How Is Type1 Or Type2 Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosed
The definitive diagnosis of either type of diabetes is done through blood testing. The amount of sugar in the blood can be determined in several ways. First, a fasting blood sugar level can be determined. Fasting blood sugar levels under 100 mg/dL are considered normal, between 100 mg/dL and 126 mg/dL are considered borderline, and over 126 mg/dL are considered diabetic.
Other tests may include a glucose tolerance test or the A1c test. The glucose tolerance test measures the way the body responds after a sugar solution is introduced. A patient’s blood is tested at various intervals after drinking the sugar solution to determine if values are normal. The A1c test measures the sugar in the red blood cells over a three-month time span. It is not a method for diagnosis, but it is helpful for monitoring and controlling the disease.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can come on over time or suddenly. Sometimes, kids dont have diabetes symptoms yet and the condition is discovered when blood or urine tests are done for another reason. Kids who show symptoms may:
- need to pee a lot
- start to wet the bed after having been dry at night
- be thirstier and drink more than usual
- feel tired often
- lose weight
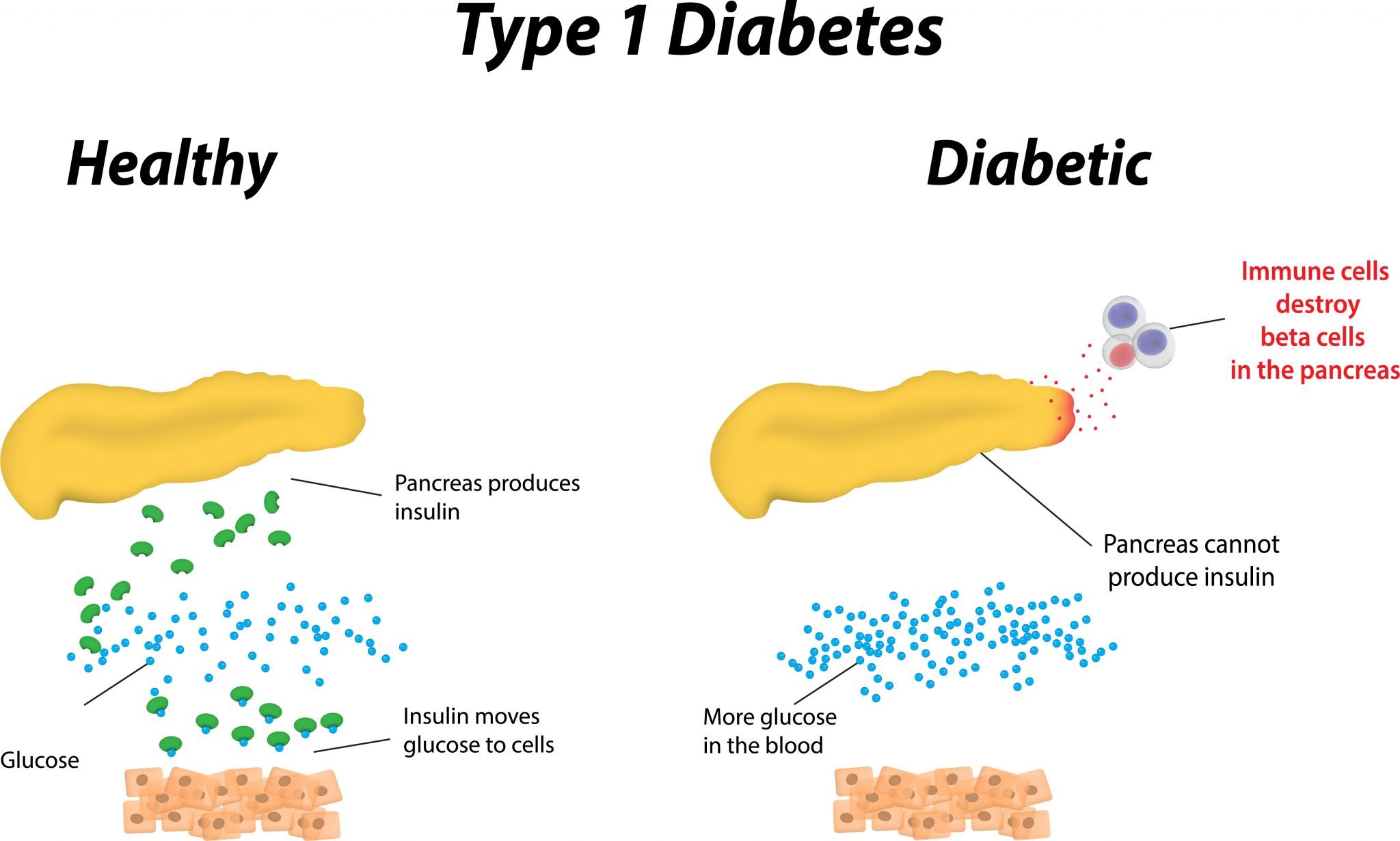
The Immune Phenotype Of Type 1 Diabetes
The pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes results from a complex interaction between the pancreatic -cell and innate and adaptive immune systems . The question of whether a trigger for the immune response against cells exists or whether the immune response is a random stochastic event has been a subject of considerable speculation and controversy. Several viral infections are associated with type 1 diabetes, with enterovirus being one of the most commonly associated infections. Enteroviral major capsid protein VP1 and RNA have been detected in islets from people with recent-onset type 1 diabetes, along with hyper-expression of the class 1 major histo compatibility complex and other indices of viral infection. One possibility is that some people with type 1 diabetes have an atypical, chronic viral infection of cells, leading to chronic inflammation and the development of autoimmunity. The viral hypothesis has been difficult to test, although both antiviral therapy and the development of vaccines targeting enteroviruses are being pursued for this purpose.
The immunopathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
