Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
What Does A1c Stand For
Hemoglobin A1C , commonly called A1C, stands for glycosylated hemoglobin. An A1C test provides information on how well-controlled a persons diabetes is. It does this by measuring the percentage of red blood cell hemoglobin protein that has sugar stuck to it and provides a three-month average of your blood glucose levels, explains , MD, a board-certified endocrinologist at the Center for Endocrinology at Mercy Medical in Baltimore. The higher blood sugar levels are, the more glucose attaches to hemoglobin. The results provide patients and their healthcare providers with information on how well their treatment, diet, and medication is working and whether adjustments are necessary.
There are a few reasons a doctor might suggest an A1C test:
- To make a diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes
- To test for prediabetes
- To monitor blood sugar levels
- To determine if treatment adjustments are needed
The A1C blood test is not for diagnosing Type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, or cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
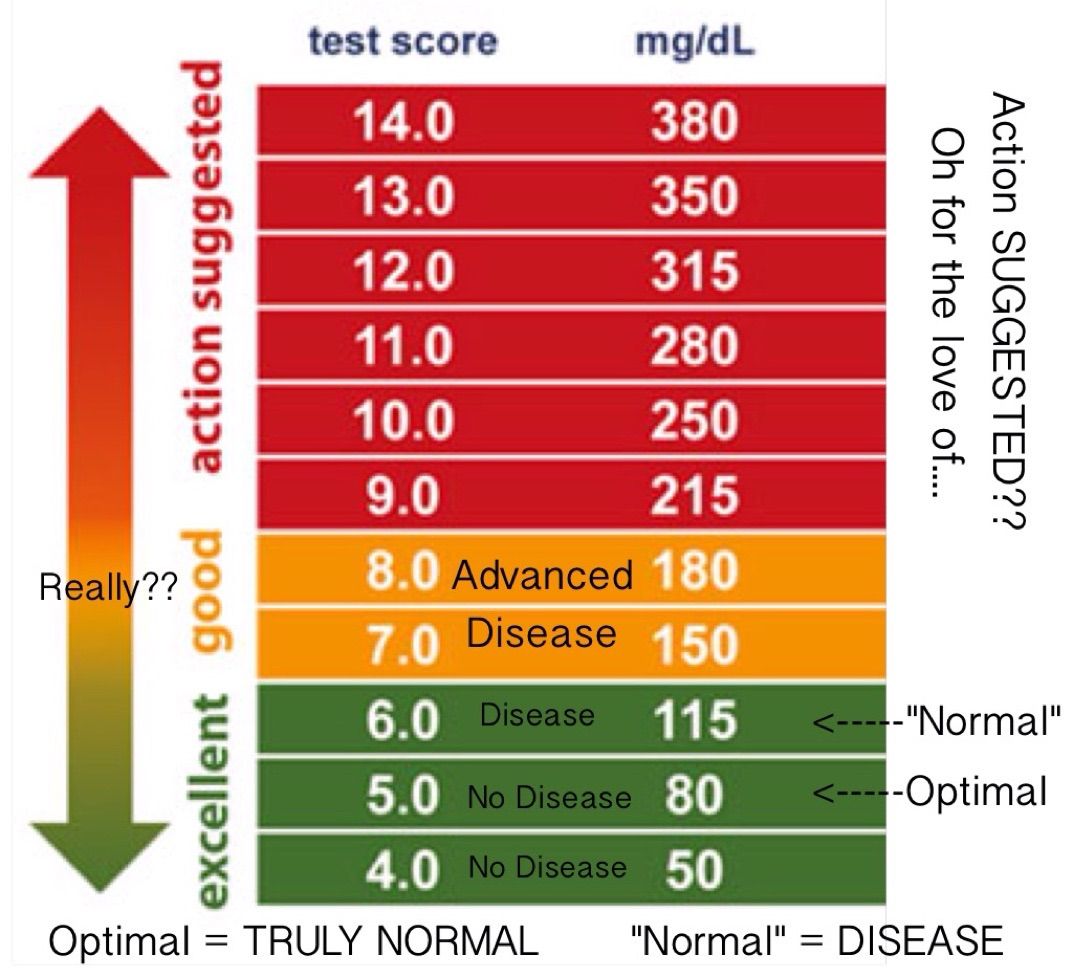
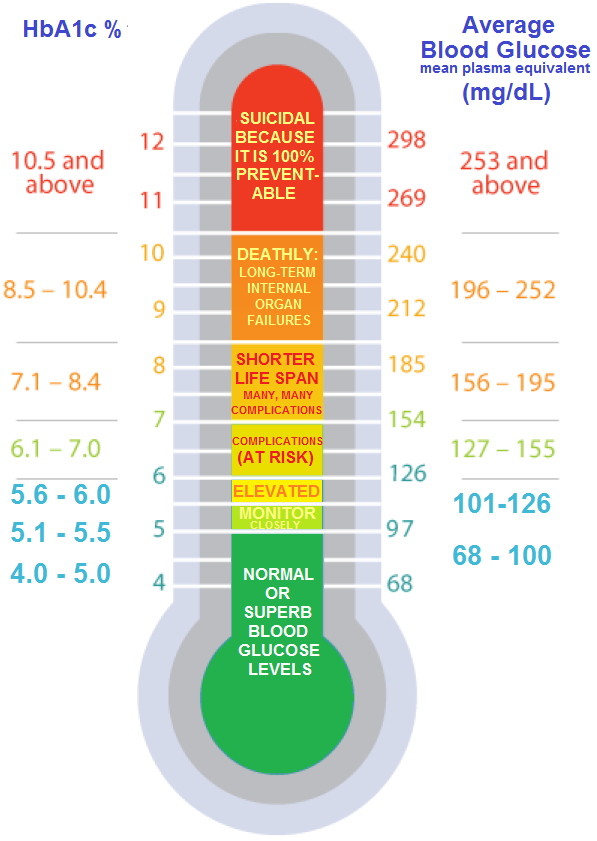
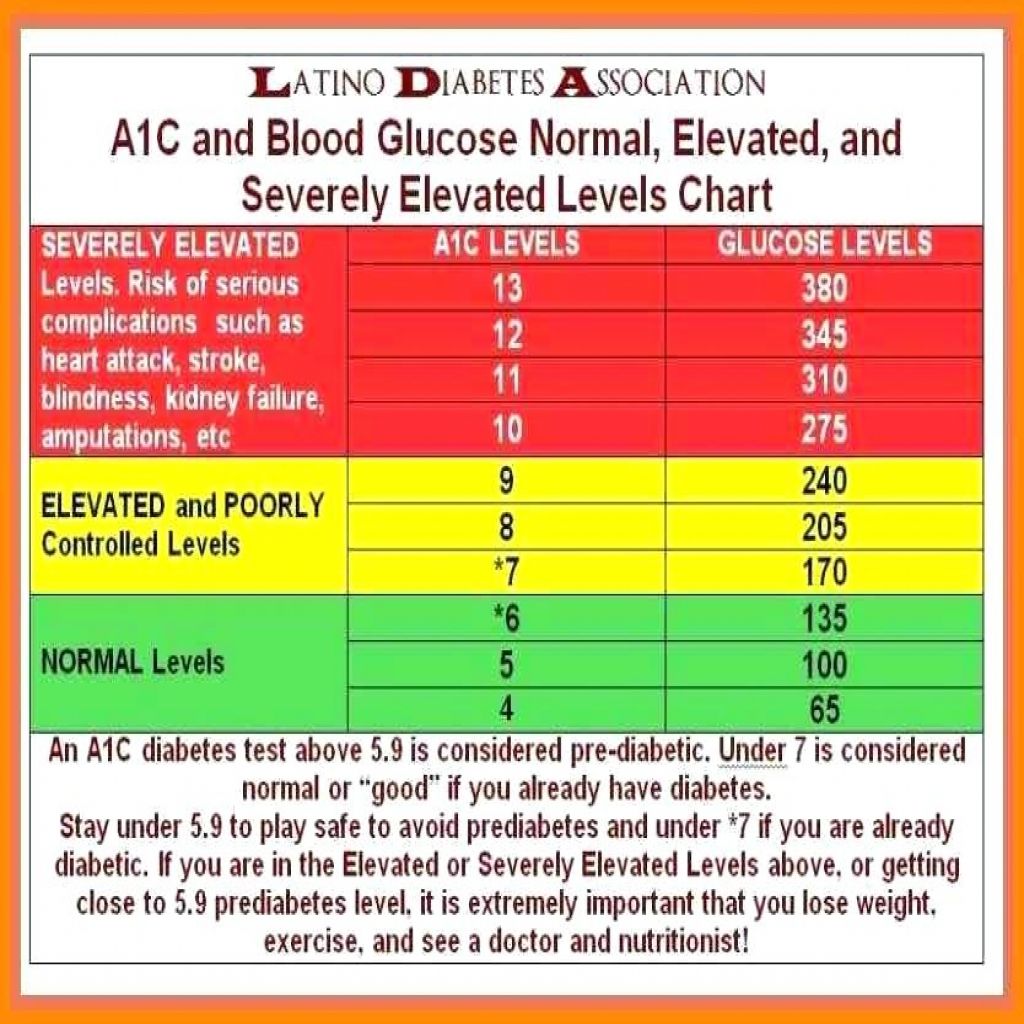
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Insulin Out Of Pocket
Why Should A Person Get The A1c Test
Testing can help health care professionals
- find prediabetes and counsel you about lifestyle changes to help you delay or prevent type 2 diabetes
- find type 2 diabetes
- work with you to monitor the disease and help make treatment decisions to prevent complications
If you have risk factors for prediabetes or diabetes, talk with your doctor about whether you should be tested.
