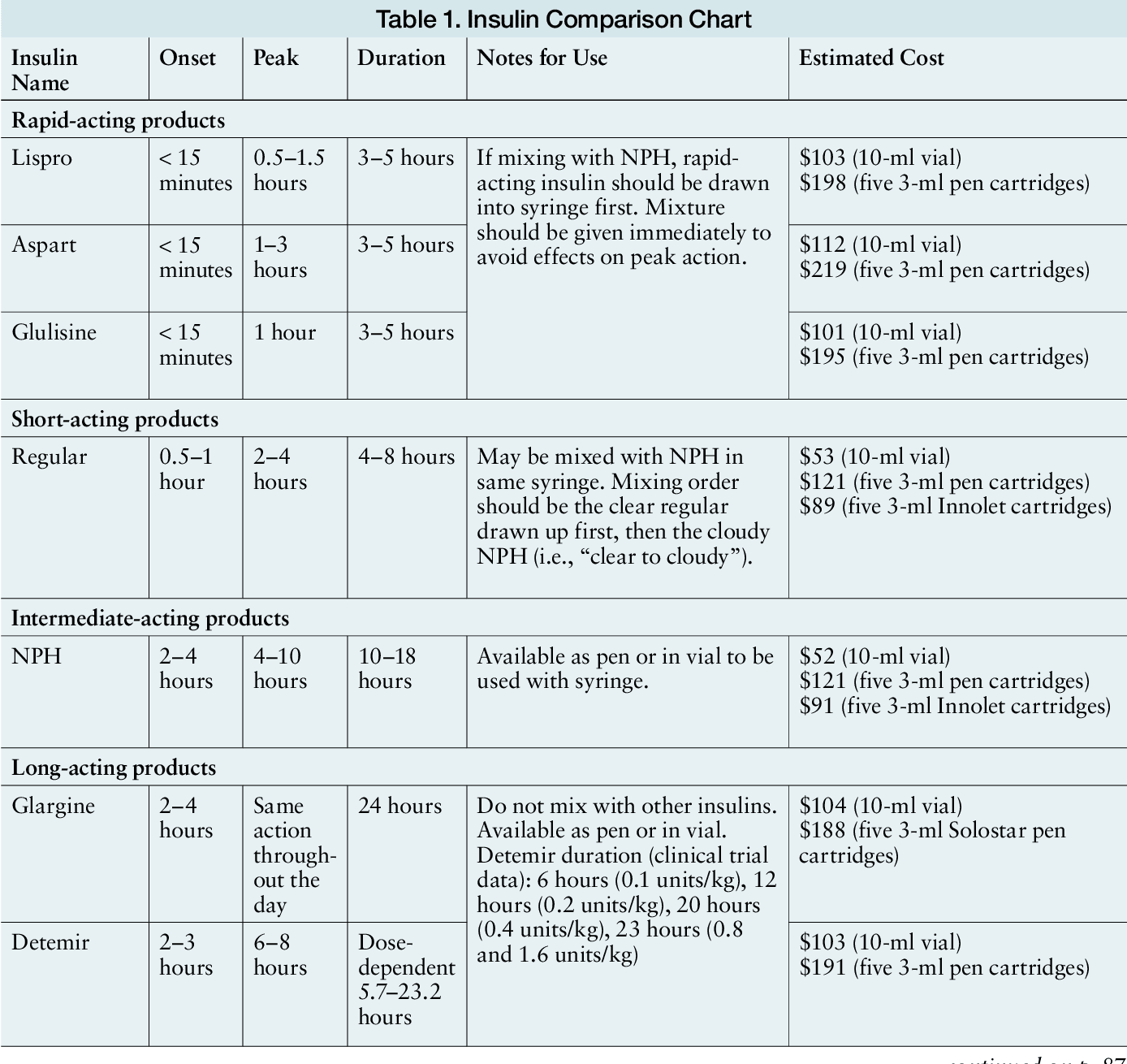
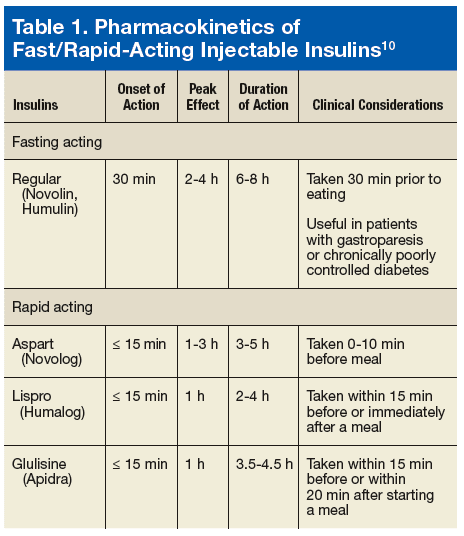
If Youre Prescribed Basal Insulin Youll Take The Same Amount Every Day
If your doctor prescribes basal insulin, theyll advise you to take a set amount of it each day. For example, they might ask you to take 10 units of long-acting insulin before bed each night.
