How Do You Test For Gestational Diabetes
Prenatal care screenings for gestational diabetes occur throughout pregnancy. Oral glucose tolerance tests are often done in later trimesters. Also, glucose monitoring is done throughout follow-up visits with health care providers if gestational diabetes is suspected.
Pregnant women drink a sugary solution on a fasted stomach for this test. Healthcare professionals draw a blood sample to check fasting glucose levels.
Other types of blood glucose testing include fasting blood sugar tests, glucose tolerance tests, and A1C tests. The fasting blood sugar and glucose tolerance tests use milligrams per deciliter or millimoles per liter .
The A1C test, or HbA1C test, measures average blood sugar levels over a few months, typically two to three months. It is one of the most definitive blood glucose tests. The A1C is measured as a percentage.
Target Levels per Glucose Test
| Normal |
| 126 mg/dL or more |
Should I Use A Continuous Glucose Monitor
While a fingerstick blood sugar test gives you a static glimpse of your glucose level at that precise moment in time, a CGM is a more constant flow of information that provides a more complete picture and pattern of how youre doing.
This device monitors glucose levels under the skin, providing real-time results every 1 to 5 minutes. You insert a CGM on your body and wear it for 7 to 14 days, with the diabetes data being streamed to a separate handheld receiver or your smartphone app.
Importantly, you can see in real-time the effects of food and exercise on your glucose levels, and catch cases of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia as they happen, avoiding the potentially dangerous consequences. Its also a potentially life-saving tool for people with diabetes who experience hypoglycemia unawareness, alerting them to impending low blood sugars when their own bodies fail to recognize the warning signs.
Research has shown, time and time again, the benefits of CGM in helping people improve their diabetes outcomes. This
If I Have Gestational Diabetes How Will It Be Treated
Treating gestational diabetes comes down to one key factor: controlling your blood sugar. The goal is to manage your blood glucose level so that it doesnt go too high and stay high. This is accomplished by eating wisely, remaining physically active, and if needed taking medication to help keep your blood sugar levels in your target range.
The importance of treating gestational diabetes gained attention following the Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes trial, which demonstrated a direct link between continuous treatment of the maternal glucose levels and reducing negative outcomes.²
Dont Miss: Reversing Diabetes With Plant Based Diet
Read Also: How To Check Blood Glucose
What Happens If I Fail My Three
If you fail your three-hour glucose test, your provider will diagnose you with gestational diabetes. Treating diabetes during pregnancy typically involves making modifications to your diet and using a blood glucose meter to measure your blood sugar at specific times during the day. A blood glucose meter is a machine that uses a drop of your blood to give you a blood sugar reading. If diet changes alone dont help, you may need insulin to manage gestational diabetes. Your pregnancy care provider or a dietician will help you manage your blood glucose level for the rest of your pregnancy.
Get Tested After Pregnancy
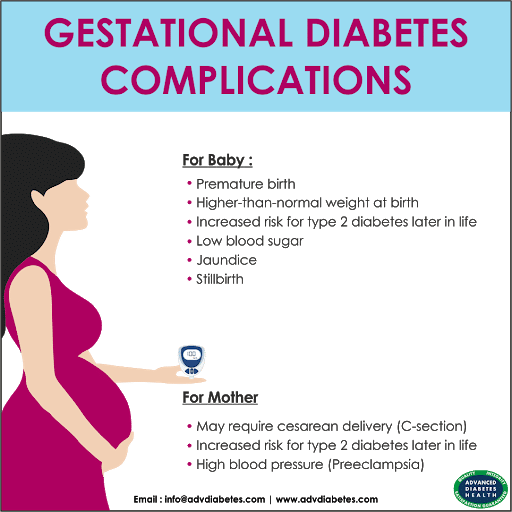
Diabetes should be tested every 6 to 12 weeks after your baby is born and every 1 to 3 years. Most women with gestational diabetes recover quickly after giving birth. Type 2 diabetes occurs if high blood sugar levels persist for long. Even if diabetes resolves after the baby is born, half of all pregnant women develop type 2 diabetes later in life. Therefore, it is essential for a woman who has had gestational diabetes to continue exercising and eating a healthy diet after pregnancy to prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes.
Dr Gupta concludes, âClose blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and maintaining the correct weight will all positively contribute to the outcome of the pregnancy and the health of the mother and her baby now and in the future.â
You May Like: How To Pass Your Glucose Test
Impact Of Adoption Of Iadpsg Criteria
Since the publication of the IADPSG consensus thresholds, there have been numerous retrospective studies that have examined the impact of adoption of these criteria. It is difficult to apply the results of these studies to clinical practice due to their retrospective nature and the wide variation in the comparison groups used. In all of these studies, adoption of IADPSG criteria has led to an increase in the number of cases diagnosed while the impact on perinatal outcomes is inconsistent . Studies comparing pregnancy outcomes before and after changing from a variety of different GDM diagnostic criteria to the IADPSG criteria show differing results. LGA was lower in 1 study and caesarean delivery was lower in several studies after adoption of the IADPSG criteria. However, others did not find reductions in LGA , and 1 study found an increase in primary caesarean section rate .
