Medicines For Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition and usually gets worse over time. Making lifestyle changes, such as adjusting your diet and taking more exercise, may help you control your blood glucose levels at first, but may not be enough in the long term.
You may eventually need to take medication to help control your blood glucose levels.
Initially, this will usually be in the form of tablets and can sometimes be a combination of more than one type of tablet. It may also include insulin or another medication that you inject.
Heart Disease And Stroke
High levels of blood glucose can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. This damage can cause a person to develop heart disease and can increase their chances of having a stroke.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , people with diabetes commonly develop heart disease at younger ages than people without diabetes.
The NIDDK also states that adults with diabetes are almost two times more likely to have heart disease or a stroke than adults without diabetes.
Diabetes And Brain Health
If you have diabetes, your doctor may screen you for depression or cognitive impairment. Older adults with diabetes are at higher risk for these conditions, compared with others their age who do not have diabetes. Having depression or cognitive impairment can make diabetes self-care challenging.
Your diabetes management plan will cover how to:
- Track your glucose levels. Very high glucose levels or very low glucose levels can be risky to your health. Your plan will show how often you should check your glucose and how often to get the A1C test. If you are managing your diabetes without taking insulin, you may not need to check your glucose as often.
- Make healthy food choices. The food you eat affects glucose levels, so its important to learn whats best for you to eat, how much, and when. If you are overweight, work with your health care team to come up with a plan to lose weight.
- Be active. Walking and other forms of daily exercise can help improve glucose levels in older people with diabetes. Set a goal to be more active most days of the week, and create a plan for being physically active that fits into your life and that you can follow. Your health care team can help.
- Take your medicines. You should take medicine as prescribed even when you feel good. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects or cannot afford your medicines. Also, let your doctor know if you have trouble taking your medicine or keeping track of your medication schedule.
Also Check: How Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Treated
The Disease Can Impact Your Emotions
A 2016 study published in the Journal of Medicine and Life showed that people living with diabetes are significantly more prone to depression than those without the disease. And that may be because of the frustrations that come with the disease.
“It’s totally okay to get frustrated and mad sometimes because of diabetes,” wrote patient Amber Rueger in a blog post for Medtronic. “Have a good cry. Tell diabetes to go where the sun doesn’t shine. We are human. Don’t let people make you feel bad because you get upset over diabetes at times. When that sadness and frustration is the dominant theme in your diabetes care is when those feelings become unhealthy.”
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
You’ll be given a special sweetened drink prior to this blood test. A test result of 11.1 mmol/L or greater taken two hours after having the sweet drink indicates diabetes.
A second test must be done in all cases . Once diabetes has been diagnosed, ask your doctor to refer you for diabetes education. Diabetes Canada also has many resources to help you understand diabetes better and live a long and healthy life. Being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and managing the disease is not easy. But it is important to know that you can live a long and healthy life by taking a number of steps including keeping your blood sugar levels in target range.
You May Like: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
People With Type 1 Diabetes Are Living Longer
- By Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing
Better blood sugar control may be the key to longer survival
Ninety years ago, type 1 diabetes was a death sentence: half of people who developed it died within two years more than 90% were dead within five years. Thanks to the introduction of insulin therapy in 1922, and numerous advances since then, many people with type 1 diabetes now live into their 50s and beyond. But survival in this group still falls short of that among people without diabetes.
A Scottish study published this week in JAMA shows that at the age of 20, individuals with type 1 diabetes on average lived 12 fewer years than 20-year-olds without it. A second study in the same issue of JAMA showed that people with type 1 diabetes with better blood sugar control lived longer than those with poorer blood sugar control.
Reasons To Stop Type 2 Diabetes In Its Tracks
If you have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, managing your disease effectively is one of the most important things you can do. When uncontrolled, this progressive disease devastates most of the body’s systems as time goes on. If it’s left unchecked or poorly managed, type 2 diabetes will not only negatively impact your health but significantly reduce your quality of life and life expectancy.
Don’t Miss: Managing Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies
Having Diabetes Makes You Much More Organized
Between checking your blood sugar and keeping track of all your medications and supplies, living with diabetes forces you to become more organized. You’re also far more in tune with your body, seeing as you have to think about what you’re doing and eating and how it will affect your blood sugar at all times.
