Official Fasting Blood Sugar Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar target of 80 to 130 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. However, the fasting blood sugar target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their health care provider.
What Happens During The Test
Most people can take an A1C test at any time without preparing beforehand. However, a doctor may sometimes request that a person avoids eating or drinking for 8 hours before the test.
Women who are pregnant may need to drink a sugary beverage 1 hour before the test.
A doctor or nurse will collect a blood sample, usually from a vein in the arm or hand. They will send the sample to a laboratory for analysis.
How To Manage Diabetes With Numbers
Diabetes self-management is a numbers game. But it’s not just about your blood sugar. There are at least eight different numbers you should be familiar with to lower your risk for complications from diabetes symptoms. “Diabetes self-management is absolutely essential,” says Enrico Cagliero, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and an associate physician at the Massachusetts General Hospital Diabetes Center. “Although managing these numbers may not improve diabetes symptoms, it can help decrease the risk of serious complications such as blindness or kidney failure down the road.”
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Symptoms Include All Of The Following Except
Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
The NIDDK states that gestational diabetes is high blood sugar that occurs during pregnancy if you were not diabetic before getting pregnant. Healthy blood sugar during pregnancy can help lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. It can also lower the risk of your baby being born prematurely, at a high birth weight, and having respiratory problems.
Blood sugar and insulin levels during the first trimester of pregnancy tend to be lower than usual, but they rise during the late second and early third trimesters. You can be diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test .
These are the steps for the 2-step strategy.
- Drink a solution with 50 grams of glucose about the amount in 1 16-oz. bottle of a soft drink
- Get your blood drawn after 1 hour. Ig the value is high, retest
- Drink a solution with 100 grams of glucose about the amount in 12 peanut butter cups
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1, 2, and 3 hours
Or, your doctor might use the 1-step strategy with a 2-hour OGTT:
- Drink a solution with 75 grams of glucose
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1 and 2 hours
These are some values to know from NIDKK related to gestational diabetes and healthy blood sugar in pregnancy.
Blood sugar can vary greatly depending on when you take it. For example, after 1 hour, a reading of at least 180mg/dl can indicate signs of gestational diabetes, while a blood sugar reading after 3 hours would need to be 140 mg/dl would be cause for concern.
Diagnosing And Treating Hyperglycemia
Diagnosing hyperglycemia is done by assessing symptoms and performing a simple blood glucose test. Depending on the severity of the condition and which type of diabetes the patient is diagnosed with, insulin and a variety of medication may be prescribed to help the person keep their blood sugar under control. Insulin comes in short, long and fast-acting forms, and a person suffering from type 1 diabetes is likely to be prescribed some combination of these.
Individuals who are either diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or are considered at risk for the disease are recommended to make alterations to their diet, lifestyle habits and exercise routine in order to lower blood sugar and keep it under control. These changes generally help to improve blood glucose control, individuals with type 2 diabetes may require medication eventually. These can include glitazones, acarbose, glucophage or sulphonylureas.
Also Check: Diabetes Type 2 Glucose Levels
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
Your Diabetes Continuing Care
You can expect to be scheduled for checkups every three to six months, depending on your overall health, the types of medications you take and your personal needs.
You should use self-blood glucose monitoring. Well also instruct you on when to report poor control or complications to your health care providers.
When you come in for follow-up visits, your health care provider will review the medications youre taking and the results of self-blood glucose monitoring. Well then evaluate occurrences of unusually high or low blood glucose levels, any changes youve made in medications, and diabetes complications or adherence problems you may have experienced. Additionally, well talk with you about psychological and social factors and other medical illnesses influencing your health.
Follow-up physical exams will include weight, height , blood pressure and foot checks. Lab tests that produced abnormal findings in previous visits will be repeated. Well run tests for glycosylated hemoglobin and, if appropriate, blood glucose. Lipid studies are checked annually in adults and every two years in children. A urine test is performed annually. If urine contains protein, well do further tests to assess kidney function.
