What Does The A1c Test Measure
When sugar enters your bloodstream, it attaches to hemoglobin, a protein in your red blood cells. Everybody has some sugar attached to their hemoglobin, but people with higher blood sugar levels have more. The A1C test measures the percentage of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated hemoglobin.
Ability Of A1c 65% To Detect Of Individuals With Diabetes
A total of 136 of 855 individuals had diabetes. A1C 6.5% identified 32.3% of all individuals with diabetes. FPG 126 mg/dl and 2-h plasma glucose 200 mg/dl detected a larger percentage . The combination of A1C 6.5% and/or FPG 126 mg/dl detected 52.2% of diabetic subjects and the combination of IFG and/or IGT detected 97.1%.
How A1c Measures Blood Sugar
An A1c test is also known as glycated hemoglobin, glycohemoglobin, or HbA1c. It measures the amount of glucose in your blood. More specifically, it checks hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein that transports oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
Glucose binds to hemoglobin, creating glycated hemoglobin compounds. The higher your blood glucose level, the more glucose attaches to the hemoglobin. Hemoglobin cells last about 90 days, so the A1C provides an overall picture of your blood sugar control for the previous three months.
For people without diabetes, A1C tests are recommended every three years in adults over the age of 45 and anyone with a high risk of diabetes. Risk factors include a family history of diabetes, a BMI above 25, high blood pressure, a history of heart disease, and a lack of physical activity.
For people with diabetes, regular A1C monitoring can catch a spike in blood sugar levels early. An increase should prompt your healthcare provider to re-evaluate your treatment plan. This may include a review of your medications, diet, and how often your test your blood sugar.
You May Like: What Does High Blood Sugar Feel Like
What Is The Cost Benefit Of Lowering A1c
Recently the ADA published analysis diabetes costs. They showed total estimated costs of $327 billion with $237 billion on direct costs and $90 billion in indirect costs.5Economic costs of diabetes continues to rise.
Data from numerous studies show that better A1C results in lower total healthcare costs.6 A study using claims data from a large health maintenance organization showed that the group of mainly type 2 patients whose A1C was lowered by 1% experienced lower total health care costs in the range of $685 to $950 less per year compared to people who had no A1C improvement.
Another analysis from a large managed care organization showed that total diabetes-related costs for people whose A1C was greater than 7% was $1,540 per patient during the 1-year follow-up. This was 32% higher than the total diabetes-related costs for people whose A1C was at or below 7%.
You May Like: Similarities Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
How Often Do You Need To Take An A1c Test
If your blood sugar levels have remained stable and your A1C is within your target range, the American Diabetes Association recommends getting the test two times a year. If your therapy has changed or you are not meeting your blood sugar targets, the ADA recommends getting the test four times per year. This simple blood draw can be done in your doctors office.
The A1C test results provide insight into how your treatment plan is working and how it might be modified to better control the condition. Often, your blood sample is sent out to a lab, though some doctors can use a point-of-care A1C test, where a finger stick can be done in the office, with results available in about 10 minutes.
While in-office tests can be used to monitor the disease, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases notes that most point-of-care tests should not be used for diagnosis. That can only be done by lab tests certified by the NGSP, an organization that standardizes A1C test results. Any in-office test results pointing to a change in your health should be confirmed by conventional lab tests.