What Should I Do After I Check My Blood Glucose
Write the blood glucose number in a log book or on a log sheet , and:
- Include all of your blood glucose numbers.
- Write a comment if there is a reason the blood glucose is above or below target.
- Take your blood glucose meter with you when you are away from home.
- Know your blood glucose numbers when you call the clinic or the doctor.
- Bring your blood glucose meter and blood glucose records to all your appointments.
- Bring a list of any questions that you may have.
Read Also: Blood Sugar Readings For Diabetics
What Should My Blood Sugar Levels Be
Your blood sugar level changes depending on what you’ve eaten, whether you’ve exercised and other factors but we have some general guidelines to determine what levels are healthy.
For generally healthy individuals who haven’t eaten for eight hours or more, a normal blood sugar level is between 70-99 mg/dL. When you’ve eaten in the past two hours, it should be no higher than 140 mg/dL. To refresh your chemistry knowledge, that unit is milligrams per deciliter and it’s measuring the amount of glucose present in your blood.
Only a medical professional can diagnose diabetes or another issue with your blood sugar, so if you’re concerned about your blood sugar levels, check with a doctor.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
Dont Miss: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
Recommended Reading: What Foods Increase Your Insulin Levels
What Are The Blood Glucose Tests To Check The Levels
Every person, irrespective of being diabetic or not, should get routine blood glucose testing. Not only does it avert the risks of diabetes, but it also indicates possibilities of other underlying chronic illnesses that arent always diagnosed on time.
With blood glucose monitoring, several blood tests can assess the levels. Some of the most important ones include:
Is Hyperglycaemia Serious
The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep blood sugar levels as near to normal as possible. But if you have diabetes, no matter how careful you are, you’re likely to experience hyperglycaemia at some point.
It’s important to be able to recognise and treat hyperglycaemia, as it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated.
Occasional mild episodes aren’t usually a cause for concern and can be treated quite easily or may return to normal on their own. However, hyperglycaemia can be potentially dangerous if blood sugar levels become very high or stay high for long periods.
Very high blood sugar levels can cause life-threatening complications, such as:
- diabetic ketoacidosis a condition caused by the body needing to break down fat as a source of energy, which can lead to a diabetic coma this tends to affect people with type 1 diabetes
- hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state severe dehydration caused by the body trying to get rid of excess sugar this tends to affect people with type 2 diabetes
Regularly having high blood sugar levels for long periods of time can result in permanent damage to parts of the body such as the eyes, nerves, kidneys and blood vessels.
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team. You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Don’t Miss: Insulin Brands For Type 2 Diabetes
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hypoglycemia happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. Low blood sugar can be caused by many things including the two different types of diabetes, certain medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, pregnancy , and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Tingling lips
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or other glucose monitoring device.
If you dont have access to these tools and start to feel the symptoms of low blood sugar, consume 15 grams of carbs or take a quick dissolve glucose tablet to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Once your blood sugar is back in its target range, you can have a snack or meal to make sure it doesnt drop again.
Here are some other lifestyle and medicinal treatments that can help treat hypoglycemia:
- Eat a healthy diet full of whole foods that are minimally processed.
- Take prediabetes or diabetes medications as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Use a glucagon kit in emergencies. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels quickly.
Change Your Life Today And Reduce Your Risk Of Diabetes
Diabetes can be a massive burden on both your health and your wallet. But, maintaining normal blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and staying physically active are great ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
If you are looking to improve your health and monitor your risk factors for disease, getting covered is a great way to relieve the financial pressures of looking after yourself.