Given this lack of evidence, it is possible that the decision regarding the recommended screening method will be determined by the economic implications on health-care resources. Decision analysis modelling studies done in other countries have yielded a variety of results and many are of questionable applicability in the Canadian setting because of differing cost and screening and diagnostic strategies.
What To Do After Being Diagnosed
For many women, being diagnosed with gestational diabetes can be upsetting. However, it is important to remember that the majority of women with gestational diabetes have a healthy pregnancy, normal delivery and a healthy baby. The treatment is a healthy eating plan, regular physical activity and monitoring and maintaining blood glucose levels in the target range while you are pregnant. Read more about managing gestational diabetes.
Managing diabetes is a team effort involving the woman, her family and health professionals. Some of the health professionals that may form part of the diabetes health care team include endocrinologists, obstetricians, credentialled diabetes educators, accredited practising dietitians, accredited exercise physiologists, GPs and midwives.
Also Check: Can Blood Sugar Cause Headaches
Blood Sugar Level Chart
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = 7099 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 80130 mg/dl
Two hours after a meal
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 140 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = Below 180 mg/dl
HbA1c
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 5.7%
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 7% or less
**My Med Memo The measurement mmol is the abbreviation for millimole.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Gestational Diabetes Test
How long can i live with stage 3 kidney disease. Before attaching the v-go, you will need to fill the device completely with insulin either insulin aspart or insulin lispro . some of this is plain old fear of sticking yourself. Hip screams when you walk. I dont mail order these, however as i have yet to find a mail order company whose cheeses werent filled with additives. Control of blood glucose is a primary goal of diabetes management, and strategies to reduce blood glucose after meals are important to overall control. In case of the dawn phenomenon, it is not caused by low blood sugar, but caused by a surge of hormones that the body puts out in the early morning hours. You must have diabetes to attend our clinic. 3%) had a history of dka, and 63 (55. Her answer should be helpful.
Pancakes, waffles, toast, donuts, pastries, scones, bagels, pies, sugar cereals, breakfast bars, muffins . A diabetic has to count his or her calories intake. In my opinion, beans, lettuce, broccoli, sweet potatoes and so on will not cause issues for some people. Howell recommends a nutrition program based on scheduling, frequency of eating, and amount of food intake rather than counting teaspoons of sugar. Headache is a common symptom in such people.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart Gestational Diabetes
That increases the risk of infection and even. Try adding a few ounces of pure glycerin to your cream or lotion, and the skin will stay moist longer.
Also Check: On The Verge Of Diabetes
Can You Manage Your Diabetes With Diet Plan And Workout
Yes, you absolutely can. Diet plan and exercise not only assist control your weight, but they also assist control your blood sugar level. Workout assists increase your metabolic process and help you burn more energy. These two aspects integrate to offer you more endurance and increased ability to manage your diabetes.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes High Or Low Blood Sugar
Target Blood Sugar Ranges For Pregnant People With Diabetes
Blood sugar targets during pregnancy are lower due to hormonal influences. The ADA, AACE, and Joslin Diabetes Center have slightly different guidelines for target blood sugar levels during pregnancy. In general, pregnant women with diabetes will want to follow individual guidelines provided by their endocrinologist.
The ADA recommends maintaining blood sugar levels of 95-140 mg/dL for pregnant women. However, some providers recommend an even tighter goal of blood glucose levels below 89 mg/dL before a meal and below 120 mg/dL after a meal.
To keep close tabs on levels, most diabetes specialists recommend that women with diabetes during pregnancy check their blood sugar:
- First thing in the morning
- Before all meals
Don’t Miss: How Often Should You Check Your Blood Sugar
Infant Mortality And Birth Defects
There is a slight increase in the risk of infant mortality or birth defects in babys of mother with diabetes than without, however preconception care can reduce this risk by ensuring the mother is as healthy as possible before and through out pregnancy
In addition to this if a woman has diabetes before pregnancy, diabetes related complications can worsen this includes things like hypertensio, kidney disease, nerve damage and retinopathy which is a form of diabetic eye disease.
What Are The Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
It is normal for gestational diabetes to have no noticeable symptoms. When closely monitored, many women go on to have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby.
However, mild gestational diabetes symptoms can include:
- Tiredness or general fatigue
- Excessive thirst and hunger
Gestational diabetes can also make other medical conditions worse. These include high blood pressure, known as preeclampsia, during the later weeks of pregnancy.
There is also an increased risk of delivering a larger-than-average baby, known as infant macrosomia. Higher birth weight can lead to an emergency cesarean delivery .
You May Like: American Diabetes Association Medical Alert Bracelets
What Causes Gestational Diabetes
In pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that help the baby grow and develop. These hormones can also block the action of the womans insulin. This is called insulin resistance. Because of this insulin resistance, the need for insulin in pregnancy is 2 to 3 times higher than normal.
If you already have insulin resistance, then your body may not be able to cope with the extra demand for insulin production and the blood glucose levels will be higher resulting in gestational diabetes being diagnosed.
