Personalizing Your Diet Based On Blood Sugar Response
In addition to seeing your healthcare provider, there are steps you can take to reduce your blood sugar levels. If you check your blood sugar after meals and keep track of those measurements, along with the types and amounts of food you ate, you may be able to see which foods are problematic.
Although an increase in blood sugar is usually due to eating high-carb foods, all carbs are not the same when it comes to raising blood sugar. Because starchy foods digest down to glucose very quickly, some starchy foods may end up having a much greater impact on blood sugar than you might expect.
For instance, even though a banana tastes sweeter than a baked potato, the potato may actually have a bigger impact on blood sugar.16
Because high-carb foods have the biggest impact on blood sugar levels, it makes sense to reduce them, no matter what type of diet you follow. The American Diabetes Association made this point in a 2019 paper on nutrition for people with diabetes.17
Sometimes making gradual changes can work best. Our guide, Eating better: six steps down carb mountain, can help you lower your carb intake, one step at a time.
If youve been diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, our guide to the best foods for people with diabetes can help you make choices that may reduce your need for blood sugar control medications.
If a food or beverage seems to be causing your blood sugar to rise too much, try leaving it out of your diet for a few days to see if you notice a difference.
How Is It Treated
If you often have symptoms of hypoglycemia, you should see your healthcare provider. Your provider can help you determine the cause. Your provider will also give you guidelines for treating low blood sugar when you are having symptoms.
When you see your provider, be sure to take your notebook or glucose meter with all of the results of your recent blood sugar checks. This helps your provider know whether you are on the right medicines and are taking the right dose at the right time of day. Without this record, it is harder for your provider to help you figure out the cause of your symptoms.
Here are some examples of guidelines your provider may give you:
- If you have diabetes and you think your blood sugar may be too low, check it with your home meter before treatment, if possible.
- Always carry some form of sugar you can eat as soon as you have any symptoms of hypoglycemia. The following amounts and types of foods will bring your blood sugar level up:
- 2 to 5 glucose tablets
- 1/2 cup fruit juice
- 1/2 cup regular soda
- 6 to 8 ounces of skim milk
- 1/4 to 1/3 cup of raisins
- 5 to 7 pieces of hard candy like Lifesavers
- a tube of glucose in gel form
- 1 tablespoon of molasses, corn syrup, or honey
If A Person Is Unconscious
If a person loses consciousness because of severe hypoglycaemia, they need to be put into the recovery position and given an injection of the hormone glucagon . The injection will raise their blood glucose level.
The injection should be carried out by a friend or family member who knows what they’re doing, or by a trained healthcare professional.
You should dial 999 to request an ambulance if:
- a glucagon injection kit isn’t available
- there’s nobody available who’s trained to give the injection
- the injection is ineffective after 10 minutes
Never try to put food or drink into the mouth of someone who’s unconscious as they could choke.
If you’re able to give a glucagon injection and the person regains consciousness, they should eat some longer-acting carbohydrate food, such as a few biscuits, a cereal bar or a sandwich.
You should continue to monitor the person for signs of recurring symptoms in case they need to be treated again.
Recommended Reading: What Is An Insulin Pump
A Low Blood Sugar Level Without Diabetes
A low blood sugar level is uncommon in people who do not have diabetes.
Possible causes include:
- a gastric bypass
- other medical conditions, such as problems with your hormone levels, pancreas, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands or heart
- some medicines, including quinine
See a GP if you think you keep getting symptoms of a low blood sugar level. They can arrange some simple tests to check if your blood sugar level is low and try to find out what’s causing it.
Diabetes & Ketones: Everything You Need To Know
These days, understanding what ketones are can be confusing, because even mainstream society and non-diabetics are talking about ketones.
What has always been something people with diabetes feared, has now become something that low-carb and ketogenic dieters strive for: ketosis.
In this article, well talk about the crucial differences between diabetic ketones , starvation ketones, and nutritional ketosis. Well also cover what to do if youve developed diabetic ketones and how to manage ketones and diabetes during an illness.
Dont Miss: Diabetic Meals Delivered To Home
Don’t Miss: Healthy Meal Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
Examples Of Easily Digestible Carbohydrates
- 1/2 cup of juice or regular soda
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 4 or 5 saltine crackers
- 3 or 4 pieces of hard candy or glucose tablets
- 1 tablespoon of sugar
Very low blood sugar is a medical emergency. If you or someone else with diabetes is experiencing severe symptoms, such as unconsciousness, its important to administer a medication called glucagon and contact emergency services immediately.
If youre at risk for low blood sugar, its important to talk with your doctor about getting a prescription for glucagon.
You should never give an unconscious person anything by mouth, as it could cause them to choke. If you have diabetes, make sure your family and friends know not to do this if you lose consciousness.
