Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms.
Most cases are only discovered when your blood sugar levels are tested during screening for gestational diabetes.
Some women may develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels gets too high , such as:
- needing to pee more often than usual
But some of these symptoms are common during pregnancy and are not necessarily a sign of gestational diabetes. Speak to your midwife or doctor if you’re worried about any symptoms you’re experiencing.
> > > Best Diabetes Solution Available
Type 2 diabetes causes the body to become resistant to the hormone insulin. This hormone unlocks cells. There are two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. While both types of the disease can cause problems, you can minimize the impact by following healthy eating and being physically active. The sooner you know more about diabetes, the better prepared you will be to deal with it. Once you know more about the disease, youll be better prepared for treatment.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that causes the body to produce too much insulin. It is also known as type 2 diabetes. If you have type 1, you can control your blood glucose levels by eating a balanced diet. If you have type 2 diabetes, you can even prevent it by adopting healthy lifestyle habits and modifying your diet. Its important to seek information that can help you be your own health advocate. There are many different types of diabetes, so its important to learn as much as you can about the condition.
We Dont Know What Causes Gestational Diabetes
But we know that you are not alone. It happens to millions of women. We do know that the placenta supports the baby as it grows. Sometimes, these hormones also block the action of the mothers insulin to her body and it causes a problem called insulin resistance. This insulin resistance makes it hard for the mothers body to use insulin. And this means that she may need up to three times as much insulin to compensate.
Gestational diabetes can also start when the mothers body is not able to make and use all the insulin it needs for pregnancy. Without enough insulin, glucose cant leave the blood and be changed into energy. When glucose builds up in the blood, its called hyperglycemia.
Whatever the cause, you can work with your doctor to come up with a plan and maintain a healthy pregnancy through birth. Ask questions. Ask for help. There are many ways to combat gestational diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Diabetic Itching
Checking Your Blood Glucose Levels Will Help You To:
- Develop confidence in looking after your diabetes.
- Better understand the relationship between your blood glucose levels and the exercise you do, the food you eat and other lifestyle influences such as travel, stress and illness.
- Know how your lifestyle choices and medication, if used, are making a difference.
- Find out immediately if your blood glucose levels are too high or too low , helping you to make important decisions such as eating before exercise, treating a hypo or seeking medical advice if sick.