Why not contact us today at Insurdinary for a free, personalized, no-obligation quote from some of the best health care providers in Canada!
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Stomach Fat
The 411 On A1c: Normal A1c Levels And 15 Ways To Lower High A1c
The hemoglobin A1C test is the closest thing to a diabetes scorecard you can find. Whether someone has had diabetes mellitus for years or if they have just been diagnosed, they have probably heard about this test. Unlike blood sugar meters people use at home, the A1C measures an average blood sugar level over the past several months by analyzing how many of a patients hemoglobin cells have glucose attached to them. The test results keep track of how well a person is managing his or her diabetes.
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner than age 45.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 and then every 3 years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Feeling Hot All The Time
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
Its especially important to keep this mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you cant always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury which raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you cant necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise like weightlifting many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, but the biggest changes happen around mealtimes. Before eating, a healthy sugar level is between 3.9-5.5mmol/L. Around 1-2 hours after eating, expect blood sugar to rise to 5-10mmol/L.
If your blood sugar doesn’t stick within these ranges, the body may have stopped regulating blood sugar effectively which can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Can I Get Rid Of Diabetes
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
Take Advantage Of A Singlecare Savings Card
With a free coupon from SingleCare, a 30-day supply of metformin can cost as little as $4. All thats required is to select a coupon based on price or local pharmacy on SingleCares metformin discount coupon page. The savings card can be printed, emailed, or sent to a smartphone and used right away to enjoy prescription discounts.
Don’t Miss: Plant Based Type 1 Diabetes
What Is A Dangerous Level Of A1c
When levels rise to 9.0, the risk of kidney and eye damage and neuropathy increases. Some people who are newly diagnosed could have levels over 9.0. Lifestyle changes and possibly medication can lower levels quickly. For someone who has long-standing diabetes, levels rise above 9.0 could signal the need for a change in their treatment plan.
Some labs estimate average blood glucose , which corresponds to home glucose meter readings , allowing patients to understand the results better.
Amy Campbell Ms Rd Ldn Cde
A Registered Dietitian and Certified Diabetes Educator at Good Measures, LLC, where she is a CDE manager for a virtual diabetes program. Campbell is the author of Staying Healthy with Diabetes: Nutrition & Meal Planning, a co-author of 16 Myths of a Diabetic Diet, and has written for publications including Diabetes Self-Management, Diabetes Spectrum, Clinical Diabetes, the Diabetes Research & Wellness Foundations newsletter, DiabeticConnect.com, and CDiabetes.com
***Learn blood sugar basics with our free guide!
***Interested in learning more about blood sugar? Check out our blood sugar chart and learn about using blood sugar monitoring to manage diabetes in Managing Your Blood Glucose Ups and Downs.
Learn more about the health and medical experts who who provide you with the cutting-edge resources, tools, news, and more on Diabetes Self-Management.
Don’t Miss: Type Of Exercise For Diabetes
Diabetes Is Diagnosed By Any One Of The Following:
Sometimes you may have symptoms of fatigue, excessive urination or thirst, or unplanned weight loss. However, often people have no symptoms of high blood glucose and find a diabetes diagnosis surprising.
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or glucose, is your body’s main energy source. We get glucose from the food we eat, and our blood carries it around to all the cells in the body to give them energy to function. Glucose mainly comes from the carbohydrates we eat, though our bodies can convert protein and fat into sugar too if needed.
Glucose from protein is typically stored in the liver and doesn’t enter the bloodstream, so eating protein-rich foods won’t raise your blood sugar too much. Fats slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, which causes a delayed rise in blood sugar. High blood sugar can be an issue because it usually leads to sugar crashes, which are no fun — symptoms include fatigue, headaches and the jitters. So, eat meals balanced with protein, fat and carbs to avoid this.
Blood sugar is closely related to insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas that helps your body use glucose that’s in the carbohydrates you eat. Insulin helps regulate your blood sugar levels — if you eat more sugar than you need in the moment, the hormone helps store the glucose in your liver until it’s needed for energy.
You probably also know about blood sugar in the context of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which people are unable to make insulin, so they need to inject the hormone in order to keep their blood sugar levels stable. People with Type 2 diabetes, which usually occurs later in life, either don’t secrete insulin or are resistant to it.
You May Like: Best Type 1 Diabetes Snacks