Humalog For Type 2 Diabetes
Humalog is also FDA-approved to help control blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes. In addition, a second type of Humalog called Humalog Mix is approved for this same use.
Type 2 diabetes explained
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the cells in your body become resistant to the effects of a hormone called insulin.
Insulin helps your body to process glucose . If your cells become resistant to insulin, they dont process sugar as well as they should. Insulin resistance can cause your blood sugar level to rise too high.
Over time, your pancreas may also stop making enough insulin. At this point, youll likely need treatment with insulin to help manage your blood sugar levels.
Humalog and Humalog Mix explained
Humalog contains insulin lispro, which is a rapid-acting insulin analog. This form of insulin works very quickly. You take it at mealtimes to help manage the surge in blood sugar that can occur after eating.
Humalog Mix contains a premixed combination of insulin lispro and a longer-acting insulin called insulin lispro protamine. Humalog Mix works very quickly, but it lasts longer than Humalog. Humalog Mix helps control mealtime surges in blood sugar and then helps manage blood sugar between meals or at night.
Each dose of Humalog Mix is intended to cover two meals or one meal and a snack.
Effectiveness for type 2 diabetes
A clinical study found Humalog to be similarly effective to insulin human for managing blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes.
Evolution Of Insulin Therapy And Hypoglycemia
Initially insulin therapy was historically available only as Regular insulin. The result was inconvenience of multiple injections, poor growth, frequent hyperglycemia and hypo-glycemia, and difficulty providing adequate basal insulin replacement. The addition of protamine to insulin, first as PZI insulin and later NPH insulin , reduced the rate of absorption of insulin and provided the first attempts at a basal insulin strategy, but often led to late, unpredictable hypoglycemia. Human insulins have now replaced animal insulins. Initially it was suspected that human insulins were more likely to predispose to serious hypoglycemia, but this has been proved not to be correct.
First Some Basic Things To Know About Insulin:
- Approximately 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight, when you are fasting and between meals. This is called background or basal insulin replacement. The basal or background insulin dose usually is constant from day to day.
- The other 50-60% of the total daily insulin dose is for carbohydrate coverage and high blood sugar correction. This is called the bolus insulin replacement.
Bolus Carbohydrate coverage
The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio.The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin.
Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of 12-15 grams of carbohydrate. This range can vary from 4-30 grams or more of carbohydrate depending on an individuals sensitivity to insulin. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress.
Bolus High blood sugar correction
The bolus dose for high blood sugar correction is defined as how much one unit of rapid-acting insulin will drop the blood sugar.
Generally, to correct a high blood sugar, one unit of insulin is needed to drop the blood glucose by 50 mg/dl. This drop in blood sugar can range from 15-100 mg/dl or more, depending on individual insulin sensitivities, and other circumstances.
You May Like: What To Give A Diabetic When Blood Sugar Is Low
Drug Forms And Strengths
There are two different types of Humalog: Humalog and Humalog Mix.
Humalog is available in two strengths: U-100 and U-200 . It contains insulin lispro.
Humalog Mix is available in only one strength: U-100. It contains a mixture of insulin lispro and insulin lispro protamine.
Humalog U-100
The U-100 strength of Humalog comes in four different forms:
- Vials. Humalog vials come in 3-mL and 10-mL sizes. You can use the vials with two different devices. One is an insulin syringe. You should use a U-100 insulin syringe to measure your dose of Humalog from the vial. The other device is called an insulin pump. It delivers a continuous dose of insulin, and it can also give extra doses at mealtimes.
- KwikPen. This is a 3-mL disposable, prefilled injection pen. It can provide up to 60 units of insulin with one injection.
- This is a 3-mL disposable, prefilled injection pen. It can provide up to 30 units of insulin with one injection.
- Cartridge. This is a 3-mL cartridge thats used with reusable insulin pens, such as HumaPen Luxura HD.
Humalog U-200
The U-200 strength of Humalog comes in one form:
- KwikPen. This is a 3-mL disposable, prefilled injection pen. It can provide up to 60 units of insulin with one injection.
Humalog Mix 50/50
Humalog Mix 50/50 contains a mixture of 50% insulin lispro protamine and 50% insulin lispro. It comes in two different forms, and each has a strength of U-100. These forms are:
Humalog Mix 75/25
Supplies youll need
What Should I Know About Insulin Lispro Vs Humalog
Humalog is a brand-name medication that contains the active drug insulin lispro. Insulin lispro is also available as a generic medication.
A generic drug is an exact copy of the active drug in a brand-name medication. The generic is considered to be as safe and effective as the original drug. Generics tend to cost less than brand-name drugs.
