Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications like Metformin, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown and there is no cure. We do know that people who develop type 1 diabetes have the genes for developing the condition. However, not all people with the genes develop type 1 diabetes. Something in the environment, such as a virus, triggers the immune system to attack the beta cells of the pancreas.
The Rotavirus has been linked with the development of type 1 diabetes. Research has found that since the Rotavirus vaccine was developed in 2007, the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children under 5 has decreased.
Other research has shown that Vitamin D supplementation can be protective against developing type 1 diabetes and that Vit D deficiency may increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Most people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes have no other relative with the condition. However, if you have a mum or dad, brother or sister with type 1 diabetes, you do have a higher chance of developing type 1 diabetes. Also, if you or a family member has another autoimmune condition such as coeliac or thyroid disease your risk of developing type 1 diabetes increases.
High Blood Sugar Levels Symptoms
High blood sugar levels or also known as hyperglycemia can occur if you don’t take enough insulin, you miss a meal, or you exercise too little. High blood sugar levels can also be caused by stress, illness, or some medications.
Signs and symptoms that your blood sugar might be on the high side include:
- Increased urination
- Fatigue
- Nausea
It’s important to treat high blood sugar levels quickly to avoid more serious problems. You can treat high blood sugar levels by drinking water and taking your diabetes medication or insulin.
It’s important to check your blood sugar levels right away and keep doing that every hour until your sugar levels are back in the normal blood sugar range.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Type 2 A1c Goals
Recommended Blood Glucose Targets For People With Diabetes
| AIC* | Fasting blood glucose/ blood glucose before meals | Blood glucose two hours after start of meal |
| Target for most patients with diabetes | 7.0% | |
| If A1C targets not being met** | 4.0 to 5.5 | 5.0 to 8.0 |
*An A1C is an average of your blood glucose levels over the past three months. Learn more about the A1C here.
**Must be balanced against the risk of hypoglycemia
Diabetes Complications In Type 1 Diabetes
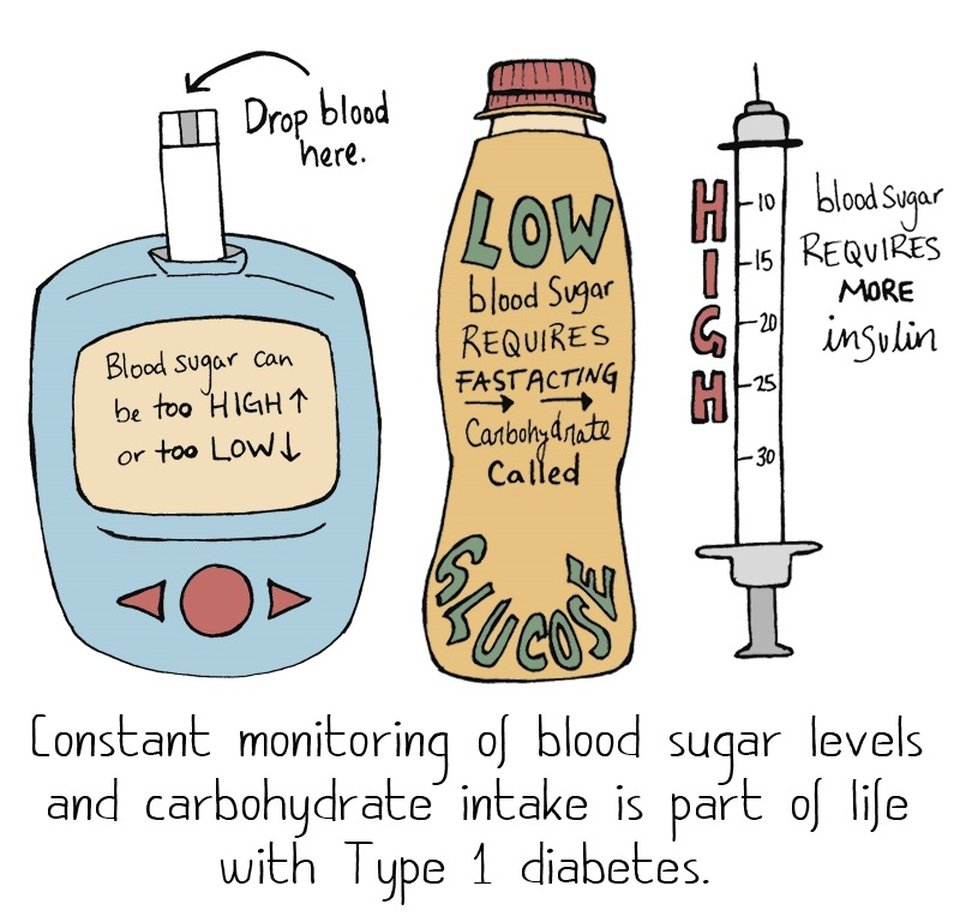
Over time, high glucose levels can damage nerves, vessels, tissues and organs of the body.