You May Like: Medicine From Canada For Diabetes
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes is also characterized by the presence of certain autoantibodies against insulin or other components of the insulin-producing system such as glutamic acid decarboxylase , tyrosine phosphatase, and/or islet cells.
When the body does not have enough insulin to use the glucose that is in the bloodstream for fuel, it begins breaking down fat reserves for energy. However, the breakdown of fat creates acidic by-products called ketones, which accumulate in the blood. If enough ketones accumulate in the blood, they can cause a potentially life-threatening chemical imbalance known as ketoacidosis.
Type 1 diabetes often develops in children, although it can occur at any age. Symptoms include unusual thirst, a need to urinate frequently, unexplained weight loss, blurry vision, and a feeling of being tired constantly. Such symptoms tend to be acute.
Diabetes is diagnosed in one of three ways a fasting plasma glucose test, an oral glucose tolerance test, or a random plasma glucose test all of which involve drawing blood to measure the amount of glucose in it.
Type 1 diabetes requires insulin treatment for survival. Treatment may also include taking other drugs to prevent kidney damage or to treat diabetes-related conditions such as high blood pressure.**
How To Reduce Blood Sugar
You can take steps to reach your blood sugar goals as soon as you find out that it is high. This is how to reduce blood sugar if you have a single high reading that may be dangerous:
- Ask your doctor what to do if you missed a dose of insulin or another diabetes medication
- Ask your doctor if your medication types and doses are still appropriate for you
- Drink water to dilute the sugar
- Exercise for 15 minutes
- Eat a small protein snack, such as a hard-boiled egg, ½ ounce of peanuts or pistachios or other nuts, ½ cup of beans, or ½ cup of plain yogurt or cottage cheese
If you have chronically high blood sugar in prediabetes or diabetes, you can follow this treatment plan:
- Exercise regularly, assuming your doctor approves it
- Lose weight if you are overweight or obese
- Eat a higher proportion of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fruit
- Limit sugary foods and beverages, fried foods, refined starches, and processed and fatty red meats
- Beware of starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, which can spike your blood sugar. Check out our guide of which veggies to avoid!
Read Also: What Helps Lower Blood Sugar
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar control over three months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment. Your healthcare provider can create a diabetes treatment plan if you are prediabetic or have diabetes.
Be sure your treatment plan includes instructions on when you would need to seek emergency medical care. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.
Chart Of Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes Age Wise
The amount of glucose present in blood fluctuates during the day and at night. Our body maintains a level of blood glucose for metabolism. The normal sugar level in a healthy body is between 90 to 100 mg/dL. But sometimes, these blood sugar levels may go high or low due to various factors. Such high or low blood glucose levels are signs of health conditions that need/ require attention and blood glucose can be kept at healthy levels with various Diabetes Reversal Methods and medical attention. This article gives in-depth information about normal blood sugar levels chart for adults with diabetes according to age.
You May Like: When Is Blood Sugar Lowest
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieve closer to normal blood sugar levels.
