What A1c Goal Should I Have
People will have different A1C targets, depending on their diabetes history and their general health. You should discuss your A1C target with your health care professional. Studies have shown that some people with diabetes can reduce the risk of diabetes complications by keeping A1C levels below 7 percent.
Managing blood glucose early in the course of diabetes may provide benefits for many years to come. However, an A1C level that is safe for one person may not be safe for another. For example, keeping an A1C level below 7 percent may not be safe if it leads to problems with hypoglycemia, also called low blood glucose.
Less strict blood glucose control, or an A1C between 7 and 8 percentor even higher in some circumstancesmay be appropriate in people who have
- limited life expectancy
How To Prevent Hyperglycaemia
There are simple ways to reduce your risk of severe or prolonged hyperglycaemia:
- Be careful what you eat be particularly aware of how snacking and eating sugary foods or carbohydrates can affect your blood sugar level.
- Stick to your treatment plan remember to take your insulin or other diabetes medications as recommended by your care team.
- Be as active as possible getting regular exercise can help stop your blood sugar level rising, but you should check with your doctor first if you’re taking diabetes medication, as some medicines can lead to hypoglycaemia if you exercise too much.
- Take extra care when you’re ill your care team can provide you with some “sick day rules” that outline what you can do to keep your blood sugar level under control during an illness.
- Monitor your blood sugar level your care team may suggest using a device to check your level at home so you can spot an increase early and take steps to stop it.
Page last reviewed: 08 August 2018 Next review due: 08 August 2021
What Do My Results Mean
When you finish the blood sugar check, write down your results and note what factors may have affected them, such as food, activity, and stress. Take a close look at your blood glucose record to see if your level is too high or too low several days in a row at about the same time. If the same thing keeps happening, it might be time to change your diabetes care plan. Work with your doctor or diabetes educator to learn what your results mean for you. It can take time to make adjustments and get things just right. And do ask your doctor if you should report results out of a certain range right away by phone.
Keep in mind that blood glucose results often trigger strong feelings. Blood sugar numbers can leave you upset, confused, frustrated, angry, or down. It’s easy to use the numbers to judge yourself. Remind yourself that tracking your blood sugar level is simply a way to know how well your diabetes care plan is working, and whether that plan may need to change.
You May Like: What Type Of Diabetes Produces Too Much Insulin
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
Why Test Blood Sugar Levels

If you take certain medication, like insulin or sulphonylureas, checking your blood sugars is a vital part of living with diabetes. It can help you work out when you need to take more medication, when you need to eat something or for when you want to get up and move around more.
Routine checks can help you know when you might be starting to go too low or too high . Its a way of getting to know your body and how it works. It can help you and your healthcare team spot patterns too. Do you write your results down? You might find that helpful.
But importantly, it will help you stay healthy and prevent serious diabetes complications now and in the future. By complications, we mean serious problems in places like your feet and your eyes. This happens because too much sugar in the blood damages your blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow around your body. This can lead to very serious problems like sight loss and needing an amputation.
The higher your blood sugar levels are and the longer theyre high for, the more at risk you are.
Also Check: Robitussin Cough Syrup For Diabetics
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood sugar levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes sugar.
- Diabetes is diagnosed at 2 hour blood sugar of greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl
|
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
|
| Normal | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | |
| Diabetes | 200 mg/dl or higher |
Also Check: How Much Is Lantus Insulin
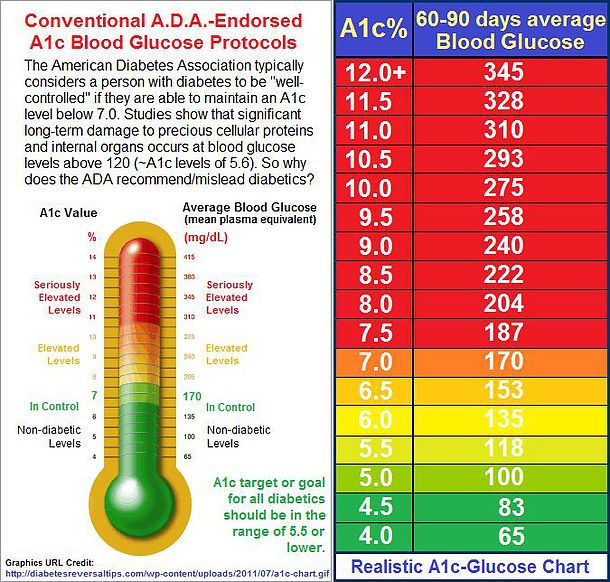
Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
Continuous glucose monitoring systems measure glucose concentrations in the interstitial fluid. Two types of devices are available. The real time CGM provides information directly to the user by displaying moment-tomoment absolute glucose levels and trending arrows, and by providing alarm notifications in the event that the glucose level is above or below a preset limit. A blinded CGM captures, but does not display, the glucose readings, which are then downloaded onto a computer for viewing and retrospective analysis by the health-care provider .