You May Like: Best Insoles For Diabetic Neuropathy
So What Do The Numbers Mean
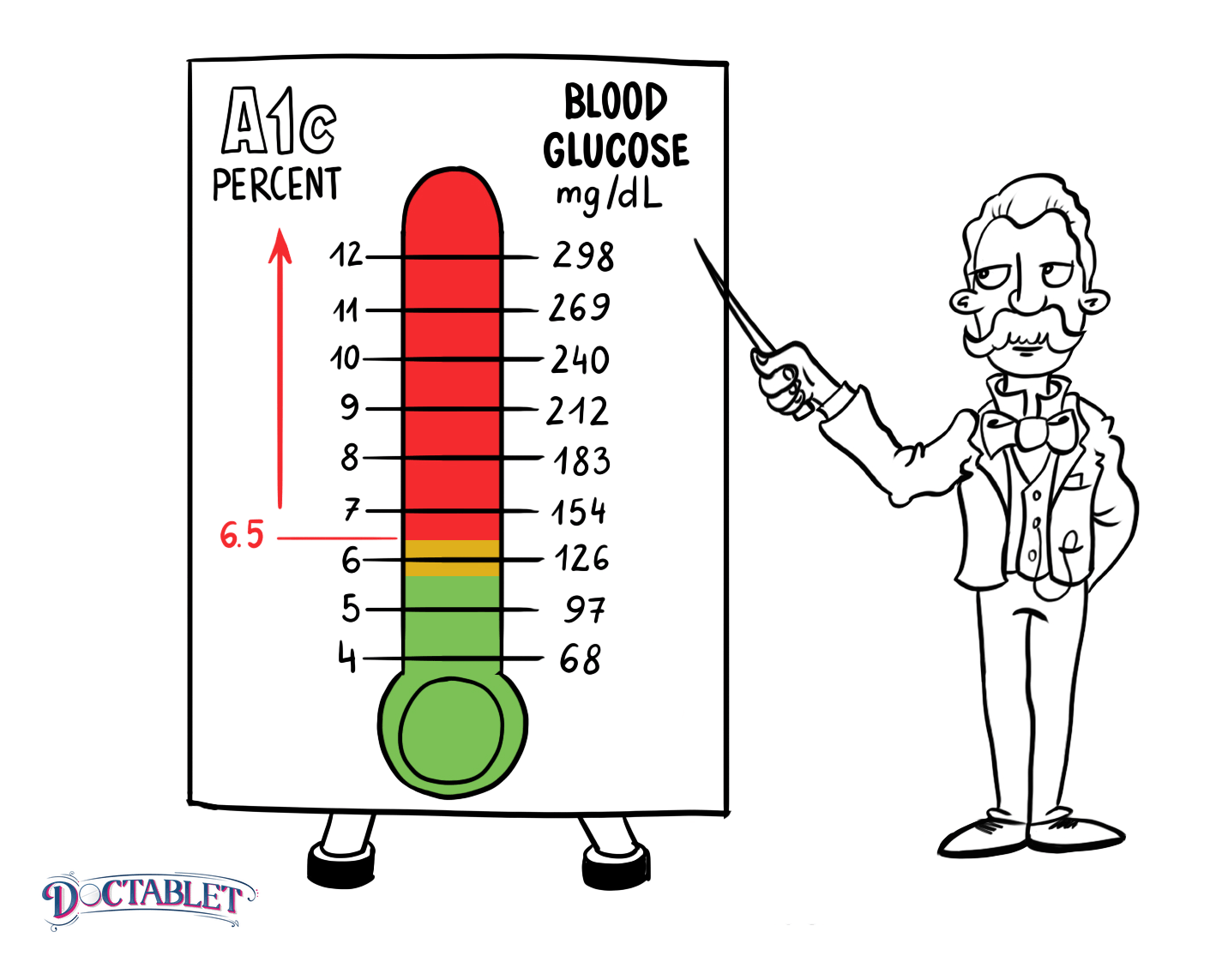
When it comes to the numbers, there’s no one-size-fits-all target. A1C target levels can vary by each person’s age and other factors, and your target may be different from someone else’s. The goal for most adults with diabetes is an A1C that is less than 7%.
A1C test results are reported as a percentage. The higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. The A1C test can also be used for diagnosis, based on the following guidelines:
- If your A1C level is between 5.7 and less than 6.5%, your levels have been in the prediabetes range.
- If you have an A1C level of 6.5% or higher, your levels were in the diabetes range.
What Are The Risks Of Chronic High Blood Glucose Level
Increase your physical activity. You dont have to train to be an Olympic athlete, but you should strive to include a few short walks in your daily routine. Every step is crucial!
- Attempt to reach and maintain a healthy BMI .
- The BMI is the most fundamental indicator, but you should also consider your waist-hip ratio. A large amount of visceral fat has been related to an increased risk of diabetes and heart disease.
- Maintain a healthy, well-balanced diet. If youre overweight, dont go over your daily calorie restriction, and attempt to eat even less. Say goodbye to processed meals and sweets.
- If you follow those recommendations, your hemoglobin A1C levels will almost certainly improve.
- A higher risk of cardiovascular disease, such as myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Theres a chance youll get chronic renal disease or perhaps kidney failure.
- Nerve injury and paresthesia are more likely.
- There is a high risk of retinopathy and vision loss.
- Infections, including as skin infections and mycoses, are common.
- Difficulties with conceiving,
- Diabetic foot, which could cause amputation!
They may diagnose you with diabetes if your A1C result is equal to or higher than 6.5 percent. If this is the case, make an appointment with your doctor away!
Recommended Reading: Best Type 2 Diabetes App
What To Do If Your A1c Is 57
An A1c of 5.7 falls into the prediabetic range between 5.7 and 6.4. People with prediabetes are likely to get type 2 diabetes within 10 years unless they make serious changes to their lifestyle.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Type 2 means that your body still produces insulin but isnt using it properly. Many people can control their blood sugar levels with lifestyle changes while others may need insulin or other medications to manage it.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar by testing at home. Its easier than ever and there are a variety of affordable blood glucose monitors available.