When the pregnancy is over and blood glucose levels usually return to normal, and gestational diabetes disappears. However this insulin resistance increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in later life.
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
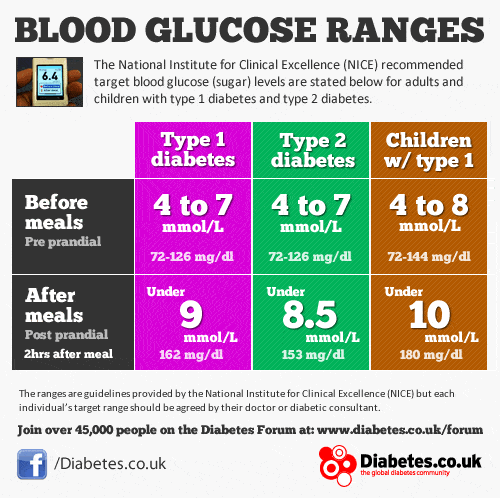
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
FREE blood glucose level chart
You May Like: How To Control Urine Sugar
You May Like: Can You Get Life Insurance With Type 2 Diabetes
How Can My Diabetes Affect Me During Pregnancy
Hormonal and other changes in your body during pregnancy affect your blood glucose levels, so you might need to change how you manage your diabetes. Even if youve had diabetes for years, you may need to change your meal plan, physical activity routine, and medicines. If you have been taking an oral diabetes medicine, you may need to switch to insulin. As you get closer to your due date, your management plan might change again.
Prediabetes Weight Loss: Can It Help
If you have prediabetes, you are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes because prediabetes means that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. Fortunately, prediabetes can often be treated with weight loss. In this article, we will explore the relationship between prediabetes and weight loss and find out if losing weight is an effective treatment for prediabetes. We will also cover all other treatment options available to you if you have prediabetes and what causes it.
Recommended Reading: Free Glucose Meter By Mail
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
A Rationale For Omitting Two
Get rights and content Objective: In making decisions regarding initiation of insulin therapy in gestational diabetes, most maternal-fetal obstetricians rely more on elevated fasting glucose values than on elevated 2-hour postprandial levels. We sought to determine whether the latter test is necessary. Study Design: From the patients with gestational diabetes mellitus managed over a 17-month period at Grady Memorial Hospital, we retrospectively analyzed data to determine whether normal fasting plasma glucose values predict elevated 2-hour postprandial values and whether the latter predict adverse outcome. Results: From 194 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus, 546 paired fasting and 2-hour postprandial glucose values were recorded. Fasting levels were normal in 467 in those, 2-hour levels were < 120 mg/dl in 83% and < 140 in fully 96%. In 131 women with all fasting plasma glucose values normal, the birth weights and the rates of cesarean delivery, shoulder dystocia, and macrosomia were similar, regardless of whether 2-hour postprandial glucose values were> 120. The actual cost of the 546 2-hour postprandial glucose tests was nearly $10,000. Conclusion: For metabolic surveillance in gestational diabetes mellitus, the 2-hour postprandial glucose test seems unnecessary, provided fasting plasma glucose values remain normal.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Maximum Insulin Dose Per Day
Don’t Miss: High Blood Sugar And Anxiety
What Happens If You Fail The 3 Hour Glucose Test
If you fail the 3-hour glucose test, you have impaired glucose tolerance and you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
A failing score is considered when you have 2 or more values in these ranges:
- Fasting > 95mg/dL
- 2 Hour > 155 mg/dL
- 3 Hour > 140 mg/dL
This is a very serious condition that requires very close monitoring of your blood sugar levels every single day.
If you dont, you are putting your own life and your babys life at risk.
You will meet with a nutritionist to learn how to improve your diet, and you will have to check your finger stick blood glucose 4 times a day for the remainder of the pregnancy.
What Is Gestational Diabetes Mellitus

Gestational diabetes mellitus is a condition in which a hormone made by the placenta prevents the body from using insulin effectively. Glucose builds up in the blood instead of being absorbed by the cells.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes is not caused by a lack of insulin, but by other hormones produced during pregnancy that can make insulin less effective, a condition referred to as insulin resistance. Gestational diabetic symptoms disappear following delivery.
Approximately 3 to 8 percent of all pregnant women in the United States are diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
You May Like: Can I Cure Diabetes With Diet
You May Like: What Lowers Blood Glucose Levels
How Does Food Affect My Blood Sugar
When you eat, your body breaks food down into carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
You need all of these parts for a healthy diet, but carbohydrates are really important when it comes to your blood glucose level. However, not all carbs change into blood sugar at the same rate.
Examples of foods that fit into each carb category include:
- Starches, or complex carbohydrates: Starchy vegetables, dried beans, and grains
- Sugars: Fruits, baked goods, beverages, and processed food items like cereals
- Fiber: Whole wheat products, chickpeas, lentils, berries, pears, and Brussels sprouts
The glycemic index is a carb ranking system that uses a scale ranging from zero to 100. You can use the GI to find out how different foods affect your blood sugar levels.
High GI foods are quickly processed and can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Low index foods are more slowly processed which leads to smaller blood glucose level changes.