When Is The Glucose Screening Test Taken During Pregnancy
You typically get a glucose screening test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. However, your provider may want you to be screened earlier than 24 weeks if a routine urine test shows a high level of sugar in your urine or if youâre considered high risk. If the results are normal, youâll be screened again at 24 to 28 weeks.
Of course, if you were diagnosed with diabetes before pregnancy, you wonât need to be screened. Instead, youâll continue to work with your provider to manage your condition during pregnancy.
Donât Miss: What Is Early Onset Diabetes
What Makes You A High
If you may be at high risk for gestational diabetes , your healthcare provider may also consider certain aspects of your medical history.The provider may take into account your pre-pregnancy weight , your age, whether anyone in your family has had gestational diabetes or diabetes, your race or ethnic background , and outcomes of any previous pregnancies.Speak to your healthcare provider to find out whether you have a high risk or low risk of developing gestational diabetes. If the provider determines your risk is low, you may not have to take the glucose challenge test.
Graphic Portrayal Of Data And Weighted Averages
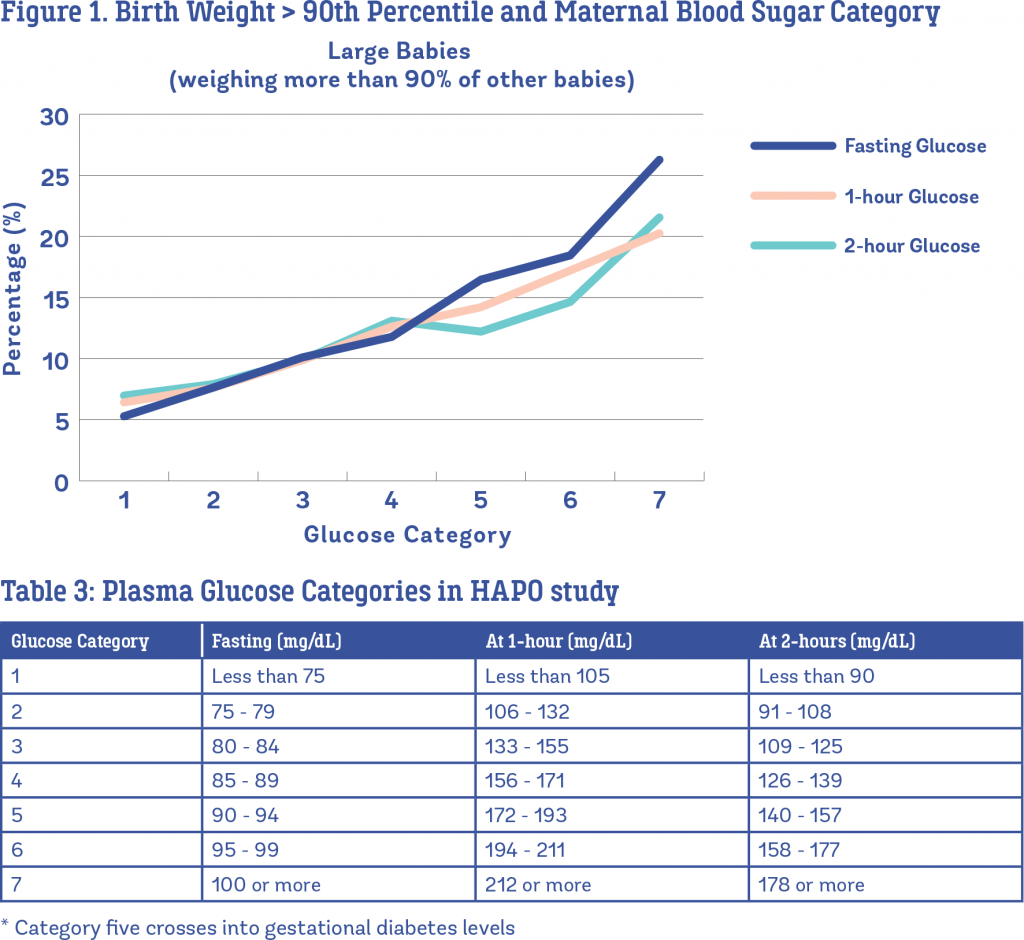
Exact data were plotted as reported in text or tables by the original authors. When data were only shown in figures, the mean and variance were taken from the graphs. In some cases, complete patterns of glycemia were not reported between meals. For graphic purposes, if a premeal value was not reported, the 24-h mean was used as the between-meal glucose concentration. In the graphs, postprandial spikes are 1 h and 2 h after a meal as reported.
