From Innate To Adaptive Immunity In T2dm
Experimental animal models of insulin resistance have demonstrated a Th2/Th1 shift in favour of Th1, shifting the Treg/Th17 shift towards Th17 and shifting the CD8/CD4 ratio in favour of CD8 and finally reduction of T-cell receptor diversity. These studies have recently been extrapolated to human subjects and confirm the observation that an increase pro-inflammatory stimuli causing M1 phenotype switching of adipose tissue macrophages result in the activation of a Th1 type response. IFN- and IL-17 produced by these T cell populations interact directly with adipocytes in addition to contributing to a pro-inflammatory loop in cells of innate immunity. IFN- inhibits the JAK-STAT pathway, and IL-17 induces the secretion of IL-6 from adipocytes. -cells isolated from T2D patients exhibit increased IL-8 and decreased IL-10 secretion. Recent studies regard the contribution of B-cell humoral immunity in adipose tissue inflammation. A study on experimental mice models involving B-cell knockout mice and anti-CD20 therapy showed a significantly improved metabolic phenotype and adipose tissue inflammation.
What Causes Metabolic Disorders
You can develop a metabolic disorder if certain organs for instance, the pancreas or the liver stop functioning properly. These kinds of disorders can be a result of genetics, a deficiency in a certain hormone or enzyme, consuming too much of certain foods, or a number of other factors.
There are hundreds of genetic metabolic disorders caused by mutations of single genes. These mutations can be passed down through generations of families. According to the
Diabetes is the most common metabolic disease. There are two types of diabetes:
- Type 1, the cause of which is unknown, although there can be a genetic factor.
- Type 2, which can be acquired, or potentially caused by genetic factors as well.
According to the American Diabetes Association, 30.3 million children and adults, or about 9.4 percent of the U.S. population have diabetes.
In type 1 diabetes, the T cells attack and kill beta cells in the pancreas, the cells that produce insulin. Over time, a lack of insulin can cause:
- nerve and kidney damage
- eyesight impairment
- increased risk of heart and vascular disease
Hundreds of inborn errors in metabolism have been identified, and most are extremely rare. However, its estimated that IEM collectively affects 1 in every 1,000 infants. Many of these disorders can only be treated by limiting dietary intake of the substance or substances the body cannot process.
The more common types of nutritional and metabolic disorders include:
What Is The Link Between Diabetes And Metabolic Syndrome
January 15, 2018 by Diabetes Care
Have you ever heard your doctor refer to the term metabolic syndrome? Are you unsure what it is, or how it relates to diabetes? This article will discuss everything you need to know about diabetes and metabolic syndrome including causes, risks, symptoms and prevention.
Read Also: Do I Have Type 2 Diabetes
Triggering Of The Innate Immune System In T2d
Both TLR-dependent and TLR-independent mechanisms function in concert. This finding is demonstrated by animal models of diabetes in which there is partly protection of pro-inflammatory cytokine production in case of deficiency of TLR2 or TLR4, whereas deficiency of a universal intracellular docking protein MyD88 required for TLR signalling, exerted total protection. Apart from FFAs, systemic inflammatory responses are also elicited by elevated glucose levels. Sustained hyperglycemia results in non-enzymatic glycation of lipids and proteins resulting in the formation of AGEs. AGEs stimulate the pattern recognition receptor RAGE. Numerous cell types, like macrophages, T cells, smooth muscle cells, neuronal cells, podocytes and cardiomyocytes, express RAGE. RAGE activates the pleiotropic pro-inflammatory transcription factor NF-B along with stress kinases ERK1 and ERK2. Excessive glucose metabolized by oxidative phosphorylation to ATP results in ROS generation that tends to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome concomitantly with FFAs. This results in release of active IL-1 along with IL-1-dependent cytokine and chemokine production.
