How Common Is Low Blood Glucose
Low blood glucose is common among people with type 1 diabetes and among people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin or some other diabetes medicines. In a large global study of people with diabetes who take insulin, 4 in 5 people with type 1 diabetes and nearly half of those with type 2 diabetes reported a low blood sugar event at least once over a 4-week period.2
Severely low blood glucose, defined as when your blood glucose level drops so low you cant treat it yourself, is less common. Among U.S. adults with diabetes who take insulin or some diabetes medicines that help the pancreas release insulin into the blood, 2 in 100 may develop severely low blood glucose each year.3
How To Prevent High Blood Sugar
The best way to treat high blood sugar is to prevent it from happening in the first place. Not only does this help to avoid a potential emergency, but it also reduces the likelihood of experiencing diabetic complications. Patients with diabetes can prevent high blood sugar by taking some of the following measures:
References and Sources:
What Are The Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia
Its especially important to know the early signs of hyperglycemia if you have type 1 diabetes. If hyperglycemia is left untreated in people with type 1 diabetes, it can develop into ketoacidosis, where ketones, which are toxic acids, build up in the blood. This condition is an emergency situation that can lead to coma or death.
Early symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- High blood sugar.
- Unusual fruity smell on the breath.
- Deep labored breathing or hyperventilation.
- Rapid heartbeat.
Read Also: Is Jamun Good For Diabetes
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Problems Associated With High Blood Sugar
Frequent high blood pressure puts patients at risk of diabetes complications that can be potentially serious. Even when blood sugar does not reach acutely dangerous levels, complications can develop over time if blood sugar is consistently above a patients target range. Serious conditions and complications associated with high blood glucose include:
- Damage to the blood vessels of the eyes
- Nerve damage in the feet and hands
- Increased risk of kidney disease
- Increased risk of heart problems like heart disease
Depending on the type of diabetes a patient has, there are two different extreme forms of hyperglycemia as well. Ketoacidosis is severe hyperglycemia that impacts people with type 1 diabetes. Ketoacidosis occurs when the body runs out of glucose and begins to use ketones, a type of toxic acid, for energy. Ketoacidosis can lead to diabetic coma or even death, and it is extremely serious. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome is a severe form of hyperglycemia that impacts people with Type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the blood glucose level goes too high and the body tries to rid itself of the excess glucose through frequent urination. If the body becomes dehydrated enough, it can go into a coma.
Read Also: How To Know If I Got Diabetes
Low Blood Glucose During Sleep
Your blood glucose level can drop while you sleep and stay low for several hours, causing serious problems.7 Symptoms of low blood glucose while you sleep can include
- crying out or having nightmares
- sweating enough to make your pajamas or sheets damp
- feeling tired, irritable, or confused after waking up
Although you may not wake up or notice any symptoms, low blood glucose can interfere with your sleep, which may affect your quality of life, mood, and ability to work. Having low blood glucose during sleep can also make you less likely to notice and respond to symptoms of low blood glucose during the day.
Your Legs And Feet Are Swollen
When there’s too much sugar in the system, it can pull water into cells, which will swell up over time if you don’t get these fluids moving through your body regularly.
The American Diabetes Association claims that people who have diabetes tend to have legs and feet up to five times larger than they should be, which can lead to complications within the circulatory system, including infections and reduced blood flow.
If you notice your feet and ankles begin to swell up, make sure to keep them elevated when possible. It’s important to treat swelling as soon as possible by elevating your legs higher.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Control My Diabetes
Correcting High Blood Sugar Levels With Insulin
If you take insulin, one way to reduce blood sugar is to inject insulin.
However, be careful as insulin can take 4 hours or longer to be fully absorbed, so you need to make sure you take into account how much insulin you may already have in your body that is yet to be absorbed by the blood. Insulin that is yet to be absorbed by the blood is called active insulin.
If you decide to correct with insulin, watch you dont over correct as this can lead to hypoglycemia and can be dangerous, particularly so before bed.
