Temporal Trends In Mortality
Analyses conducted for Diabetes in America, 3rd edition, based on U.S. death certificates with diabetes listed as the underlying cause of death yielded diabetes-specific death rates . Between 1950 and 2009, there has been a marked downward trend in type 1 diabetes mortality, which appears to have leveled off during the 1990s. This trend likely reflects improvements in type 1 diabetes care, as incidence of type 1 diabetes is increasing in the United States . A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analysis of diabetes-related mortality prior to age 20 years showed a decrease of 61% . Children age < 10 years with type 1 diabetes showed a more significant decline in mortality than those age 1019 years .
In the Pittsburgh EDC study, at 25 years duration of type 1 diabetes, cumulative mortality declined by 80% from 35% for those diagnosed in the 1950s to 7% for those diagnosed in the early 1970s .
Improvements in Life Expectancy
As discussed, life expectancy for type 1 diabetes improved dramatically after the discovery of insulin as an effective therapy in the 1920s. Both the Joslin Clinic and the Steno Clinic showed type 1 diabetes life expectancy to increase by 15 years between 1933 and 1972 .
What Other Risks Did The National Diabetes Audit Find
The study found that the risk of death for a person with type 1 diabetes is 2.6 times higher than that of the general population. For people with type 2 diabetes it is 1.6 times higher.
In younger people, the difference in mortality rates is even bigger. For example, women between 15 and 34 years of age who have type 1 diabetes are nine times more likely to die than women in the general population, and women of this age with type 2 diabetes are six times more likely to die.
The report also found a strong link between deprivation and increased rates of early death. Among under-65s with diabetes, death rates among people from the most deprived backgrounds were double that of those from the least deprived. Death rates also vary according to where people live London has the lowest mortality rates from both type 1 and 2 diabetes, while the highest mortality rates were in the north east of England.
The studys lead clinician Dr Bob Young, consultant diabetologist and clinical lead for the National Diabetes Information Service, said, For the first time we have a reliable measure of the huge impact of diabetes on early death. Many of these early deaths can be prevented. The rate of new diabetes is increasing every year. So, if there are no changes, the impact of diabetes on national mortality will increase. Doctors, nurses and the NHS working in partnership with people who have diabetes should be able to improve these grim statistics.
How Many Canadians Are Newly Diagnosed With Diabetes Each Year
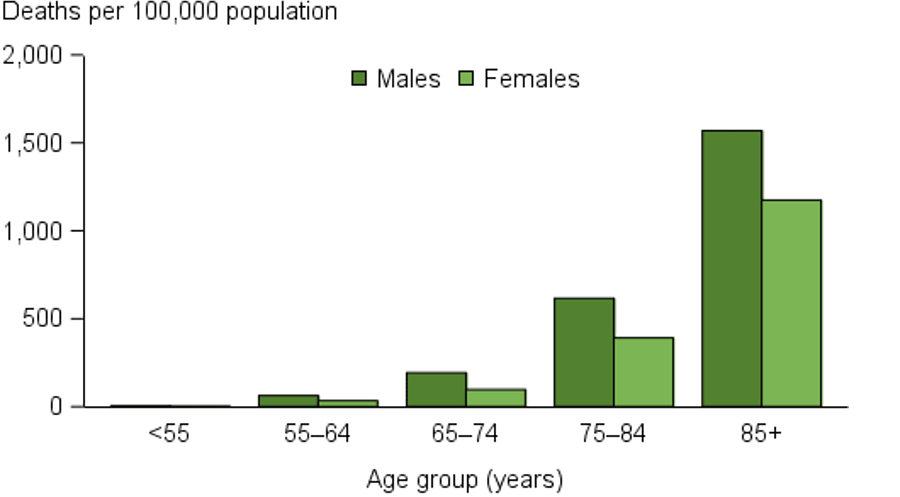
In 20132014, close to 200,000 Canadians were newly diagnosed with diabetes . This represented 0.4 new cases per 1,000 population among children and youth and 7.6 new cases per 1,000 population among adults. Following a pattern similar to the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes, incidence generally increases with age and is higher among males than among females , both overall and in most age groups .
