Approaching A Paradigm Shift In T1d Immunotherapy
However, there is hope for potentially making insulin treatments obsolete. Researchers from all over the world have come a long way in recent years investigating alternative therapy options that offer the promise to delay T1D onset and improve life for patients.
There has always been an enormous enthusiasm among researchers to try and find better ways to predict and prevent T1D but also to arrest the progression of the disease because we as clinicians see what a terrible disease it is, says Prof Mathieu. One promising approach are immunotherapies that target the underlying cause of the disease by reprogramming the immune system so that it no longer attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Is Diet And Exercise Enough Or Do I Need Metformin
In the past few years, the American Diabetes Association has seen changes to its guidelines related to the effectiveness of diet and exercise in managing diabetes. It is current practice to start metformin early to protect beta cells from further damage.
Metformin can lower A1C by 1-2 percent. It should be used in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes for this reason, along with its protective mechanism related to beta cells in the pancreas. Most people with diabetes will want to achieve an A1C of less than 7 percent in order to avoid the long term complications of diabetes.
Your healthcare provider will look at your A1C numbers, and determine the need for interventions, including diet, exercise, oral medications, non-insulin injectable medications for diabetes, or insulin. Generally, what happens is that a person with diabetes will do well on metformin for a number of years, and then they tend to start seeing their A1C creep up.
It becomes more difficult to keep the A1C below 7 percent with diet, exercise, and metformin. At this point, your healthcare provider may be looking at adding in a number of different oral medications for diabetes, or adding a GLP-1 injectable, and eventually insulin if A1C goal is not achieved by other means.
Some important factors that should be taken into consideration when picking a diabetes medication are:
- the costs,
- side effects , and
- the risk of a low blood sugar.4
Key Messages For People With Diabetes
- Insulin therapy is required for the treatment of type 1 diabetes.
- There are a variety of insulins and methods of giving insulin to help manage type 1 diabetes.
- Insulin is injected by pen, syringe or insulin pump.
- Your health-care provider will work with you to determine such things as:
- The number of insulin injections you need per day
- The timing of your insulin injections
- The dose of insulin you need with each injection
- If and when an insulin pump is appropriate for you
- Your pump settings if you are giving insulin that way.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
The Role Of Food In Diabetes Management
It is important to understand how food impacts blood glucose for children with diabetes.
Food causes blood glucose to go up. Insulin causes blood glucose to go down. Too much food with not enough insulin can cause blood glucose to go too high. Not enough food with too much insulin can cause blood glucose to go too low. Further, the type and amount of food will affect how much and how quickly the blood glucose goes up. Balancing food and insulin together can help keep blood glucose in a normal range.
Carbohydrates, also known as carbs, are an important source of energy. They are also the main nutrient the body turns into blood glucose, also known as blood sugar. Everyone needs to eat some carbohydrates to stay healthy. Common carbohydrate foods include: bread, crackers, cereal, pasta, rice, fruit, and milk.
- Carbohydrates that are high in fiber such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables slow digestion and contribute to a feeling of fullness. High-fiber food can also reduce spikes in blood glucose after eating.
- Processed carbohydrates that are low in fiber can raise blood sugars too high. Eating fewer processed carbohydrates helps manage blood glucose levels.
A dietitian can help determine the right amount of carbohydrates and types for your child.
A healthy diet can mean different things to different people. A dietitian is very important to help with meal planning and understanding the right balance of foods for your child.
Type 1 Diabetes Causes
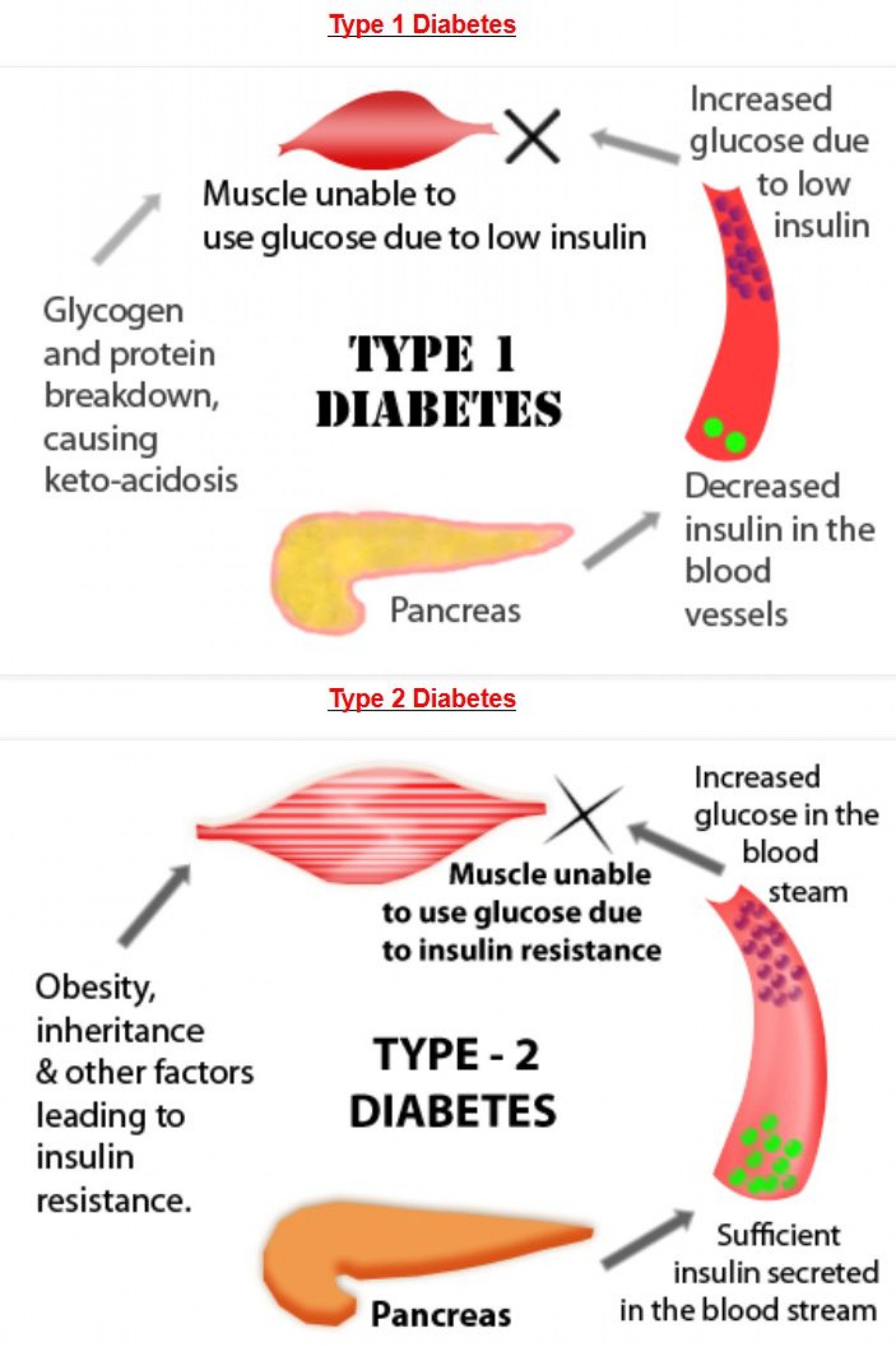
Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar, or glucose, into your body’s tissues. Your cells use it as fuel.
Damage to beta cells from type 1 diabetes throws the process off. Glucose doesnât move into your cells because insulin isnât there to do the job. Instead, it builds up in your blood, and your cells starve. This causes high blood sugar, which can lead to:
- Dehydration. When thereâs extra sugar in your blood, you pee more. Thatâs your bodyâs way of getting rid of it. A large amount of water goes out with that urine, causing your body to dry out.
- Weight loss. The glucose that goes out when you pee takes calories with it. Thatâs why many people with high blood sugar lose weight. Dehydration also plays a part.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis . If your body can’t get enough glucose for fuel, it breaks down fat cells instead. This creates chemicals called ketones. Your liver releases the sugar it stores to help out. But your body canât use it without insulin, so it builds up in your blood, along with the acidic ketones. This mix of extra glucose, dehydration, and acid buildup is known as ketoacidosis and can be life-threatening if not treated right away.