Also Check: Ways To Manage Type 2 Diabetes
Current Therapy For T1d
Current T1D therapy focuses on matching exogenous insulin and food intake while incorporating daily activities such as exercise and sleep. Remarkable advances have been made in insulin formulation and diabetes technology, including methods for insulin delivery and glucose monitoring . Additionally, T1D clinical care is evolving to incorporate mobile technology and provide greater emphasis on behavioral and psychosocial aspects, the social determinants of health, and health care access/cost. The goal is near normoglycemia while avoiding hypoglycemia and allowing for normal daily activities. Traditionally, the glycemic goal in T1D has been an A1C of 7.0 or lower, with this target individualized for age, comorbidities, and lifestyle . Importantly, hypoglycemia, a major adverse effect of intensive glycemic control, is a substantial, lifelong burden of current therapy for T1D .
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
How Can Parents Help
Now is the perfect time to help your child to create healthy habits for life. Heres how:
- Get involved with daily care. Help your child put their care plan into action every day. From counting carbs, to calculating insulin doses, and giving injections, theres a lot to learn at first. Share the responsibilities with your child. Over time, theyll be able to take on more on their own. Turn to your childs care team with any questions about the care plan or daily care.
- Learn all you can about diabetes. The more you know about type 1 diabetes, the more confident youll feel about helping your child manage it day to day. And a solid understanding of diabetes lets you advocate for your child. You can share your knowledge with important people in your childs life, like grandparents, teachers, coaches, and babysitters. Doing so helps you build a community of support for your child.
- Encourage your child. It can take a while to adjust to the new responsibilities that come with type 1 diabetes. Remind your child that many kids their age have type 1 diabetes, and they follow a similar care plan. If your child has concerns that youre not sure how to handle, ask the care team. Theyll connect you with the right resources.
Having a child with type 1 diabetes may seem overwhelming at times, but you’re not alone. If you have questions or problems, reach out to your childs diabetes care team they can help with all kinds of issues, and will guide your family through this journey.