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
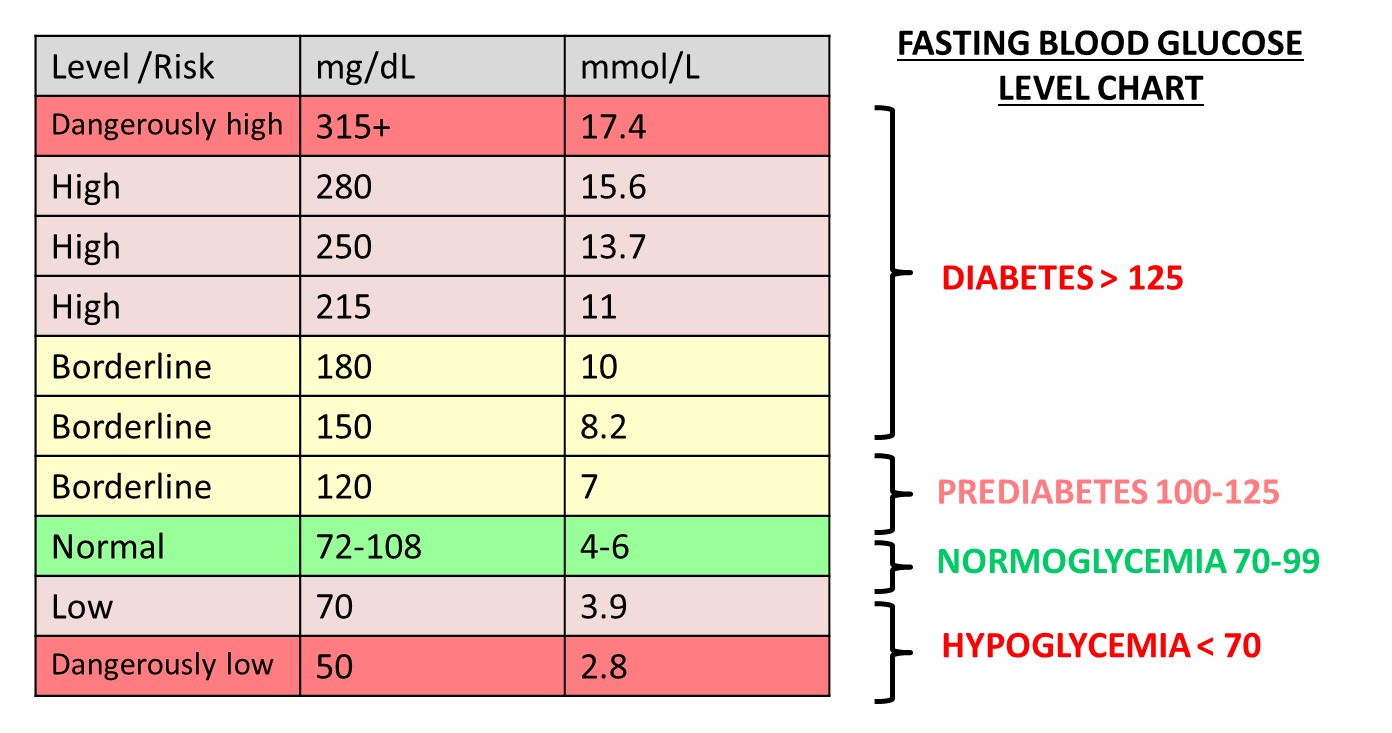
FREE blood glucose level chart
You May Like: Best App To Track Diabetes
Think About What’s Going On
Irene Dunbar of Durham, NC woke up one morning to discover that her blood sugar was at 119, which was high for her. “I had a cold and had had orange juice yesterday, and I normally do not drink orange juice,” said Dunbar, who thought, ‘I better not do that.”
Sometimes, determining the cause of an elevated level may make you feel like a detective. But it’s important to ask yourself questions about potential causes, such as diet and exercise habits, changes in your treatment plan, or personal life adjustments. Determining the answers to these questions can help pinpoint what might be going wrong, according to MedlinePlus.
What High Blood Sugar Feels Like
The symptoms can include:
- Breath that smells like fruit
- Confusion
These are symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis . Your body burns glucose for energy. When your cells donât get enough of it, they burn fat. That produces chemicals called ketones. When these build up, your blood becomes more acid-like. This can be life-threatening if itâs not treated.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Free Diabetic Supplies
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Blood glucose levels can be measured at any time, for example, when someone fasts , before they eat, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating, is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
A Few Final Notes On Keeping Blood Sugar Stable
Taking an active, intentional approach to your blood sugar levels is crucial to your quality of life and overall health, ONeill says. Avoiding too-high or too-low blood sugar levels will help you avoid adverse symptoms and health complications, and staying within your target range can enable you to feel your best and do whatever you want to do in life, she says.
Test your blood sugar regularly, listen to your body, and dont ever hesitate to reach out to your doctor.
Additional reporting by Karen Appold.
Read Also: Boost Or Glucerna For Diabetics
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Healthy Individuals
Youreconsidered as a diabetic, a term used to call an individual with diabetes, whenthe level of your blood sugar is higher than normal. Unfortunately, some people are probably unaware whentheir level is high since they dont know what diabetes symptoms look like.
Accordingto NIDDK ,a staggering 25 percent of individuals with diabetes dont realize they livewith the disease. Furthermore, 1 out of 3 people probably has acondition called pre-diabetes, one CDC report suggests. Pre-diabetes isborderline diabetes, a phase when your blood sugar is higher than normal butits not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Its usually hard to tell whether or not youre diabetic if you only rely on the symptoms. The best way to accurately catch it is by measuring your blood sugar level! This can help figure out whether youre in a healthy range.