Complications may be:
- nerve damage to feet which can lead to lower limb amputation
- heart and vessel disease and stroke
- gum and tooth disease
- sexual dysfunction in both men and women.
- damage to the nerves that control the automatic functions of the internal organs such as digestion and bowel function, blood pressure and heart rate
Also Check: Contour Next One Blood Glucose Meter
What Is The Metabolic Abnormality That Underlies The Characteristic Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus
t able to perform their capabilities adequately anymore We have specialists doing research and helping individuals, and animals secure from diabetes Younger T1D patients require continuous assist by Normal Blood Sugar Level For Type 1 Diabetes an adult Normal Blood Sugar Level For Type 1 Diabetes parents, faculty personnel, and coaches in sports activities through sharing with particular alert settings Speed is a vital factor for deciding the effectivity of the CGM machine The greatest machines deliver readings in 10 seconds and less Choose a machine that will eat less time and does not mess up with your schedule.
It is also really helpful that women with a history of GDM bear lifelong screening for the development of diabetes or prediabetes at least each three years If your eye doctor thinks you might have extreme diabetic retinopathy or DME, they might do a check called a fluorescein angiogram This test lets the physician see footage of Normal Blood Sugar Level For Type 1 Diabetes the blood vessels in your retina .
Alarming Facts About Diabetes
You May Like: Where Can I Get Free Diabetic Supplies
Amy Campbell Ms Rd Ldn Cde
A Registered Dietitian and Certified Diabetes Educator at Good Measures, LLC, where she is a CDE manager for a virtual diabetes program. Campbell is the author of Staying Healthy with Diabetes: Nutrition & Meal Planning, a co-author of 16 Myths of a Diabetic Diet, and has written for publications including Diabetes Self-Management, Diabetes Spectrum, Clinical Diabetes, the Diabetes Research & Wellness Foundations newsletter, DiabeticConnect.com, and CDiabetes.com
***Learn blood sugar basics with our free guide!
***Interested in learning more about blood sugar? Check out our blood sugar chart and learn about using blood sugar monitoring to manage diabetes in Managing Your Blood Glucose Ups and Downs.
Learn more about the health and medical experts who who provide you with the cutting-edge resources, tools, news, and more on Diabetes Self-Management.
Whats The Difference Between Mmol/l And Mg/dl
Both sets of units are used to measure blood sugar levels and both give a measurement of the concentration of glucose in the blood, albeit in slightly different ways.
mmol/L gives the molarity, which is the number of molecules of a substance within a specified volumen, in this case within 1 litre. mg/dL gives the concentration by the ratio of weight to volumen, in this case milligrams per decilitre.
mmol/L is the most common measurement used in the UK with mg/dL predominantly used in the USA and continental Europe.
- mg/dL Unit for measuring concentration of glucose in the blood in the USA milligrams per decilitre. : Milligrams per 100 millilitres
Blood glucose typically varies from 4 mmol/L to 6 mmol/L for people without diabetes.
Blood sugar needs to be tightly controlled in the human body to minimise the risk of complications developing.
- Formula to calculate mmol/l from mg/dl: mmol/l = mg/dl / 18
- Formula to calculate mg/dl from mmol/l: mg/dl = 18 × mmol/l
Read Also: Is It Possible To Reverse Type 1 Diabetes
How Does Hyperglycemia Happen
Insulin is a hormone that lets your body use the sugar in your blood, which comes primarily from carbohydrates in the food that you eat. Hyperglycemia happens when your body has too little insulin to use the sugar in your blood.
People with type 1 diabetes can have episodes of hyperglycemia every day. Although this can be frustrating, it rarely creates a medical emergency. Not taking enough insulin can lead to hyperglycemia .
Other things that can cause hyperglycemia include:
- Caffeine
- Having trouble seeing or concentrating
- Experiencing stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Having sweet-smelling or fruity breath
- Cuts or sores that do not heal, infections, and unexplained weight loss may also be signs of long-term hyperglycemia.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should check your blood sugar. If your blood sugar is very high, you should also test for ketones in either your blood or urine.
What Number Should My Blood Glucose Be
Blood glucose is measured in mg/dl. The normal range for blood glucose for people without diabetes is 70 to 120 mg/dl.
The Diabetes Center has guidelines for blood glucose readings. This is called a target range. There may be times when your healthcare provider gives you a different target range, like for bedtime, with exercise, or after eating.