Whats The Difference Between Pre
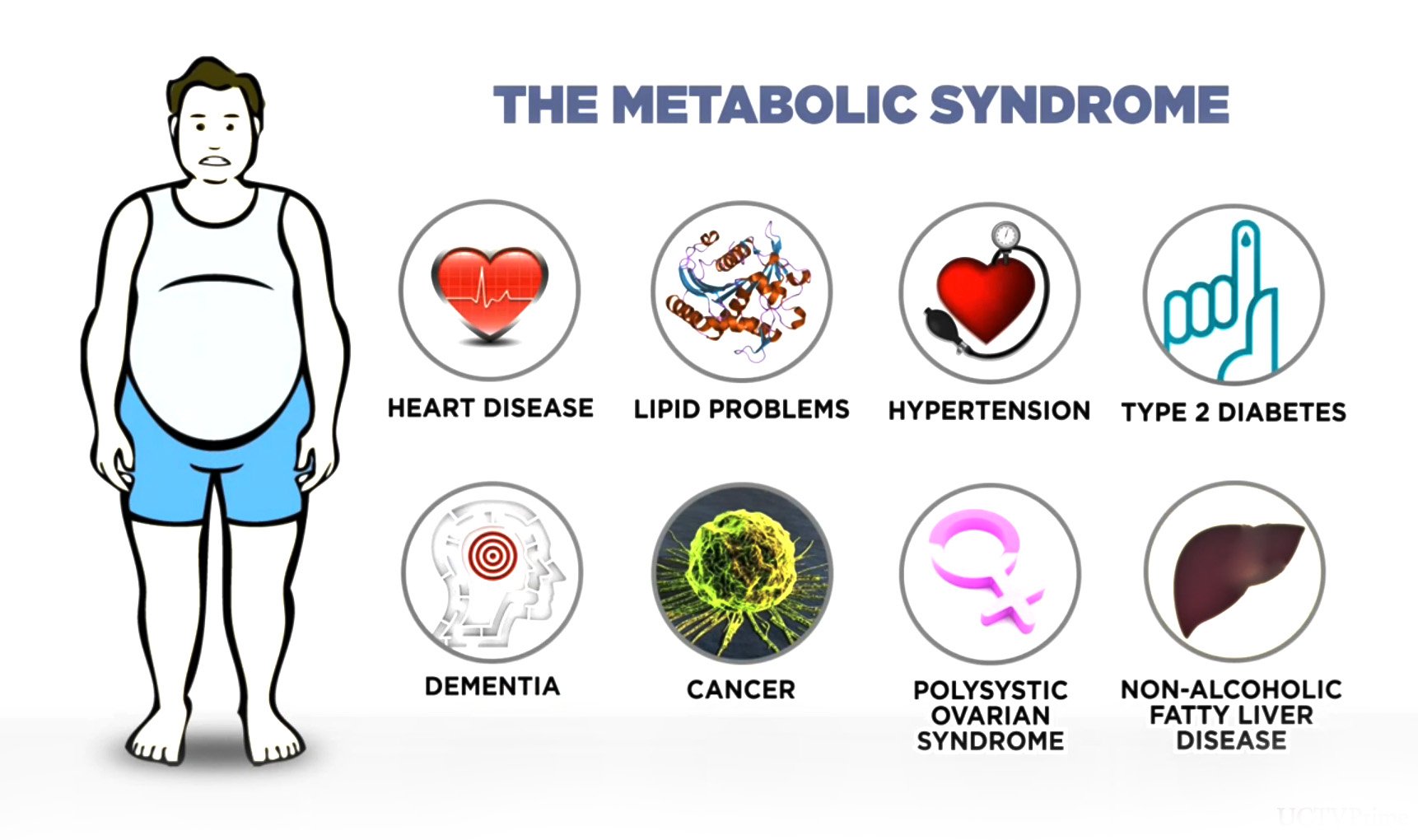
Metabolic syndrome and pre-diabetes share one common characteristic: an increased level of sugar in the blood. Individuals risk contracting full-blown diabetes, stroke, and heart disease without proper intervention. Understanding the difference between prediabetes and metabolic syndrome can help patients prevent the progression of the disease.