- Know when to seek the advice of your diabetes health team about adjusting your insulin, tablets, meal or snack planning when blood glucose goals are not being met.
What Should I Aim For
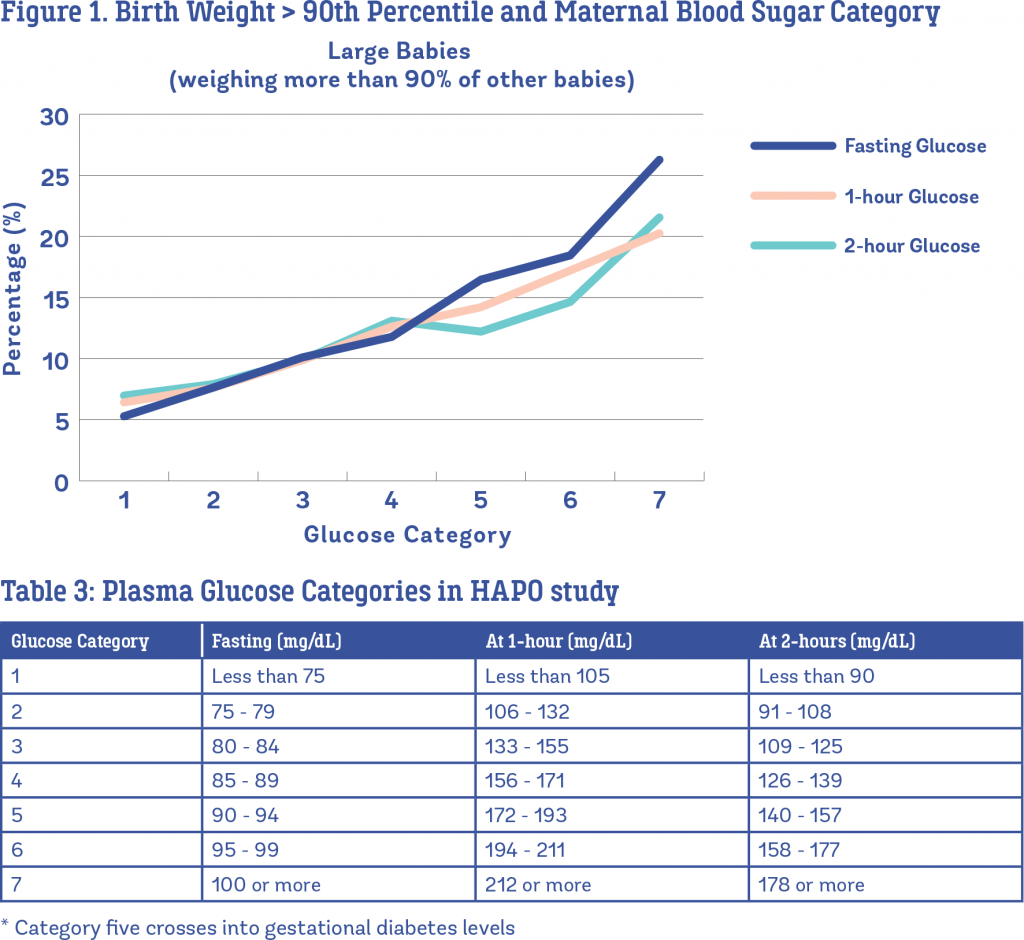
Effective management of diabetes is all about aiming for a careful balance between the foods you eat, how active you are and the medication you take for your diabetes. Because this is a delicate balance, it can be quite difficult to achieve the best possible blood glucose management all the time.
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individuals circumstances. While it is important to keep your blood glucose levels as close to the target range of target range between 4 to 6 mmol/L as possible to prevent complications, it is equally important to check with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator for the range of blood glucose levels that are right and safe for you. Therefore the following information should be treated only as a general guide.
Don’t Miss: Dr Comfort Custom Diabetic Inserts
Normal Blood Sugar Range For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetics
Regular fasting and before meals blood sugar range is from 70 to 130 mg/dl and less than 180 mg/dl two hours after meals. For people with type 2 diabetes, normal blood glucose levels before meals are usually between 80 and 130 mg/dl, while normal levels two hours after meals are typically below 180 mg/dl. However, these targets may differ for older people with other health conditions or who take certain high-risk medications such as concentrated insulins.
If you have diabetes, its important to work with your diabetes doctor to determine your target blood sugar levels. As an endocrinologist/diabetes doctor, I advise everyone individually what their goal should be. The general guidelines we discussed above apply for most new diabetics. But older patients with a long history of diabetes, end-stage kidney disease, liver disease, etc may need different goals.
Knowing this, you can still use a normal blood sugar level chart like this one to help you track your progress and make sure youre staying within your target range.
Various factors, including your age, overall health, and diabetes management goals, can influence your recommended blood sugar range.
The charts in this article will help you understand the recommended blood glucose and A1C ranges.
The recommended blood sugar levels can help you determine whether your blood sugar is within a normal range.
Monitoring Your Own Glucose Levels
Breadcrumb
HomePregnancyHubPregnancy complicationsGestational diabetes Monitoring your own glucose levels
You measure your glucose levels through a finger-prick test. You should have been shown how to do this when you were told that you had gestational diabetes. You will also have discussed the ideal blood glucose levels for you during your pregnancy.
The ideal target glucose levels are below but your team may have talked to you about your individual target level:
- fasting: 5.3 mmol/litre
- 1 hour after meals: 7.8 mmol/litre
- 2 hours after meals: 6.4 mmol/litre.
