Health Problems Linked To Type 2 Diabetes
If your blood sugar is frequently imbalanced, you may be at a greater risk for the following type 2 diabetes complications.
Cardiovascular disease
Diabetic retinopathy In diabetic retinopathy, high blood sugar weakens the capillaries that supply the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the inner eye.
The capillaries then swell, become blocked, or leak blood into the center of the eye, blurring vision. In advanced stages, abnormal new blood vessels grow.
Diabetic neuropathy Neuropathy, or nerve damage, can affect any nerve in your body. Most commonly, it affects the nerves in the feet, legs, hands, and arms this condition is called peripheral neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy can cause tingling, burning, pain, or numbness in the affected areas.
The pain of peripheral neuropathy is difficult to control, though some find topical products that contain capsaicin to be helpful.
Diabetic nephropathy In diabetic nephropathy, the nephrons in the kidneys become damaged from chronic high blood sugar.
High blood pressure compounds the problem, and high cholesterol appears to contribute to it as well.
In the early stages of diabetic nephropathy, you may not notice any symptoms, but standard blood and urine tests can detect early signs of dysfunction, and early treatment can stop or slow its progression.
Diabetic ulcer People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing foot ulcers .
Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Diabetics
The American Diabetes Association recommends that the blood sugar 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal be less than 180 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. This is typically the peak, or highest, blood sugar level in someone with diabetes. Again, this target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their health care provider.
Diet Weight Control And Physical Activity
- Diet. What you eat is absolutely central to your blood glucose control, as well as your general health. Please read our separate leaflet called Type 2 Diabetes Diet for more information. Your practice nurse or dietician can give you more information and support.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Getting to a perfect weight is unrealistic for many people. However, losing some weight if you are obese or overweight will help to reduce your blood glucose and blood pressure levels . Recent evidence from Professor Taylor, Newcastle University, has shown that weight loss alone can put diabetes into drug-free remission in at least a third of patients.
- Do some physical activity regularly. If you are able, a minimum of 30 minutes’ brisk walking at least five times a week is advised. Anything more vigorous and more often is even better – for example, swimming, cycling, jogging, dancing. Ideally, you should do an activity that gets you at least mildly out of breath and mildly sweaty. You can spread the activity over the day – for example, two fifteen-minute spells per day of brisk walking, cycling, dancing, etc. Regular physical activity also reduces your risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
You May Like: Easy To Follow Diabetic Diet
How Should Blood Sugar Levels Be Before And After Eating
Ideally, before eating , your blood sugars should be between 80-130 mg/dL. One to two hours after eating , your blood sugars should be below 180 mg/dL.
Blood glucose levels can be affected by the type of food consumed, how much, and when but also many other different factors like physical activity, taking other medications, having other medical conditions, stress, age, an illness, and even menstrual periods.
You May Like: Can Type 2 Diabetes Make You Tired
Why Test My Blood Glucose
Blood testing is the best way to stay in control of your diabetes because it tells you what is happening at any particular moment. It can help determine if you are at risk of a hypoglycaemic episode or a hyperglycaemic episode . You should never change any long-term medication you are taking in response to a one-off high or low reading. You should first try to work out if there is a pattern before making any changes and always talk to your diabetes care team first.
Also Check: High Blood Levels In Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Can You Lose Weight If You Have Diabetes
Measuring Blood Sugar Levels In A Laboratory
Blood sugar levels can be measured a lot more accurately by taking a blood sample from a vein and having it tested in a laboratory. Blood sugar is sometimes measured as part of a routine blood test in hospital or at the doctors. A special kind of test called a glucose tolerance test involves taking blood samples to see how the body deals with larger amounts of sugar. You have to drink a liquid with a lot of sugar in it before the blood samples are taken.
Most people with diabetes have the HbA1c levels in their blood measured regularly. HbA1c is a measure of how high your blood sugar levels have been on average over the last two to three months This indicates how well controlled your blood sugar is and whether your diabetes treatment might need to be adjusted.
Whats My Target Range
You might be asking, whatâs the normal range for blood sugar levels? The answer is, there is a healthy range that you should ideally be aiming for. The infographics above show the general guidelines, but your individual target range for your blood sugar levels may be different. Youll healthcare team will agree with you what it is.