In some cases, the brand-name drug and the generic version may come in different forms and strengths.
If youd like to know about taking the generic version of Humalog, talk with your doctor.
Also Check: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Type 2 Diabetes
When To Throw Away Your Insulin Pens
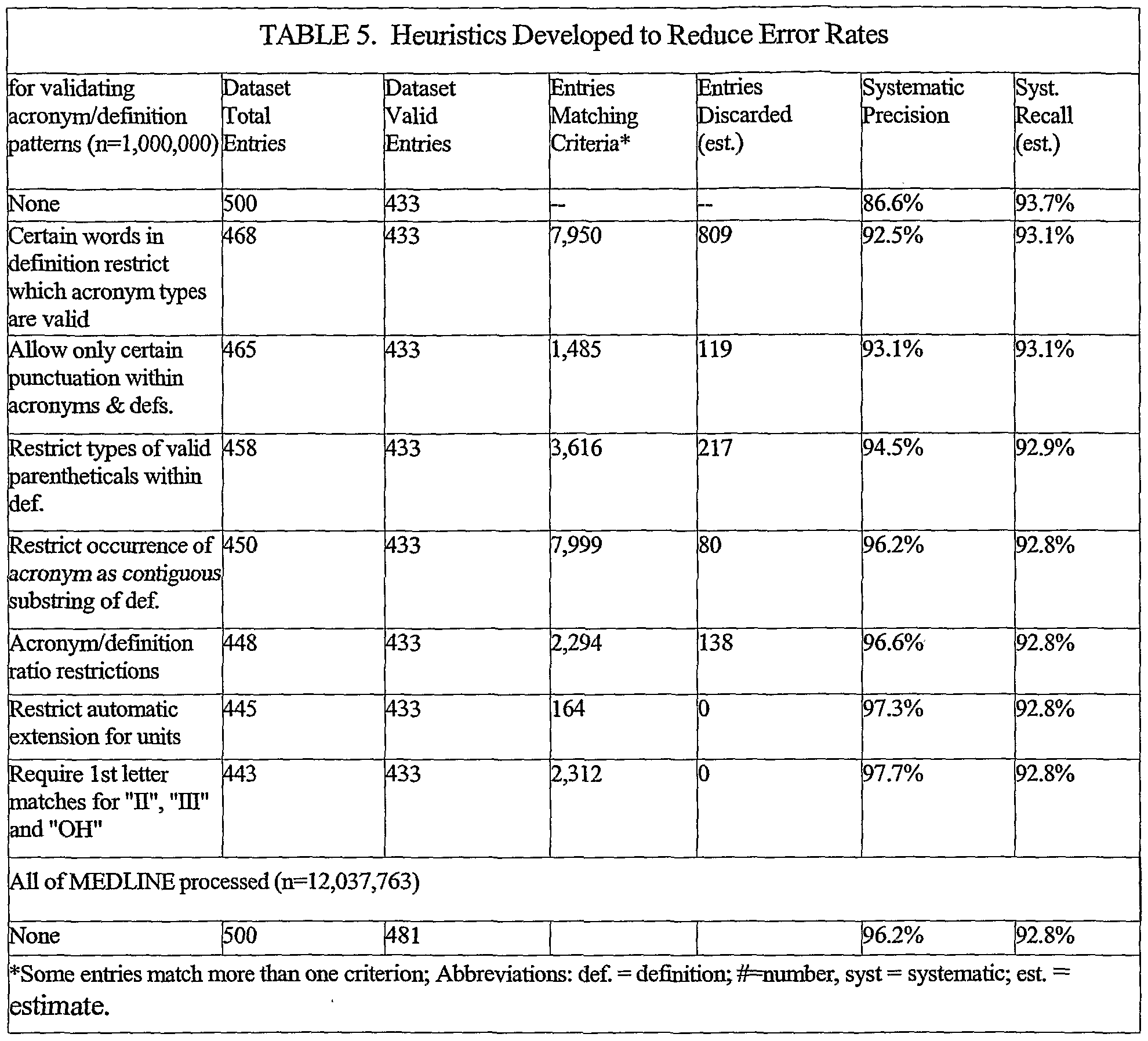
Youll use the same insulin pen over and over for a certain number of days. The number of days depends on the type of insulin pen youre using. The table below lists some common types of insulin pens and the number of days you can use each one. You can also read the instructions that come with your insulin pens.
| Insulin Type |
|---|
Whenever you start using a new insulin pen:
For example, if you start using a Lantus SoloStar insulin pen on January 1st, count ahead 28 days to January 28th. Write January 28 on a piece of paper tape and put the paper tape on the pen. Throw away the pen on January 28th, even if theres still insulin in it.
