Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms.
Most cases are only discovered when your blood sugar levels are tested during screening for gestational diabetes.
Some women may develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels gets too high , such as:
- needing to pee more often than usual
But some of these symptoms are common during pregnancy and are not necessarily a sign of gestational diabetes. Speak to your midwife or doctor if you’re worried about any symptoms you’re experiencing.
How Are The Results Of The Glucose Tolerance Test Evaluated
Glucose tolerance tests may lead to one of the following diagnoses:
- Normal response: A person is said to have a normal response when the two hour glucose level is less than 140 mg/dl, and all values between 0 and 2 hours are less than 200 mg/dl.
- Impaired glucose tolerance : A person is said to have impaired glucose tolerance when the fasting plasma glucose is less than 126 mg/dl and the two hour glucose level is between 140 and 199 mg/dl. This is sometimes referred to as “prediabetes” because people with IGT have a higher risk of developing diabetes.
- Diabetes: A person has diabetes when two diagnostic tests done on different days show that the blood glucose level is high. This means either the two hour levels is greater than 200 mg/dl or the fasting glucose is noted as greater than 126 mg/dl. A glycosylated hemoglobin level of 6.5% or more also supports a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
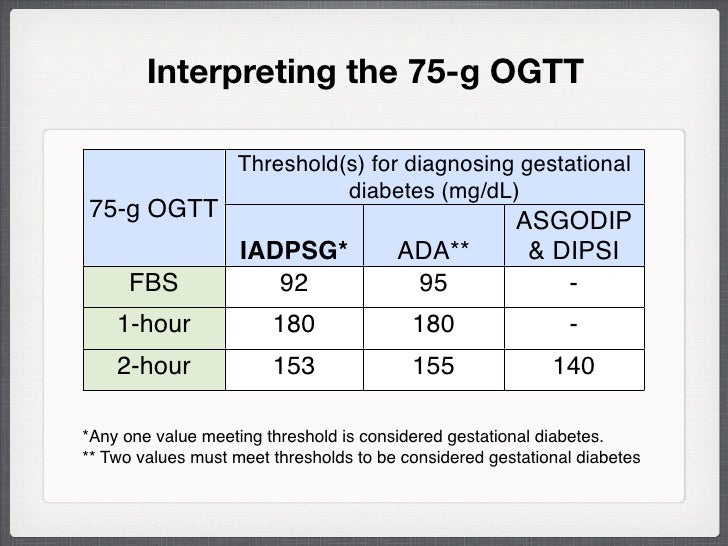
- Diabetes during pregnancy: A pregnant woman has diabetes if she has a fasting plasma glucose of over 92 mg/dl, or a two hour glucose level greater than 153 mg/dl.
Is There Anything I Can Do To Help Me Pass The Glucose Tests
No. If you have gestational diabetes, the glucose tolerance test will detect it. However, there are steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing gestational diabetes, as well as to keep your blood glucose levels stable even if you do have the condition. These are:
- Healthy eating: Opt for whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which are high in fiber, and cut back on foods and drinks that are high in added sugars.
- Exercise:Moderate exercise, such as walking briskly and swimming, can help keep your blood sugar under control.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Use our pregnancy healthy weight gain calculator to estimate how much you can expect to gain and whether you are on target.
Also Check: What Does It Mean If Glucose Is High
Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes
Whether you had diabetes before you got pregnant or you developed diabetes during your pregnancy, youll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Tight control will help you avoid complications and long-term health problems for both you and your baby. Youre eating differently because your body needs more energy to help your baby grow and be healthy. And your changing hormones affect how your body makes and uses insulin. In the later parts of your pregnancy, you may become more insulin resistant, so blood sugar builds up to higher levels. How often should you check your blood sugar? Pre-existing diabetes: Before and after meals and before bedtime If you are pregnant and have type 1 diabetes, your doctor might sometimes ask you to check your blood sugar in the middle of the night, around 3 a.m. You should check your fasting urine ketones every day, too. For every type of diabetes, if youre pregant you need to see your doctor at least once a month, perhaps as often as once a week.Continue reading > >
Diabetes Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Also Check: Diabetes 2 Meal Plan For A Week
Glucose Tolerance Testing Diet
You will eat three meals per day and have a bedtime snack, and your meals should consist of at least 50% carbohydrates. 10 servings of carbohydrates equal approximately 150 grams of carbohydrates. You may check the package nutrition labels on most foods, as most labels will indicate the number of grams of carbohydrates the food contains. You must have at least 150 grams of carbohydrates each day for three days prior to your test.