Because test statistics were not uniformly reported and methodologies for measuring glucose concentrations were variable, a formal meta-analysis was not possible. Thus, this is a pooled analysis of 12 studies that met our inclusion criteria. Weighted means and SDs were calculated as the product of the mean reported value and sample size for each study. The sum of the products across studies was then calculated and divided by the total number of study participants. In addition, mean 1- and 2-h PP glucose concentrations were calculated across three meals . Data are presented as weighted mean ± SD.
Don’t Miss: Skin Conditions Related To Diabetes
How Does Gestational Diabetes Affect Pregnancy
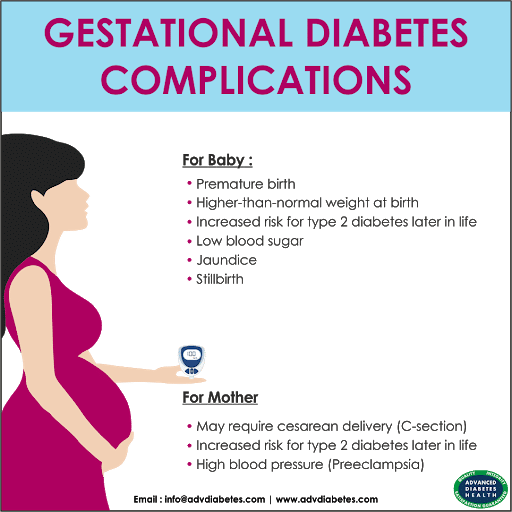
If left untreated, the high blood sugar levels associated with gestational diabetes can lead to various issues during pregnancy, such as:
-
Giving birth to a large baby , increasing the risk of injury during birth for both the baby and the mother. The chances of requiring a Caesarean section also increase at high birth weights.
-
Increased risk of miscarriage, birth defects, and stillbirths.
-
High blood pressure, which can harm both long-term and short-term health.
-
Preeclampsia, a rare complication characterized by high blood pressure with possible kidney or liver damage.
Fasting Vs Nonfasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood sugar is a test that measures blood sugar and is used to determine if an individual has diabetes. When a person takes this test, they cannot eat or drink for at least eight hours prior to the test. The results determine whether a person is prediabetic or diabetic.
The results are measured in milligrams per deciliter, or mg/dL. The following results indicate whether a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
To test nonfasting blood sugar, an A1C test is administered to determine the average blood sugar level of an individual over a period of two to three months. The following results indicate whether a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
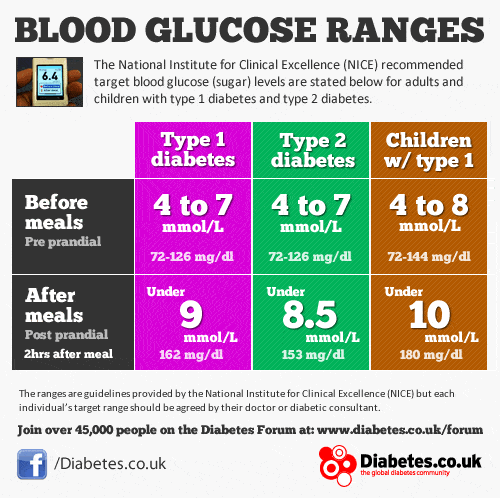
Blood sugar levels among people with type 1 diabetes should be:
- Before meals: From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
- At bedtime: From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
Blood sugar levels among people with type 2 diabetes should be:
- Before meals: From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
- At bedtime: From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
Don’t Miss: How To Check For Type 2 Diabetes At Home
How Can My Diabetes Affect Me During Pregnancy
Hormonal and other changes in your body during pregnancy affect your blood glucose levels, so you might need to change how you manage your diabetes. Even if youve had diabetes for years, you may need to change your meal plan, physical activity routine, and medicines. If you have been taking an oral diabetes medicine, you may need to switch to insulin. As you get closer to your due date, your management plan might change again.
Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms.
Most cases are only discovered when your blood sugar levels are tested during screening for gestational diabetes.
Some women may develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels gets too high , such as:
- needing to pee more often than usual
But some of these symptoms are common during pregnancy and are not necessarily a sign of gestational diabetes. Speak to your midwife or doctor if you’re worried about any symptoms you’re experiencing.
Read Also: Normal Blood Sugar For Gestational Diabetes
Risks And Possible Complications
There are numerous risks when gestational diabetes is not properly controlled and blood glucose levels remain high.
For the mother:
- Excess amniotic fluid, increases the risk of premature birth
- Risk of caesarean section or a more difficult vaginal birth
- Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia
- Higher risk of staying diabetic after the birth or of developing type 2 diabetes in the future .
For the baby:
- Bigger than normal at birth
- Hypoglycemia at birth
- Risk of the babys shoulders getting stuck in the birth canal during the birth
- Risk of obesity and glucose intolerance in early adulthood
Slight risk of:
- Jaundice, especially if the baby is premature
- Lack of calcium in the blood
- Breathing problems
Proper diabetes control considerably reduces the risks of complications.
What Happens During The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The oral glucose tolerance test involves quickly drinking a sweetened liquid , which contains 50g of glucose. The body absorbs this glucose rapidly, causing blood glucose levels to rise within 30 to 60 minutes. A blood sample will be taken from a vein in your arm about 60 minutes after drinking the solution. The blood test measures how the glucose solution was metabolized .
Read Also: Healthy Meal Prep For Diabetics
What Happens If You Fail The 3 Hour Glucose Test
If you fail the 3-hour glucose test, you have impaired glucose tolerance and you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
A failing score is considered when you have 2 or more values in these ranges:
- Fasting > 95mg/dL
- 2 Hour > 155 mg/dL
- 3 Hour > 140 mg/dL
This is a very serious condition that requires very close monitoring of your blood sugar levels every single day.
If you dont, you are putting your own life and your babys life at risk.
You will meet with a nutritionist to learn how to improve your diet, and you will have to check your finger stick blood glucose 4 times a day for the remainder of the pregnancy.
Basis For The Currently Recommended Therapeutic Targets
The current clinical recommendations for treatment targets in pregnancies complicated by diabetes are not uniform internationally or primarily based on the studies listed in Table 1. Although the therapeutic targets were chosen to attenuate the risk for fetal macrosomia, they have never been prospectively tested compared with lower targets . Even when current glucose targets are achieved in the pregnancy affected by diabetes, macrosomia still occurs and in utero programming may have a lasting metabolic impact on the offspring .
Don’t Miss: Dosage Of Berberine For Type 2 Diabetes
Oral Gtt In Pregnancy
Oral GTTs are commonly used to screen women for gestational diabetes. There is a strong correlation between increasing maternal glucose levels at 2432 weeks gestation and a range of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes. Several different strategies are used worldwide in the screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association offers two approaches to gestational diabetes screening a one-step approach with a single 2 hour 75 g OGTT, or a two-step approach with a 1 hour 50 g screening OGTT followed by a confirmatory 3 hour 100 g OGTT in patients who screen positive.
The Australian Diabetes in Pregnancy Society Consensus Guidelines for the Testing and Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Australia recommend early testing for gestational diabetes mellitus in women with risk factors, in a tiered approach to early glucose testing.
Moderate risk factors include the following:
-
Ethnicity: Asian, Indian subcontinent, Aboriginal, Torres Strait Islander, Pacific Islander, Maori, Middle Eastern, nonwhite African
-
Body mass index of 2535 kg/m2
High risk factors include the following:
-
Previous gestational diabetes mellitus
Contributor Information and Disclosures
Jiun-Lih Jerry Lin, MBBS, MS Clinical Associate Lecturer, MD Program Research Supervisor, Sydney Medical School, University of Sydney Orthopaedic Registrar, Mona Vale Hospital, AustraliaDisclosure: Nothing to disclose.