You can keep unused insulin pens in the refrigerator until the expiration date listed on the pen label. Once an insulin pen reaches the expiration date listed on the pen label, throw it away.
How To Store And Dispose Of Your Home Medical Sharps
Dont throw your medical sharps directly into the trash or flush them down the toilet. Put them into a sharps container. You can use an empty, hard, opaque plastic container that has a screw-on cap, such as a laundry detergent bottle. Dont store sharps in glass bottles, soda bottles, milk jugs, aluminum cans, coffee cans, or paper or plastic bags. For more information, read the resource How to Store and Get Rid of Your Home Medical Sharps.
Stop using your sharps container when its a little more than half full. Wrap the lid or cap with strong tape to create a more secure seal and keep it from leaking. Label the bottle by writing on it Home Sharps: not for recycling.
If you live in New York City, you can place the sealed container in with your regular trash for collection. Dont put it with your recyclables. If you live in a different county of New York or another state, check with your local department of health. You can also use the resources below to find more information specific to your area.
- Safe Needle Disposal
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Kidney Disease And Diabetes
Using Your Sliding Scale
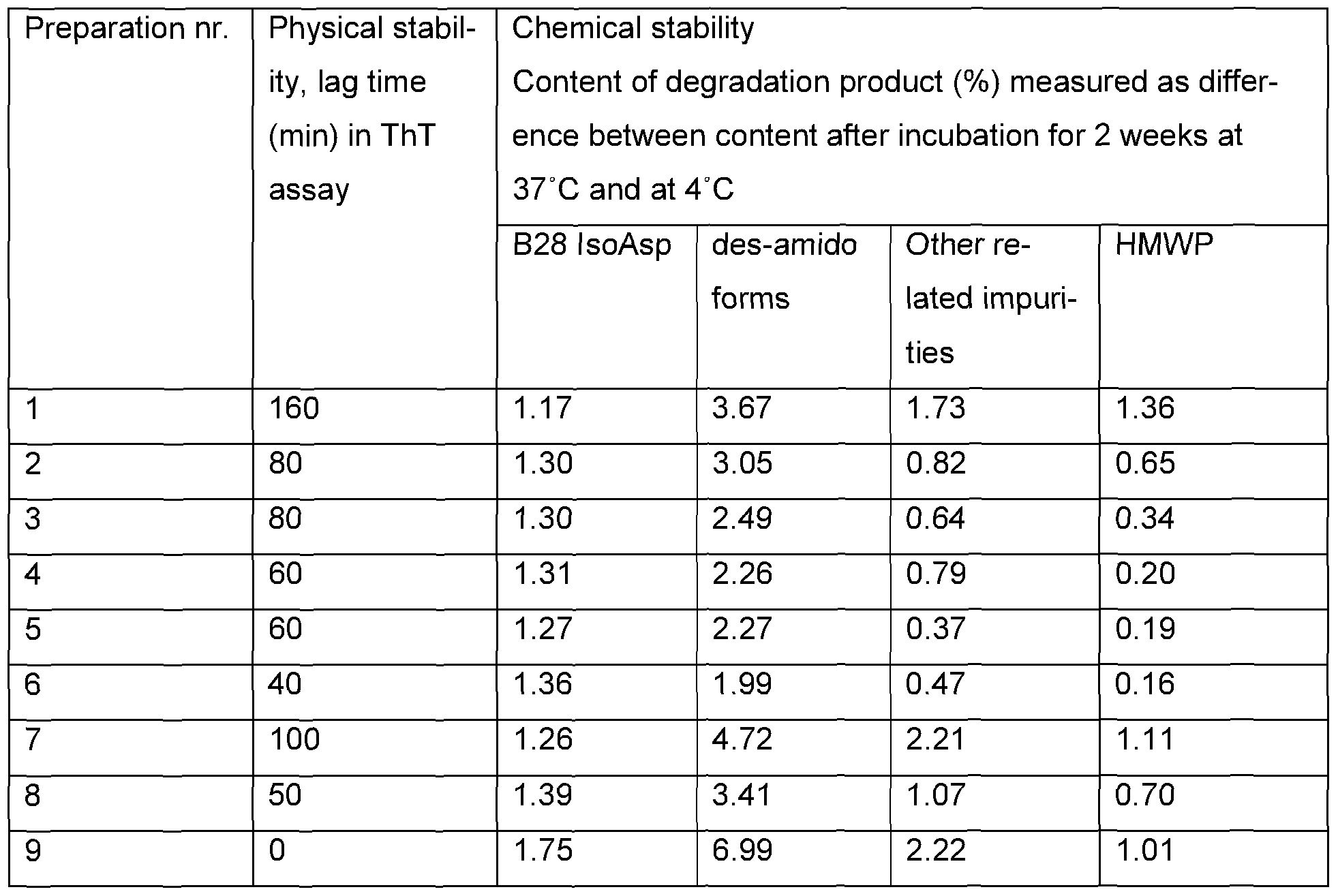
A sliding scale is what you will use to determine how much insulin you need to give to correct an elevated blood sugar and/or for food. There are two parts. Correction factor and insulin to carb ratio. In our example, the correction factor is half a unit will lower the blood sugar 25 points, and the insulin to carb ratio is half a unit will cover 10 grams of carbs.