Also Check: What Is Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
General Treatment Of Diabetes
People with diabetes benefit greatly from learning about the disorder, understanding how diet and exercise affect their blood glucose levels, and knowing how to avoid complications. A nurse trained in diabetes education can provide information about managing diet, exercising, monitoring blood glucose levels, and taking drugs.
|
|
Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome Can Be Treated With A Novel Class Of Compounds
| Font : A-A+ |
A new class of compounds the scientists developed can improve multiple aspects of metabolic syndrome, shows a study in mice led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.An increasingly common group of conditions that often occur together, metabolic syndrome includes type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, fat buildup in the liver, and excess body fat, especially around the waist. This syndrome often leads to cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death worldwide.
SWELL1 acts as a signaling molecule, turning on cellular tasks that govern how well cells use insulin and also facilitates the pancreas’ secretion of insulin into the bloodstream
You May Like: Are Green Beans Good For Diabetics
Programs That Can Make A Difference
Bridging the Gap
To help address the growing challenge of diabetes, our company’s Foundation established Bridging the Gap: Reducing Disparities in Diabetes Care. This initiative aims to improve access to high-quality diabetes care and reduce disparities in health outcomes among vulnerable and underserved populations with type 2 diabetes in the U.S.
Connection Between Diabetes And Alzheimer’s Disease
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by high blood glucose levels resulting from increased hepatic glucose production, impaired insulin production by pancreatic cells, and insulin resistance, which closely resembles brain insulin resistance observed in AD patients. Furthermore, age-related alterations of mitochondrial function represent the driving force behind increased oxidative stress in T2DM contributing to the progression and development of AD pathology. T2DM and AD share common abnormalities including impaired glucose metabolism, increased oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and amyloidogenesis. Thus T2DM is a risk factor for AD .
Joseph Bamidele Awotunde, … Muyideen Abdulraheem, in, 2021
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Is Treated With