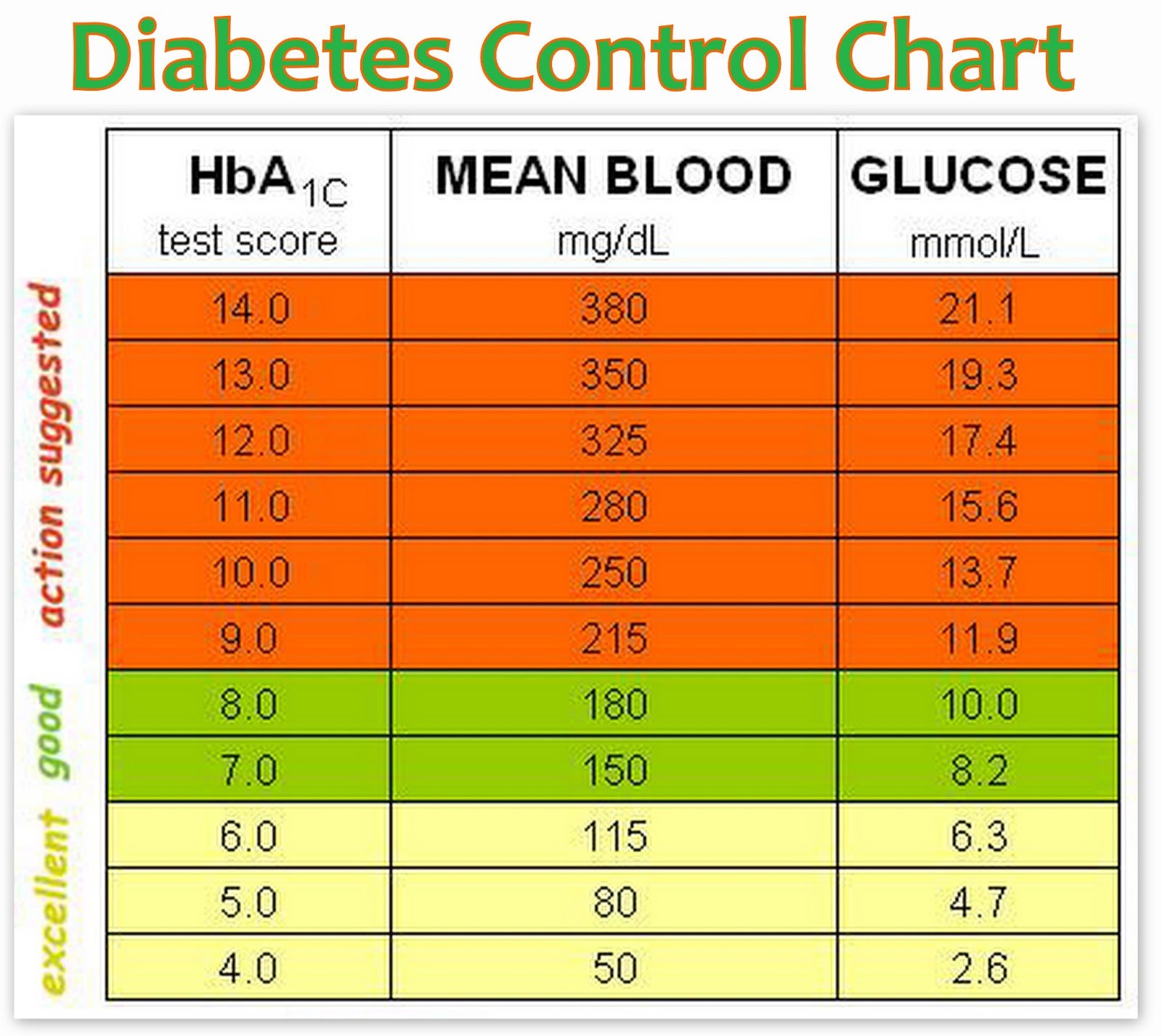
If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
What Factors Affect Blood Sugar
You can guess that carbohydrate intake and insulin production are at least partly responsible for your blood sugar levels. But the list is much longer — almost every lifestyle choice you make can affect your blood sugar. Here’s just a partial list.
- Exercise can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to lower blood sugar for up to 48 hours.
- Alcohol intake increases insulin production, causing low blood sugar.
- Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar, because your body wants access to energy in order to escape what it perceives as a dangerous situation.
- Medications, especially statins and diuretics, can raise blood sugar. Statins are used to treat cholesterol, and diuretics for high blood pressure.
- Diet is a major player in blood sugar. Eating too many simple carbs at once can cause levels to skyrocket, while protein intake leads to a slower increase in blood sugar.
- Dehydration raises blood sugar, because with less water in your body the glucose concentration will be higher.
Other surprising factors can affect your blood sugar, like a sunburn or gum disease, so if you’re dealing with a blood sugar issue and can’t figure out what’s causing your spikes and dips, talk to a healthcare professional.