The following are examples of one serving of carbohydrates :
- 1 slice of bread
- 1/2 cup of starchy vegetables
What Does The Blood Glucose Test Involve
All pregnant women are offered this screening test between 24-28 weeks gestation. When other risk factors are present, such as obesity, the test may be offered earlier and then repeated if initially normal. The screening test for GD is called a glucose challenge, which aims to see how your body is handling sugars. The measurement is taken 1 hour after you consume a glucose drink. This test can be conducted at any time of day as it is not a fasting test. If your blood sugar is normal after the challenge, you will not require any more testing. If it is high, you will have a second test. This test is done in the morning while you are fasting and will require you not to eat prior to the test. You will have your glucose tested before consuming a glucose drink and then tested again 1 and 2 hours later. If your glucose is higher than specific cut-off values, it means you have GD. See the table for more specific information.
|
Screening for gestational diabetes |
| Higher than 9.0 mmol/L = GD |
Also Check: Quickest Way To Lower Blood Sugar
Who’s At Risk Of Gestational Diabetes
Any woman can develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but you’re at an increased risk if:
- your body mass index is above 30 use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI
- you previously had a baby who weighed 4.5kg or more at birth
- you had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- 1 of your parents or siblings has diabetes
- you are of south Asian, Black, African-Caribbean or Middle Eastern origin
If any of these apply to you, you should be offered screening for gestational diabetes during your pregnancy.
What Do The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Results Mean
A blood glucose level of 140mg/dL or higher will identify 80% of women with gestational diabetes. When that cutoff is lowered to 130mg/dL, the identification increases to 90%. If your blood glucose level was greater than 130 mg/dL, your provider will likely recommend you take another diabetes screening test that requires you to fast before the test.
During this second test, called the 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test, your blood glucose level will be tested four times during a three-hour period after drinking the sweetened cola-like drink. If two out of the four blood tests are abnormal, you are considered to have gestational diabetes.
You May Like: Diabetic Diet To Reduce Blood Sugar Levels
Glucose Tolerance Testing In Preventative Medicine
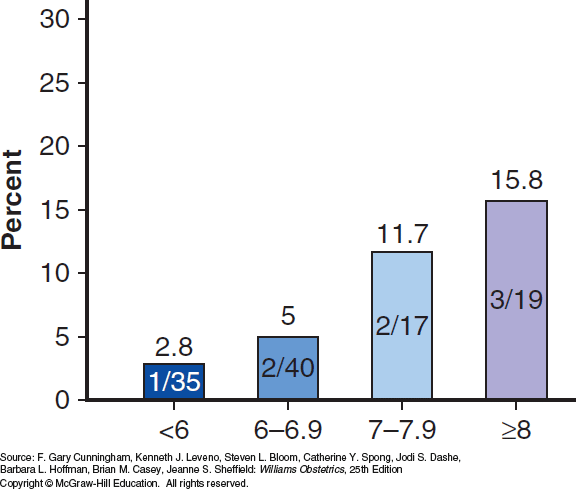
A glucose tolerance test can be used to identify patients at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes based on clinical risk factors, with a view to beginning preventive therapy. Approximately 25% of patients with either impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose will develop type 2 diabetes over the following 3-5 years. However, the results of a glucose tolerance test cannot distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cannot be used to predict response to therapy, or likelihood of future complications. Although glucose tolerance testing is more specific than other options, fasting blood glucose and haemoglobin A1c testing are usually more convenient and thus are used more frequently for screening.
Higher plasma glucose levels are linked to increased cardiovascular risk, with this risk increase extending into the non-diabetic range. Impaired glucose tolerance has also been demonstrated to be a better predictor of increased cardiovascular risk and mortality than fasting glucose.