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Another kind of blood test, an oral glucose tolerance test, may be done in certain situations, such as screening pregnant women for gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes For women who have diabetes before they become pregnant, the risks of complications during pregnancy depend on how long diabetes has been present and whether complications of diabetes, such… read more or testing older people who have symptoms of diabetes but normal glucose levels when fasting. However, it is not routinely used for testing for diabetes because the test can be very cumbersome.
In this test, people fast, have a blood sample taken to determine the fasting blood glucose level, and then drink a special solution containing a large, standard amount of glucose. More blood samples are then taken over the next 2 to 3 hours and are tested to determine whether the glucose in the blood rises to abnormally high levels.
Is Diabetes A Metabolic Disorder
Insulin is required to transport sugar from the blood in to the cells. This sugar undergoes various metabolic process in order to provide us energy as well as to store excess energy. This process of transferring glucose in producing and storing energy is said to be a metabolic process and any disorder altering this process is a metabolic disorder.
Don’t Miss: What To Know About Diabetes
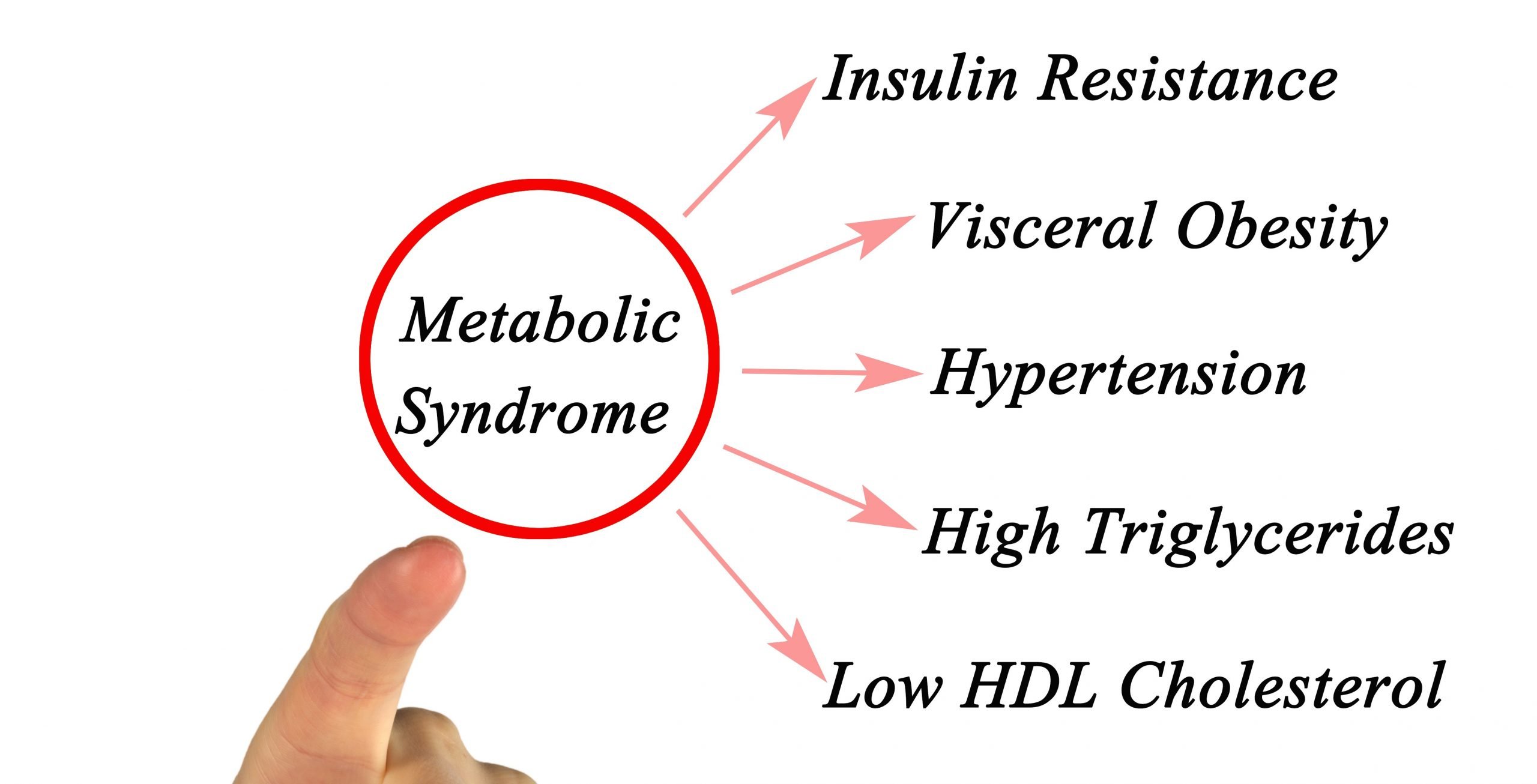
What Causes Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is more common in people who are overweight or obese. However, even if you are not obese, you may be at greater risk for metabolic syndrome if a parent or other close relative has type 2 diabetes.
Insulin resistance is another key cause of metabolic syndrome. When your cells resist insulin the hormone that regulate blood sugar levels you eventually accumulate too much sugar in your bloodstream. This increases your risk of metabolic syndrome, as well as prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Role Of Inflammation In Insulin Resistance
Insulin is a key endocrine hormone produced by -cells of pancreatic islets. Insulin is regarded as hormone of abundance owing to the array of functions it performs, the effects of which extend from metabolic to mitogenic activity .2). It is likely that disruption of insulin-mediated pathways will have pleiotropic effects that are not confined to carbohydrate metabolism only. Various mechanism working separately or in synergy have been linked to the development of insulin resistance among which chronic inflammation represents as a triggering point.
Various hormone functions of insulin.
