Do I Need To Check If My Blood Sugar Level Is Normal
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, tracking your blood sugar regularly will help you understand how medication, food, and physical activity affect it. Checking your blood glucose level also gives you the chance to see when it’s rising and take action to correct it.
Managing your blood sugar levels is the most important thing you can do to prevent complications from diabetes, like blindness, heart attacks, amputation, kidney disease, and stroke.
Others who may want to track their blood glucose regularly include people:
Get A Head Start On Protein
Breakfast seems to be a particularly good time to load up on protein. In a study published in April 2015 in the Journal of Nutrition, people with diabetes who ate 25 to 30 grams of protein at breakfast had lower blood sugar spikes after both breakfast and lunch than those who ate less. Reduced-fat cheese and egg whites are excellent , according to the ADA. Other protein-rich ideas for breakfast when you have diabetes include a breakfast burrito, for example. But because people respond differently to different foods, says Champion, its important to keep tracking your blood sugar to see how various breakfast foods affect you specifically.
You May Like: Where Can I Get A Free Diabetes Test
How Long Does It Take For Blood Sugar Levels To Peak After Eating
After consuming foods that contain carbohydrates, it’s normal to see a rise in blood sugar levels.
Video of the Day
Your blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, will temporarily go up after eating a meal until your body’s insulin is able remove the extra sugar from the bloodstream. In general, blood sugar “peaks 90 minutes after you consume a meal,” says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDE, author of 2-Day Diabetes Diet. “But it’s going to vary based on what you ate.”
This type of peak is a normal part of digestion. Sometimes, however, a person’s body does not respond as it should, and blood sugar levels rise too high. When this happens, it can indicate a risk for prediabetes or diabetes. Frequent spikes in blood sugar can lead to additional long-term medical problems, as well. Here’s what you can do to protect your health.
Read more:How to Lower Blood Sugar Levels Fast
Also Check: How To Control Blood Sugar Level
How Do I Treat Low Blood Glucose
If you begin to feel one or more symptoms of low blood glucose, check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose level is below your target or less than 70 mg/dL, follow these steps
No Symptoms Be Alarmed

Surprisingly, the most dangerous episodes of hypoglycemia occur with little or no warning. When low blood glucose occurs on a regular basis, the body can become used to the warning signs and the person may stop noticing symptoms. This is a particularly dangerous condition known as hypoglycemic unawareness. People with this condition might not realize they have low blood glucose until it’s dangerously low seizures and coma are sometimes the first indication of a problem. The good news is that this condition can often be reversed allowing people to once again notice the signs of low blood glucose if hypoglycemia is avoided for a few weeks through careful monitoring of blood glucose.
You May Like: Lantus Insulin Patient Assistance Program
Exercise Food And Alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, maintaining the correct blood glucose level involves balancing how much insulin you inject, the amount of food you eat, and how much energy you burn during exercise.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if you’ve taken your dose of insulin as usual, but your carbohydrate intake is lower than normal or has been used up more quickly. This may happen if you delay or miss a meal or snack, don’t eat enough carbohydrate, or exercise more than usual.
People with diabetes who’ve drunk too much alcohol, or drank alcohol on an empty stomach, can also get hypoglycaemia.
However, it’s not always possible to identify why a particular episode of hypoglycaemia has occurred, and sometimes it happens for no obvious reason.