Prediabetes Flies Under The Radar
You can have prediabetes for years but have no clear symptoms, so it often goes undetected until serious health problems show up. Thats why its important to talk to your doctor about getting your blood sugar tested if you have any of the risk factors for prediabetes, which include:
- Being overweight
- Being 45 years or older
- Having a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes
- Being physically active less than 3 times a week
- Ever having gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds
Race and ethnicity are also a factor: African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, American Indians, Pacific Islanders, and some Asian Americans are at higher risk.
Ready to find out your risk? Take the 1-minute prediabetes risk test and be sure to share the results with your doctor.
Read Also: Where To Get Diabetic Test Strips
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, treatment, and complications from type 2 diabetes may vary from person to person. The following information will help you learn more about this disease and provide you with helpful tools, assessments and resources.
-
If left untreated or improperly managed, diabetes can lead to a variety of life-threatening complications.
Support To Help You Thrive
If youve been recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it can come as a shockleaving you feeling frustrated, confused, and needing help navigating your diabetes journey. But the American Diabetes Association® has your back!
Thats why we created the Living With Type 2 Diabetes program. This program is designed to help you learn about type 2 diabetes, discover diabetes management techniques, and so much more.
Join us for this free 12-month programavailable in English and Spanishthat will help you get your diabetes under control so you can live a long and healthy life.
Our Living With Type 2 Diabetes program provides:
- Six e-booklets, each with a topic aimed to meet you where you are after diagnosis. E-booklet topics include:
- Staying on track
Plus, if you submit your phone number when you sign up, youll receive an invitation to participate in the monthly Ask the Experts Q& A series , where you can:
- Ask diabetes-related questions to American Diabetes Association experts
- Receive giveaways to help thrive with diabetes
- Learn the link between diabetes and heart health
Ready to join?
Don’t Miss: Is Diabetes A Metabolic Disorder
Ways Your Life Changes After A Diabetes Diagnosis
While a diagnosis of diabetes can be life-altering, it isnt a death sentence. After all, statistics show that 30.3 million Americans, or 9.4% of the population, currently have diabetes. And with 84.1 million Americans considered prediabetic, the burden of managing diabetes definitely isnt lonely.
At Walker Family Care, weve put together some information about ways your life may change after a diabetes diagnosis.
This diagnosis is easier to handle when youre working with a trained and knowledgeable physician. At Walker Family Care, Rogers Walker, MD, and the rest of our team are here to help you navigate this disease. With a focus on compassionate care, Dr. Walker helps you control your diabetes and live as normal a life as possible.
Sexual Function And Diabetes

Reduced blood supply and nerve damage can affect sexual function. Erectile dysfunction in men is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. This is a common problem for men of all ages and is more common in men with diabetes. Erectile dysfunction is not a disease, but a symptom of some other problem physical, psychological or a mixture of both. Most cases of erectile dysfunction are physical, such as nerve or blood vessel damage. In women, sexual dysfunction is also reported, although there is a lack of research in this area. It is difficult to know whether this is directly related to hormonal changes such as menopause, or to diabetes.It is important to seek help from your doctor, diabetes educator or organisations such as Healthy Male Andrology Australia.
You May Like: How To Tell If Your Child Has Type 1 Diabetes
Mental Health And Diabetes
Living with and managing either type 1 or type 2 diabetes can lead to stress, anxiety and depression. This can affect your blood glucose levels and how you manage your diabetes in general. Over time, this can affect your health.It is important to talk to your doctor if you are going through times of stress, depression or anxiety. Your doctor can refer you to a counsellor or psychologist by providing a diabetes mental health plan. This is Medicare rebated.Other help is available, including:
- online resources
Advances In Diabetes Care
Improvements in life expectancy with diabetes could be due, in part, to more accurate information on death rates and causes of death. However, diabetes treatment and management is continuing to improve in many ways including:
-
More effective medications including injectable insulin, intensive insulin therapy , inhaled insulin, and oral medications to help regulate insulin and blood glucose.
-
Easier-to-use blood glucose monitoring tools including less painful lancing devices and continuous glucose monitoring.
-
More support for self-management from professionalssuch as certified diabetes educators and nurse educators experienced in training patients to effectively self-manage diabetes.
You May Like: What Is Type Ii Diabetes
Your Weight Has Nothing To Do With How You Manage Type 1
ae0fcc31ae342fd3a1346ebb1f342fcb
Because type 2 diabetes is so closely linked to obesity, people often wrongly assume that type 1 diabetes must also be linked to a person’s weightbut that’s not the case. For people with type 1 diabetes, no amount of weight loss or weight gain will have any effect on the severity of the disease.