CGM technology incorporates a subcutaneously inserted sensor, an attached transmitter and, in the case of real-time CGM, a display unit . In professional CGM, the transmitter captures and retains the data. In Canada, 2 real-time CGM and 2 professional CGM are available. Real-time CGM has been consistently shown to reduce A1C in both adults and children with type 1 diabetes with and without CSII, and to reduce A1C in adults with type 2 diabetes . Real-time CGM also has been shown to reduce the time spent in hypoglycemia . Professional CGM has been shown to reduce A1C in adults with type 2 diabetes and in pregnant women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes .
Recommended Reading: Is It Possible To Reverse Type 1 Diabetes
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
Know Your Numbers: Kidney Function
A yearly test to check for protein in your urine can tell your doctor if diabetes has affected your kidneys. Kidney damage and failure is a common complication of diabetes. Microalbumin levels above 30 suggest kidney damage. It’s treatable if caught early, but if you wait until these numbers are above 300, the damage has a tendency to be permanent, Levesque says.
Recommended Reading: Can You Reverse Diabetic Neuropathy
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Controlling Your Glucose Levels
Getting satisfactory readings on your blood glucose meter requires controlling your diet. If you have hypoglycemia not related to diabetes, eat frequent meals and snacks with a balanced amount of complex carbohydrates, protein and fat. If you have diabetes, base your diet on grains, vegetables and fruits and aim to get 10 to 20 percent of your calories from protein, recommend University of Maryland experts. Limit high carbohydrate foods including starchy vegetables and sweets. Insulin injections may also be necessary.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Immunosuppression
How Precise Is The A1c Test
When repeated, the A1C test result can be slightly higher or lower than the first measurement. This means, for example, an A1C reported as 6.8 percent on one test could be reported in a range from 6.4 to 7.2 percent on a repeat test from the same blood sample.3 In the past, this range was larger but new, stricter quality-control standards mean more precise A1C test results.
Health care professionals can visit www.ngsp.org to find information about the precision of the A1C test used by their lab.
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is a measurement of the amount of glucose in your blood.
When you eat carbohydrates, your body breaks down those carbs into glucose. This becomes your body’s main source of energy, and fuels the vital functions in your brain, heart, liver, and muscles, says Nestoras Mathioudakis, MD, a diabetes expert at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
For people without diabetes, the pancreas releases insulin to help your cells absorb glucose and fuel your body. But for people with diabetes, the body does not produce insulin or it doesn’t work properly, and as a result, blood sugar levels must be carefully regulated to prevent health complications.
Also Check: How Does Metformin Work For Diabetes
Official Fasting Blood Sugar Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar target of 80 to 130 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. However, the fasting blood sugar target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
What Is Blood Glucose Anyway
Blood glucose, or sugar, is sugar that is in your blood . It comes from the food that you eat foods that contain carbohydrate, such as bread, pasta and fruit are the main contributors to blood glucose. The cells in our bodies need glucose for energy and we all need energy to move, think, learn and breathe. The brain, which is the command center, uses about half of all the energy from glucose in the body.
Also Check: Diabetes And High Eye Pressure
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
Diabetes Blood Sugar Level Goals
Upon waking before breakfast
- 70-130 mg/dl
- 4-7.2 mmol/l
Two hours after meals
- Under 180 mg/dl
- Under 10 mmol/l
Bedtime
- 90-150 mg/dl
- 5-8.3 mmol/l
The above levels, for people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, are the general goals set by the American Diabetes Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
As suggested earlier, there is some variation in the blood sugar levels goals set by different organizations. And additionally, your physician or healthcare team may set your goals at a more stringent level.
For instance, fasting levels:
- Between 70-100 mg/dL or 4-5.6 mmol/l
- 70-110 mg/dL or 4-6 mmol/l
- 70-130 mg/dL or 4-7.2 mmol/l
Once you have a type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the overall goals you should aim for is to get your blood sugar levels as close to normaloptimal levels as you possibly can.
BUT, as suggested above, often goals are set with higher targets initially. For instance, if you have a high reading of 250 or 300 , your physician or health practitioner may recommend 200 be an initial goal, then 180 , before gradually working toward 140 and lower.
The reason this is often recommended is you can experience symptoms of hypoglycemia if you bring your levels down very quickly. So working toward tighter and tighter control does take some time.
You should work with your healthcare team on this. But overall the most optimal targets to work toward are a fasting glucose under 100 mg/dl or 6 mmol/l. And an after-meal reading below 140 or 7.8.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes And Metabolism Impact Factor