Here, were just looking at the insulin to carb ratio. You can see if I eat 60 grams of carbs at a meal, Ill need three units of insulin to cover it. Before you eat, you need to check your blood sugar. Lets say, my blood sugar is 220. Look on the scale to find 220. To help lower my blood sugar before I eat, Ill need to give two units. So, in total, before this meal, Ill give five units of insulin two units of insulin for correction and three units of insulin to cover the carbs.
Determine The Cause Of The Hypoglycaemia
In order to determine what adjustments should subsequently be made to insulin doses, it is necessary to determine the cause of the hypoglycaemia. If in doubt, consult an endocrinologist or general physician.
Illness states causing hypoglycaemia: such states, e.g. sepsis or glucocorticoid deficiency, are beyond the scope of these guidelines. See ‘Special Circumstances’ on the landing page.
Hypoglycaemia due to an excessive dose of bolus or supplemental insulin: if not directly due to an illness state, hypoglycaemia within 3-4 hours of a bolus or supplementary dose of insulin can be assumed to be due to it. In such cases the hypoglycaemia is unrelated to the basal insulin and the basal insulin should not be reduced or withheld.
A bolus dose may simply have been too large, or the following meal may have been smaller than normal or vomited. A careful history should elucidate whether subsequent bolus doses need to be reduced.
If hypoglycaemia follows administration of supplemental insulin, first check that the supplemental insulin has been charted and given no more frequently than every 4-6 hours. Stat doses given in addition to a sliding scale are risky and should be used with caution. If administration has been correct according to a sliding scale, then a sliding scale should still be continued, but re-charted with reduced doses.
Recommended Reading: Cerave Moisturizing Cream For Diabetics Dry Skin
Data Collection And Analysis
Two review authors independently extracted data, assessed trials for risk of bias, and evaluated the overall certainty of evidence utilising the GRADE instrument. We synthesised data using a randomeffects model metaanalysis with 95% prediction intervals, if possible, or descriptive analysis, as appropriate.
Risk Factors For Serious Hypoglycemia In Type 2 Dm
Certain factors may predispose to serious hypoglycemia in type 2 DM. In a large study of Medicaid enrollees, aged 65 years or older, who used insulin or sulfonylureas from 1985 through 1989, Shorr and colleagues found that the rates of serious hypoglycemia were 2.76 per 100 person-years among insulin users. Predictors of subsequent hypoglycemia included: recent discharge ârelative risk of serious hypoglycemia was 4.5 from 1 to 30 days after discharge advanced age black race and use of 5 or more concomitant medications .
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
Whats The Dosage Of Humalog For Children
Humalog is approved for use in children.
But Humalog hasnt been studied in children under the age of 3 years. It also hasnt been studied in children with type 2 diabetes.
The manufacturer of Humalog doesnt provide dosing recommendations for the medication. Humalog dosage will vary for each person. If your childs doctor recommends Humalog, they will help determine the right dose of the drug for your child.
If you have questions about using Humalog for your childs treatment, talk with your doctor.
The dosage of Humalog or Humalog Mix youre prescribed may depend on several factors. These include:
- the type of diabetes you have and its severity
- which form of the medication you use
- your weight
- goals you have for your blood sugar level
- other medical conditions you have
- other medications you take
Key Points About Taking Humalog
In addition to referring to the pamphlet and website mentioned above, here are some key points about taking Humalog:
- If youre using a Humalog KwikPen or Humalog cartridge in a reusable pen, dont share your pen with another person, even if youve changed the needle. And if youre using Humalog vials, dont share needles or insulin syringes with other people. Sharing needles could put you at risk for catching or spreading infections that are carried in the blood.
- If you use more than one type of insulin, always check the label on your insulin before having an injection. Taking the wrong insulin by accident could cause you to have low blood sugar.
