Us Adults Should Begin Diabetes Screening At 35 Medical Panel Recommends
Angela Underwood’s extensive local, state, and federal healthcare and environmental news coverage includes 911 first-responder compensation policy to the Ciba-Geigy water contamination case in Toms River, NJ. Her additional health-related coverage includes death and dying, skin care, and autism spectrum disorder.
Why Do Pregnant Women Need To Be Screened For Diabetes
During pregnancy, some women develop a type of diabetes known as gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes happens to about 48% of all pregnant women. It can lead to problems for both mother and baby if it is not treated. This is why all pregnant women should be screened for diabetes. Read more about gestational diabetes.
Benefits Of Early Detection And Treatment
Screening for Diabetes
The USPSTF found 2 randomized clinical trials, the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment In People with Screen Detected Diabetes in Primary Care Cambridge 24-26 and the Ely study ,27-29 that evaluated the effect of screening for diabetes on health outcomes. ADDITION-Cambridge was a cluster randomized trial that randomly assigned practices to no screening, screening followed by intensive treatment of screen-detected diabetes , or screening followed by routine care of screen-detected diabetes. In the Ely study, the treatment of persons with screen-detected diabetes was managed by primary care clinicians as they deemed appropriate. Neither trial found a reduction in all-cause or type-specific mortality with screening compared with no screening over approximately 10 years of follow-up, which notably may have been too short to detect an effect on health outcomes. Neither trial found statistically significant differences in cardiovascular events, quality of life, nephropathy, or neuropathy between screening and control groups, but data collection for these outcomes was limited to a minority of trial participants.
Effect of Interventions for Screen-Detected Type 2 Diabetes or Prediabetes on Health Outcomes
Effect of Interventions for Newly or Recently Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes on Health Outcomes
Effect of Interventions for Prediabetes on Progression to Diabetes
Recommended Reading: Pain Medicine For Diabetic Neuropathy
When To Seek Medical Care
Random Blood Sugar Test
This measures your blood sugar at the time youre tested. You can take this test at any time and dont need to fast first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
| 140 mg/dL or below | N/A |
*Results for gestational diabetes can differ. Ask your health care provider what your results mean if youre being tested for gestational diabetes.Source: American Diabetes Association
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Control Diabetes With Diet And Exercise
Diagnostic Criteria And Testing
The 1997 ADA consensus guidelines lowered the blood glucose thresholds for the diagnosis of diabetes.5 This increased the number of patients diagnosed at an earlier stage, although no studies have demonstrated a reduction in long-term complications. Data suggest that as many as 5.7 million persons in the United States have undiagnosed diabetes.6 Table 1 compares specific diagnostic tests for diabetes.1114
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
| Test | |
|---|---|
|
Random blood glucose level11 |
|
|
140 mg per dL |
|
|
150 mg per dL |
|
|
160 mg per dL |
|
|
170 mg per dL |
|
|
180 mg per dL |
|
|
$14, serum test or point of-care test |
|
|
78.2 to 88.2 |
NPV = negative predictive value OGTT = oral glucose tolerance test PPV = positive predictive value.
*Calculated based on prevalence of 6 percent.
Based on 2009 rates.
Information from references 11 through 14.
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
| Test | |
|---|---|
|
Random blood glucose level11 |
|
|
140 mg per dL |
|
|
150 mg per dL |
|
|
160 mg per dL |
|
|
170 mg per dL |
|
|
180 mg per dL |
|
|
$14, serum test or point of-care test |
|
|
78.2 to 88.2 |
NPV = negative predictive value OGTT = oral glucose tolerance test PPV = positive predictive value.
*Calculated based on prevalence of 6 percent.
Based on 2009 rates.
Information from references 11 through 14.
How The Test Is Performed
TWO-STEP TESTING
During the first step, you will have a glucose screening test:
- You do not need to prepare or change your diet in any way.
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose.
- Your blood will be drawn 1 hour after you drink the glucose solution to check your blood glucose level.
If your blood glucose from the first step is too high, you will need to come back for a 3-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test.
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose, 100 grams .
- You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 3 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 3 hours for this test.
ONE-STEP TESTING
You need to go to the lab one time for a 2-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test.
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose .
- You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 2 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 2 hours for this test.
Don’t Miss: Development Of Type 2 Diabetes
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It happens when your body is not able to produce enough insulin to keep the amount of glucose in your blood at proper levels. Untreated GD increases the likelihood of having a large baby, and is associated with birth complications as well as health risks for the newborn . Untreated GD also increases the risk of stillbirth late in pregnancy . Women who develop GD are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, there is excellent treatment for GD, and most women diagnosed with GD have normal deliveries and healthy babies.
Tests For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. Youll probably be tested between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes , your doctor may test you earlier. Blood sugar thats higher than normal early in your pregnancy may indicate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than gestational diabetes.
You May Like: Cauliflower Pizza Crust For Diabetics
Who Should Have A Diabetes Test
You should have a diabetes test if you are at a high risk of type 2 diabetes. An AUSDRISK score of 12 or more is considered high risk.