Conditions That Can Mimic Hypoglycemia
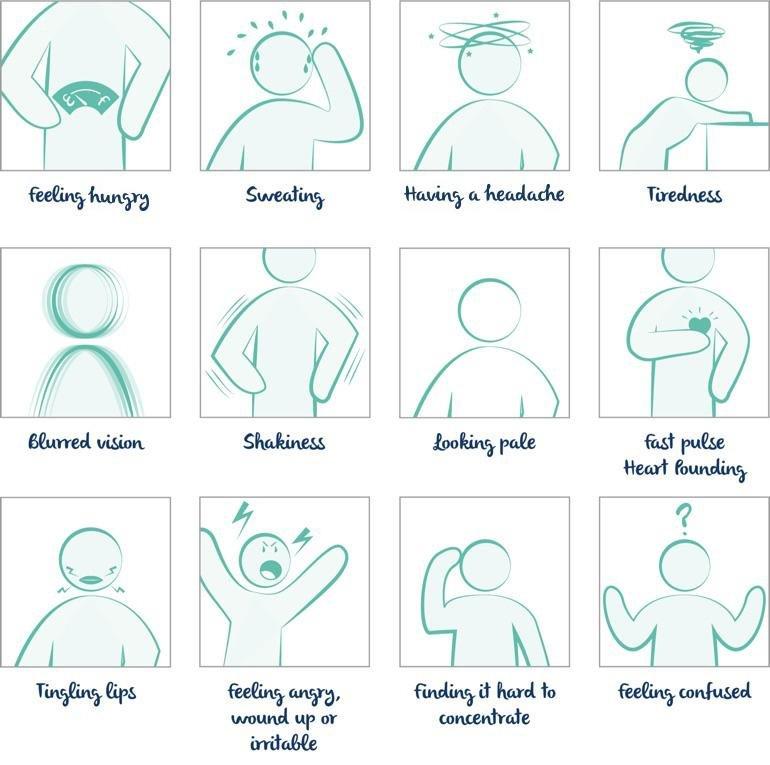
Conditions other than hypoglycemia can have some of the same symptoms, including dizziness, weakness, sweating, and rapid heartbeat. These include a wide variety of conditions, such as:
To decide if your symptoms are due to hypoglycemia, your healthcare provider will look for signs of the “Whipple Triad.” This includes:
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Low plasma glucose measurements while you have symptoms
- No symptoms when your glucose increases to normal levels
Without these three indications, your healthcare provider will likely evaluate you for other conditions that have similar symptoms.
Don’t Miss: How Does Diabetes Cause Heart Disease
Examples Of Easily Digestible Carbohydrates
- 1/2 cup of juice or regular soda
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 4 or 5 saltine crackers
- 3 or 4 pieces of hard candy or glucose tablets
- 1 tablespoon of sugar
Very low blood sugar is a medical emergency. If you or someone else with diabetes is experiencing severe symptoms, such as unconsciousness, its important to administer a medication called glucagon and contact emergency services immediately.
If youre at risk for low blood sugar, its important to talk with your doctor about getting a prescription for glucagon.
You should never give an unconscious person anything by mouth, as it could cause them to choke. If you have diabetes, make sure your family and friends know not to do this if you lose consciousness.
Low blood sugar can occur for a number of reasons. Its usually a side effect of diabetes treatment.
Why Does My Blood Sugar Drop After Eating
- Sluggish and shaky after finishing a big meal?
- Low blood sugar doesn’t only happen to diabetics
- Certain lifestyle factors can cause blood sugar to drop during the day
Hypoglycaemia is the term used to describe what happens when our blood sugar drops. It can cause weakness, hunger, sweating, heart palpitations, tremors or shakiness, fainting, dizziness, nausea, headache, and disturbed vision. It may become so severe that it causes mental symptoms like confusion.
While hypoglycaemia most often affects diabetics after a large dose of insulin, non-diabetics may also sometimes experience these symptoms, especially when the body secretes a large amount of insulin.
So, if youve ever felt shaky, sweaty and weak after a meal in the absence of diabetes, it may be reactive hypoglycaemia when blood sugar drops as a result of too much insulin.
Why can this happen?
When you are at work, this might be particularly unpleasant, especially when you need to focus on an important task.
However unpleasant, in most cases hypoglycaemia after a meal isnt life-threatening. It is the result of your body producing too much insulin after consuming a heavy, carb-laden meal. The extra insulin removes too much glucose from your bloodstream, resulting in the symptoms mentioned above.