A prediabetes A1c reading is a call to action. At a minimum youll need to make some lifestyle changes. You and your doctor can discuss whether medication is necessary.
Start Measuring Your Blood Glucose Levels With A Dietitian
The best thing to do for your health is to learn more about how your body handles its blood sugar and what causes it to spike. A continuous glucose monitor lets you see how your body responds to foods with varying glycemic index values.
Those with diabetes have been using these safe, effective, FDA-approved devices for years. Now, you can get your own with NutriSense, which offers the same technology for the public for the first time, to use alongside their team of world-class Registered Dietitians. NutriSense CGMs come with an innovative app that lets you track your blood glucose levels.
Don’t Miss: Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines
Random Plasma Glucose Test
A random blood glucose test is a blood test thats performed any time of day that you arent fasting. It measures the sugar level in your blood at that moment in time.
An RPG result thats over 200 mg/dL is indicative of diabetes, especially if youre having symptoms of diabetes such as excessive thirst, hunger, or urination.
If your level is higher, your doctor will use one of the other tests listed to confirm the diagnosis.
Family History Of Type 2 Diabetes
Prediabetes has a hereditary factor. If someone in your immediate family has T2Dor has had T2D in the pastyou are more likely to develop prediabetes and type 2 diabetes yourself.
Your race and ethnicity also affect your likelihood of developing prediabetes. There is a genetic component, but research has shown that racial disparities in who develops diabetes have more to do with socio-economic status and the accessibility of health care and healthy food in your community than your genes.
Recommended Reading: Pre Diabetic Meal Plan Chart
Reasons Your A1c Might Be High When Youre Not Diabetic
Are you worried youâre at risk of diabetes because of high blood sugar levels on your A1C test? Does your blood sugar spike even when youâre eating healthy foods like apples and pears?
While high blood sugar is a common sign of diabetes, itâs not exclusive to those with the health condition. In fact, people often encounter high levels even if they donât have a history of diabetes.
Relation Of Glycemic Measures To Metabolic Variables In Nondiabetic Individuals
FPG was more strongly correlated with A1C than was 2-h plasma glucose in nondiabetic subjects . The correlations of 2-h plasma glucose with Si, systolic blood pressure, and triglycerides were stronger than the corresponding correlations of A1C. FGP had also more robust correlations with fasting insulin, AIR, obesity, and systolic blood pressure than did A1C.
Spearman correlation coefficients for the relationship between glycemic measures as well as with other metabolic variables in nondiabetic participants
| . |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Tooth Removal For Diabetic Patient
How To Lower Your A1c
Now that you have a thorough understanding of A1c and time-in-range, as well as why looking at your A1c in isolation isnt optimal, the obvious question is:
How do you lower your A1c while improving or sustaining your time-in-range?
I will cover the four most important things you can do below but its always recommended that you start by having a conversation with your medical team before making changes to your diabetes management.
Relationship Among Glycemic Measures Si And Air In Nondiabetic Individuals
In linear regression analysis, A1C explained 7.4% of the Si variance and FPG and 2-h plasma glucose accounted for 10.3 and 13.8%, respectively. Si accounted for 11.3% of the AIR variance, but addition of A1C to the model increased the variance explained by 4.2%, addition of FPG by 10.2%, and addition of 2-h plasma glucose by 8.7%.
A multivariate linear regression model was fitted with Si as the dependent variable and age, sex, race/ethnicity, research center, and all three glycemic measures as independent variables. Expressed per 1 SD, regression coefficients demonstrated that A1C , FPG , and 2-h plasma glucose were independently related to Si. Similarly, we fitted a second model with AIR as the dependent variable and demographic variables, Si, and all three glycemic measures as independent variables. A1C , FPG , and 2-h plasma glucose were also independently associated with AIR.
In separate models, there was strong effect modification of race/ethnicity on the relation of each glycemic measure to Si . In African Americans, 2-h plasma glucose was weakly related and A1C and FPG were not related to Si. Sex had an interaction effect on the relationship between A1C and Si and between 2-h plasma glucose and AIR . Obesity had a similar effect on the relation of each plasma glucose measure to AIR .
Recommended Reading: How To Prepare For Gestational Diabetes Test
What Is The A1c Test Measuring
There can be several reasons for a spike in blood sugar levels, and itâs a good idea to know whatâs causing yours. But first, itâs essential to understand what A1C is and what the A1C test measures.