If that isnt enough to manage your blood sugar levels, they can prescribe more insulin. If your blood sugar management improves with time, they can reduce your dose. The amount of insulin will be adjusted based on your blood sugars.
Pipeline Agent: Insulin Icodec
Insulin icodec is a once-weekly, ultralong-acting, basal insulin analogue that is currently in development for the treatment of diabetes. This novel approach was developed by reengineering the ultralong oral basal insulin known as OI338.26 The two significant modifications made to OI338 to form insulin icodec consist of the strong, reversible binding to albumin and reduced insulin receptor affinity to slow down clearance and provide the continuous action of the insulin. Recent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies show that insulin icodec has a half-life of approximately 196 hours, ideal for a once-weekly injection.27
Two phase II studies of insulin icodec have had encouraging findings. The first study compared insulin icodec with once-daily insulin glargine U-100 in patients who had not previously received insulin treatment. Results revealed that insulin icodec had a glucose-lowering effect and a safety profile similar to insulin glargine U-100.28
In a phase II, multicenter, open-label, treat-to-target clinical trial, U-100 was switched to insulin icodec in patients who were also receiving one or more glucose-lowering medications. The switch from insulin glargine U-100 to insulin icodec was well tolerated and demonstrated improvements in glycemic control. The hypoglycemia risk was not increased for insulin icodec versus insulin glargine U-100.29
Titration Monitoring And Goals Of Therapy
The ADA recommends that an insulin regimen be adjusted once or twice weekly until self-monitoring of blood glucose targets are reached.9,25 AACE/ACE guidelines differ slightly, recommending adjustment every two or three days.10Table 430 and Figure 125 show different approaches to insulin titration depending on the type of insulin used and the resulting SMBG readings. It should be noted that these recommendations were developed before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved new, highly concentrated insulins.
| Fasting blood glucose levels for 3 consecutive days | Adjustment of basal insulin dose | Premeal or bedtime blood glucose levels for 3 consecutive days | Adjustment of rapid-acting insulin dose |
| Titration schedule for basal insulin* | Titration schedule for rapid-acting insulin | ||
| > 180 mg per dL | 8 | ||
| < 60 mg per dL | 4 |
The ADA suggests a target A1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant patients with type 2 diabetes. An A1C goal of less than 6.5% may be appropriate for patients with short duration of type 2 diabetes that is treated with lifestyle changes or metformin only, a long life expectancy, and no significant cardiovascular disease, as long as significant hypoglycemia or other adverse effects do not occur. For patients with a history of severe hypoglycemia, limited life expectancy, advanced microvascular or macrovascular complications, extensive comorbidities, or long duration of type 2 diabetes, an A1C goal of less than 8% or more may be appropriate .9
Also Check: When Is Insulin Prescribed For Type 2 Diabetes
Total Daily Insulin Requirement:
= 500 ÷ TDI = 1unit insulin/ 12 g CHO
This example above assumes that you have a constant response to insulin throughout the day. In reality, individual insulin sensitivity varies. Someone who is resistant in the morning, but sensitive at mid-day, will need to adjust the insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio at different meal times. In such a case, the background insulin dose would still be approximately 20 units however, the breakfast insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio might be breakfast 1:8 grams, lunch 1:15 grams and dinner 1:12 grams.
