The Major Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes And Whos Most At Risk
Type 2 diabetes is a condition marked by chronically high levels of sugar in your bloodstream which, if left untreated, can cause devastating complications down the line.
Consider that the SparkNotes definition of a complicated condition that affects more than 30 million Americans, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Here, we’ll dig deeper into what you should know about type 2 diabetes, from the first symptoms to the most common treatments.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, treatment, and complications from type 2 diabetes may vary from person to person. The following information will help you learn more about this disease and provide you with helpful tools, assessments and resources.
-
If left untreated or improperly managed, diabetes can lead to a variety of life-threatening complications.
Recommended Reading: Best Type 2 Diabetes App
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include
- numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- sores that do not heal
- unexplained weight loss
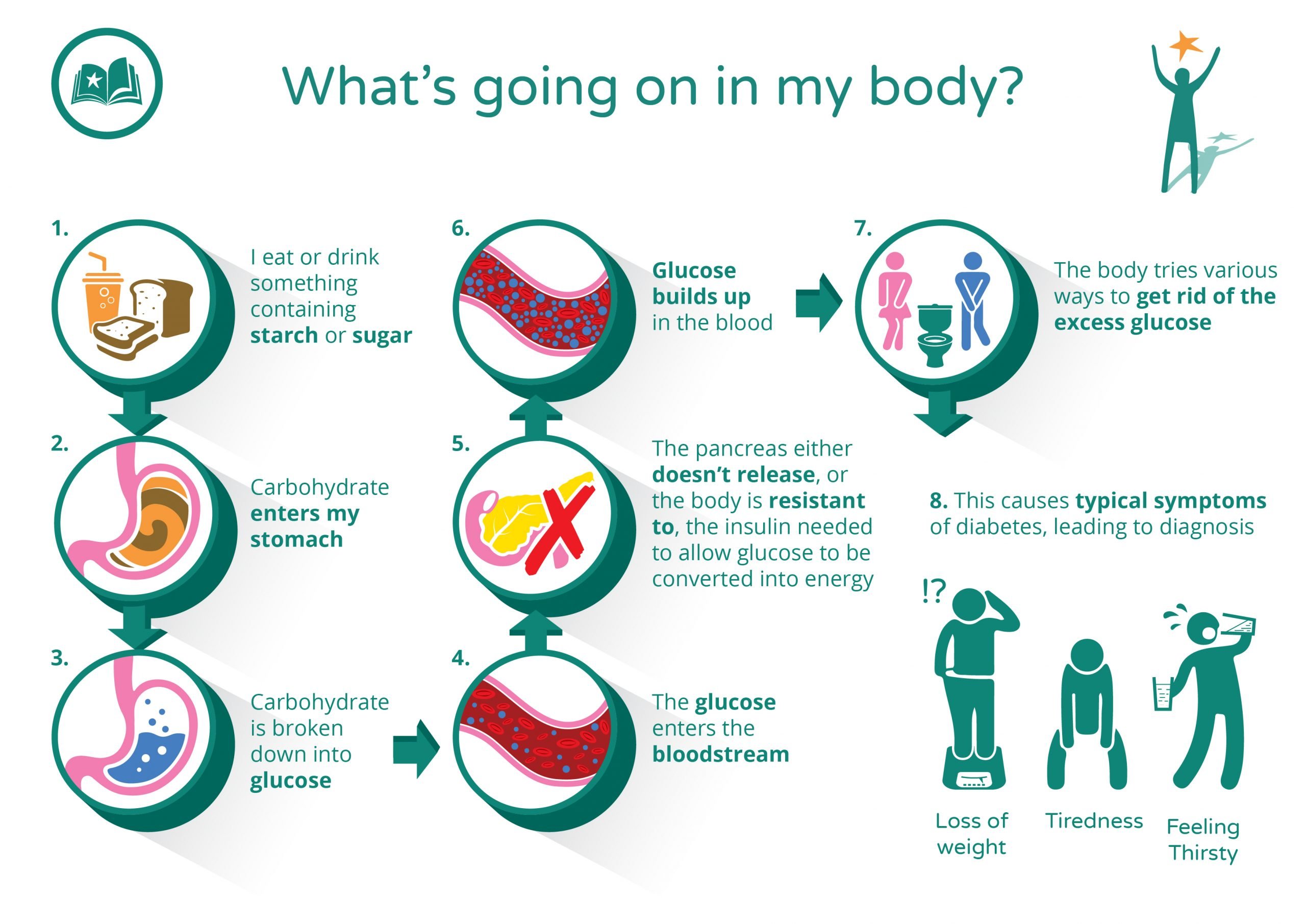
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowlyover the course of several yearsand can be so mild that you might not even notice them. Many people have no symptoms. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart disease.