Any sugar that enters your bloodstream attaches itself to your hemoglobin on your red blood cells. The A1C test measures the amount of glucose âstuckâ to the hemoglobin, which provides a good proxy of how much average blood glucose was in your bloodstream over a two to three-month period.
A simple way to remember how to read the results is: the higher the percentage, the higher the risk of diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, under 5.7% is a regular A1C reading. A reading between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered a pre-diabetic range, while values above 6.4% indicate diabetes.
Before you start overanalyzing your results, remember that there are variables at play. For example, the U.S. National Library of Medicine found that adults without a history of diabetes often have A1C levels at 6% or greater. This means not every higher test result is cause for concern. Still, itâs worth checking with a doctor if you see consistently high values. High A1C levels lead to impaired fasting glucose, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
How Quickly Can You Lower Your A1c
Because A1c is simply a measure of your average blood sugar over 2-3 months, it can decrease by any amount over that time period. If you, from one day to the next, decreased your daily average blood sugar from 300 mg/dl to 120 mg/dl , your A1c would decrease from 12% to 6% in around two months.
However, it may not be a good idea to lower your A1c so quickly, as I will explain below.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of A Diabetic Foot
Target Levels In People With Diabetes
A doctor will set a persons target A1C level based on many factors. The right target varies from person to person.
For someone with diabetes, the target A1C level may depend on:
- the persons age
- how long they have had diabetes
- their prescribed treatment plan
- any history of adverse effects from the treatment, including episodes of low blood glucose, or hypoglycemia
- any complications from diabetes
- the persons preferences and treatment priorities
In general, a doctor might recommend aiming for A1C levels under 6.5% if a person:
- is young and has a long life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a short period
- is effectively managing their diabetes with lifestyle changes or metformin alone
- is otherwise in good health
A doctor might recommend A1C targets of 7.08.5% if a person:
- is older and has a shorter life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a longer period
- has diabetes that is hard to manage, even with multiple medications
- has a history of severe hypoglycemia or other adverse effects of treatment
- has experienced complications of diabetes
- has other chronic health conditions
A person should work with their doctor to reassess and adjust their A1C targets over time. The condition and treatment goals may change.
To screen for diabetes, a doctor may order an A1C test for someone older than 45. They may also do this for younger people who have other risk factors.
After diagnosing diabetes, a doctor determines how often to test A1C levels.
Symptoms of high blood glucose levels include:
Clinical Measurements And Procedures
Baseline and follow-up examinations required two visits. During the first visit, a 75-g OGTT was administered to assess glucose tolerance status. During the second visit a week later, insulin sensitivity and first-phase insulin secretion were directly measured by the frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test with two modifications to the original protocol. First, an injection of regular insulin was used to ensure adequate plasma insulin levels for the accurate computation of insulin sensitivity across a broad range of glucose tolerance . Second, the reduced sampling protocol was used because of the large number of subjects. Insulin sensitivity, expressed as the insulin sensitivity index , was calculated using mathematical modeling methods . First-phase insulin secretion, expressed as acute insulin response , was computed as the mean of 2- and 4-min insulin concentrations after glucose administration.
Anthropometric variables were measured by trained personnel. Plasma glucose and serum lipid, lipoprotein, and insulin concentrations were determined as described previously . A1C was measured by an automated microparticle immunoassay using whole blood .
Read Also: Can You Go Blind From Diabetic Retinopathy
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The oral glucose tolerance test takes a little more time than the other two glucose tests for diabetes. In this test, your blood is taken after an overnight fast, and then again two hours after you drink a sugary drink.
Its normal for blood sugar to rise after the drink. Normal blood sugar falls to below 140 mg/dL within two hours, however.
If your blood sugar is between 140 and 199 mg/dL, your doctor will diagnose prediabetes. Anything 200 mg/dL or above is diagnostic for type 2 diabetes.
| Type of results |
You should have healthy fats each day as well.
Using the information from your food log, you can begin to make small changes. The goal is to choose less processed, whole foods, instead of highly processed foods that contain added sugar, little fiber, and unhealthy fats.
For example, if you arent eating the recommended servings of vegetables, try adding one serving of vegetables a day to your diet.
You can do this by having a salad with lunch or dinner, or snacking on carrot sticks. Just be careful about add-ons such as salad dressing or dips. They can sneak in unhealthy fats or extra calories. Check out these 10 healthy salad dressing recipes.
Youll also want to work on reducing the number of empty-calorie foods and beverages youre consuming, as well as switching out simple carbohydrate foods for complex carbohydrates. Examples of substitutions you can try to include: