Signs And Symptoms Of G6pd Deficiency
Most patients with G6PD deficiency are asymptomatic. Clinical manifestations may include the following:
- Neonatal jaundice
- Episodes of intravascular hemolysis and consequent anemia, triggered by infections, medicines that induce oxidative stresses, fava beans, and ketoacidosis. Hemolysis begins 24 to 72 hours after exposure to oxidant stress. Patients with severe hemolysis present with weakness, tachycardia, jaundice, and hematuria.
- Chronic hemolytic anemia
References
Guide to G6PD deficiency rapid diagnostic testing to support P. vivax radical cure. World Health Organization. Available at . 2018 Accessed: July 19, 2021.
Nkhoma ET, Poole C, Vannappagari V, Hall SA, Beutler E. The global prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2009 May-Jun. 42:267-78. .
Beutler E. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a historical perspective. Blood. 2008 Jan 1. 111:16-24. .
Peters AL, Van Noorden CJ. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and malaria: cytochemical detection of heterozygous G6PD deficiency in women. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009 Nov. 57:1003-11. . .
Beutler E, Westwood B, Prchal JT, Vaca G, Bartsocas CS, Baronciani L. New glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutations from various ethnic groups. Blood. 1992 Jul 1. 80:255-6. .
Beutler E. G6PD deficiency. Blood. 1994 Dec 1. 84:3613-36. .
What Remains To Be Done
Much has been learned about G6PD deficiency and its effects in the past 50 years, but as in every field of science there is still much to learn. Here I can only mention a few of the problems that I consider to be important now.
The development of simple means of testing new drugs in vitro to determine whether they will cause hemolysis in patients has eluded us. Simply incubating drugs with red cells is unreliable, at least in part because it is usually drug metabolites, not the original drug, that are hemolytic. Several different model systems have been proposed, but none have been extensively validated. Perhaps the most attractive of these is the use of plasma from a normal subject ingesting the drug and determining whether it increases metabolism by way of the hexose monophosphate shunt.
Another area of importance is the most devastating result of G6PD deficiency: kernicterus. There has been a resurgence of severe neonatal jaundice and kernicterus in recent years, and G6PD deficiency is one of the causes. Should all newborns be screened? Is the human and the financial cost worth it? Should the screening be limited to ethnic groups who are known to have high gene frequencies, and if so, how will they be identified? Or would it be better simply to monitor bilirubin levels of newborns more closely, thus saving infants from the tragedy of kernicterus, regardless of cause?
Recommended Reading: What Is A1c In Relation To Diabetes
Who Is At Risk For G6pd Deficiency
G6PD deficiency occurs most often in men. It is rare in women.
The disorder affects about 10% of African-American men in the U.S. It is also common in people from the Mediterranean area, Africa, or Asia.
The severity of the disorder varies, depending on the group. In African-Americans, the problem is mild. It mainly affects older red blood cells. In whites, the disorder is often more serious. In this group, young red blood cells are affected.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes And Kidney Failure
Key Points About G6pd Deficiency
- G6PD deficiency is the lack of an enzyme in the blood.
- It is a genetic health problem that is most often inherited by men. Women do not usually get it. But they can be carriers and pass it to their children.
- It can cause hemolytic anemia. This is when the red blood cells break down faster than the body can make them.
- It affects about 10% of African-American men in the U.S. It is also common in people from the Mediterranean area, Africa, or Asia.
- Treatment includes avoiding certain medicines, foods, and environmental exposures.
What Factors Trigger Hemolysis And Other Conditions Related To G6pd Deficiency

According to some researchers, eating fava beans is the most common trigger. Other common triggers are:
- Certain foods, including legumes soybeans, peanuts and peas, and foods that have artificial food dyes.
- Emotional stress.
Its important to know that G6PD deficiency affects people differently. That means not everyone who has the genetic condition will have the same reaction. If youve been diagnosed with G6PD deficiency, ask your healthcare provider about genetic testing to identify your specific G6PD gene mutation so they can recommend ways you can avoid severe G6PD deficiency symptoms.
Read Also: Is Stevia Safe For Diabetics
Molecular Structure Analysis Using Pymol
The crystallized partial G6PD structure was retrieved from PDB . Only non-synonymous variants that were not previously investigated in Doss et al. and whose native residues were crystallized in 2BHL were analyzed. PyMol version 2.4.1 was used to model the 18 selected variants in order to visualize the potential structural changes they introduce to the native protein structure .