Read Also: Lower Blood Sugar Without Insulin
People With Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy. Often, it is a temporary condition, but it can lead to pregnancy complications.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with a diagnosis of gestational diabetes aim for blood sugar levels similar to those for people without diabetes, although individual targets may vary.
The ADA offers the following as a guideline:
| Blood sugar level |
A wide range of complications can also result, such as slow wound healing and frequent infections. Other possible complications include:
How Gestational Diabetes Can Affect Your Pregnancy
Most women with gestational diabetes have otherwise normal pregnancies with healthy babies.
However, gestational diabetes can cause problems such as:
- your baby growing larger than usual this may lead to difficulties during the delivery and increases the likelihood of needing induced labour or a caesarean section
- polyhydramnios too much amniotic fluid in the womb, which can cause premature labour or problems at delivery
- premature birth giving birth before the 37th week of pregnancy
- pre-eclampsia a condition that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy and can lead to pregnancy complications if not treated
- your baby developing low blood sugar or yellowing of the skin and eyes after he or she is born, which may require treatment in hospital
- the loss of your baby though this is rare
Having gestational diabetes also means you’re at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Read Also: How Does It Feel When You Have Diabetes
Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels
Topic Overview Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems such as diabetic eye disease , kidney disease , and nerve disease . Some people can work toward lower numbers, and some people may need higher goals. For example, some children and adolescents with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, people who have severe complications from diabetes, people who may not live much longer, or people who have trouble recognizing the symptoms of low blood sugar may have a higher target range. And some people, such as those who are newly diagnosed with diabetes or who don’t have any complications from diabetes, may do better with a lower target range. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood sugar range. This will help you achieve the best control possible without having a high risk of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Canada suggests the following A1c and blood glucose ranges as a general guide.Continue reading > >
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets For Most People With Diabetes*
Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart. Your targets are important and should be specific to you.
| A1C** | |
| 4.0 to 7.0 | 5.0 to 10.0 |
* This information is based on the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada and is a guide.** A1C is a measurement of your average blood sugar control for the last two to three months and approximately 50 per cent of the value comes from the last 30 days.
Also Check: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Level And After Meal Blood Sugar For Average Person
The standard blood sugar range for people without diabetes is the same regardless of age or health condition. A doctor, on the other hand, may set different goals based on your specific circumstances.
For example, if you have several diabetes risk factors, your doctor may want your blood sugar to be within a narrower range.
The chart below depicts the normal blood glucose range for people who do not have diabetes.
| Recommended blood sugar range chart for non-diabetics
99 mg/dL or less during fasting 1-2 hours after eating: 140 mg/dL or less |
Inconsistent Highs & Lows
Sometimes you may get a lower or higher blood glucose reading than usual and you may not be able to figure out the reason. When you are sick with a virus or flu, your blood glucose levels will nearly always go up and you may need to contact your doctor. There are a number of other common causes for blood glucose levels to increase or decrease. These include:
- Food time eaten, type and amount of carbohydrate for example: bread, pasta, cereals, vegetables, fruit and milk
- Exercise or physical activity
- Other medications
- Blood glucose checking techniques.
Contact your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator if you notice that your blood glucose patters change or are consistently higher or lower than usual.
Also Check: Vegetarian Diabetic Meal Plan Chart
What If The Blood Glucose Check Result Doesnt Sound Right
If youre not convinced that a result is correct, heres a suggested check list:
- Have the strips expired?
- Is the meter too hot or too cold?
- Is the calibration code correct?
- Is the battery low or flat?
All meters will give a different result with a different drop of blood. As long as there is not a big difference there is not usually cause for concern.
The accuracy of all meters can be checked with meter-specific liquid drops called control solutions. If you are concerned, you can arrange to have your meter checked with a control solution. Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator or pharmacist can help you with this.