The GTT procedure is as follows
Urgent Advice: Contact Your Diabetes Team Straight Away If:
- you find out you’re pregnant
You’ll need to make an urgent appointment.
Keeping your blood glucose levels stable can be more difficult in early pregnancy as your hormones change, especially if you have morning sickness. Low blood sugars can happen more easily. It is important to check your blood glucose often. Carry hypo treatment with you in case your blood glucose goes too low.
You’ll have extra appointments with your maternity and diabetes teams when you’re pregnant. This usually means check-ups every 2 weeks, as well as extra tests and scans.
You can have a normal birth, but it’s recommended you have your baby in hospital. You might be advised to have your labour started early .
Don’t Miss: Does Medicare Cover Diabetic Testing Supplies
Will I Get Type 2 Diabetes
Because you had gestational diabetes, you have a greater chance of having type 2 diabetes. But it wonât definitely happen, and you can take action to prevent that.
Your blood sugar levels will likely return to normal about 6 weeks after childbirth. If it does, you should get follow-up tests every 3 years.
To lower your risk:
- Try to keep your weight in a healthy range. Not sure what that is? Ask your doctor.
- Eat a good diet that includes lots of vegetables, whole grains, fruits, and lean protein.
- Make exercise a habit.
If you plan to have another baby, keep in mind that you are more likely to get gestational diabetes again. Ask your doctor if there are any lifestyle changes that would help you avoid that.
Show Sources
Sugar Level During Pregnancy What’s Normal
The form of diabetes which develops during pregnancy is known as gestational diabetes. This condition has become predominant in the recent pastaccording to the 2009 article in American Family Physician. For instance, in the United States alone, it affects around 5% to 9% of all the pregnant women. Pregnancy aggravates the preexisting type 2 and type 1 diabetes. During pregnancy the sugar level may tend to be high sometimes, posing problems to the mother and the infant as well. However, concerning the sugar level during pregnancy, what’s normal? Blood sugar control is one of the most essential factors that should be undertaken during pregnancy. When measures are taken to control blood sugar level during pregnancy, it increases chances of a successful pregnancy.
Also Check: What Is Type Ii Diabetes
Timing And Route Of Delivery
In gestational diabetes, shoulder dystocia is the complication most anticipated at the time of delivery. In one study,36 this complication occurred in 31 percent of neonates weighing more than 4,000 g who were delivered vaginally to unclassified mothers with diabetes. No prospective data support the use of cesarean delivery to avoid birth trauma in women who have gestational diabetes. One remaining limiting factor is the 13 percent error rate in estimating fetal weight by ultrasonography.37
A decision analysis38 that evaluated the cost and efficacy of a policy of elective cesarean delivery for an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g in mothers with diabetes found that 443 cesarean deliveries would need to be performed to prevent one case of brachial plexus injury, at a cost of $930,000. A reasonable approach is to offer elective cesarean delivery to the patient with gestational diabetes and an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g or more, based on the patient’s history and pelvimetry, and the patient and physician’s discussion about the risks and benefits. There are no indications to pursue delivery before 40 weeks of gestation in patients with good glycemic control unless other maternal or fetal indications are present.
New Thresholds For Diagnosis Of Diabetes In Pregnancy
Midwives should diagnose women with gestational diabetes if they either have a fasting plasma glucose level of 5.6 mmol/litre or above, or a 2-hour plasma glucose level of 7.8 mmol/litre or above, according to NICE.
24 February 2015
Midwives should diagnose women with gestational diabetes if they either have a fasting plasma glucose level of 5.6 mmol/litre or above, or a 2-hour plasma glucose level of 7.8 mmol/litre or above, according to NICE.
on diabetes in pregnancy lower the fasting plasma glucose thresholds for diagnosis, and include new recommendations on self-management for women with type 1 diabetes.
Around 35,000 women have either pre-existing or gestational diabetes each year in England and Wales.