Figure 2: Incidence of diagnosed diabetes , by age group and sex, Canada, 20132014
| Age group | |
|---|---|
| 6.5 | 5.3 |
Note: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
Also Check: Men’s Insulin Pump Underwear
Causes Of Death In Type 1 Diabetes
Limitations of Death Certificates
Epidemiologic studies have long relied on death certificates to obtain mortality data, specifically data relating to the cause of death. A notable Swedish study in 1976 used registry data to validate the cause of death listed on 1,156 death certificates and found that the death certificates were valid for most forms of cancer, stroke, and respiratory disease but not for diabetes . In the United States, misclassification, as well as substantial underreporting of mortality from diabetes, is also prevalent .
Only one study from Germany has specifically examined the reliability of the cause of death on death certificates in individuals with type 1 diabetes . A mortality review committee found that only 25% of hypoglycemic deaths were listed as such on the death certificate, and similarly, only 57% of deaths from diabetic ketoacidosis actually listed DKA on the death certificate . The committee only agreed with death certificates when the cause of death was not diabetes-related . The discrepancies result both from significant overlap between complications in type 1 diabetes and from the lack of formal training for physicians on death certificate completion. Thus, death certificates alone are not reliable when determining the true clinical outcome of deceased type 1 diabetes patients.
DERI Mortality Classification
Complication-Specific Findings
More People Than Ever Have Diabetes More People Than Ever Are At Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes If Nothing Changes We Predict That 55 Million People Will Have Diabetes In The Uk By 2030
Around 90% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. Around 8% of people with diabetes have type 1 diabetes. About 2% of people with diabetes have rarer types of diabetes.
Were fighting for a world where diabetes can do no harm.
We do it by campaigning to make sure everyone with diabetes gets the care they need to live well with diabetes. We provide advice and support so people can get to grips with their condition. And our research increases what we know about diabetes, discovers new treatments and will, one day, find a cure.
Don’t Miss: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
Diabetic Burden And Risk Factors
The calculations for the attributable burden of a given risk-outcome pair was explained in GBD 2017, attributable DALYs or mortality were estimated as total DALYs or mortality for the outcome multiplied by the population attributable fraction . The PAF represents the proportion that the outcome would be reduced in a given population and time if there was exposure to the counterfactual level of the theoretical minimum risk exposure level. 13 risks factors were obtained including metabolic , environmental and occupational , behavioral , dietary , alcohol use, low physical activity). As there were interactions between risk factors, all risk factors associated with DALYs may not be equal to the sum of each one.
Chapter 3 The Health System And Economic Impact Of Diabetes
- In 2008/09, adults aged 20 to 49 years with diabetes saw a family physician twice as often as those without diabetes, and specialists two to three times more often.
- Individuals with diabetes were three times more likely to have been hospitalized at least once during the year than those without diabetes, and had a longer hospital stay.
- Annual per capita health care costs have been estimated to be three to four times greater in a population with diabetes compared to a population without the disease.
- The most recent cost estimates available for this report are outdated by 11 years, which is a major information gap. Therefore, it is difficult to assess the real economic burden of diabetes. However, it is expected that costs will only continue to rise with the increasing prevalence of diabetes and its associated health care costs.
Also Check: How Many Carbs Should A Pre Diabetic Eat Per Day
Us Diabetes Death Statistics
Diabetesis caused by an inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively within the body. Insulin allows blood sugar to enter cells where it can be used for energy. When the body lacks insulin or is unable to effectively use it, blood sugar rises and can have serious health consequences. High blood sugar can lead to heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, and other complications.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, and accounts for about 5 to 10 percent of all diabetes cases. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin throughout their lives to survive. Type 2 diabetes, also called adult-onset diabetes, accounts for roughly 90 to 95% of all cases. Unlike with type 1, there are a variety of measures that can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. They include such lifestyle changes as exercising and maintaining a healthy diet.