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Like type 1 diabetes, LADA is an autoimmune disease. Also known as type 1.5 diabetes, LADA most often sets in around age 30. For that reason, it is sometimes initially misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes. One telltale difference between the two is that LADA is not associated with weight gain.
With LADA, the body attacks the beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin, severely limiting the body’s insulin production over time. This may happen quickly or be drawn out over a longer period of time.
People affected by LADA may have a family history of autoimmune conditions or a genetic predisposition to type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Treatment for LADA involves supporting the body’s existing insulin production for as long as it lasts, then transitioning to regular insulin, other medications , and a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
Don’t Miss: Does Chromium Picolinate Help With Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus And Mortality
Well controlled diabetes reduces the risk of diabetes related complications from developing.
However with consistently elevated blood glucose readings it can lead to the development of vision loss, even blindness, end-stage renal disease and in some cases premature death. Just as important as conrolling blood glucose levels is controlling blood pressure, lipids and weight.
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus face a three times higher level of mortality than the general population.
Mortality rates from cardiovascular disease are five times higher amongst men with diabetes and eight times higher amongst women with diabetes.
HbA1c level radically influences risk of death, with every 1% increase adding 21% to mortality.
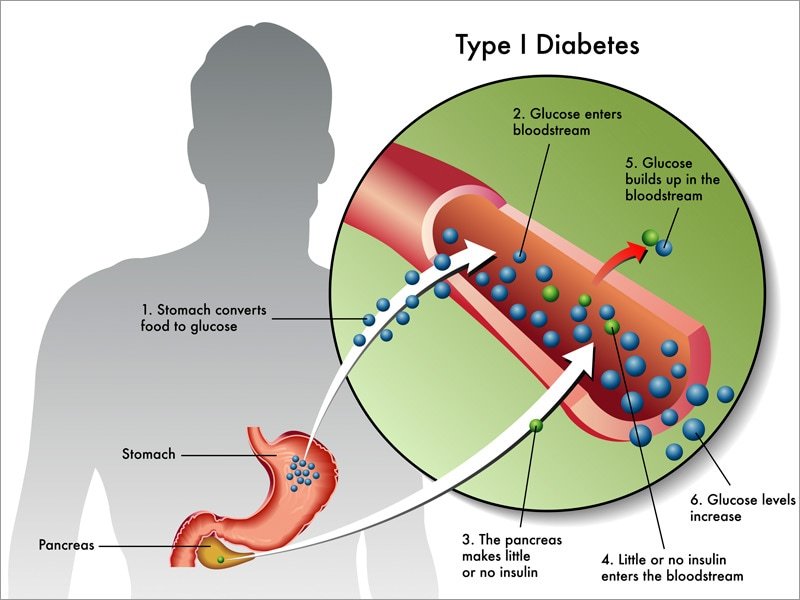
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
The goal of type 1 diabetes treatment is to control glucose levels and prevent your childs blood sugar from being too high. The ideal diabetes management regimen includes insulin therapy, glucose and ketones monitoring, regular exercise, and healthy eating.
Insulin therapy replaces insulin the body cannot make on its own. Usually, this is done with both long-acting and short-acting insulin injections. Many people with type 1 diabetes use insulin pumps instead of injections. Your diabetes team can teach you more about insulin pumps.
Glucose monitoring It is very important to monitor glucose levels throughout the day. You can do this with finger-stick blood glucose checks and/or with a continuous glucose monitor . CGM devices measure blood sugar with a subcutaneous glucose sensor and report a value every five minutes. Some devices can report values directly to a parent or patients mobile phone. The FDA has approved some CGM devices for use as a replacement for finger-stick tests.
Ketone monitoring When the body doesnt have enough insulin, the liver compensates by producing extra ketones, a chemical that converts fat into energy. High levels of ketones in the blood can become a medical emergency. Therefore, in addition to monitoring glucose levels, it is very important to monitor ketones when your childs glucose level is very high or when your child is sick.