Youll get different readings at different times of the day, depending on things like what youve eaten and how much you are moving around. Heres a guide to help you get started on finding your target range:
If youre an adult with type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 5 to 7mmol/l
- before meals at other times of the day: 4 to 7mmol/l
If you have type 2 diabetes
- before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- two hours after meals: less than 8.5mmol/l
Don’t Miss: What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Drops To 30
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
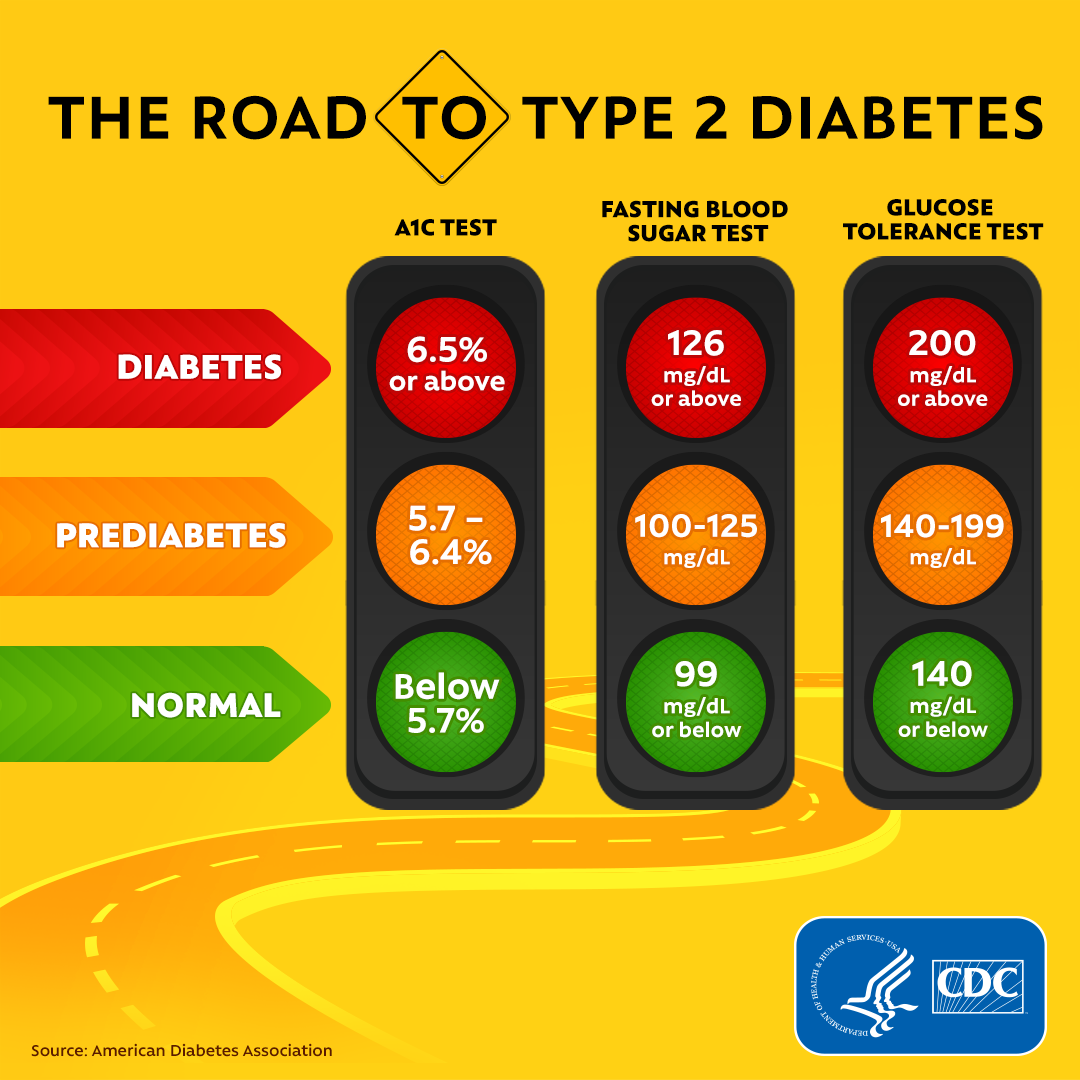
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Below chart displays possible blood sugar levels . Units are expressed in mg/dL and mmol/L respectively. Additional topics: What is diabetes? How do you know if you have diabetes? How to test for diabetes? Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently? Diet for people with diabetes You can also download or print this chart by clicking here. Reference: American Diabetes Association, Additional topics: What is diabetes? How do you know if you have diabetes? How to test for diabetes? What is normal blood sugar level? Why is it important to measure your blood sugar levels frequently? Diet for people with diabetesContinue reading > >
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat Low Blood Sugar
Tests For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. Youll probably be tested between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes , your doctor may test you earlier. Blood sugar thats higher than normal early in your pregnancy may indicate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
Medicines For Type 2 Diabetes
There are many types of diabetes medications and they work in different ways to control blood glucose. If you have diabetes, over time it can change, meaning your medications may need to change too. For example, you may need more than one medication to control your blood glucose levels. Some people with type 2 diabetes may eventually need insulin to manage their condition.