Blood sugar levels are usually classified into two categories when fasting and after eating . In most healthy individuals, these are as follows :
It seemsthe normal level may also vary from person to person. For some people, 60 mg/dL is probably still OK ask a doctor for more guidance!
What Is High Blood Glucose
To fully understand your blood glucose levels, itâs important to know: a) what values are actually considered high, and b) factors that can cause your elevated reading in the first place.
High blood glucose, also known as hyperglycemia, occurs when there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is the result of too little glucose in the bloodstream. Hyperglycemia usually occurs because your body doesnât produce enough insulin or canât properly use the available insulin to remove the glucose from the bloodstream.
Using milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood for measurement, high blood glucose readings after a meal indicating prediabetes can fall between 140 and 199 mg/dL. Levels reaching 200 mg/dL two hours after eating indicate you may already be insulin resistant or diabetic, though that diagnosis will need to come from your doctor. By comparison, the typical standard for normal glucose readings is to remain under 140 mg/dL throughout the day and under 100 mg/dL after eight hours of fasting.
A range of lifestyle factors, habits, and health conditions can cause high blood sugar. To debunk common hyperglycemia myths, review causes and symptoms, and discuss the best ways to address them, we spoke with two experts on high blood sugar levels: registered dietitian and For The Love of Diabetes creator Lori Zanini and registered dietitian nutritionist and diabetes management expert .
Read Also: Which Rice Is Good For Diabetic Patients
High Blood Sugar Symptoms: Causes Signs And Taking Control
If youve had diabetes for any length of time at all, youve probably seen lists of the signs and symptoms of high blood sugar dozens of times. Doctors and diabetes educators hand them out. Hundreds of websites reprint them. Most diabetes books list them. You likely know some of the items on the list by heart: thirst, frequent urination, blurry vision, slow healing of cuts, and more.
But have you ever stopped to wonder why these symptoms occur? How does high blood sugar cause frequent urination, make your vision go blurry, or cause all of those other things to happen? Here are some answers to explain whats going on in your body when you have high blood sugar.
To get cutting-edge diabetes news, strategies for blood glucose management, nutrition tips, healthy recipes, and more delivered straight to your inbox, !
The 411 On A1c: Normal A1c Levels And 15 Ways To Lower High A1c
The hemoglobin A1C test is the closest thing to a diabetes scorecard you can find. Whether someone has had diabetes mellitus for years or if they have just been diagnosed, they have probably heard about this test. Unlike blood sugar meters people use at home, the A1C measures an average blood sugar level over the past several months by analyzing how many of a patients hemoglobin cells have glucose attached to them. The test results keep track of how well a person is managing his or her diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Sugar Diabetes In A Man
High Blood Glucose: Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia means that you have too much blood glucose. It happens when your blood glucose level is around 200 mg/dL or higher. Hyperglycemia can happen if you miss taking your diabetes medications, eat too much or do not get enough exercise. Sometimes, the medications you take for other problems cause high blood glucose.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- Having blurry vision
- Having to urinate often
If you have these symptoms, check your blood glucose right away. If its too high, follow these steps:
- Check your blood glucose every four hours. If your level does not go down after two checks or your symptoms get worse, call a member of your diabetes team.
- Drink water or other sugar-free liquids, such as diet soda or Crystal Light.
- You may need to take an extra dose of insulin. Your diabetes educator talks with you more about this.
Is Hyperglycaemia Serious
The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep blood sugar levels as near to normal as possible. But if you have diabetes, no matter how careful you are, you’re likely to experience hyperglycaemia at some point.
It’s important to be able to recognise and treat hyperglycaemia, as it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated.
Occasional mild episodes aren’t usually a cause for concern and can be treated quite easily or may return to normal on their own. However, hyperglycaemia can be potentially dangerous if blood sugar levels become very high or stay high for long periods.
Very high blood sugar levels can cause life-threatening complications, such as:
- diabetic ketoacidosis a condition caused by the body needing to break down fat as a source of energy, which can lead to a diabetic coma this tends to affect people with type 1 diabetes
- hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state severe dehydration caused by the body trying to get rid of excess sugar this tends to affect people with type 2 diabetes
Regularly having high blood sugar levels for long periods of time can result in permanent damage to parts of the body such as the eyes, nerves, kidneys and blood vessels.
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team. You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Erectile Dysfunction
How Often Is A1c Tested
To keep A1C levels in check, patients should have the test repeated regularly. If the A1C is less than 5.7, indicating you dont have diabetes, you should have it checked every three years, according to Robert Williams, MD, a family doctor and geriatrician in Lakewood, Colorado, and a medical advisor for eMediHealth. If it is between 5.7 and 6.4, indicating you are at risk of developing diabetes, you should have it rechecked every one to two years. If you have a confirmed diabetes diagnosis, and your blood sugar is well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every six months. If you already have diabetes and your medications change, or your blood sugar is not well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every three months.