Early Signs Of Type 2 Diabetes
There is a reason why type 2 diabetes is also known as silent disease. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes take years to develop as the disease progresses gradually. In fact, most affected people show very mild or no symptoms in the beginning, but often go on to develop full-fledged type 2 diabetes over several years, without realizing they have a problem.
But if you know what symptoms to watch out for, especially when you have a family history of disease, are overweight or have excessive belly fat, it is possible to get a diagnosis before the disease has progressed to a dangerous level, which also increases your risk of many disabling and even life threatening health complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, blindness, depression, and fungal infections.
The purpose of this blog is to understand these early signs of diabetes as timely diagnosis and treatment can help slow down or even prevent the development of serious complications that may affect the quality of your life in a huge way. But first, lets understand what happens in type 2 diabetes and what are the major risk factors involved in the disease development.
Also Check: How Does Diabetes Affect Your Feet
Frequent Urination And Excessive Thirst
Excess of glucose in your bloodstream makes you pee more. This happens because the kidneys are now working overtime and producing more urine to flush out excess of sugar from the blood. You may even feel the need to wake up at night to urinate.
Frequent urination also makes your thirsty as your body is losing so much of water. Drinking more water will further increase your need to pee, creating a disturbing cycle of frequent urination and excessive thirst, two very important symptoms of type 2 diabetes that can be caught at an early stage.
In addition, high blood sugar also damages millions of small blood vessels in your kidneys. These tiny blood vessels work as filters to remove waste material from the blood and retain useful substances such as proteins. Excessive blood sugar damages these filtering units and impairs the ability of the kidneys to filter the blood. Diabetic kidney damage or diabetic nephropathy does not happen overnight, and one can take steps to reduce the risk or slow down kidney damage by controlling their blood sugar level.
Diabetes may also cause nerve damage in the bladder, which makes it difficult to fully empty one’s bladder. Urine pressure can cause bladder dysfunction and further kidney damage. People with diabetes are also more prone to developing urinary tract infection.
Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Teens
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But its not always because family members are related it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
- Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks
- Eating more fruits and vegetables
- Making favorite foods healthier
- Making physical activity more fun
Healthy changes become habits more easily when everyone makes them together. Find out how to take charge family style with these healthy tips.
Read Also: Psoriasis And Diabetes Type 1
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
Recommended Reading: How To Get Tested For Diabetes
What Glucose And A1c Ranges Are Used For A Diabetes Diagnosis
A diabetes diagnosis can be confirmed in a number of ways such as determining ones fasting plasma glucose, an oral glucose tolerance test , an A1c, and a random plasma glucose test.
The fasting plasma glucose checks your blood sugar levels if you havent had anything to eat or drink for at least 8 hours. Diabetes is diagnosed if your blood sugar is at or greater than 7.0 mmol/L126 mg/dL. A normal fasting glucose is less than 5.5 mmol/L100 mg/dL and prediabetes is considered to be from 5.5 mmol/L100 mg/dL to 6.9 mmol/L125 mg/dL.
The oral glucose tolerance test is conducted by checking your blood sugar levels before and 2 hours after consuming a sweet drink. The test determines how well your body uses carbohydrates. A diabetes diagnosis is confirmed if your blood sugar is equal to or greater than 11.1 mmol/L200 mg/dL after 2 hours. Normal is considered less than 7.8 mmol/L140 mg/dL and prediabetes ranges from 7.8 mmol/L140 mg/dL to 11.1 mmol/L199 mg/dL.
The random or casual plasma glucose test determines a diabetes diagnosis through testing how much glucose is in your blood at a random time. For this test, it doesnt matter if youve eaten or fasted. A diabetes diagnosis is given if your blood sugar is equal to or greater than 11.1 mmol/L200 mg/dL. For further confirmation, another random test or fasting glucose test may be conducted.