Why Postprandial Blood Sugar Matters For Metabolic Health
Poor blood-sugar control can set off a domino effect in the onset of metabolic syndrome. Prolonged elevated blood sugar can lead to insulin resistance and the exhaustion of insulin-producing beta cells, a cardinal feature of Type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is commonly characterized by a value known as the hemoglobin A1c, or HbA1c. This value measures the percentage of hemoglobin molecules bound to sugar the more sugar in the blood, the higher the HbA1c will be.
A study conducted in France found the loss of postprandial blood sugar control was the first step showed metabolic dysfunction even before elevations in fasting blood sugar. In the study, 130 patients with Type 2 diabetes were placed in five groups according to their HbA1c levels, ranging from under 6.5% to over 9%. Participants used continuous glucose monitors to measure their blood sugar levels over three days as most ate a prescribed diet of 45-50% carbohydrates, 35% fats and 15-20% protein .
Postprandial blood sugar can help you understand how your body responds to a specific food or foods.
The study found elevated postprandial glucose numbers as HbA1c climbed above 6.5%, even as fasting glucose remained normal or near-normal. In groups with higher HbA1c levels, blood glucose levels remained high postprandially and during fasting windows, including overnight.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly.
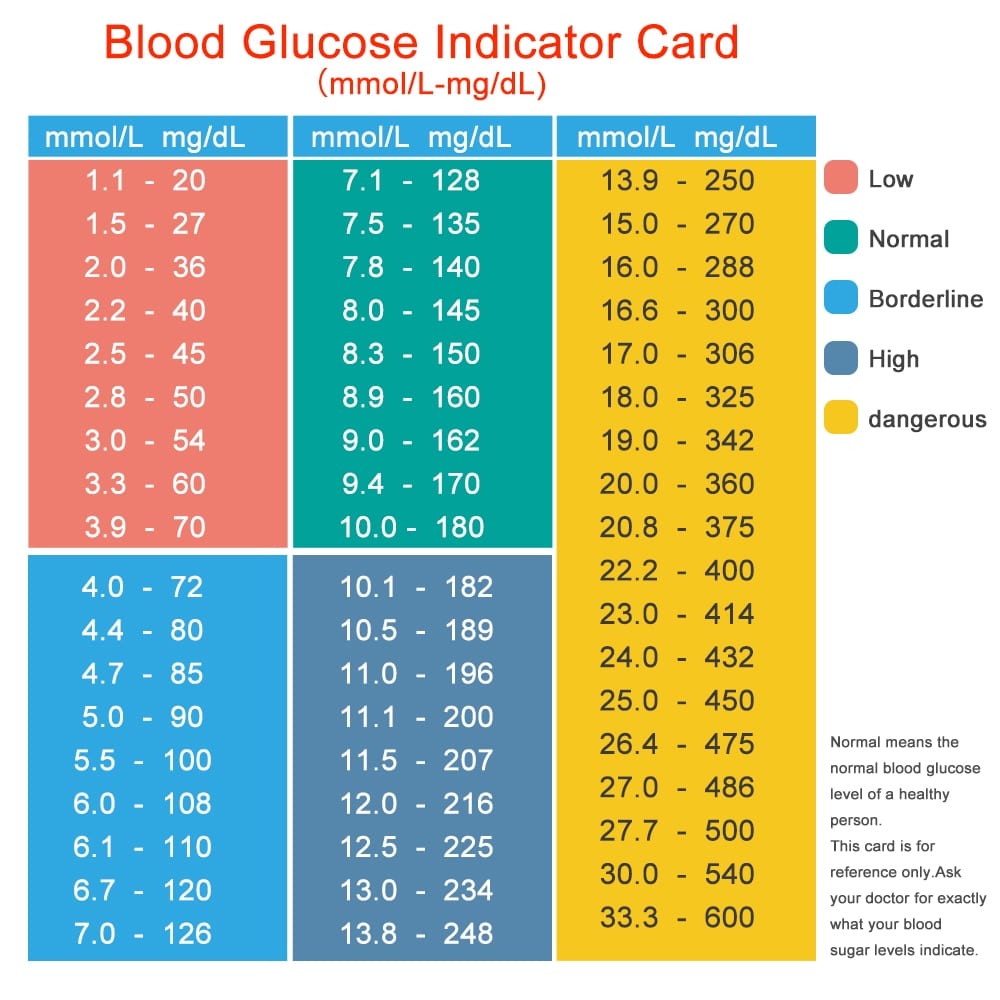
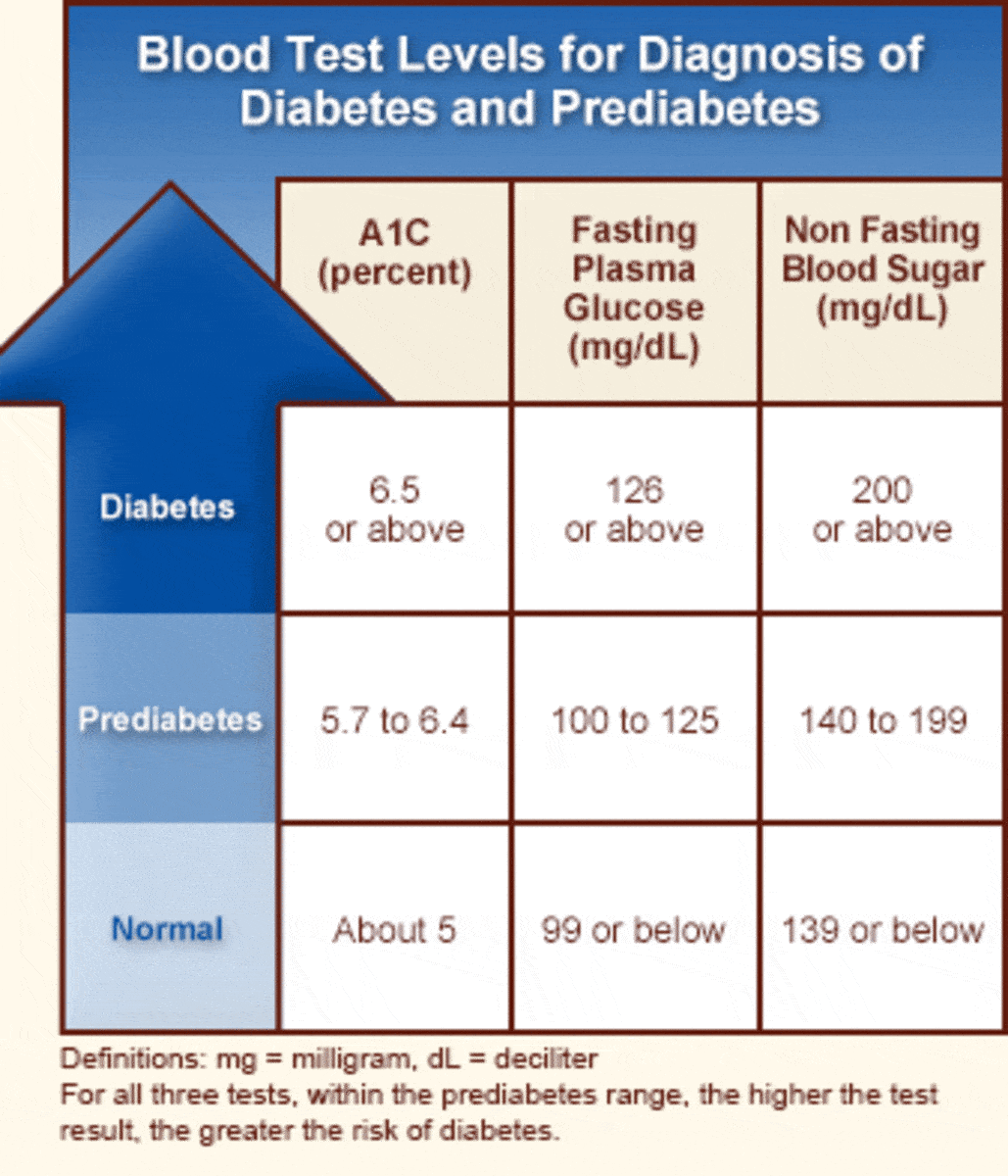
The following blood sugar and A1c results are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note:Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly that they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in ourDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Fasting Glucose Goal: 72
Why? Previously we discussed that the ADA considers normal fasting glucose as anything < 100 mg/dl. However, multiple research studies show that as fasting glucose increases, there is an increased risk of health problems like diabetes and heart disease even if it stays within the normal range. The highlights of some of the study results include:
- Men whose fasting blood glucose was greater than 85 mg/dl had a significantly higher mortality rate from cardiovascular diseases than men with blood sugars less than 85 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels in the high normal range had significantly increased cardiovascular disease risk than people whose levels remained below 80 mg/dl.
- Children with fasting glucose levels 86-99 mg/dl had more than double the risk of developing prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes as adults when compared with children whose levels were less than 86 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels between 91-99 mg/dl had a 3-fold increase in Type 2 diabetes risk compared to those with levels less than 83 mg/dl.