The insulin to carbohydrate ratio may vary during the day.
First Some Basic Things To Know About Insulin:
- Approximately 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight, when you are fasting and between meals. This is called background or basal insulin replacement. The basal or background insulin dose usually is constant from day to day.
- The other 50-60% of the total daily insulin dose is for carbohydrate coverage and high blood sugar correction. This is called the bolus insulin replacement.
Bolus Carbohydrate coverage
The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio.The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin.
Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of 12-15 grams of carbohydrate. This range can vary from 4-30 grams or more of carbohydrate depending on an individuals sensitivity to insulin. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress.
Bolus High blood sugar correction
The bolus dose for high blood sugar correction is defined as how much one unit of rapid-acting insulin will drop the blood sugar.
Generally, to correct a high blood sugar, one unit of insulin is needed to drop the blood glucose by 50 mg/dl. This drop in blood sugar can range from 15-100 mg/dl or more, depending on individual insulin sensitivities, and other circumstances.
You May Like: Men’s Insulin Pump Underwear
Example #: Formulas Commonly Used To Create Insulin Dose Recommendations
This example illustrates a method for calculating of your background/basal and bolus doses and estimated daily insulin dose when you need full insulin replacement. Bear in mind, this may be too much insulin if you are newly diagnosed or still making a lot of insulin on your own. And it may be too little if you are very resistant to the action of insulin. Talk to your provider about the best insulin dose for you as this is a general formula and may not meet your individual needs.
The initial calculation of the basal/background and bolus doses requires estimating your total daily insulin dose:
Baseline Characteristics In Patients Between The Two Groups
A total of 188 patients were recruited for the study. At the conclusion of the study, patients in the metformin add-on CSII therapy and CSII only therapy group numbered 95 and 93, respectively. There were no significant demographic differences in terms of mean values age, body-mass index, fasting plasma glucose concentrations, fasting plasma insulin concentrations, HOMA-IR, HOMA-B, Insulinogenic index, and Matsuda index between groups at baseline .
Table 1 Characteristics in patients at baseline between the two groups.
You May Like: Renal Cysts And Diabetes Syndrome
The Younger The Sooner The Better
The key to when to start insulin is to identify the appropriate glycated haemoglobin target for an individual patient. Despite the promulgation of various ‘guidelines’, there is no single HbA1c concentration which suits everyone. For example, the younger patients already on maximal oral therapy and as much lifestyle modification as they can manage, would benefit greatly in the long term from early introduction of insulin, even if their HbA1c is only minimally elevated . The important point here is the early introduction of insulin, as the lifetime risk of complications for young patients is great. On the other hand, older patients who are not symptomatic and have no microvascular complications such as retinopathy, can be allowed to remain in ‘secondary failure’ at an HbA1c of 8-9%. In these patients, prognosis is governed mainly by macrovascular disease, which is not greatly influenced by glycaemic control.
What If I Miss A Dose
What to do about a missed Mounjaro dose depends on when you remember the missed dose:
- Its been 4 days or less since your missed dose: Give yourself the missed dose of Mounjaro as soon as you remember. Then resume your regular dosing schedule.
- Its been more than 4 days since your missed dose: Wait to take your weekly dose at the next usually scheduled time.
Do not take a double dose of Mounjaro to make up for a missed dose. You should also not take a dose of the drug if its been less than 72 hours since your last dose. If youre unsure when to take your next dose of Mounjaro, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
If you need help remembering to take your dose of Mounjaro on time, try using a medication reminder. This can include setting an alarm or downloading a reminder app on your phone. You can also use a paper calendar or planner if that works better for you.
Do not use more Mounjaro than your doctor prescribes, as this can lead to serious side effects.
Recommended Reading: How Close Are We To Curing Diabetes
Insulin Dosages On A Fixed Dose Therapy
If you are on a fixed dose insulin therapy, your doctor or diabetes health team will help you to pick the dose, or doses, which you need to take each day.
If your blood glucose levels are running either too high or too low, contact your health team who will be able to help you make any dosage adjustments as appropriate.
Check what the recommended sugar levels are, referred to as your target blood glucose levels.