Specifics for collection and panels are as follows:
-
Specimen type: Blood serum or plasma
-
Container: Vacutainer, red top gray top
-
Collection method: Venipuncture
Related tests include serum or plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, urinalysis, C-peptide, and insulin.
How Effective Are Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
An OGTT can be used to effectively diagnose various types of diabetes, including prediabetes.
Its useful for confirming a diagnosis after an abnormal HbA1c test result. An A1C test is often part of routine blood tests, but its less sensitive than an OGTT. Because of this, an OGTT can help with making an official diagnosis.
This can alter the results, potentially leading to a misdiagnosis.
An OGTT is also time consuming. You may need to take off from work or school. Theres currently no alternative for the test, according to 2018 research.
An OGTT is considered to be a safe test.
Be sure to eat a meal the night before. This may help reduce discomfort caused by fasting.
For some people, drinking the concentrated glucose solution causes side effects such as:
Additional side effects, such as diarrhea and heart palpitations, are more likely to affect people whove had bariatric surgery.
Other OGTT risks are the same as getting your blood drawn for any reason:
- skin irritation from adhesive on a bandage
If you have any concerns, talk with a doctor before taking the test.
You May Like: Risk Factors Of Diabetes Mellitus
Recommended Reading: Long Acting Insulin Side Effects
Understanding Your Glucose Challenge Screening Results
There are some standard benchmark numbers used to separate those considered at low-risk for gestational diabetes from those who need to graduate to the three-hour blood glucose tolerance test. So whats the one-hour glucose test normal range? According to the Mayo Clinic:
- Blood sugar level below 140 mg/dL is normal and considered passing.
- Blood sugar level between 140 mg/dL and 190 mg/dL is elevated, and requires the follow-up three-hour glucose tolerance test to confirm gestational diabetes
- Blood sugar level of 190 mg/dL or higher indicates gestational diabetes. Your doctor will advise about the need for repeat or secondary testing. When results are this high, though, they may skip this step altogether and begin monitoring and treatment
Dont panic if your doctor or midwife informs you that your one-hour glucose test number comes back elevated . It doesnt necessarily mean you have gestational diabetes. This is just a screening test, and nearly 25 percent of patients fail this initial test, says Pope. A confirmatory three-hour glucose test is next.
Glucose Tolerance Test Procedure

The GTT procedure is as follows
- At first a zero -time or baseline blood sample is drawn.
- Then the patient is given a specific dose of glucose solution to drink
- After that the blood samples are drawn at regular intervals to measure the blood sugar levels and also insulin levels in certain cases. The blood sampling can be done as requested by the doctor and could involve up to 6 hours of testing.
Recommended Reading: Healthy Meal Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
The American Diabetes Association encourages doctors to routinely screen pregnant women for signs of gestational diabetes. If you have no known history of diabetes and normal blood sugar levels at the beginning of your pregnancy, your doctor will likely screen you for gestational diabetes when youre 24 to 28 weeks pregnant.
Read Also: Can High Cholesterol Lead To Diabetes
Screening For Gestational Diabetes
During your first antenatal appointment at around week 8 to 12 of your pregnancy, your midwife or doctor will ask you some questions to determine whether you’re at an increased risk of gestational diabetes.
If you have 1 or more risk factors for gestational diabetes you should be offered a screening test.
The screening test is called an oral glucose tolerance test , which takes about 2 hours.
It involves having a blood test in the morning, when you have not had any food or drink for 8 to 10 hours . You’re then given a glucose drink.
After resting for 2 hours, another blood sample is taken to see how your body is dealing with the glucose.
The OGTT is done when you’re between 24 and 28 weeks pregnant. If you’ve had gestational diabetes before, you’ll be offered an OGTT earlier in your pregnancy, soon after your booking appointment, then another OGTT at 24 to 28 weeks if the first test is normal.
Find out more about an OGTT.
Read Also: Can Keto Diet Cause Diabetes
What Makes You A High
If you may be at high risk for gestational diabetes , your healthcare provider may also consider certain aspects of your medical history.The provider may take into account your pre-pregnancy weight , your age, whether anyone in your family has had gestational diabetes or diabetes, your race or ethnic background , and outcomes of any previous pregnancies.Speak to your healthcare provider to find out whether you have a high risk or low risk of developing gestational diabetes. If the provider determines your risk is low, you may not have to take the glucose challenge test.