Nationwide Childrens Hospital Diabetes Center Target Blood Glucose Ranges
| Age |
The goal is to keep the blood glucose within the target range most of the time.
You May Like: What Is Worse Diabetes 1 Or Diabetes 2
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Your blood sugar, or glucose, level is found in your blood and serves as your main source of energy. During digestion, carbohydrates, which are sugars, starches, and fiber, are changed into glucose. Your body then uses this as energy, or stores whatever isn’t used in your cells for later use.
Your blood sugar is influenced by the food you eat, your age, stress, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol use. It is also impacted by heart issues or diabetes, a group of conditions where too much glucose builds up in the bloodstream.
Danie Drankwalter / Verywell
This article explores the range of glucose levels an individual may experience after eating. It will also cover how different types of food impact blood sugar, as well as how to manage glucose levels.
Can I Check My Own Blood Sugar
You can do blood sugar level check by doing a finger-prick test, or by using an electronic blood sugar monitor called a flash glucose monitor or CGM. You can do this several times a day helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take. Find out your ideal target range.
Not everyone with diabetes needs to check their levels like this. Youll need to if you take certain diabetes medication. Always talk to your healthcare team if youre not sure whether thats you theyll give you advice on whether to check them yourself and how often.
And theres also something called an HbA1c, which is a blood test to measure your average blood sugar level over the last three months. Everyone with diabetes is entitled to this check.
High blood sugar levels increase your risk of developing serious complications. However you manage your diabetes, stay in the know about your blood sugar levels
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes By Losing Weight
What Is Blood Glucose Anyway
Blood glucose, or sugar, is sugar that is in your blood . It comes from the food that you eat foods that contain carbohydrate, such as bread, pasta and fruit are the main contributors to blood glucose. The cells in our bodies need glucose for energy and we all need energy to move, think, learn and breathe. The brain, which is the command center, uses about half of all the energy from glucose in the body.
Who Develops Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood, teenage years , or in early adulthood before the age of 30, but it can be diagnosed at any age.
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adulthood , also known as type 1.5 diabetes, is also autoimmune in nature. However, it develops more slowly than classic type 1 diabetes.
People with LADA often get misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes because they have some of the features of type 2 diabetes:
- do not usually need insulin at diagnosis
- are above the age of 30
- may be overweight.
People with LADA will usually need insulin therapy within 6 months to 6 years from diagnosis. 10% of people originally diagnosed with type 2 diabetes actually have LADA.
Also Check: Free Diabetes Tester And Strips
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Heart Eyes Feet Nerves And Kidneys
Blood vessels are located throughout our bodys tissues and organs. They surround our bodys cells, providing a transfer of oxygen, nutrients and other substances, using blood as the exchange vehicle. In simple terms, diabetes doesnt allow glucose to get into cells and it damages blood vessels in/near these organs and those that nourish nerves. If organs, nerves and tissues cant get the essentials they need to properly function, they can begin to fail.Proper function means that your hearts blood vessels, including arteries, are not damaged . In your kidneys, this means that waste products can be filtered out of your blood. In your eyes, this means that the blood vessels in your retina remain intact. In your feet and nerves, this means that nerves are nourished and that theres blood flow to your feet. Diabetes causes damage that prevents proper function.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
Also Check: Meals For Gestational Diabetes During Pregnancy
How Does Type 1 Diabetes Affect Life Expectancy
Because people with type 1 diabetes often develop the condition at a young age, many decades of high blood sugar levels challenge the body. While research is sparse, a 2020 study revealed that type 1 diabetes may reduce life expectancy by about eight years. However, as more people gain access to appropriate treatment with improved diabetes therapy and technology, life expectancy for people with type 1 diabetes is approaching that of the general population.
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Shot Once A Month
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
Type 1 diabetes can be diagnosed through any of the following tests:
An A1C test, formally called a glycated hemoglobin test or HbA1C test. This blood test gives an estimate of a persons average blood sugar levels from the past two or three months. An A1C of 6.5% or higher is considered diabetes
A fasting plasma glucose test measures a persons blood glucose level after a period of fasting for eight hours. An FPG of 126 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
An oral glucose tolerance test measures the body’s blood glucose level two hours after consuming a sugary drink. An OGTT result of 200 mg/dl or higher at two hours indicates diabetes.
In someone with symptoms of high blood sugar , a random plasma glucose test can be used to check blood sugar levels. A blood sugar level above 200 mg/dl indicates diabetes.
Your healthcare professional may also suggest a diabetes-related antibody test to specifically confirm a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
Blood Sugar Levels In Children With Diabetes:
Summary
Also Check: How To Calculate Insulin Dose Type 2 Diabetes