If you are living with type 2 diabetes you can join the National Diabetes Services Scheme for free to access a range of resources, support services and subsidised diabetes products. Visit Diabetes Australia for information and resources.
You May Like: Can Diabetics Get Teeth Implants
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Two hours after a meal.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For People With Type 2 Diabetes
Together with your doctor, you can determine your ideal blood sugar goals for different times throughout the day.
Adults with type 2 diabetes should normally aim for the following typical ranges:
-
Before you eat: 70130 mg/dl
-
After you eat: less than 180 mg/dl
-
At bedtime: 100140 mg/dl
These numbers may differ from person to person, depending on underlying conditions, treatment, and age.
Don’t Miss: Vitamin C For Diabetes Type 2
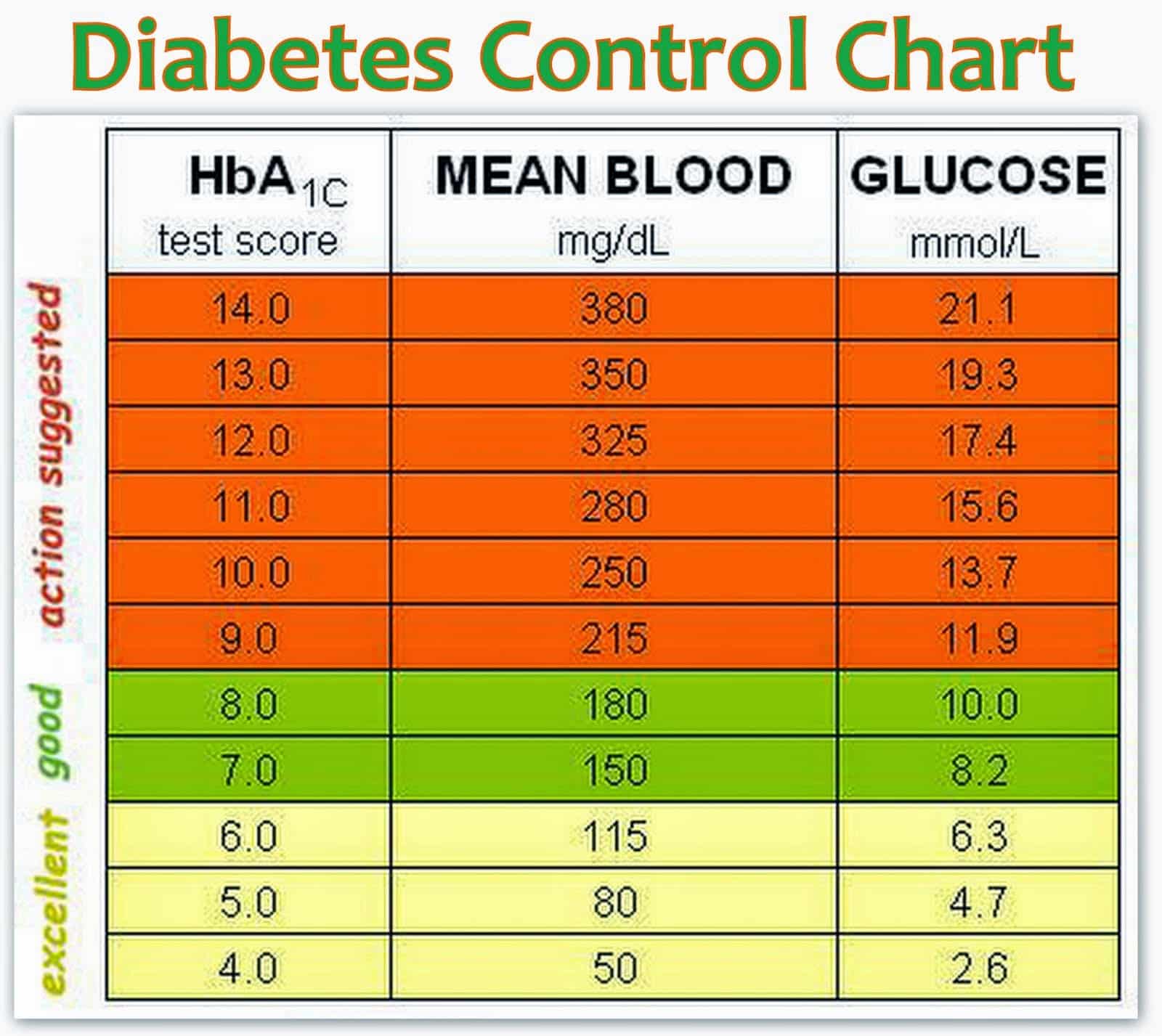
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
Can I Check My Own Blood Sugar
You can do blood sugar level check by doing a finger-prick test, or by using an electronic blood sugar monitor called a flash glucose monitor or CGM. You can do this several times a day helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take. Find out your ideal target range.
Not everyone with diabetes needs to check their levels like this. Youll need to if you take certain diabetes medication. Always talk to your healthcare team if youre not sure whether thats you theyll give you advice on whether to check them yourself and how often.