Why Are Males More Likely To Have G6pd Deficiency
G6PD deficiency is inherited as an X-linked recessive condition. Heres what that means:
- Males are more likely to have G6PD deficiency because they only have one X chromosome, which increases the odds a male will pass on the mutated G6PD gene.
- Females, however, have two X chromosomes, which increases the odds a female will pass on a normal G6PD gene instead of a mutated G6PD gene.
- Most females can carry the mutated gene and dont have G6PD deficiency. Some females may be affected if one or both copies of the G6PD gene are mutated. Females with one mutated gene may have lower G6PD activity and less risk of developing symptoms.
You May Like: Which Is Worse Type 1 Diabetes Or Type 2 Diabetes
Clinical Features Of G6pd Deficiency
The vast majority of individuals that harbor a mutant form of the G6PD gene go their entire lives without knowing they carry a mutation. The acute hemolysis that is the only common clinical manifestation in G6PD mutations can rapidly be compensated for and thus, may remain undetectable.
The most common symptoms of G6PD deficiency are neonatal jaundice and acute hemolytic anemia. The acute hemolytic attacks are the result of reduced antioxidant capacity of red blood cells with the result being membrane lipid peroxidation and consequent cell lysis.
The accumulation of reactive oxygen species in G6PD deficiency also leads to aberrant oxidation of the cysteine sulfhydryl groups in the globin proteins in hemoglobin. This results in significant cross-linking of hemoglobin tetramers which can be visualized microscopically. The cross-linked hemoglobin forms what is referred to histologically as Heinz bodies. The presence of Heinz bodies is diagnostic for G6PD deficiency versus erythrocyte pyruvate kinase deficiency which is not associated with the formation of these inclusion bodies.
Analysis of extracts from fava beans demonstrated that the toxic compounds are the pyrimidine aglycones, divicine and isouramil, that are derived from the pyrimidine glycosides vicine and convicine, respectively. Both divicine and convicine rapidly oxidize GSH to GSSG.
How Is G6pd Deficiency Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider can diagnose G6PD deficiency with a simple blood test. You may need this test if:
- Your family comes from an area where this condition is common
- You have a family history of G6PD deficiency
- You have an unknown form of anemia
Your provider may repeat tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Read Also: Is Propel Water Good For Diabetics
Overexpression Of Wt G6pd And Canton Variant In Sh
Prior to the cellular-based assays using SH-SH5Y cells, the duration of overexpression of WT G6PD and Canton variant was examined by transfecting the cells seeded in a 12-well plate. The genes encoding human WT G6PD and Canton variant were first PCR-amplified, which was then inserted into pcDNA 3.1/myc-His C using HindIII and XhoI restriction enzyme sites. 0.5g of cDNA and 1.5g of lipofectamine were diluted in 50L of Opti-MEM medium, respectively and incubated for 5min. The diluted DNA was combined with diluted lipofectamine, which was followed by incubation for 20min prior to the addition to cells. The transfected cells were collected at different time points , and the overexpressed G6PD levels were examined by Western blot. The transfection was carried out in 50% serum-starved cells. Once the duration of expression was confirmed, other cellular-based assays were performed.
G6pd Variants In The Qatari Population
We identified from the WGS data of 6,045 QGP participants 375 variants in/nearby the G6PD gene. These include 20 high-impact, 16 moderate-impact, 19 low-impact, and 320 modifier-impact variants . We focused on the high-impact and moderate-impact variants as previously indicated in Sect. 2.3. The five most common variants seen in the Qatari population and their corresponding frequencies in other databases are indicated in Fig. . The high-impact and moderate- impact variants are indicated in a liner protein diagram in Fig. , constructed using DOG V 2.0.1 based on the annotation mentioned in the literature .
Fig. 1
Recommended Reading: Daily Sugar Intake For Diabetics
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
You should see your healthcare provider any time you develop G6PD deficiency symptoms. Seek immediate medical help if your symptoms are severe and come on quickly.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If youve been diagnosed with G6PD deficiency, you may feel better knowing most people with G6PD deficiency never have symptoms. But if youre among those who do, or you have a newborn baby who does, youre probably worried about what to expect.
G6PD deficiency cant be cured, but its symptoms can be managed. You can take care of yourself by knowing what food and medications to avoid and by developing healthy habits such as drinking alcohol in moderation, getting enough rest and exercise and avoiding tobacco smoke. You can take care of your newborn baby by monitoring jaundice symptoms that are a sign of G6PD deficiency. Ask your healthcare provider for information to help you manage the impact G6PD deficiency may have on your daily life.
Usmle Step 2 Style Questions Usmle
A 30-year-old male presents to the emergency room with severe, intractable abdominal pain localized to the right upper quadrant area of his abdomen. He reports that he had been having intermittent pain over the past few weeks, but this episode has been unrelenting. An ultrasound reveals numerous . The patient is taken to the operating room for a . After the removal of , its contents were exposed, revealing numerous small, black gallstones. Which of the following is most likely finding on this patients medical history?
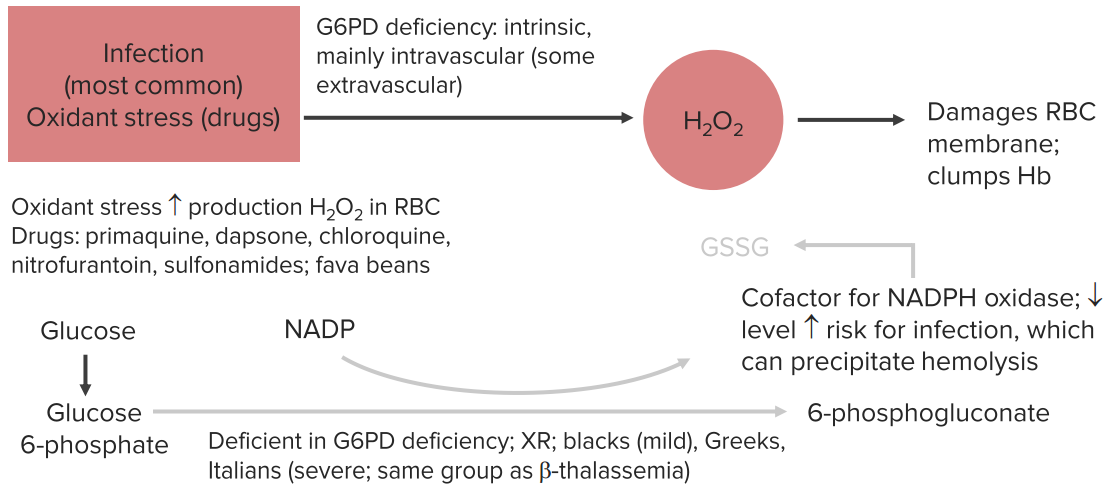
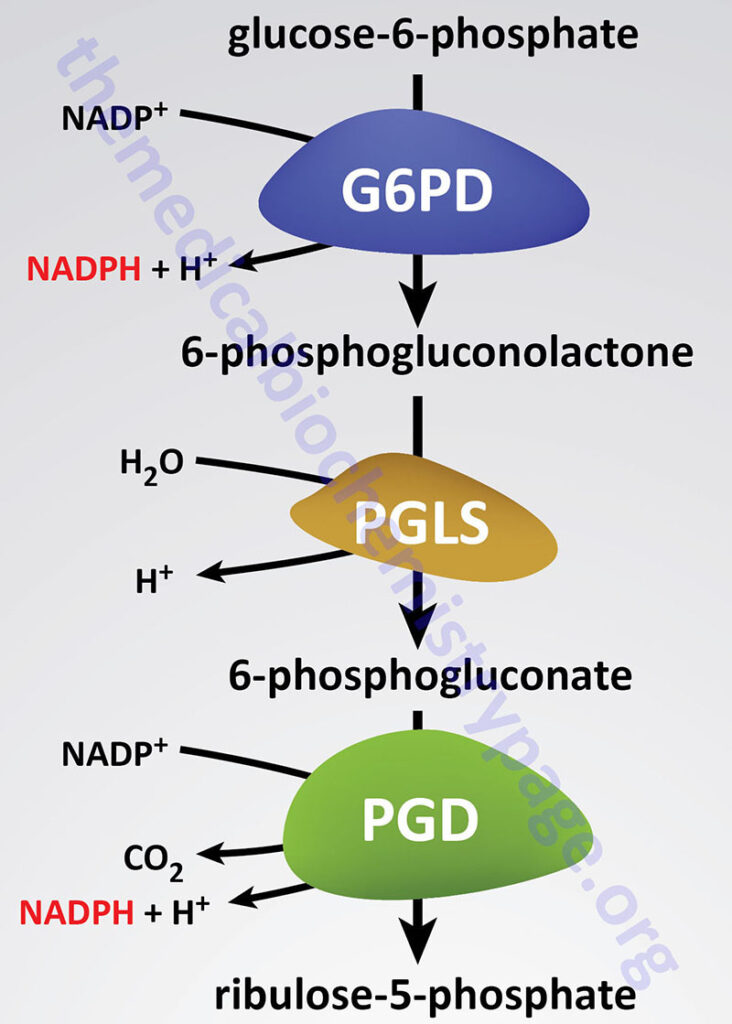
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, or , is a genetic disorder characterized by decreased levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, which leads to the destruction of red blood cells.