Blood Sugar Tests Help You Understand Your Insulin Needs
To learn how well your current treatment plan is working, its important to test your blood sugar according to your doctors recommendations. For example, theyll likely advise you to use home testing equipment to monitor and log your blood sugar each day. Theyll also order A1C tests, which provide information about your average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
If you find it hard to manage your blood sugar levels using your current treatment plan, talk to your doctor. They might recommend changes to your insulin regimen or other prescribed treatments.
Read Also: Doterra Essential Oils For Diabetes
Example #: Carbohydrate Coverage At A Meal
First, you have to calculate the carbohydrate coverage insulin dose using this formula:
CHO insulin dose = Total grams of CHO in the meal ÷ grams of CHO disposed by 1 unit of insulin .
For Example #1, assume:
- You are going to eat 60 grams of carbohydrate for lunch
- Your Insulin: CHO ratio is 1:10
To get the CHO insulin dose, plug the numbers into the formula:
CHO insulin dose =
- The carbohydrate coverage dose is 6 units of rapid acting insulin.
- The high blood sugar correction dose is 2 units of rapid acting insulin.
Now, add the two doses together to calculate your total meal dose.
Carbohydrate coverage dose + high sugar correction dose = 8 units total meal dose!
The total lunch insulin dose is 8 units of rapid acting insulin.
When To Start Insulin
Insulin is usually started when oral medicines and lifestyle changes have failed to lower a persons HbA1c level to less than 7%. However, a recent consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes suggested that insulin is a reasonable choice if a persons HbA1c level remains above 7% while he is taking metformin alone.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Learn More About Treatment Approaches> >
Large studies of people with Type 2 diabetes have shown that only about 30% of people taking two oral medicines have an HbA1c level of less than 7% after three years. Insulin is usually recommended as the initial therapy for diabetes if a persons HbA1c level at diagnosis is greater than 10% or if someones fasting blood glucose level is consistently above 250 mg/dl.
Studies have shown that many doctors wait until someones HbA1c level is higher than 9% to start insulin therapy, which often results in months or years of high blood glucose and an increased risk of developing complications later on. One unfortunate reality is that many busy medical practices are not set up to address the needs of people who take insulin. Starting insulin requires education and easy access to health-care providers who are knowledgeable about insulin therapy, including diabetes nurse educators, pharmacists, and doctors.
How Much Insulin To Take Per Carb
The average person will take about 1 unit of insulin for every 12 to 15 grams of carbohydrates consumed.
There is some variation to this, depending on how sensitive you are to insulin. For some people, this range is 1 unit for every 6 grams of carbohydrates, while for others, its 1 unit for every 30 grams of carbohydrates.
Recommended Reading: How Long You Can Live With Diabetes
The High Blood Sugar Correction Factor:
Correction Factor = 1800 ÷Total Daily Insulin Dose = 1 unit of insulin will reduce the blood sugar so many mg/dl
This can be calculated using the Rule of 1800.
Example:
= 1800 ÷ TDI = 1 unit insulin will drop reduce the blood sugar level by 45 mg/dl
While the calculation is 1 unit will drop the blood sugar 45 mg/dl, to make it easier most people will round up or round down the number so the suggested correction factor may be 1 unit of rapid acting insulin will drop the blood sugar 40-50 mg/dl.
Please keep in mind, the estimated insulin regimen is an initial best guess and the dose may need to be modified to keep your blood sugar on target.
Also, there are many variations of insulin therapy. You will need to work out your specific insulin requirements and dose regimen with your medical provider and diabetes team.