And theres also something called an HbA1c, which is a blood test to measure your average blood sugar level over the last three months. Everyone with diabetes is entitled to this check.
High blood sugar levels increase your risk of developing serious complications. However you manage your diabetes, stay in the know about your blood sugar levels
Also Check: When Was Type 2 Diabetes Discovered
Lets Crunch Some Numbers
Ill give these numbers to you in a written, chart, and visual format because it will make sense to you depending how you read it.
Depending where you live in the world, numbers can vary slightly. And your numbers will either be mg/dl or mmol/l. Youll find the numbers for both of these readings below.
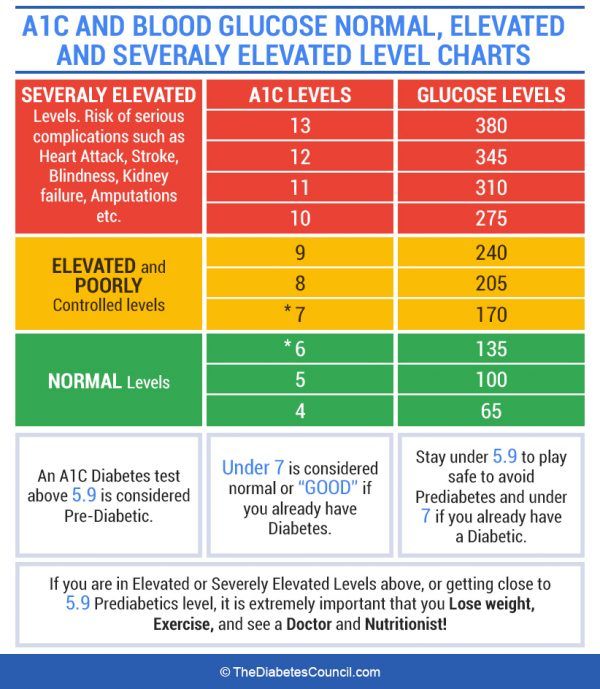
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting glucose 70-99 mg/dl or 4-6 mmol/l
2 hours post meal glucose Less than 140 mg/dl or less than 7.8 mmol/l
Pre-diabetes diagnostic ranges also called impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
Fasting glucose 100-125 mg/dl or 6.1-6.9 mmol/l
2 hours post meal glucose level 140-199 mg/ dl or 7.8-11 mmol/l
Type 2 Diabetes diagnostic ranges
Fasting glucose More than 126 mg/dl or more than 7.0 mmol/l
2 hours glucose level More than 200 mg/dl or more than 11.1 mmol/l
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
A diagnosis of diabetes is usually made when fasting blood sugar is above 126 mg/dL or the A1Cc is above six percent.