Normally, as a part of the , our produces free radicals like hydrogen peroxide, or H2O2.
Free radicals can damage the cells in many ways including destroying the DNA, proteins, and the .
Now, we have a molecule in our called glutathione which acts as an antioxidant and goes around and neutralizes these free radicals.
In order to function, these molecules need to be in the reduced state where they can donate an electron to the H2O2 and convert them into harmless water and oxygen.
However this causes the glutathione to become oxidized, so before it can get back to work, an enzyme called glutathione reductase will use an NADPH as an electron donor and and reduce the oxidized glutathione back into its working state.
Read Also: Medtronic Minimed Insulin Pump Lawsuit
How Is G6pd Deficiency Treated
In most cases, G6PD deficiency does not cause problems. Problems may occur if you are exposed to medicines or foods that may harm your blood cells. Depending on your gene flaw, you may be able to handle a small amount of these exposures.
Your healthcare provider will figure out the best treatment based on:
- Your age, overall health, and medical history
- How sick you are
Study Inclusion Criteria And Study Selection
All original studies describing association between G6PD deficiency and malaria were included in this systematic review. All eligible studies irrespective of publication type, study design, language and publication date were considered in the qualitative systematic review. There was no restriction on certain population, age, race, ethnicity, or geographic area. Only variables reported by two or more studies and whose primary data can be extracted were included in the meta-analysis. We limited included studies to those performed on human subjects. Reviews, case studies, case series, editor correspondences, news, letters, book chapters and studies whose data could not be reliably retrieved or extracted were excluded. We omitted studies whose data is overlapped with another included study. Two reviewers independently performed initial screening and study selection. Preliminary assessment of the title and abstracts was performed to identify relevant articles. Thereafter, full texts of eligible articles were downloaded and reviewed for qualitative analysis and potential inclusion in the data synthesis. Inclusion of a study by both reviewers was conclusive while discrepancies and disagreements as regards study eligibility were resolved by discussion and/or consensus with a third reviewer.
You May Like: Best Insoles For Diabetic Neuropathy
Chronic Nonspherocytic Hemolytic Anemia
This rather cumbersome heading originates from history. Hereditary spherocytosis has been, for over a century, a prototype of congenital hemolytic anemias , but in some patients with this kind of condition, spherocytes may not be prominent on a blood smear: after G6PD deficiency was discovered, some of them were found to be G6PD deficient.
In contrast to the high prevalence of G6PD deficiency that entails the risk of AHA, chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia is a rare disease . The clinical picture is generally similar to that of HS, including jaundice and gallstones, with wide-ranging severity : from mild to severe enough to require recurrent blood transfusion. Unlike in HS, a history of NNJ , often severe, is the rule. Needless to say, all agents capable of causing AHA in any G6PD-deficient person will cause acute on chronic hemolysis in patients with CNSHA. In some transfusion-dependent patients, splenectomy has proven highly beneficial .
Assessment Of The High
High- and moderate-impact variants were annotated using different databases such as Human Gene Mutation Database and ClinVar. They were also assessed through pathogenicity prediction tools including sorting intolerant from tolerant , Polyphen, combined annotation-dependent depletion , and dbNSFP-Polyphen2-HDIV. Allele frequencies of those variants were determined using the QGP dataset, the genome aggregation database , Greater Middle East , and the 1000 Genomes Project database.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar 136 After Eating
The Cloning Of G6pd And Definition Of Mutations
It was possible to show quite rapidly that Yoshidas deduction that G6PD A was a result of a substitution of aspartic acid for asparagine had been quite correct. Interestingly, it became apparent that G6PD A is not a single variant but a group of variants that had in common the same mutation as G6PD A+, together with one additional mutation, usually c.202 GA .