- Damage to your body. Over time, high glucose levels in your blood can harm the nerves and small blood vessels in your eyes, kidneys, and heart. They can also make you more likely to get hardened arteries, or atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Don’t Miss: A1 Diabetes And Medical Supply
Importance Of Monitoring Blood Glucose
It is always important to monitor your blood sugar when you are trying to keep your diabetes in control. Using your glucometer, you can keep track of how many blood sugars are in your target range. Generally, your target range will be 80-130 mg/dl fasting . Two hours after a meal, your blood sugar target should be less than 180 mg/dl. Your healthcare provider may adjust your targets based on individual factors.
It is also a good idea to write a daily journal that chronicles what you eat, what your blood sugar levels are, and any medicine that you take, along with exercise completed.
In order to get the right combination of medications to live healthy with diabetes, you should work with your diabetes care team. Your team may include:
- nurses
- pharmacists
- or any number of other specialists that you may need for your individual diabetes care.
To learn about how to put together the perfect diabetes care team, see our article here:
Tips for keeping your AC1 under 7 percent:
- Make a plan and stick to it
- Build a support system network
- Read food labels look for serving size, and total carbohydrates
- Shop for whole foods
- shop and prep meals in advance
- Eat small frequent meals, instead of larger meals
- Get out and get moving. Turn off the TV, or watch and work out
Having Your Blood Glucose Levels Checked
You’ll be measuring your blood glucose yourself every day, to check your levels.
Your GP or diabetes care team will also carry out a different blood test every two to six months, called the HbA1c test.
This gives a clearer idea of how well your treatment plan is working, by measuring how stable your glucose levels have been over the past 6-12 weeks.
It measures the amount of haemoglobin, which is the oxygen-carrying substance in red blood cells that has glucose attached to it. A high HbA1c level may indicate that your blood glucose level is consistently high and that your diabetes treatment plan needs to be altered.
The ideal HbA1c target for people with diabetes is below 53 mmol/mol.
Don’t Miss: On Call Express Diabetes Testing Kit
Risk Factors For Type 1 Diabetes:
Any combination of the following factors may put people at a higher risk for type 1 diabetes:
- Self-allergy : The immune system usually protects us from disease, but in the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system turns against the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin . If you have any type of autoimmune disease, your risk of developing diabetes increases. Doctors can test for diabetes antibodies, specifically one called GAD65. Measuring this antibody early in the disease can help your medical team determine if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- Genes: People with type 1 diabetes are more likely to have inherited genes putting them at risk. Over 50% of those diagnosed with type 1 diabetes also have a close relative with the disease.
Insulin Isnt The Bad Guy
Naturally, the fear of giving oneself an injection or shot, can increase anxiety and stress. But what if I told you that once you get past that initial fear of giving yourself an injection, insulin will help you manage your diabetes and live a longer, healthier life?
If your doctor tells you that you have to go on insulin injections, remember that there is a reason for it. Your doctor has your best interests in mind when he recommends insulin to you. Before getting to this point, you have probably already tried diet and exercise, several oral medications, and maybe even a GLP-1 weekly injection.
With time, your body has started making less and less of its own insulin, and as a result, more and more of your beta cells have died out. At this point, when the beta cells in the pancreas have stopped making insulin, it becomes inevitable that you need to take insulin injections to keep your A1C in a range that decreases the chances of future diabetes complications.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Average Cost Of An Insulin Pump
Bolus Insulin And Basal
Bolus insulin refers to rapid- or short-acting insulin given to control the glycemic rise at meals and to correct hyperglycemia. The prandial injection dose is decided based on carbohydrate content, carbohydrate-to-insulin ratio for each meal, planned exercise, time since last insulin dose and blood glucose level. Bolus insulins include rapid-acting insulin analogues and short-acting insulin .
Preprandial injections of rapid-acting insulin analogues result in a lower postprandial glucose and improved overall glycemic control . Insulin aspart, glulisine and lispro should be administered 0 to 15 minutes before the start of the meal while short-acting regular insulin should be administered 30 to 45 minutes before the start of the meal. Faster-acting insulin aspart may be administered at the start of the meal or, when necessary, up to 20 minutes after the start of the meal . When required, insulin aspart, glulisine and lispro can be administered from 0 to 15 minutes after the start of a meal although better control of postprandial hyperglycemia is seen with preprandial injections.