Get the CNET Now newsletter
Don’t Miss: Do You Need Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level For Adults
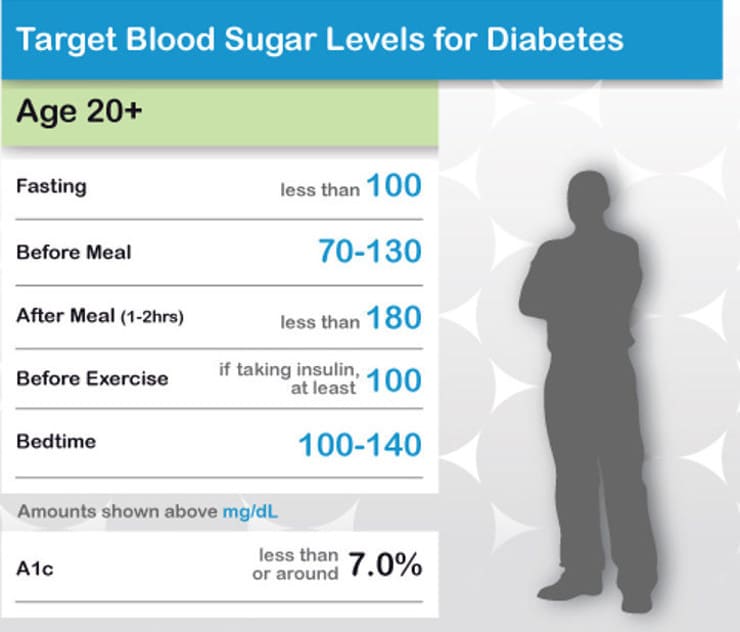
As we age, our bodies become less able to regulate blood sugar levels as well as they used to. That’s why the ADA recommends that older adults aim for a fasting blood sugar level of less than 100 mg/dL. After eating, it’s ideal that your blood sugar level is below 180 mg/dL.
The ADA recommends that most adults with diabetes aim for the following blood sugar goals:
- Fasting: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Preprandial : 70-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dL
- Bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL
If you experience high blood sugar levels or low blood glucose levels compared to this range you should speak to your doctor.
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is the main sugar content in your blood. It comes from the food you eat, and it’s your body’s main source of energy. Blood glucose levels are a measure of how much sugar is in your blood. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate during the day and night because of various reasons. What we eat, how active we are, and even stress can all affect our blood sugar levels.
You May Like: Does Sleeve Gastrectomy Cure Diabetes
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1C is a lab test. It indicates an average blood glucose reading for the last 90 days. It is done when you find out you have diabetes, and every 3 months after that at clinic visits. A person without diabetes has a Hemoglobin A1C of less than 5.6%.
|
Target Hgb A1C is 7.5% for all children and adults with diabetes. |
The chart below shows the Hemoglobin A1C result compared with the blood glucose number.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly.
The following blood sugar and A1c results are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note:Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly that they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in ourDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat Diabetic Sores
Random Blood Sugar Level Chart
Random blood sugar testing is done at any time of the day. This test is done outside the regular testing timetable. It confirms diabetes, during and after the treatment of diabetes. A level of 200 mg/dl or greater indicates diabetes mellitus.
The major objective of an RBS test is to check random blood sugar levels. An Random Blood Sugar range of 200mg/dl or above clearly shows the presence of diabetes. The test helps to timely treat the disease via monitoring during and after treatment. The random blood sugar level test is recommended if an individual complains of the following signs:
- Recurrent urination
How Do You Know What Your Blood Glucose Level Is
For the most part, you cant feel what your blood glucose level is unless its fairly high or its low. You may not even always have symptoms of either high or low blood glucose.
The best way to know your blood glucose level is to check it with a glucose meter. This means doing a fingerstick with a lancet and getting a drop of blood onto a test strip, then inserting the strip into the meter for a reading. Your doctor may be able to give you a meter free of charge, but youll likely need to pay for test strips and lancets. But check with your health plan, as there are likely one or two preferred meters that they want you to use.
Another way to know what your glucose levels are up to is to use a continuous glucose monitor, or CGM, which reads glucose in the interstitial fluid about every 5 minutes. Continuous glucose monitoring is expensive and may or may not be covered by your health plan.
Don’t Miss: What Is Sugar Level For Type 2 Diabetes