If your fasting blood sugar levels are between 100 and 126 mg/dL you can be diagnosed with prediabetes.
Diabetes develops quite quickly and this can cause even higher blood sugar levels and range between 200 mg/dL and 400 mg/dL or above.
If you have any of the following symptoms, it’s important to speak to your doctor:
- Increased urination
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Slow-healing cuts and bruises
A diagnosis of diabetes is a serious matter, but it doesn’t mean your life has to change dramatically. There are many treatments available that can help you manage your condition and live a long, healthy life. Treatment usually involves a combination of medication, diet, and exercise. You’ll work with your healthcare team to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
There are two types of diabetes, type one and type two. Type one diabetes is when the pancreas does not produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to process glucose from food. Type two diabetes is when the body does not use insulin properly. People with either type of diabetes need to control their blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Good Diet For Type 2 Diabetes
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
Blood glucose numbers are measured in milligrams per deciliter .
The American Diabetes Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists have different recommendations for blood glucose targets for most people with type 2 diabetes:
| Timing | ||
| 2 hours after eating a meal | < 180 mg/dL for nonpregnant adults | < 140 mg/dL |
Talk to your doctor to learn more about your blood glucose targets. Your doctor can help you determine which guidelines to target. Or they can work with you to set your own glucose targets.
Managing Blood Glucose Levels
Maintain blood glucose levels within the recommended range. You can help keep your blood glucose levels as near as possible to normal by:
- eating healthily
- losing weight if you are overweight and trying to maintain weight loss
- doing regular physical activity, including sitting less. If you are not sure what type of exercise is suitable for you, check with your doctor.
Glucose-lowering medications, and insulin, may also be needed to manage blood glucose levels.
Blood glucose targets are individualised. However, if you are taking either diabetes tablets that can cause hypos or insulin, the blood glucose levels generally recommended are:
- 6 to 8 mmol/L before meals
- 6 to 10mmol/L 2 hours after meals.
Check with your doctor or diabetes educator about the targets recommended for you.
Keeping your blood glucose levels within the target range can help prevent long-term problems that can affect your heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves.
Read Also: Non Fasting Blood Sugar Level Chart
Preeclampsia And Gestational Hypertension
A population-based, retrospective cohort study of 1,010,068 pregnant women examined the association between preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy and the risk of developing diabetes post partum. Results showed the incidence rate of diabetes per 1000 person-years was 6.47 for women with preeclampsia and 5.26 for those with gestational hypertension, compared with 2.81 in women with neither condition. Risk was further elevated in women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension comorbid with gestational diabetes.
Why Is It So Important To Check My Blood Levels
Regular checking and recording of your blood glucose level can reinforce your healthy lifestyle choices as well as inform you of your response to other choices and influences.
Importantly, blood glucose level pattern changes can alert you and your health care team to a possible need for a change in how your diabetes is being managed.
Recommended Reading: Best Diet For Type One Diabetes
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Will I Need Medication Or Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
Some people take medication to manage diabetes, along with diet and exercise. Your healthcare provider may recommend oral diabetes medications. These are pills or liquids that you take by mouth. For example, a medicine called metformin helps control the amount of glucose your liver produces.
You can also take insulin to help your body use sugar more efficiently. Insulin comes in the following forms:
- Injectable insulin is a shot you give yourself. Most people inject insulin into a fleshy part of their body such as their belly. Injectable insulin is available in a vial or an insulin pen.
- Inhaled insulin is inhaled through your mouth. It is only available in a rapid-acting form.
- Insulin pumps deliver insulin continuously, similar to how a healthy pancreas would. Pumps release insulin into your body through a tiny cannula . Pumps connect to a computerized device that lets you control the dose and frequency of insulin.
Read Also: What Happens When A Diabetic Takes Too Much Insulin