Read Also: Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes In Child
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Other Forms Of Diabetes
In 1% to 5% of people who have diabetes, other conditions might be the cause. These include diseases of the pancreas, certain surgeries and medications, and infections. In these cases, your doctor might want to keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
Show Sources
American Diabetes Association: “Frequently Asked Questions about Pre-Diabetes,” “Type 2 Diabetes,” “The Dangerous Toll of Diabetes,” tion: “Gestational Diabetes,” “About Insulin and Other Drugs.”
National Library of Medicine: “Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Education Project: “About Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse : “National Diabetes Statistics, 2011.”
Merck Manual Consumer Version: âDiabetes Mellitus .â
CDC: âAbout Diabetes,â âPrediabetes: Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes.â
World Journal of Diabetes: âType 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents.â
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
Don’t Miss: Protein Shake For Diabetic Patients
Emerging And Future Therapies To Treat Or Prevent T1d
At this dawn of the next century after insulins discovery, anticipated new therapies fall into three broad categories : exogenous insulin replacement cell-based insulin delivery from new sources of insulin-producing cells and protection of endogenous cells by immunomodulation.
Emerging or future T1D therapies.
Exogenous insulin replacement includes insulin analogs designed to optimize absorption, integrated closed-loop systems combining insulin delivery devices and glucose-sensing technology, and personalized algorithms to tailor insulin replacement. Cell-based insulin delivery options include transplantation of islets or insulin-producing cells , strategies to stimulate cell proliferation or regeneration, and approaches that encourage transdifferentiation of host cells into insulin-producing cells. Protective strategies include immunomodulatory approaches to block inflammatory cytokines or pathogenic immune cells and prevent damage or loss of cells. See text for additional information.
In summary, since insulins discovery, there has been much progress in understanding the pathogenesis of T1D and in using insulin to improve the lives of individuals with T1D. These efforts are incomplete in that T1D continues to be a substantial burden for individuals with T1D and their families. Hopefully, the opportunities discussed here will be realized, leading to the prevention of T1D and its associated burdens.
Can You Be Born With Diabetes Is It Genetic
You arent born with diabetes, but Type 1 diabetes usually appears in childhood. Prediabetes and diabetes develop slowly over time years. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.Scientists do believe that genetics may play a role or contribute to the development of Type 1 diabetes. Something in the environment or a virus may trigger its development. If you have a family history of Type 1 diabetes, you are at higher risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. If you have a family history of prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes, youre at increased risk of developing prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
You May Like: What Is An Insulin Pump
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing artificial pancreas technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
Complications Of Type 1 Diabetes
The discovery of insulin in 1922 transformed type 1 diabetes from a terminal to a treatable disease. Despite the advances in care discussed previously, the disease continues to be associated with substantial medical, psychological, and financial burden. Hypoglycaemia and ketoacidosis are persistent potentially life-threatening complications. Severe hypoglycaemic events requiring treatment assistance from another person occur at rates of 1620 per 100 person-years hypoglycaemic events leading to loss of consciousness or seizure occur at a rate of 28 per 100 person-years. Recurrent hypoglycaemia results in an increased likelihood of hypoglycaemia unawareness and subsequent severe hypoglycaemic events, since recurrent hypoglycaemia reduces the glucose concentration that triggers the counter-regulatory responses to return to euglycaemia. Hypoglycaemia unawareness can improve with edu cation, support, and glucose targets that are aimed at avoiding biochemical hypoglycaemia, while maintaining overall metabolic control.
An additional noteworthy complication of type 1 diabetes is the patient-reported burden of adverse also their family, friends, and caregivers. Fear of hypoglycaemia is a prevalent issue, particularly for the families of very young children with type 1 diabetes. Furthermore, poor quality of life is predictive of subsequent poor glycaemic control.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hormone Replacement Therapy Used To Treat Diabetes