- Among young, healthy men, higher fasting plasma glucose levels within the normal range constitute an independent risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. This means that as fasting glucose increases, even if the level is still considered normal, it could indicate a significantly higher risk of developing diabetes, and this is particularly pronounced if BMI is greater than 30. .
Recommended Reading: Can You Buy Insulin Over The Counter At Walgreens
How Do I Get Ready For This Test
You must fast for 12 hours before the test and then eat a meal with at least 75 grams of carbohydrates. After the meal, don’t eat anything else before having the test. Plan to rest during the 2-hour waiting period, because exercise can cause blood sugar levels to rise. You may not have to fast if you’re pregnant.
Be sure your healthcare provider knows about all medicines, herbs, vitamins, and supplements you are taking. This includes medicines that don’t need a prescription and any illegal drugs you may use.
Still Frustrated With Your Blood Sugar And A1c Results
Your blood sugars and your insulin or medication needs never stay in one place. If you gain weight or lose weight, your insulin and medication needs will change. If you become more active or less active, your needs will change. If you make drastic or even small changes to your nutrition, your needs will change!
Working with your diabetes healthcare team, and diabetes coaches who can teach you how to make changes in your overall diabetes management plan are essential. Diabetes is a lifelong learning process.
Take a deep breath and be patient. If you dont like what youre seeing on your glucose meter, dont get madget studying! Take good notes and work with your team to make changes to reach your goals.
Read Also: How Dangerous Is Type 2 Diabetes
How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
How To Manage Blood Sugar Spikes After Meals
If you’re trying to manage diabetes, you already know it’s important to keep track of your blood sugar levels. But how do you handle a spike that comes after you eat? It’s called “postprandial” blood glucose, and if you take some simple steps, you can get it under control and help avoid health problems.
You May Like: What Medicine Do You Take For Diabetes
Idiopathic Postprandially Reactive Hypoglycemia
Idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia occurs at the 3rd hour of OGTT. It occurs mostly in teenagers and nonobese. The cause and pathophysiological importance have not been fully elucidated. This type of hypoglycemia usually does not develop diabetes. Tamburrano et al. reported that increased insulin sensitivity represents a feature of idiopathic reactive hypoglycemia.
Why The Test Is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs of diabetes . More than likely, the doctor will order a fasting blood sugar test.
The blood glucose test is also used to monitor people who already have diabetes.
The test may also be done if you have:
- An increase in how often you need to urinate
- Recently gained a lot of weight
SCREENING FOR DIABETES
This test may also be used to screen a person for diabetes.
High blood sugar and diabetes may not cause symptoms in the early stages. A fasting blood sugar test is almost always done to screen for diabetes.
If you are over age 45, you should be tested every 3 years.
If you’re overweight and have any of the risk factors below, ask your health care provider about getting tested at an earlier age and more often:
- High blood sugar level on a previous test
- Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher, or unhealthy cholesterol levels
- History of heart disease
- Member of a high-risk ethnic group
- Woman who has been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary disease
- Close relative with diabetes
- Not physically active
Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Oral Insulin Pills For Type 1 Diabetes
Question : What Is The Contribution Of Ppg To The Long
Controlled clinical trials, such as the DCCT and the Stockholm Diabetes Study in type 1 diabetes and the Kumamoto Study and UKPDS in type 2 diabetes, have established that therapies directed at achieving normal glycemia are effective in reducing the development and delaying the progression of long-term microvascular diabetic complications.
Even before these clinical trials were completed, observational studies demonstrated a positive association between retinopathy and hyperglycemia. The epidemiological studies relied predominantly on measures of chronic glycemia, such as HbA1c. In the relatively few studies in which HbA1c, FPG, and 2-h OGTT value were measured, all were similarly associated with the risk for retinopathy. Considering the interrelationships among these glycemic measures , these results are not surprising.
Interventional studies have not demonstrated a convincing beneficial effect of glucose lowering on CVD outcomes , and no clinical trials have examined whether treatments that primarily lower PPG decrease cardiovascular events. Associations of CVD and CVD risk factors with glycemia have been demonstrated over a broad range of glucose tolerance, from normal to diabetic, in several epidemiological studies. Whether the FPG or a postchallenge glucose level is an independent risk factor for CVD in these studies is controversial and requires further study.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
The answer to the question what is a normal blood sugar level is as follows:
Fasting normal blood sugarNormal for person without diabetes: 7099 mg/dl Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: 80130 mg/dl
Normal blood sugar 2 hours after mealsNormal for person without diabetes: Less than 140 mg/dl Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: Less than 180 mg/dl
HbA1cNormal for person without diabetes: Less than 5.7%Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: Less than 7.0%
Source: American Diabetes Association: Checking Your Blood Sugar, American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
Recommended Reading: Life Insurance For Diabetics Type 2
Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications like Metformin, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
Question : What Is The Relationship Among Ppg Fpg And Hba1c
Hemoglobin A1c is a measure of the degree to which hemoglobin is glycosylated in erythrocytes and is expressed as a percentage of total hemoglobin concentration. It reflects the exposure of erythrocytes to glucose in an irreversible and time- and concentration-dependent manner. HbA1c levels provide an indication of the average blood glucose concentration during the preceding 23 months, incorporating both pre- and postprandial glycemia.