You may also be at high risk of diabetes if you:
- have had a heart attack or stroke
- have had gestational diabetes
- take medications to treat psychosis
You should have a diabetes test every year if you have pre-diabetes.
Should We Screen For Prediabetes And Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes represent a pathophysiological and clinical continuum.
Table I.
| 100125 mg/dl | 126 mg/dl | |
| 2 hour plasma glucose after ingestion of a 75g glucose load | 140 199 mg/dl | 200 mg/dl |
| 5.76.4% | 6.5% |
There is no direct evidence from a randomized controlled trial on the cost-effectiveness of screening. However, economic modeling studies have suggested that targeted opportunistic screening for prediabetes and/or type 2 diabetes would be cost effective. In addition, there is robust evidence on the beneficial effects of early treatment of prediabetes, and similar evidence is accumulating on early treatment for undiagnosed diabetes. There is therefore a strong rationale for undertaking screening for prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes among high-risk people in clinical settings.
Scope of the problem burden of hyperglycemia
The global prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among adults was 6.4% in 2011, and is projected to increase to 7.1% by 2030. Almost 30% of adult Americans have prediabetes, and over 40% have hyperglycemia of any kind, i.e. prediabetes or diabetes. Compared to patients with normoglycemia, those with prediabetes have an 8%-60% increased mortality, a 20% increase in macrovascular disease, and an increased risk of microvascular complications, including retinopathy neuropathy , and chronic kidney disease .
Identifiable preclinical phases
You May Like: What To Do If You Think Your Diabetic
The Only Way You Can Find Out If You Or A Loved One Has Diabetes Is From Blood Tests That Measure You Blood Glucose Levels These Can Be Arranged Through Your Gp
A diagnosis of diabetes is always confirmed by laboratory results. Youll usually get the results of your blood test back in a few days. If you have symptoms that came on quickly and youve been taken into hospital, the results should come back in an hour or two.
A finger prick test using a home testing kit may show you have high blood sugar levels but won’t confirm you have diabetes.
A normal blood test result will show you don’t have diabetes. But the result will also show if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What Abnormal Results Mean
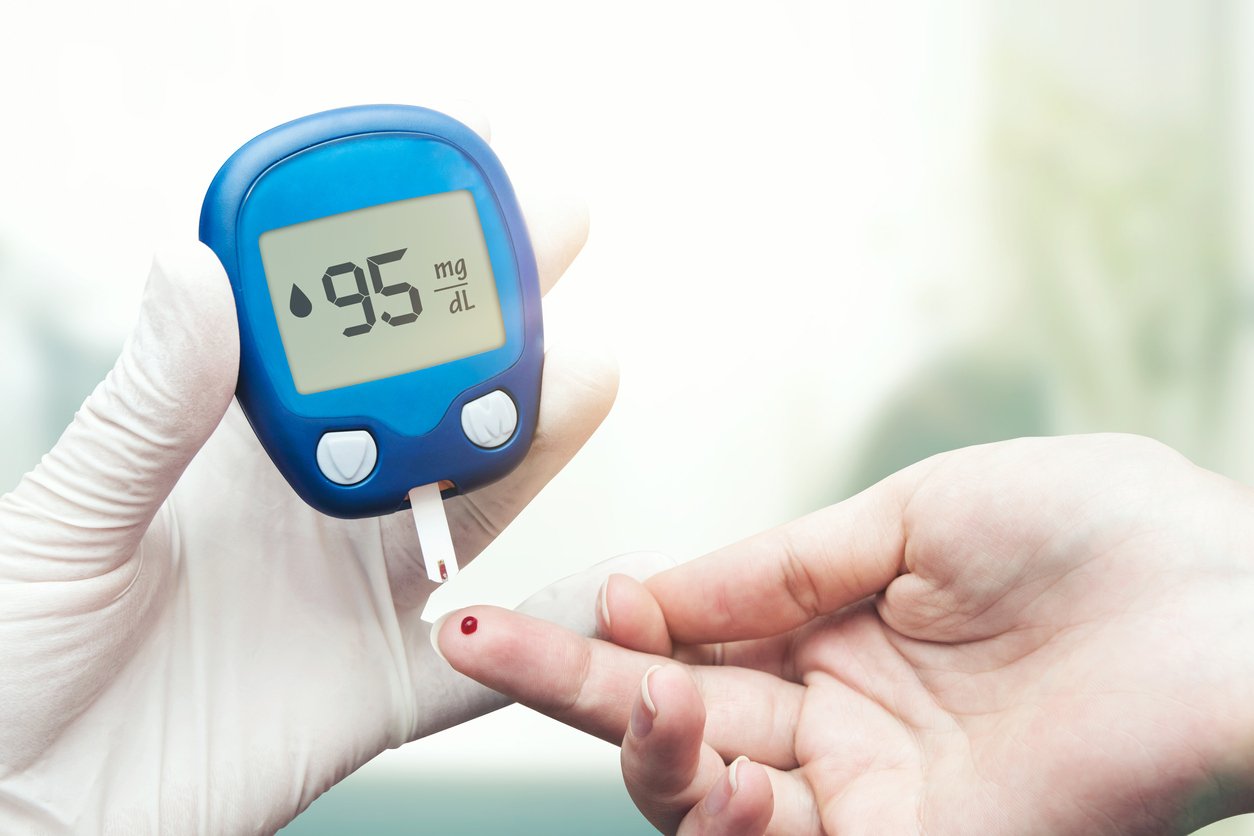
Abnormal blood values for a 3-hour 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 95 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 155 mg/dL
- 3 hour: greater than 140 mg/dL
ONE-STEP TESTING
Abnormal blood values for a 2-hour 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test are:
- Fasting: greater than 92 mg/dL
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL
- 2 hour: greater than 153 mg/dL
If only one of your blood glucose results in the oral glucose tolerance test is higher than normal, your provider may simply suggest you change some of the foods you eat. Then, your provider may test you again after you have changed your diet.