Can You Get Rid Of Gestational Diabetes While Pregnant
Unlike other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes usually goes away on its own and soon after delivery blood sugar levels return to normal, says Dr. Tania Esakoff, clinical director of the Prenatal Diagnosis Center. “There is no need for gestational diabetes to take away from the joys of pregnancy.”
Also Check: Medtronic Vs Tandem Insulin Pump
What Does The Glucose Tolerance Test Measure
The classic oral glucose tolerance test measures blood glucose levels five times over a period of three hours. Some physicians simply take a baseline blood sample followed by a sample two hours after drinking the glucose solution. In a person without diabetes, the glucose levels rise and then fall quickly. In someone with diabetes, glucose levels rise higher than normal and fail to come back down as fast.
People with glucose levels between normal and diabetic levels have so-called impaired glucose tolerance . People with impaired glucose tolerance do not have diabetes.
Each year, 5% to 10% of people whose test results show impaired glucose tolerance actually develop diabetes. Weight loss and exercise may help people with impaired glucose tolerance return their glucose levels to normal. In addition, some physicians advocate the use of medications, such as metformin , to help prevent/delay the onset of overt diabetes. Studies have shown that impaired glucose tolerance itself may be a risk factor for the development of heart disease, and whether impaired glucose tolerance turns out to be an entity that deserves treatment itself is something that physicians are currently debating.
How To Prepare For The Glucose Challenge Screening Test
The good news is that you dont really need to do much of anything to get yourself ready for this glucose screening test. We want to see how your body responds naturally to glucose, so just eat what you would regularly eat or drink, advises Greves.
Pope echoes this recommendation, but stresses that having long-term healthy lifestyle habits can ultimately improve your chances of passing: There really is no preparation besides trying your best to always eat as healthy as you can, and exercise routinely. This helps with glucose metabolism.
Still, if youve been doing your own internet sleuthing to figure out what to eat before your glucose testor in the hopes of sourcing hacks to help you pass the testknow that any touted tips are unproven and ill-advised. Patients always try and trick the system to try and pass the test. Theres no secret to this, says Pope. Whats more, you shouldnt want to cheat if youre at risk for gestational diabetes, you need to know so you can take the necessary next steps.
Also Check: Does High Glucose Make You Tired
Is Gestational Diabetes High Risk Pregnancy
Women who develop diabetes during pregnancy, known as gestational diabetes mellitus , may need high-risk pregnancy care due to complications that can arise during pregnancy and childbirth. Women with GDM have an increased risk of preeclampsia, a condition that leads to pregnancy-induced high blood pressure.
What Can I Expect If Getting An Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Before doing an OGTT, a doctor might perform a glucose challenge test first. This is a shortened version of the OGTT.
A glucose challenge test requires no fasting. During the test, youll drink a beverage containing 50 grams of glucose. After 1 hour, a healthcare professional will take a blood sample to check your blood sugar level.
If your blood glucose is higher than 140 mg/dL, it might indicate diabetes. In this case, youll need an OGTT.
An OGTT requires some preparation. Youll need to fast for about 8 hours before the test is performed. This means you cant eat breakfast or drink any liquids, except water, beforehand.
An OGTT includes the following steps:
- A health worker will take a blood sample from your fingertip, earlobe, or a vein. Theyll test the sample for blood glucose, which will serve as a baseline measurement.
- Youll drink a concentrated glucose beverage. Most solutions contain 75 grams of glucose.
- Youll sit or lay down for 1 hour.
- After 1 hour, healthcare staff will take a blood sample.
- A healthcare professional may take another blood sample after 2 hours and again at 3 hours.
- A medical team will measure the blood glucose levels at each test time.
Between testing times, youll need to stay still and avoid drinking a lot of water. Thats because excessive movement and hydration can alter the results.
You might receive an OGTT without receiving a glucose challenge test first.
You May Like: Can Keto Diet Cause Diabetes
Recommended Reading: Does Melatonin Lower Blood Sugar