Inflammation is an important component linking insulin resistance with nutrient overload and increased visceral adipocyte mass. During an insulin-sensitive state, the signalling cascade of insulin upon binding to its receptor results in phosphorylation of tyrosine residues of the insulin receptor substrate 1 ensuing in downstream insulin signalling. However, in an insulin-resistance state, pro-inflammatory molecules activate various other serine kinases like JNK, inhibitor of NFB kinase subunit , extracellular-signal regulated kinase , ribosomal protein S6 kinase , mammalian target of rapamycin , PKC and glycogen synthase kinase 3. The activation of these kinases inhibits insulin action by phosphorylating serine residues instead of tyrosine residues in the insulin signalling pathway.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Common Form Of Diabetes
Are You At Risk For Metabolic Syndrome
The following risk factors increase your risk of having metabolic syndrome:
- Obesity
- Low HDL cholesterol levels
- High triglyceride levels
- Older age: your chances of getting it increase as you get older
- Ethnic background: the condition is more common among African Americans, Asians, Hispanics and Native Americans
Key Points About Metabolic Syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome is a condition that includes a cluster of risk factors specific for cardiovascular disease.
- The cluster of metabolic factors include abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, impaired fasting glucose, high triglyceride levels, and low HDL cholesterol levels.
- Metabolic syndrome greatly raises the risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, stroke, or all three.
- Management and prevention of metabolic syndrome include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, eliminating the use of cigarettes or other tobacco products, and being physical active.
Recommended Reading: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
Diabetes Mellitus And Metabolic Disorders
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders of carbohydrate metabolism characterized by high blood glucose levels and usually resulting from insufficient production of the hormone insulin or an ineffective response of cells to insulin . Secreted by the pancreas, insulin is required to transport blood glucose into cells. Diabetes is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as well as a leading cause of adult blindness. Other long-term complications include kidney failure, nerve damage, and lower limb amputation due to impaired circulation.
Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age but often begins in late childhood with the pancreas failing to secrete adequate amounts of insulin. Type 1 diabetes has a strong genetic link, but most cases are the result of an autoimmune disorder, possibly set off by a viral infection, foreign protein, or environmental toxin. Although elevated blood sugar is an important feature of diabetes, sugar or carbohydrate in the diet is not the cause of the disease. Type 1 diabetes is managed by injections of insulin, along with small, regularly spaced meals and snacks that spread glucose intake throughout the day and minimize fluctuations in blood glucose.
Er Stress And Upr Pathways
Triggering of inflammatory signals by three pathways of UPR is initiated by activation of JNKs and NF-B in B cells. This activation acts as the linkage point between metabolic and immune pathways since the activation of these very kinases is analogous to that elicited by an immune response. JNKs play an important role in T2D, as increased activity has been shown to promote insulin resistance .
The first responses for opposing ER stress involve decreasing the translation of proteins. This involves phosphorylation of subunit of eIF2 by PERK. In humans and mice, loss of PERK expression is linked to dysregulation of the UPR response which is fundamental to ER stress, resulting in increased cell death and T2D. A permanent form of neonatal diabetes in humans is related to elevated ER stress markers as a result of a mutation in PERK, confirming the pivotal role of PERK in regulating ER stress during fetal development.
The third pathway of UPR involves the activation of ATF6, the basic leucine zipper domain protein, that upregulates PERK1 and IRE1 pathways by suppressing the apoptotic UPR signalling cascade under chronic ER stress. The role of ATF6 activation in -cell dysfunction has been concluded in studies that showed decreased expression of insulin gene by ER stress-induced ATF6 activation and a decrease in ER chaperones along with induction of apoptosis in ATF6 knockdown insulinoma cells.
Don’t Miss: Does Sleeve Gastrectomy Cure Diabetes
Activation Of Inflammasome In T2d
Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes in the intracellular machinery responsible for production of bioactive IL-1 in response to multiple stimuli. NLRP is a subfamily of Nod-like receptors containing a central nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain with flanking C-terminal leucine-rich repeats and N-terminal caspase recruitment or pyrin domains. The NOD-like receptor family, the pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome is in a pathway that controls the production of IL-1 and IL-18. Unlike TLR, a potential role of NLR in metabolic abnormalities has not been extensively investigated. NLRP forms a constituent of the inflammasomes responsible for maturation and release of IL-1, and thus is a relevant candidate for metabolic disorders and T2D. NLRP3-dependent activation of inflammaosomes in diabetes was proposed by studies implicating the release of IL-1 as a consequence of elevated levels of glucose, FFAs and human islet amylopeptide . However, the effective metabolites involved in activation of inflammasomes are not clearly elucidated yet .