Other, more serious causes of reactive hypoglycaemia include pancreatic tumours, alcohol, surgeries such as gastric bypass or ulcer treatment, or insulin resistance .
Recommended Reading: Diabetic Diet Plan Menu Week
What Factors Affect Blood Sugar
You can guess that carbohydrate intake and insulin production are at least partly responsible for your blood sugar levels. But the list is much longer — almost every lifestyle choice you make can affect your blood sugar. Here’s just a partial list.
- Exercise can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to lower blood sugar for up to 48 hours.
- Alcohol intake increases insulin production, causing low blood sugar.
- Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar, because your body wants access to energy in order to escape what it perceives as a dangerous situation.
- Medications, especially statins and diuretics, can raise blood sugar. Statins are used to treat cholesterol, and diuretics for high blood pressure.
- Diet is a major player in blood sugar. Eating too many simple carbs at once can cause levels to skyrocket, while protein intake leads to a slower increase in blood sugar.
- Dehydration raises blood sugar, because with less water in your body the glucose concentration will be higher.
Other surprising factors can affect your blood sugar, like a sunburn or gum disease, so if you’re dealing with a blood sugar issue and can’t figure out what’s causing your spikes and dips, talk to a healthcare professional.
Get the CNET Now newsletter
Balancing Your Blood Sugar: What’s Healthy How To Measure And More
Your blood sugar is affected by a range of factors. Here’s how to tell if yours is healthy.
Caroline Roberts
Digital Editorial Intern
Caroline Roberts writes articles and notifications for CNET. She studies English at Cal Poly, and loves philosophy, Karl the Fog and a strong cup of black coffee.
High blood sugar levels are a problem, even if you don’t have a family history of diabetes. Blood sugar that’s consistently higher than ideal can coexist with Type 2 diabetes and cause serious health conditions like kidney disease, nerve problems or stroke.
While that’s no reason to panic, when it comes to our health, it’s important to know exactly what’s going on inside of our bodies. Let’s get into what blood sugar means, how to measure it and everything else you need to know.
Don’t Miss: When Was Type 2 Diabetes Discovered
Improving Hypo Awareness Signs
If you are suffering from impaired hypo unawareness, you may be advised to increase your window of blood glucose control for a period of time to get your numbers higher and prevent hypos from occurring so often.
Studies have found this method to be successful.
If you have frequent hypos you may need to test your blood sugar more often, to help get better control as well as to catch hypos earlier. Try to record which events lead to hypos so you can spot trends and prevent them in future.
Insulin And Blood Sugar

Insulin is an important hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar levels. The pancreas makes insulin. It helps control your blood sugar levels by assisting the cells that absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body doesnt make insulin. This means you have to inject insulin every day.
If diet and exercise arent enough to manage blood sugar, those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications to help keep blood sugar levels within target ranges.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body produces insulin, but may not use it properly or produce enough of it. Your cells dont respond to insulin, so more sugar keeps circulating in the blood.
Exercise can help the cells respond better and be more sensitive to insulin. The proper diet can also help you avoid spikes in blood sugar. This can help keep your pancreas functioning well since high blood sugar levels decrease pancreatic function.
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar Levels 1 Hour After Eating
Treating Low Blood Glucose If You Take Medicines That Slow Down Digestion
Some diabetes medicines slow down the digestion of carbohydrates to keep blood glucose levels from rising too high after you eat. If you develop low blood glucose while taking these medicines, you will need to take glucose tablets or glucose gel right away. Eating or drinking other sources of carbohydrates wont raise your blood glucose level quickly enough.
How Can I Measure My Blood Sugar Levels
You can measure your blood glucose levels with a glucometer. First, you prick your finger with a small device called a lancet to get a drop of blood. Your blood goes on a test strip which you put into the glucometer. Then, the device tells you your blood sugar levels.