Interested In Learning More Read About Normal Blood Glucose Numbers Getting Tested For Type 2 Diabetes And Using Blood Sugar Monitoring To Manage Diabetes
Want to keep track of your blood glucose readings to help you better manage your condition? With our free printable diabetes logbook sheets, youll be able to monitor the effects of food, exercise, medicines and more. One sheet tracks levels for a week. Download your free blood sugar logbook today to start analyzing your patterns!
You May Like: Can Diabetes Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 35. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every three years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner and repeat testing may be recommended more often.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 or the onset of puberty and then every three years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
The Initial Causes Gestational Diabetes Monitoring Chart
Type 2 diabetes is a common condition in many people. This type is caused by a lack of insulin and is a result of an unhealthy lifestyle. The bodys inability to process glucose from the blood can damage many parts of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Fortunately, there are some things you can do to avoid diabetes. Here are five tips to help you lower your risk: Eat more vegetables and fruits, get regular exercise, and avoid smoking.
High levels of triglycerides in the blood are another factor that can cause diabetes. These triglycerides are caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the blood. A high triglyceride level causes the body to misrepresent insulin as a molecule, which causes glucose to build up in the blood. A simple blood glucose test can confirm your diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. By following these tips, you can begin living a healthy life and avoid the complications of diabetes.
A person with type 2 diabetes must consume less sugar. Glucose causes thirst and dehydration because the body releases energy stores into the bloodstream instead of using insulin. If untreated, diabetes can lead to weight loss and diabetic ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition whereby the cells are deprived of energy. To prevent the condition, you must make sure that your diet is low in glycemic load and that you exercise regularly.
Don’t Miss: How Many Carbohydrates Daily For Type 2 Diabetes
When Should I Measure My Blood Glucose
Throughout the rest of your pregnancy, you will need to measure your blood glucose levels at various points through the day, to check that they are within the limits you have been given at each of those times:
When you get up You need to measure your blood glucose levels each morning when you get up, before you have anything to eat or drink. This blood glucose level is called your fasting blood glucose level because you will have an empty stomach. You must not have eaten or drunk anything apart from water overnight, for at least eight hours.
Your team should have discussed this with you and agreed the ideal morning blood glucose level for you to aim for.
Before or after every meal You will probably be asked to measure your blood glucose level around the time of a meal. Some services measure before eating while others measure one or two hours after a meal .
Again, you will have discussed and agreed an ideal blood glucose level after meals with your diabetes team. These levels will be higher than your fasting blood glucose levels, as you will just have eaten.
If you are taking insulin to help to control your blood glucose levels, you may need to do a separate test before you go to bed, or even during the night, although this is unusual.
“When we did go out for a special meal or two, and I’d have a little bit of cheesecake or something, it really affected my sugar levels. But that would’ve been just twice in the whole pregnancy.” Gemma, mum of one
What Is The Normal A1c Level And A1c Chart
A1c level measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It is expressed as a percentage and can be measured with a simple blood test. A normal A1c level is below 5.7%, while a level of 6.5% or above indicates diabetes. How does the A1c level correspond to average blood glucose levels? Below is a chart that breaks it down:
The chart below shows whether your A1C result is normal or whether it could be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes.
A1C result chart for diabetes diagnosisTypical 5.7% or less Prediabetes ranges between 5.7% and 6.5%. More than 6.5% have diabetes. |
People with diabetes of any type are generally recommended to keep their A1C below 7%.
Read Also: What Do High Glucose Levels Mean
Alarming Facts About Diabetes
Screening For Gdm One Or Two Step
- ACOG supports the 2 step approach , followed by a 100g 3 hour oral glucose tolerance test if positive
- Note: Diagnosis of GDM is based on 2 abnormal values on the 3 hour OGTT
- ACOG recommends that currently there is insufficient evidence to diagnose GDM based on only one abnormal value
- Patients with only one elevated value may require additional surveillance
Don’t Miss: Is Cassava Flour Good For Diabetics