Tracking mortality data for diabetes comes with caveats. The statistics shown here”Diabetes as Contributing Cause of Death”are based on the CDC’s Multiple Cause of Death data, where diabetes was present in the deceased but not necessarily listed as the underlying cause of death . Because diabetes increases the risk of other deadly maladiesfor example, cardiovascular diseaseusing MCD statistics can help give a fuller picture of the disease’s impact.
Box : What’s In The Data
The data used in this publication are from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System , a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in health insurance registries.
While CCDSS data reflect the health status of the Canadian population, they may also reflect changes in data collection methods, coding and classification systems, or clinical guidelines and billing practices. These factors must also be taken into consideration when interpreting time trends.
Definition of diagnosed diabetes in the CCDSSCanadians aged 1 year and older are identified as having diagnosed diabetes if they have: at least one hospitalization record or at least two physician claims in a two-year period with an International Classification of Diseases code for diabetes. Females aged 10 to 54 years diagnosed with diabetes 120 days preceding or 180 days following a pregnancy-related visit are removed, to exclude possible cases of gestational diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Boost Or Glucerna For Diabetics
Cdc: Heart Disease Diabetes Deaths Rose In 2020
As COVID-19 spread through the U.S. in 2020, the death rates for heart disease and diabetes saw significant increases, according to data from the CDC’s Mortality Dashboard.
In 2019, the death rate for heart disease was 161.5 deaths per 100,000 population. That rose to 167 in 2020 about a 3.4 percent rise.
The death rate for diabetes jumped nearly 14 percent between 2019 and 2020. In 2019, the diabetes death rate was 21.6 per 100,000 population, rising to 24.6 in 2020.
While the CDC did not provide information on the reasons behind the increases, many studies over the last year have focused on pandemic-related delays in care. A November study published in JAMACardiology, for example, found the survival rate for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest dropped 17 percent during the first few months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A separate study, published May 26 in Health Affairs, found that as emergency calls for heart issues fell by 27.2 percent in the Boston area, out-of-hospital cardiac arrests jumped nearly 36 percent, compared to historical baselines.
To access the CDC’s Mortality Dashboard, which includes data on 16 causes of death,
Type 1 Diabetes Hypoglycemia Deaths Per Year
This JDRF ad sparked controversy but reveals a fact that needs to be known. 1 in 20 Type 1 Diabetics will die from hypoglycemia.
Several times a year I hear of severe hypoglycemia taking the life of another Type 1 diabetic. Most of us are familiar with Dead in Bed syndrome, which is the term used to refer to severely low blood sugars taking the lives of children as they sleep. Since these deaths almost always can be prevented with proper management of the disease, I set out to discover just how many Type 1s were losing every year, in particular due directly to severe hypoglycemia. Sure, a far greater number of diabetics are passing away indirectly from complications brought on by years of mismanaged blood sugars, but given that Ive landed in the ER twice since being diagnosed in 2004, Ive grown curious as to how many Type 1s are dying directly from severely low blood sugars.
Finding an answer to this question proved to be far more difficult than I had imagined. In fact, according to the Medtronic website and various other sources online, there is no official mortality rate for how many people die each year from hypoglycemia. This is unfortunate news. However, it is not due to mere ignorance. The problem is that after death the body can still release glucose, thereby making it difficult to determine if the deceased had suffered a hypoglycemic incident at the time of death.
Recommended Reading: Gluten And Diabetes Type 2
Exclusive: Us Diabetes Deaths Top 100000 For Second Straight Year
Insulin supplies are pictured in the Manhattan borough of New York City, New York, U.S., January 18, 2019. REUTERS/Carlo Allegri
Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
The new figures come as an expert panel urges Congress to overhaul diabetes care and prevention, including recommendations to move beyond a reliance on medical interventions alone. A report released earlier this month calls for far broader policy changes to stem the diabetes epidemic, such as promoting consumption of healthier foods, ensuring paid maternal leave from the workplace, levying taxes on sugary drinks and expanding access to affordable housing, among other areas.