Can You Die From Diabetes Type 1 And Type 2 Life Expectancy
Diabetes is a disease which is caused either due to the lack of proper production of insulin by the pancreas or due to the improper use of insulin in the human body. This gives rise to the blood sugar level or the glucose level in the body as it is the hormone insulin which is responsible for the breakdown of the carbohydrates and the other essential nutrients in the food to release the much-needed energy by the cells. It is a disease which adversely affects the primary function of metabolism in the body thereby exposing our body to several other complications.
Diabetes affects different people in different manners and as such, it takes several forms. The most common type of diabetes is type 1 and type 2 diabetes. There are various factors and causes which contribute to each type and form of the disease.
Due to the several complications that are associated with this condition, diabetes is often considered a deadly disease that can kill you. It is not uncommon to hear of people who have died of diabetes in the past few years. In this article, we shall further deep dive into the various issues that diabetes accompanies and might lead to the death of the diabetic patient.
Don’t Miss: How To Cook Potatoes For Diabetics
The Importance Of Preventing Diabetes Progression And Heart Disease
What’s important to remember, in the absence of cardiovascular disease, is life expectancy is going to depend on the progression of diabetes, Rinker says. This means its important to eat well, exercise, and take medicine if recommended by your doctor.
Equally crucial, be sure to prevent or manage any additional conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or chronic inflammation. When a person is diagnosed with diabetes, their healthcare provider will require them to be examined for heart disease and take care to reduce their risk of developing it in the future. To that end, a diabetes diagnosis can be the first step to managing or reversing more life-threatening conditions, potentially leading to a longer life.
To someone who is depressed about the diagnosis of diabetes, I’ll say, This disease is going to make you do things you should be doing anyway. You should be eating well and exercising anyway. It might actually prolong their lives because theyll be doing things they wouldn’t have done before the diagnosis, Dr. Munshi says.
For some people, these measures can have incredible benefits: A report published in September 2017 in the British Medical Journal suggested maintaining a healthy weight and lowering blood glucose levels may even help reverse type 2 diabetes.
Managing Carbohydrates Becomes A Fixture In Your Life
Your body processes carbs as blood glucose. But some carbs are processed more quickly than others. As a diabetic, you learn which foods contain fast carbs and which contain slow carbs. For example, your body processes sugars found in bread and sweet treats quicker than the carbs found in fruits and vegetables.
Read Also: What Does Type 1 Diabetes Do
Treatment For Low Blood Glucose
If you have type 2 diabetes that’s controlled using insulin or certain types of tablets , you may experience episodes of hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia is where your blood glucose levels become very low.
Mild hypoglycaemia can make you feel shaky, weak and hungry, but it can usually be controlled by eating or drinking something sugary.
If you have a hypo, you should initially have a form of carbohydrate that will act quickly, such as a sugary drink or glucose tablets.
This should be followed by a longer-acting carbohydrate, such as a cereal bar, sandwich or piece of fruit.
In most cases, these measures will be enough to raise your blood glucose level to normal. You should aim for a hypo to be treated and to recheck your blood glucose level within 15 minutes.
If blood glucose still less than 4mmol/l then repeat the treatment using a fast acting carbohydrate. When your blood glucose returns to normal then have your longer acting carbohydrate.
If you develop severe hypoglycaemia, you may become drowsy and confused, and you may even lose consciousness.
If this occurs, you may need to have an injection of glucagon into your muscle or glucose into a vein. Glucagon is a hormone that quickly increases your blood glucose levels.
You may require input from a health care professional. If the glucagon is not successful, you may require an injection of dextrose into your vein.
Your diabetes care team can advise you on how to avoid a hypo and what to do if you have one.