Calculating Insulin Dose In Type 1 Diabetes From Diabetes Education Online
Your doctor will prescribe an insulin dosing regimen for you to get you started on your type 1 diabetes that will include the three components of intensive insulin therapy: Basal Insulin Dosage a once or twice daily dose of long acting insulin Bolus Dosage a short acting insulin dosage based on the amount of the carbohydrates in each meal . Bolus Correction Dose For A High Blood Sugar a correction factor dosage to bring your blood sugar level back to the target range when it gets too high . However, each of these three dosages can change over time or even throughout the day and you will learn how to adjust up or down each of these three components. Of course, your diabetes team should always be available by phone or internet to counsel you on an appropriate insulin dosage for any of the three components of intensive insulin therapy if youre unsure. What follows are the first three examples* from Calculating Insulin Dosage from Diabetes Education Online which will show you how you will do it: *Example #4, Formulas commonly used to create insulin dose recommendations is in the next post of my blog study notes . First, some basic things to know about insulin: Approximately 40-50% of the total daily insulin dose is to replace insulin overnight, when you are fasting and between meals. This is called background or basal insulin replacement. The basal or background insulin dose usually is constant from day to day. The other 50-6Continue reading > >
Read Also: How To Fill Out Fmla Paperwork For Diabetes
Analogue Versus Human Insulin
Glucose control, adverse effects, cost, adherence, and quality of life need to be considered when choosing a type of insulin. In general, analogue insulin is similar to human insulin in controlling diabetes, although some trials have found higher mean A1C levels in patients taking analogue insulin compared with human insulin. 17 Analogue insulin usually causes less postprandial hyperglycemia and delayed hypoglycemia. 18,19 In a recent meta-analysis, glycemic control was not improved with analogue insulin compared with human insulin, but nocturnal hypoglycemia was reduced.17
An industry-funded cost-effectiveness analysis found that the increased cost of medication is more than off set by the reduction in hypoglycemic events. 20 However, the analysis assumed a cost differential of 14 percent, which is inconsistent with current pricing . 20,21 Cost-effectiveness analyses have differed regarding the long-term cost savings of using analogue insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes, with industry-sponsored studies finding reduced cost22 and government-sponsored studies finding no cost reduction. 23 Measures of adherence and quality of life have been improved with analogue insulin compared with human insulin. 24,25
You May Like: Can You Get Insulin For Free
Disposal Of Used Insulin Syringes
Used syringes, pen needles, cannulas and lancets must be disposed of in an Australian Standards-approved sharps container, which is puncture-proof and has a secure lid. These containers are usually yellow and are available through pharmacies, local municipal councils and state or territory diabetes organisations such as Diabetes Victoria.
Procedures to dispose of sharps containers vary from state to state.
For sharps disposal information and help, you can contact:
- state or territory diabetes organisations, such as Diabetes Victoria
- state Department of Health
Insulin needs to be stored correctly. This includes:
- Store unopened insulin on its side in a fridge.
- Keep the fridge temperature between 2 and 8 °C.
- Make sure that insulin does not freeze.
- Once opened, keep it at room temperature for not more than one month and then dispose of it safely.
- Avoid keeping insulin in direct sunlight.
Extreme temperatures can damage insulin so it doesn’t work properly. It must not be left where temperatures are over 30 °C. In summer your car can get this hot so don’t leave your insulin there.
There are various insulated insulin carry bags available for transporting insulin.
Recommended Reading: Glucose Meter False High Reading
Glenmark Has Launched Zitapiomet Indias First Triple Fixed
Shares of Glenmark Pharmaceuticals rallied nearly 6% in intraday trade on Wednesday, in an otherwise weak broader market, after the pharma major launched ZitaPioMet, the countrys first triple fixed dose combination for high insulinresistant type 2 diabetes. The single pill contains Teneligliptin + Pioglitazone + Metformin in a sustained release formulation, it said in an exchange filing today.
Cheering the news, Glenmark Pharma shares opened higher at 411.45, snapping four sessions losing streak, as against its previous closing price of 409.20 on the BSE. During the session so far, the pharma stock gained as much as 5.9% to hit an intraday high of 433.25, while the market capitalisation climbed to 12,220.70 crore. The stock has fallen nearly 7% in the last four sessions.
The surge in Glenmark Pharma share was in sync with the BSE healthcare index, which topped the sectoral chart by rising 1.7%, led by IOL Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Lal PathLabs, Solara Active Pharma Sciences, and Morepen Laboratories. In contrast, the BSE benchmark Sensex was trading 114 points lower at 61,588 levels at the time of reporting.
This offers patients with Type 2 diabetes the convenience of once daily dosing to improve their glycemic control and achieve the targeted HbA1c within 24 weeks, Glenmark said.