Activation of inflammasomes in type 2 diabetes into active IL-1. -cell-derived IL-1 promote the release of chemokines and recruitment of macrophages that are activated by human islet amyloid polypeptide, leading to deleterious concentrations of IL-1. FFA: Free fatty acid IL: Interleukin.
Antipsychotic Medications And Hyperglycemia
Case reports and retrospective database analyses suggest that conventional and atypical antipsychotics are associated with significant increases in fasting glucose concentrations. This hyperglycemia can result in new-onset type 2 diabetes, metabolic acidosis or ketosis, and even hyperglycemia-related deaths. Most cases of new-onset type 2 diabetes occur within the first 6 months of treatment and are often, although not always, associated with significant weight gain or obesity. A family history for diabetes is also associated with an increased risk.
There seems to be variability among the specific second-generation antipsychotics with respect to the incidence rates of diabetes. Koro et al., in a large population-based, case-control study, found the risk of diabetes associated with antipsychotics to be quite variable. Olanzapine had 4.2 times the risk associated with conventional agents and 5.8 times the risk associated with no treatment. Risperidone had 1.6 times the risk of conventional drugs and 2.2 times the risk of no treatment. Several large population retrospective studies have found that olanzapine and clozapine are associated with a significantly higher rate of diabetes than the conventional antipsychotics risperidone and quetiapine. The risk of diabetes,however, is higher with antipsychotic treatment use than in a general patient population sample.,,
Recommended Reading: What Can People With Type 2 Diabetes Eat
Effect Of Renal Function And Insulin Sensitivity
The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome was 36% in patients with a creatinine clearance in the normal range, 34% in patients with a mild decrease in renal function, and 60% in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment . Patients with ESRD were excluded from the analysis. shows the relationship between insulin sensitivity, as assessed by eGDR and creatinine clearance at different stages of nephropathy. Most patients with type 1 diabetes and normal AER and renal function had normal insulin sensitivity. On the other hand, patients with microalbuminuria were more insulin resistant, whereas decreased renal function was most obvious in those with macroalbuminuria. When patients with normal AER were compared with those with microalbuminuria, there was only a small difference in creatinine clearance , whereas the difference in insulin sensitivity was large . When patients with microalbuminuria were compared with those with macroalbuminuria, there was a marked difference in creatinine clearance and a further decrease in insulin sensitivity .
Living With Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a lifelong condition that will require changes in your lifestyle. If you already have heart disease or diabetes, follow your healthcare providers recommendations for managing these conditions.
Lifestyle changes involved in managing metabolic syndrome include:
- A healthy diet
- Stopping smoking if youre a smoker or use other tobacco products
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese
Don’t Miss: How I Reversed My Diabetes
When To See A Doctor
See a doctor if you or your child:
- Is losing or gaining weight without intending to, or isnt growing
- Feels hungry or thirsty a lot, even if you are eating and drinking
- Has to urinate often
- Is lethargic and has no energy
- Vomits or complains of belly pain often
- Has yellowish skin color or other skin changes
- Cant do what other children the same age are able to do
Take your child to all checkups so the pediatrician can make sure your child is growing normally.
Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders
Scientific Indexing Services ID: 6720
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders is an international online peer reviewed open access journal with the ISSN 2381-201X. The Journal encompasses both clinical and medical research and is at the forefront to publish the standard excellence in diabetes and metabolic disorders. To prevent and cure diabetes, researchers with their cutting-edge research focus to develop new therapies to treat patients ensuring healthy lives besides educating and training next generation researchers.
This journal spans from the fundamental to advanced aspects of diabetes and metabolic disorders. Journal mainly stands to present the uniqueness alongside quality and visibility in publishing quality articles, with the support of diverse diabetes health care providers and endocrinologists as editors and reviewers. The published articles of the journal empower the current research and helps escalating better therapeutic opportunities. Editorial board members with their collaborative culture and creative spirit help flourish the journal.
The wide arena of topics includes:
Current Issue
Read Also: How To Stop Sugar Diabetes