Cholesterol And Triglyceride Tests
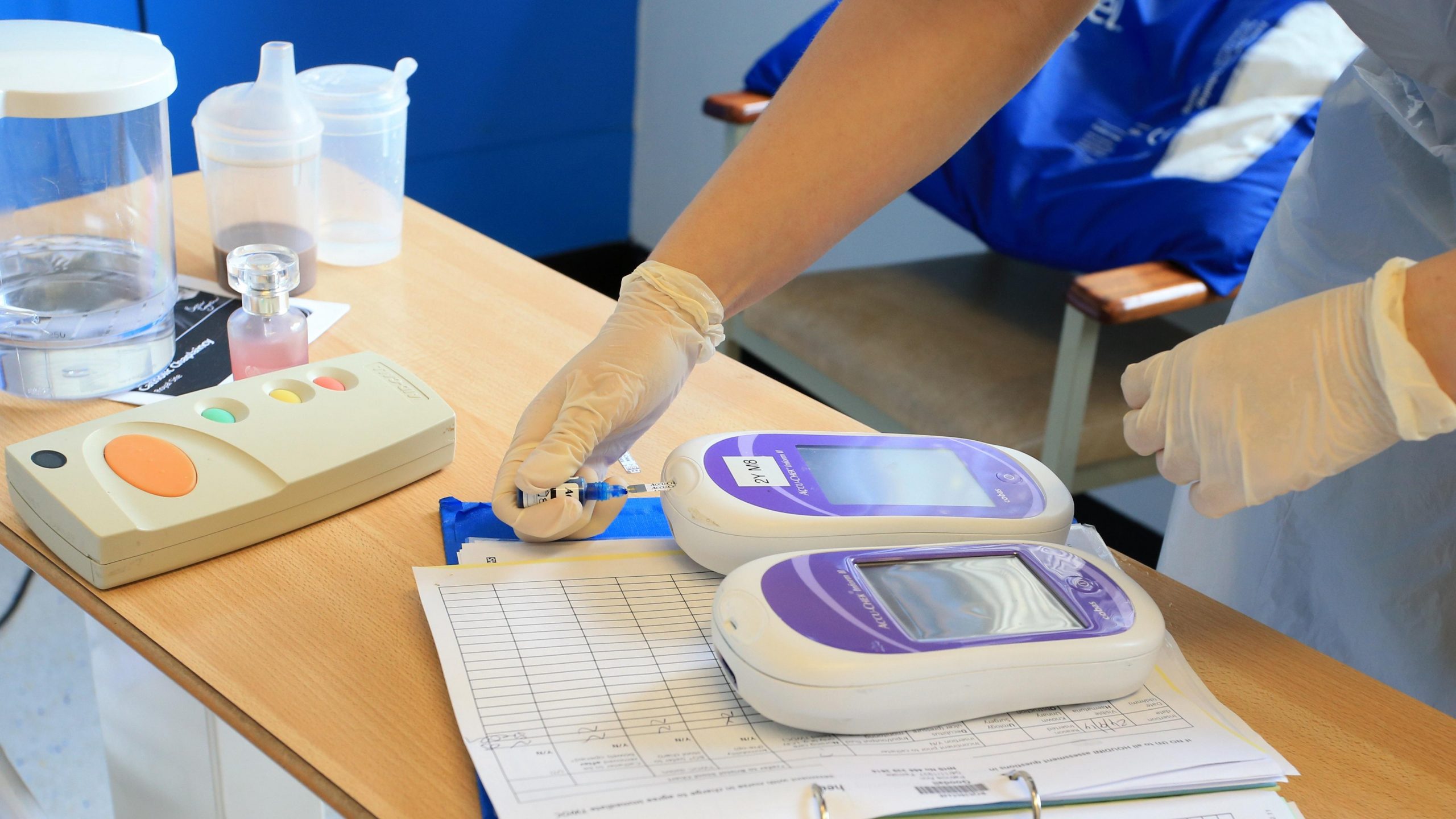

Have a cholesterol and triglyceride test at least once a year. Aim for total cholesterol less than 4.0 mmol/L and triglycerides less than 2.0 mmol/L.
There are a number of causes of high cholesterol, including your family history and your diet. Too much saturated fat in your diet can increase the LDL cholesterol in your blood and result in the build-up of plaque in your blood vessels.
Foods high in saturated fats include full-fat dairy products, fatty meats, pastries, biscuits, cakes, coconut cream or coconut milk, palm oil and fatty take-away foods.
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes And Kidney Failure
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes include feeling very thirsty, passing more urine than usual, and feeling tired all the time.
The symptoms occur because some or all of the glucose stays in your blood and isn’t used as fuel for energy. Your body tries to get rid of the excess glucose in your urine.
The main symptoms of type 2 diabetes are:
- urinating more often than usual, particularly at night
- itchiness around the genital area, or regular bouts of thrush
- cuts or wounds that heal slowly
- blurred vision caused by the lens of the eye becoming dry
The signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes are usually obvious and develop very quickly, often over a few weeks.
These signs and symptoms aren’t always as obvious, however, and it’s often diagnosed during a routine check-up.
This is because they are often mild and develop gradually over a number of years. This means you may have type 2 diabetes for many years without realising it.
Early diagnosis and treatment for type 2 diabetes is very important as it may reduce your risk of developing complications later on.