In 2019, diabetes was the seventh-leading cause of death in America and claimed more than 87,000 lives, reflecting a long-running failure to address the illness and leaving many more vulnerable when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, creating new hurdles to accessing care.
Register now for FREE unlimited access to Reuters.com
“The large number of diabetes deaths for a second year in a row is certainly a cause for alarm,” said Dr. Paul Hsu, an epidemiologist at UCLA’s Fielding School of Public Health. “Type 2 diabetes itself is relatively preventable, so it’s even more tragic that so many deaths are occurring.”
U.S. Senator Patty Murray, a Democrat from Washington who chairs the Senate health committee, helped create the commission in 2017 and said she is studying the recommendations closely.
MORE CASES, WORSE PROGNOSIS
United States Compared To Other Countries
Prior to the 1970s, few studies differentiated participants as having type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and fewer still used standardized methodologies to compare type 1 diabetes both nationally and internationally. A study from Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1971, was the first real attempt to standardize type 1 diabetes cohorts and compare cumulative mortality at different clinics. At 25 years diabetes duration, cumulative mortality in Cincinnati was 20%, compared to 19% in Boston and 22% in Stockholm, Sweden .
-
CONVERSIONS
Recommended Reading: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
How Many Canadians Live With Diabetes
According to the most recent data , about 3.0 million Canadians were living with diagnosed diabetes in 20132014, representing 1 in 300 children and youth , and 1 in 10 adults . The prevalence of diagnosed diabetes generally increases with age and is higher among males than among females , both overall and in most age groups .
Figure 1: Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes , by age group and sex, Canada, 20132014
| 8.7 | 7.6 |
Note: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
Global And National Socioeconomic Status
Gross national income , a measure of the total domestic and foreign output, was calculated using the World Bank Atlas method. Countries were divided into 4 categories according to GNI in 2017. Low income $995 Lower-Middle income $996 to $3,895 Upper-Middle income $3,896 to $12,055 High income $12,056. Socio-demographic Index , an indicator of a locations socio-demographic development, was calculated on average income per person, educational attainment, and total fertility rate. The SDI ranges from 0 to 1, with a higher value implying a higher level of socioeconomic development. 2017 National SDI data were obtained from the Global Health Data Exchange: high SDI , high-middle SDI , middle SDI , low-middle SDI , and low SDI .
Also Check: Long Acting Insulin Side Effects
Highlights From The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects Canadians of all ages. If left uncontrolled, diabetes results in consistently high blood sugar levels , which can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, vision loss, kidney failure, nerve damage, and amputation. Fortunately, it is possible to remain healthy with diabetes through appropriate management and care.
The Public Health Agency of Canada , in collaboration with all provinces and territories, conducts national surveillance of diabetes to support the planning and evaluation of related policies and programs. This fact sheet presents an overview of diagnosed diabetes data from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System .
What Was The Reports Main Finding
Researchers estimated that in total there were about 16,000 more deaths among people with diabetes than would been expected if their mortality risk was the same as the general population. By linking these results to records of national death certificates they estimated 24,000 excess deaths each year in people with diabetes.
The risk of death for patients with type 1 diabetes was estimated to be 2.6 times higher than that of the general population, and for people with type 2 diabetes the risk was estimated to be 1.6 times higher. Across the country there were variations in mortality, from 1,852 deaths out of 100,000 people with type 1 diabetes in London to a high of 2,351 out of 100,000 in the northeast. For type 2 diabetes the figures ranged from 1,246 out of 100,000 in London to 1,668 out of 100,000 in the northeast.
Recommended Reading: Can You Swim With An Insulin Pump