Nearly 90 per cent of the women who have diabetes during pregnancy, have gestational diabetes, which may or may not resolve after pregnancy. Rates have increased in recent years to due rising obesity rates among the general population, and increasing number of pregnancies among older women.
Of the women with diabetes in pregnancy who do not have gestational diabetes, 7.5 per cent of women have type 1 diabetes, and the remainder have type 2 diabetes, both of which have also increased recently.
Following a number of developments, such as new technologies and research on diagnosis and treatment of gestational diabetes, NICE has updated its guidelines on diabetes in pregnancy.
Also Check: Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Eat Mac And Cheese
How To Pass The 3 Hour Glucose Tolerance Test
Just like the 1 hour glucose test, there isnt any special way to ensure that you pass the 3 hour oral glucose tolerance test aka the ogtt.
Your best bet is to eat a well-balanced diet leading up to the test and minimize the consumption of simple carbs like cereal, white flour, juice, and soda.
Making these changes the night before or the week before is unlikely to make a big difference. You should make these changes months in advance.
Its also a good idea to try and maintain these habits postpartum as well. Unfortunately, 60% of women with gestational diabetes will develop Type 2 diabetes later in life.
The Night Before The Test
Do not eat or drink anything other than plain water from 10pm the evening before your test. This includes not eating mints, chewing gum and medication for heart burn.
Please note that if you forget and you eat something in the morning, it is important that you contact the antenatal clinic as your test will have to be rearranged.
You May Like: How To Check Blood Sugar At Home Naturally
Understanding Your Glucose Challenge Screening Results
There are some standard benchmark numbers used to separate those considered at low-risk for gestational diabetes from those who need to graduate to the three-hour blood glucose tolerance test. So whats the one-hour glucose test normal range? According to the Mayo Clinic:
- Blood sugar level below 140 mg/dL is normal and considered passing.
- Blood sugar level between 140 mg/dL and 190 mg/dL is elevated, and requires the follow-up three-hour glucose tolerance test to confirm gestational diabetes
- Blood sugar level of 190 mg/dL or higher indicates gestational diabetes. Your doctor will advise about the need for repeat or secondary testing. When results are this high, though, they may skip this step altogether and begin monitoring and treatment
Dont panic if your doctor or midwife informs you that your one-hour glucose test number comes back elevated . It doesnt necessarily mean you have gestational diabetes. This is just a screening test, and nearly 25 percent of patients fail this initial test, says Pope. A confirmatory three-hour glucose test is next.
Hemoglobin A1c Levels Normal Range
In most labs, the normal range for hemoglobin A1c is 4% to 5.9%. In well-controlled diabetic patients, hemoglobin A1c levels are less than 7.0%. In poorly controlled diabetes, its level is 8.0% or above. The benefits of measuring hemoglobin A1c is that is gives a more reasonable view of whats happening over the course of time to the.
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetes And Kidney Failure
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
Normal Fasting Plasma Glucose Levels During Pregnancy: A Hospital
Abstract Recently, the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups have suggested new criteria for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes including a fasting glucose level of 92 mg/dL. We determined reference levels for normal fasting plasma glucose levels throughout pregnancy and evaluated the new normal cut-off for fasting glucose level. Charts of patients who delivered in our hospital between June 2001 and June 2006 were reviewed. Women with pregestational diabetes, fasting glucose level > 105 mg/dL or delivery at < 24 weeks were excluded. Fasting glucose levels were assessed in 11 time categories between three months prior and four months postpartum in 7946 women. Compared to preconception levels, fasting glucose levels decreased by a median of 3 mg/dL in the first trimester . During the third trimester a slight further glucose reduction was observed . After delivery fasting glucose levels increased sharply . Throughout pregnancy 5.2-9.0% of pregnant women had a fasting glucose level of 92 mg/dL . Fasting glucose levels decrease early in pregnancy with only slight further decrease later on. It seems that the same fasting glucose cut-off can be used throughout pregnancy for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Discover the world’s research 14+ million members 100+ million publications 700k+ research projects Join for freeContinue reading > >
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Diabetes Is Affecting Your Feet