Low blood sugar can occur for a number of reasons. Its usually a side effect of diabetes treatment.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
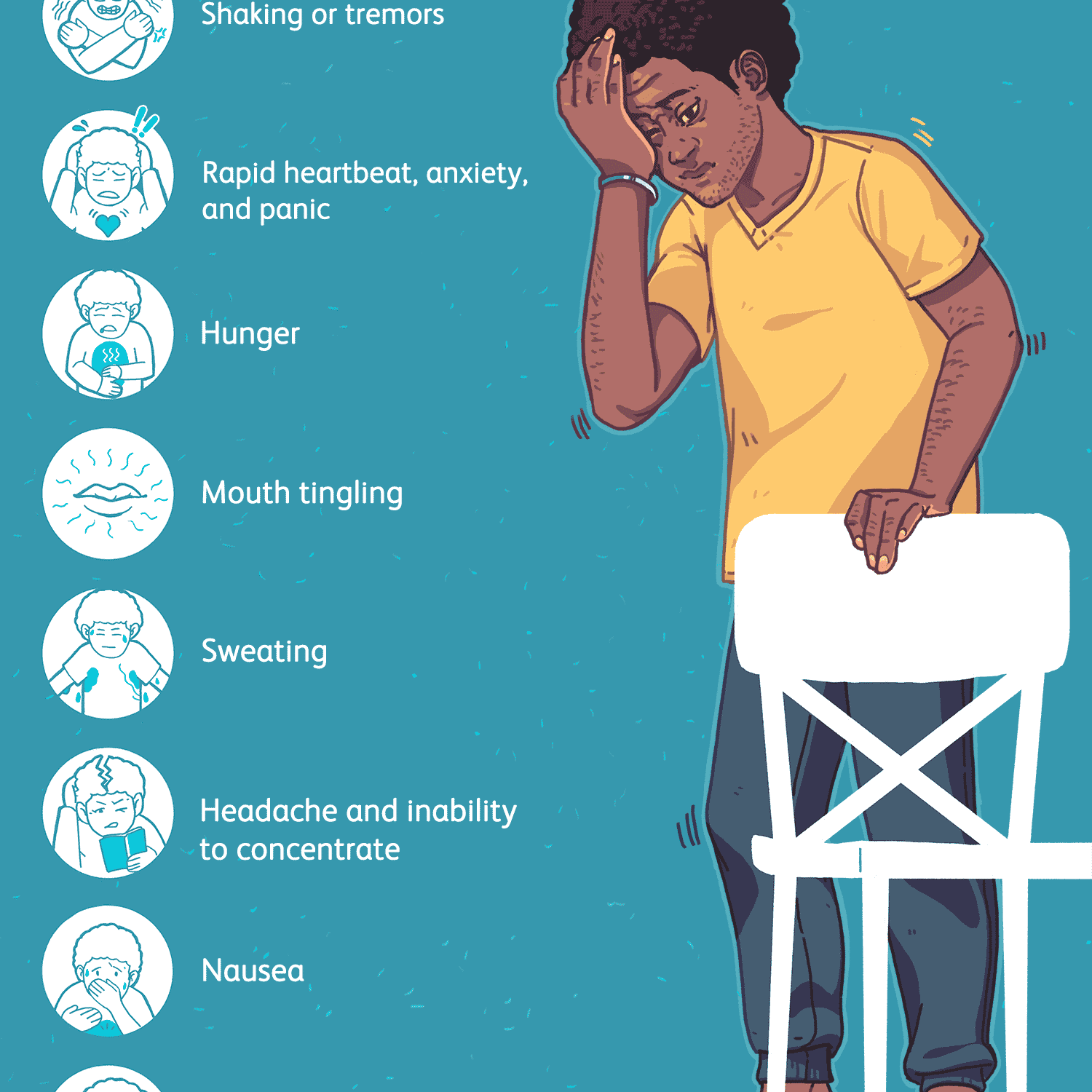
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
Read Also: What Are The Beginning Symptoms Of Diabetes
Overdose Of Diabetes Medication
A common cause of hypoglycaemia is taking too much insulin for your current needs. Insulin is a medication that helps control your blood glucose levels. It’s commonly used to treat type 1 diabetes and is also recommended for some people with type 2 diabetes.
A fall in blood glucose levels can also occur after taking too much oral hypoglycaemia medication, such as sulphonylurea, which causes a release of insulin. This medication is often used to lower blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Why Am I Having Lows
If you are experiencing low blood glucose and youre not sure why, bring a record of blood glucose, insulin, exercise, and food data to a health care provider. Together, you can review all your data to figure out the cause of the lows.
The more information you can give your health care provider, the better they can work with you to understand what’s causing the lows. Your provider may be able to help prevent low blood glucose by adjusting the timing of insulin dosing, exercise, and meals or snacks. Changing insulin doses or the types of food you eat may also do the trick.
Recommended Reading: When Should You Check Your Blood Sugar
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
What If Fasting Sugar Is Normal But Postprandial High
A high 2 hr pp blood sugar combined with a normal fasting blood sugar is a condition called pre-diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. No need to bother with a HbAiC. Look for associated atherothrombotic disease risk factors such as cigarette smoking, dyslipidemia, and hypertension and treat those.
How does fasting affect your blood sugar levels?
Fasting can definitely raise blood glucose. This is due to the effect of insulin falling and the rising counter-regulatory hormones including increased sympathetic tone, noradrenaline, cortisol and growth hormone, in addition to glucagon. These all have the effect of pushing glucose from liver storage into the blood.