You can also use a continuous glucose monitoring device, which uses a sensor that’s placed under your skin to automatically check your levels every few minutes.
Recommended Reading: Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase G6pd Deficiency
Check Your Blood Sugar Often
Regularly checking your blood sugar level can help you keep it in your target range. If youve had low blood sugar episodes in the past, you may want to check your blood sugar levels before driving or operating machinery.
Talk with your doctor about when and how often you should check your blood sugar.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Dont Miss: Can You Reverse Diabetic Neuropathy
Also Check: Wound Healing Diet For Diabetics
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, comes from the food you eat. Your body creates blood sugar by digesting some food into a sugar that circulates in your bloodstream.
Blood sugar is used for energy. The sugar that isnt needed to fuel your body right away gets stored in cells for later use.
Too much sugar in your blood can be harmful. Type 2 diabetes is a disease thats characterized by having higher levels of blood sugar than whats considered within normal limits.
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to problems with your heart, kidneys, eyes, and blood vessels.
The more you know about how eating affects blood sugar, the better you can protect yourself against diabetes. If you already have diabetes, its important to know how eating affects blood sugar.
Your body breaks down everything you eat and absorbs the food in its different parts. These parts include:
- vitamins and other nutrients
The carbohydrates you consume turn into blood sugar. The more carbohydrates you eat, the higher the levels of sugar youll have released as you digest and absorb your food.
Carbohydrates in liquid form consumed by themselves are absorbed more quickly than those in solid food. So having a soda will cause a faster rise in your blood sugar levels than eating a slice of pizza.
Fiber is one component of carbohydrates that isnt converted into sugar. This is because it cant be digested. Fiber is important for health, though.
- white grain products, such as pasta and rice
- cold processed cereals
Signs And Symptoms Of Reactive Hypoglycemia
Symptoms of reactive hypoglycemia can include:
When talking about the signs of reactive hypoglycemia, its important to note that many of these symptoms can be experienced without actually having low blood sugar
In fact, it is rare for such symptoms to be caused by falling blood sugar levels after eating, with the actual cause for many people often relating to what food was eaten or variations in the timing of the food moving through the stomach and intestinal tract.
If there is no hypoglycemia at the time of the symptoms, you may have what is known as postprandial syndrome.
You May Like: Difference Between Diabetes 1 And 2
How To Treat Low Blood Sugar
If you think you have low blood sugar, be sure to check it.
Keeping your blood sugar levels on target as much as possible can help prevent or delay long-term, serious health problems. While this is important, closely managing your blood sugar levels also increases your chance for low blood sugar . Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low. If you think you have low blood sugar, check it. If you arent able to check it, go ahead and treat it.
Untreated low blood sugar can be dangerous, so its important to know what to do about it and to treat it immediately.
Other Ways To Prevent Reactive Hypoglycemia
Using extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil or nut- or seed-based oils for cooking can deliver healthy fats to your body, says Zumpano. Use these to cook your lean meats or add to cooked vegetables and salads to make a healthy, delicious combo. Limit high heat cooking with extra virgin olive oil and certain nut and seed oils.
Targeting foods that can deliver all these needs carbohydrates, protein and healthy fat at once is also a great way to maintain a good balance, she says. Nuts are a great example because, depending on what type youre eating, they feature all three of these and make a great snack that can keep your blood sugar better controlled.
Zumpano also suggests that if youre going to be drinking alcohol, be sure to drink with food instead of on an empty stomach.
And eating more often, such as consuming small meals or snacks every two-to-four hours, can also help. Eating more regularly can help prevent reactive hypoglycemia, so making sure youre keeping things balanced is good.
Be sure to listen to your body, too, she adds. Talk to your doctor or healthcare provider if you feel that you may be experiencing the symptoms associated with reactive hypoglycemia. Seek a dietitian to help support you in minimizing the symptoms by changing your diet.
Recommended Reading: When Do You Start Taking Insulin For Diabetes