Read Also: Oral Insulin Pills For Type 1 Diabetes
G6pd Deficiency And Malaria
A close geographic correlation between the frequency of G6PD deficiency and malaria endemicity, reminiscent of what is well known for Hb S, has been observed in very many studies as a result, the coexistence of the 2 abnormalities is not infrequent, and it was natural to wonder whether G6PD deficiency makes sickle cell anemia worse. Overall, the effect is small. When G6PD-deficient red cells are infected by Plasmodium falciparum, they are sensed by macrophages as abnormal at an early stage they are removed, which seems a highly plausible protective mechanism. The original notion that protection is a prerogative of heterozygous females, as in classic balanced polymorphisms, has been confirmed by several recent studies. Perhaps G6PD deficiency protects against cerebral malaria but not against malaria with severe anemia, although this finding has been challenged as possibly due to collider bias. It remains counterintuitive that having only a portion of G6PD-deficient red cells is more protective than having all G6PD-deficient red cells . A convincing mechanistic explanation is still needed.
1960. Based on the close geographic correlation between the frequency of G6PD deficiency and the endemicity of P falciparum malaria, Allison and Motulsky independently suggested that the latter had been a factor in Darwinian selection of the former.
Recommended Reading: Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Gestational Diabetes
Pearls And Other Issues
A special situation exists in the management of G6PD patients with methemoglobinemia. Methemoglobin forms in red blood cells when the iron in the heme group of hemoglobin molecules undergoes oxidation from the normal ferrous state to the ferric state. This ferric state is a poor binder of oxygen. Symptoms of hypoxia begin to develop when the level of methemoglobin reaches 10%, and death can occur when the level reaches greater than 50%.
Methemoglobinemia should be considered in patients presenting with central cyanosis and hypoxia whose symptoms are resistant to supplemental oxygen. A specific antidote for severe acute methemoglobinemia is methylene blue. Intravenously injected methylene blue is reduced to leucomethylene blue through NADPH-dependent mechanisms. Leucomethylene blue is then used as a substrate to reduce methemoglobin back to hemoglobin. However, patients who are deficient in G6PD lack sufficient NADPH to properly reduce methylene blue. Unreduced methylene blue can cause further oxidative damage in the G6PD-deficient patient resulting in hemolysis and even death. Therefore, it is important that patients who are known or suspected to have any degree of G6PD deficiency not receive methylene blue. Alternative therapies for G6PD deficient patients presenting with methemoglobinemia include transfusing packed red blood cells or providing hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
What Can Parents Do
The best way to care for a child with G6PD deficiency is to limit exposure to anything that triggers symptoms. Check with your doctor for instructions, and a list of medicines and other things that could be a problem for a child with G6PD deficiency.
With the right care, G6PD deficiency should not keep a child from living a healthy, active life.
Recommended Reading: Is 5g Of Sugar A Lot For A Diabetic
Protein Expression And Purification
G6PD and its variants were expressed in E. coli C43 . When the culture density reached an OD600 of 0.50.6, 0.5mM IPTG was added to induce the protein expression. After culturing at 28°C overnight, the bacteria were centrifuged, and the pellets were lysed by sonication in buffer containing 50mM Tris , 300mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 0.4mM PMSF, 1mgmL1 lysozyme, 0.1% Triton X-100 and protease inhibitor cocktail . G6PD was then purified by incubating the supernatant with TALON Superflow resin equilibrated with 1 bed volume of equilibration buffer , 300mM NaCl and 5mM imidazole) at 4°C for 1h. The resin was washed with 5 bed volumes of wash buffer , 300mM NaCl and 20mM imidazole) in a gravity-flow column and resuspended in 5mL of equilibration buffer for size exclusion chromatography and 150mM NaCl). Bovine thrombin was added to the resin, which was followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with gentle shaking. Tag-less G6PD was eluted and applied onto HiLoad 16/600 Superdex 75pg size exclusion chromatography. Fractions containing G6PD were pooled and concentrated using 10kDa MWCO membrane. The final concentration of G6PD was determined by Bradford method, and the protein was stored in 40% glycerol at 80°C.