Because blood glucose concentrations vary widely during a 24-h period and from day to day in diabetes, the measurement of HbA1c is the most accepted indicator of long-term glycemic control. However, the HbA1c level does not provide a measure of the magnitude or frequency of short-term fluctuations of blood glucose, which are particularly great in type 1 diabetes.
The relative contributions of FPG and PPG to HbA1c have been studied only recently. Data from several large cohorts with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes were presented at the conference. In general, FPG, PPG, and especially mean plasma glucose concentrations, defined by the average of multiple measurements of glucose taken throughout the day, are highly correlated with HbA1c. In contrast, postprandial glucose excursions , defined as the change in glucose concentration from before to after a meal, and the incremental glucose area, defined as the area under the glucose curve that is above the premeal value, are poorly correlated with HbA1c.
Read Also: Where Should I Inject My Insulin
What Is The Target Blood Sugar Level Everyone Should Achieve
| Thi gian kim tra | ||
| Trong khong thi gian 3 tháng, lng HbA1C trong máu. | Ít hn 5,7%. | Ít hn 7%. |
| Thi gian kim tra |
| Quá cao: Tìm cách làm gim lng ng trong máu. | |
| 240 300 mg / dl | Quá cao: ây có th là du hiu ca vic qun lý lng ng huyt không hiu qu, vì vy, hãy i khám bác s. |
| 300 mg / dl tr lên | Rt cao: Cn tìm kim s chm sóc y t ngay lp tc. |
Please dialHOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and receive 20% off for consultation fee at the first appointment MyVinmec app is also available and convenient for your bookings management andTelehealth service with Vinmec doctors all in one.
XEM THÊM:
Timing And Route Of Delivery
In gestational diabetes, shoulder dystocia is the complication most anticipated at the time of delivery. In one study,36 this complication occurred in 31 percent of neonates weighing more than 4,000 g who were delivered vaginally to unclassified mothers with diabetes. No prospective data support the use of cesarean delivery to avoid birth trauma in women who have gestational diabetes. One remaining limiting factor is the 13 percent error rate in estimating fetal weight by ultrasonography.37
A decision analysis38 that evaluated the cost and efficacy of a policy of elective cesarean delivery for an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g in mothers with diabetes found that 443 cesarean deliveries would need to be performed to prevent one case of brachial plexus injury, at a cost of $930,000. A reasonable approach is to offer elective cesarean delivery to the patient with gestational diabetes and an estimated fetal weight of 4,500 g or more, based on the patient’s history and pelvimetry, and the patient and physician’s discussion about the risks and benefits. There are no indications to pursue delivery before 40 weeks of gestation in patients with good glycemic control unless other maternal or fetal indications are present.
Recommended Reading: Is Jamun Good For Diabetes
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Definition Of 2 Hours Of Glucose Level :
Postprandial glucose
Recommended Reading: What Effects Does Diabetes Have On The Body
Question : Under What Circumstances Should People With Diabetes Be Tesed For Ppg
The only setting in which PPG monitoring has been shown to improve outcomes is gestational diabetes. In one study, women with gestational diabetes were randomly assigned either to a treatment program in which therapy was adjusted to achieve predefined FPG and PPG levels or to one targeting premeal and bedtime glucose levels . The women assigned to postprandial monitoring achieved a lower HbA1c and required fewer Caesarian sections for cephalopelvic disproportion, and their babies suffered less frequently from macrosomia and neonatal hypoglycemia. Whether similar outcomes could have been achieved with premeal monitoring if lower premeal targets had been selected is unknown. There are no comparable randomized clinical studies in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes examining whether PPG monitoring improves outcomes.
Are there other clinical situations in which PPG monitoring should be considered part of the overall treatment plan? There are no adequate randomized clinical trial data to answer this question, but the following are clinical situations in which PPG monitoring could be considered:
How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Recommended Reading: Diet Plan For Diabetes Cancer Patient