Why does my blood sugar go down after eating?
It may be due to a phenomenon called reactive hypoglycemia. This refers to low levels of blood glucose that react to high levels. According to Mayo Clinic, it can occur within 4 hours of eating a meal.
Don’t Miss: How To Use True Metrix Blood Glucose Meter
How Do I Treat Low Blood Glucose
If you begin to feel one or more symptoms of low blood glucose, check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose level is below your target or less than 70 mg/dL, follow these steps
How Do I Detect Spikes In My Sugar Levels

The exact timing of blood sugar spikes can vary from person to person and meal to meal. However, on average, the post-meal peaks tend to be about one hour and 15 minutes after starting a meal.
The best way to measure post-meal patterns is by using a continuous glucose monitor or Flash monitors. These devices can give you a clear view, including graphs, of what happens with the glucose levels after meals without the need for finger pricking . You can ask your diabetes health team if they are available for you as they are not available to everybody.
If you are not using a CGM, then please speak to your healthcare team about the best way to do this for you with finger prick testing.
How do I know it is a spike?
There is no universal answer or specific guidelines on when a sugar level is too high after meals. However, if post-meal readings are consistently above your target range , then you should discuss whether it would be beneficial for you to address these spikes and how to do this, with your healthcare team .
If you are reviewing your post-breakfast sugar levels, you should also be aware of changes in your hormones in the morning, which cause increases in sugar levels . This Digibete video may help.
Some ways to reduce blood sugar spikes after meals
1. Choose low glycaemic index foods
When blood sugar levels are low or hypoglycaemic we need high glycaemic index foods , such as dextrose tablets or juice, that are absorbed quickly to raise our levels and to treat the hypo.
Recommended Reading: Could You Have Diabetes And Not Know It
Blood Sugar Levels Before And After Eating
Blood sugar levels in our bodies will fluctuate depending on various conditions and circumstances. Here are the different levels:
1. Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
According to the American Diabetics Association, normal blood sugar levels after meals should be 70 mg/dl 140mg/dl.This should be the reading 2 hours after a meal. If the levels are lower than 70mg/dl, it might mean that you have hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar is slightly higher than 140mg/dl, it does not necessarily mean that you have diabetes. However, you might need to have an oral glucose tolerance test later on to determine the severity of your elevated post-meal blood sugar.
2. Normal Levels of Fasting Blood Sugar
This blood sugar level is taken first thing when you wake up before your first meal. A normal level of fasting blood sugar lies from 70mg/dl to 92mg/dl. This is also the blood sugar level for a normal person who has not eaten for the past few hours.
3. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 1 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets should lie between the following:
Before eating your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-130mg/dl
After 1 to 2 hours after meals, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: less than 180mg/dl
When going to bed, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-150mg/dl
4. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 2 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets for people with type 2 diabetes:
- Adults: 70-130mg/dl
When To Call The Doctor
If signs of low blood sugar do not improve after you have eaten a snack that contains sugar, have someone drive you to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number. Do not drive when your blood sugar is low.
Get medical help right away for a person with low blood sugar if the person is not alert or cannot be woken up as this is a medical emergency.
Recommended Reading: Freestyle Lite Blood Glucose Test Strips
Blood Sugar Testing At Home
A person can test their blood sugar levels at home.
In most cases, doctors ask people to measure fasting blood sugar immediately upon waking and before they have anything to eat or drink. It may also be appropriate to test blood sugar before eating or 2 hours after a meal, which is when blood sugar returns to normal levels.
The right time to test depends on treatment goals and other factors. For example, most people with diabetes do not need to test between meals unless they are using a diabetes drug that can lower blood sugar. Other people may test between meals if they feel their sugar levels may be low.
Because people with type 1 diabetes do not make enough insulin, they need to test their blood sugar levels several times a day so they can adjust their insulin doses.
A person will test blood sugar levels by:
- preparing the testing strip and glucose monitor to be ready for the blood sample
- using an alcohol swab to clean the testing area, which is usually the side of a fingertip
- lancing the testing area and bracing against a firm surface to help resist the impulse to pull away
- squeezing the testing area around the wound to maximize blood flow
- squeezing a drop of blood onto the test strip
- putting the strip into the monitor
- recording the time, blood sugar reading, and recent food intake in a log
How Can I Prevent Low Blood Glucose
Your best bet is to practice good diabetes management and learn to detect hypoglycemia so you can treat it earlybefore it gets worse.
Monitoring blood glucose, with either a meter or a CGM, is the tried and true method for preventing hypoglycemia. Studies consistently show that the more a person checks blood glucose, the lower his or her risk of hypoglycemia. This is because you can see when blood glucose levels are dropping and can treat it before it gets too low.
If you can, check often!
- Check before and after meals.
- Check before and after exercise .
- Check before bed.
- After intense exercise, also check in the middle of the night.
- Check more if things around you change such as, a new insulin routine, a different work schedule, an increase in physical activity, or travel across time zones.
Don’t Miss: What To Eat If You Have High Cholesterol And Diabetes