If more than one of your blood glucose results is higher than normal, you have gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Nursing Allied Health And Interprofessional Team Interventions
The screening process invariably involves nursing personnel who usually obtain finger stick readings and perform the blood draw. Nurse Practitioners and Certified Diabetes Educators play a crucial role in education, medication reconciliation, and demonstrating the proper use of devices and medication. Their active involvement assists the medical team to recognize the cases that could benefit from screening assists with early detection. A hematologist and the nephrologist may consult on the validity of a result where multiple factors could affect the test results. For example, a person with anemia or kidney disease could have altered HbA1C values. The endocrinologist may assist and identify a group of patients who potentially have a higher risk of diabetes and recommend early/more frequent screening, such as those with other autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease. Complex cases such as those with cystic fibrosis, HIV, and post-transplant patients can be discussed with an endocrinologist to decide the usefulness of screening in such patients to form an individualized management plan. Hence a team effort could lead to better screening outcomes and prevent the diagnosis from going undetected.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About Diabetes Testing
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, you will need to monitor blood glucose levels daily, often several times a day. Your health care provider can recommend a kit you can use at home. Most kits include a lancet, a device that pricks your finger. You will use this to collect a drop of blood for testing. There are some newer kits available that don’t require pricking your finger. Some pregnant women with gestational diabetes may also need to monitor their glucose levels in this way.
People with type 2 diabetes will also have to check their blood sugar on a regular basis. If you have type 2 diabetes, talk to your provider about how often it should be checked.
People with type 2 diabetes may also need to have their insulin levels checked regularly. Insulin plays a key role in keeping glucose at the right levels. An insulin in blood test is done at a provider’s office.
Recommended Reading: Diabetic Supply Companies That Accept Medicaid
Uk Nsc Screening Recommendation Based On The Last Uk Nsc Review Of This Condition That Occurred In November 2019
Screening is not currently recommended for this condition.
The UK NSC does not currently recommend screening for type 2 diabetes . This is because:
- there is no evidence that screening is more beneficial than not screening
- there is no evidence that finding T2DM early by screening results in a greater health benefit than usual health care
- more research is needed to review tests and benefits of screening for T2DM.
What If I Have Gestational Diabetes
GD is increasingly common, with about 7% of women having the condition. If you are found to have GD, you will work closely with your health care provider to keep your blood glucose levels in a healthy range. This involves choosing a healthy diet, gaining the recommended weight during your pregnancy, getting exercise, and if needed, taking insulin or pills to lower your blood sugar. Your babys wellbeing will be carefully monitored by regular measurements of growth and amniotic fluid volume. If you have GD you will be offered a repeat glucose tolerance test between 6 weeks and 6 months postpartum to detect prediabetes and diabetes. You may also be offered induction between 38-40 weeks of pregnancy. Finally, it is strongly recommended that women with GD breastfeed their infants.
Don’t Miss: Walmart 70 30 Insulin Pen
Response To Public Comment
A draft version of this recommendation statement was posted for public comment on the USPSTF website from March 16 to April 12, 2021. Many comments agreed with the USPSTF recommendation. In response to public comment, the USPSTF clarified that disparities in the prevalence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are due to social factors and not biological ones, and incorporated person-first language when referring to persons who have overweight or obesity. Some comments requested broadening the eligibility criteria for screening to all adults, or to persons with any risk factor for diabetes, and not confined to persons who have overweight or obesity. The USPSTF appreciates these perspectives however, the available evidence best supports screening starting at age 35 years. The USPSTF also added language clarifying that overweight and obesity are the strongest risk factors for developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. In response to comments, the USPSTF also noted that metformin appears to be effective in reducing the risk of progression from prediabetes to diabetes in persons with a history of gestational diabetes, based on post hoc analyses of the DPP and DPPOS.
More research is needed to evaluate the following.
Metformin . Bristol Myers Squibb. Accessed June 29, 2021.
What Are The Diabetes Risk Factors
Common risk factors for diabetes include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Also Check: Chromium Picolinate Dosage For Diabetes