Financial Support And Benefits
Some people with diabetes may be eligible to receive disability benefits and incapacity benefits, depending on the impact the condition has on their life.
The main groups likely to qualify for welfare benefits are children, elderly people, people with learning disabilities or mental health problems, and those with complications of diabetes.
People over 65 who are severely disabled, may qualify for a type of disability benefit called Attendance Allowance.
Carers may also be entitled to some benefit too, depending on their involvement in caring for the person with diabetes.
Staff at your local Citizens Advice Bureau can check whether you’re getting all of the benefits you’re entitled to. Both they and your diabetes specialist nurse should also be able to give you advice about filling in the forms.
GOV.uk has more information about benefits, and the Diabetes UK website has further advice about the Disability Living Allowance .
You May Like: Is Stage 2 Diabetes Reversible
Moving Research Forward Solving The Mysteries Of T1d Together
To advance their immunotherapy as a safe and effective therapy for patients with early T1D, Imcyse has joined forces with INNODIA, gaining access to a broad supportive research network. To really make a difference, everyone needs to work together, says Prof Mathieu. Newly diagnosed patients need to get the opportunity to participate in these studies, clinicians need to inform their patients about ongoing intervention trials, companies need the patient perspective, there is this aspect of public funding and the industry side. This is why networks such as INNODIA are so important.
Treating Type 1 Diabetes

It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
You May Like: Ginger For Diabetes Type 2
Types Of Diabetes Tests
- Fasting blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked after fasting for between 12 and 14 hours. You can drink water during this time, but should strictly avoid any other beverage. People with diabetes may be asked to delay their diabetes medication or insulin dose until the test is completed.
- Random blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked at various times during the day, and it doesnt matter when you last ate. Blood glucose levels tend to stay constant in a person who doesnt have diabetes
- Oral glucose tolerance test a high-glucose drink is given. Blood samples are checked at regular intervals for two hours.
Efficacy And Safety In Type 2 Dm
A clinical situation during the development of type 2 DM is that it might be inadequately controlled by OADs. A typical response is to intensify the therapeutic regimen. Intensive treatment of patients with type 2 DM is in line both with the consensus algorithm and the guidelines.30
In 2007, a Cochrane database analysis was published that evaluated advantages of the treatment with basal insulin analogs in comparison with NPH insulin in type 2 DM. Six studies with insulin glargine and two studies with detemir were analyzed. Their duration was from 24 to 54 weeks. No differences between basal insulin analogs and NPH insulin in HbA1c have been shown however, a significantly lower rate of symptomatic, overall and nocturnal hypoglycemia were found in favor of basal insulin analogs.31 This review concluded: For insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus, NPH is an effective, safe substance which has been tested over decades. In such cases where a proven effective therapy is available, the introduction of new substances should only be advised if there is a major improvement in efficacy, or if the new substance is proven both effective and safe.
In a second study,35 a 26-week long therapy of 505 patients resulted in comparable glycemic control but significantly lower within-subject variability and less weight gain in the detemir group compared to patients treated with NPH insulin . Insulin detemir was well tolerated and had a similar safety profile to NPH insulin.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Diabetes In Toddler Girl
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
The goal of type 1 diabetes treatment is to control glucose levels and prevent your childs blood sugar from being too high. The ideal diabetes management regimen includes insulin therapy, glucose and ketones monitoring, regular exercise, and healthy eating.
Insulin therapy replaces insulin the body cannot make on its own. Usually, this is done with both long-acting and short-acting insulin injections. Many people with type 1 diabetes use insulin pumps instead of injections. Your diabetes team can teach you more about insulin pumps.
Glucose monitoring It is very important to monitor glucose levels throughout the day. You can do this with finger-stick blood glucose checks and/or with a continuous glucose monitor . CGM devices measure blood sugar with a subcutaneous glucose sensor and report a value every five minutes. Some devices can report values directly to a parent or patients mobile phone. The FDA has approved some CGM devices for use as a replacement for finger-stick tests.
Ketone monitoring When the body doesnt have enough insulin, the liver compensates by producing extra ketones, a chemical that converts fat into energy. High levels of ketones in the blood can become a medical emergency. Therefore, in addition to monitoring glucose levels, it is very important to monitor ketones when your childs glucose level is very high or when your child is sick.