- You should inject Humalog just under the skin of your thigh, abdomen , buttock, or upper arm. Dont inject it into a vein or muscle.
- Use a different injection site each time you inject Humalog. This reduces the risk for lipodystrophy .
- Dont inject Humalog into skin thats tender, bruised, scaly, hard, scarred, or damaged.
Read Also: How Does Diabetes Cause Immunosuppression
Why It Is Important To Do This Review
Sliding scale insulin is one of the most frequently used therapies in the metabolic control of diabetic inpatients. However, this strategy may be associated with poor glycaemic control causing more complications . Several nonsystematic review articles have addressed the SSI scheme . Given the potential public health relevance, we have systematically collected and examined all randomised controlled trials on SSI treatments for noncritical diabetic hospitalised people in order to establish the risk and benefits of this therapy.
What Are The Typical Dosages Of Humalog
Your doctor will likely start you on a low dosage. Then theyll adjust your dosage over time to reach the right amount for you. Your doctor will ultimately prescribe the smallest dosage that provides the desired effect. There is no maximum dose for Humalog.
The information below describes dosages that are commonly used or recommended. But be sure to take the dosage your doctor prescribes for you.Your doctor will determine the best dosage to fit your needs.
Dosage for type 1 diabetes
The manufacturer of Humalog doesnt provide dosing recommendations for Humalog medications. The dose your doctor prescribes can depend on several factors, such as your weight, how well your diabetes is managed, and other conditions you may have.
With type 1 diabetes, youll typically calculate a total insulin dose for each day. Then youll take half of your insulin as long-acting insulin and the other half as rapid-acting insulin.
To find the best Humalog or Humalog Mix dose for you, your doctor will teach you how to calculate a total daily insulin dose.
Based on recommendations from the American Diabetes Association, the dose for type 1 diabetes is about 0.4 to 1.0 units of insulin per kilogram of body weight.
When you use the medication will depend on which type youre prescribed:
If you have questions about your Humalog or Humalog Mix dose, talk with your doctor.
Dosage for type 2 diabetes
When you use the medication will depend on which type youre prescribed:
Read Also: Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Diet
Monitoring Of Diabetes To Adjust Insulin Therapy
SMBG is crucial to successful and safe insulin therapy. The frequency required should be individualized, but generally should be increased in those with an increased risk of hypoglycemia, particularly with hypoglycemia unawareness. In general, one should test routinely before meals and at bedtime. Occasional tests in the middle of the night are required to rule out nocturnal hypoglycemia. Testing before driving and when working with dangerous machinery is also indicated. Testing at times of anticipated peak insulin action is helpful to learn how to determine the glucose nadir effect of the meal insulin. With hypoglycemia unawareness, patients may be surprised that they are hypoglycemic much more frequently than they suspect. Similarly, CGM may reveal periods of either undertreatment or overtreatment, often overnight, that were not suspected. illustrates basal insulin overtreatment at night, which was masked at times because of persistent hyperglycemia from prior meals.
Detection of overnight hypoglycemia with continuous glucose monitoring.
The area contained within the square in shows 2 nights with marked hypoglycemia. Other nights the tendency to hypoglycemia may be masked by the tendency to prolonged hyperglycemia after the last meal or snack of the day, as depicted in traces from several other nights.
Alternatives To Sliding Scale Insulin
Due to the downsides of sliding scale insulin, you may want to try another insulin therapy regimen. However, talk to your doctor before switching up your insulin as they will know what’s best for you.
- Once- or twice-daily long-acting insulin is ideal for people with type 2 diabetes who have persistently high blood sugar and do not have extreme glucose fluctuations after meals, says Peter. It’s more convenient than SSI since it only requires one or two daily injections.
- Basal-bolus insulin, which entails a combination of both long-acting and short-acting insulin up to four times a day. This is the American Diabetes Association’s preferred blood sugar control method for hospitalized patients as it mimics the body’s natural release of insulin. However, it requires more injections than SSI.
- Insulin pumps are small wearable devices that deliver insulin through a catheter, providing both a continuous stream of insulin or a fast-acting, on-demand dose as needed. This method also mimics the body’s natural release of insulin, but the downside is that the cumbersome pump needs to be worn at all times.
- Once-daily or weekly injectable GLP-1 agonists are non-insulin diabetes medications that work well for those who only experience high blood sugar after meals, says Peter. This option means fewer injections than SSI. Additionally, a 2020 meta-analysis found that these medications are associated with an average weight loss of 3 to 5.5 pounds.
Recommended Reading: How To Test For Diabetes Without Taking Blood