Exercise & Physical Activity
Since Chauveu & Kaufmans remarkable observation in 1887 that When a horse chews on hay the concentration of glucose in the blood draining its masseter muscle substantially decreases74 a large body of evidence supports the role of exercise in improving insulin sensitivity and its beneficial outcomes in insulin resistant states. Epidemiological studies such as the US Physicians Health Study have reported substantial decreases in the relative risk of type 2 diabetes with lifelong regular physical activity.75 Large scale randomised controlled clinical trials such as the Diabetes Prevention Program76 and the Finnish Prevention Study77 demonstrate a 58% reduction in progression of impaired glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes by intensive lifestyle modification which included a minimum of 2030 minutes of exercise per day. Acute exercise increases GLUT 4 translocation to sarcolemmal membrane, whereas chronic exercise training increases Glut 4 mRNA expression.78 In addition to this insulin-dependent mechanism, enhanced glucose uptake into exercising muscle occurs by multiple insulinin dependent mechanisms.79 Exercise training appears to enhance insulin sensitivity by increased post-receptor insulin signalling 80 increased insulin-mediated glucose transport appears to be related to enhanced signal transduction at the level of IRS proteins and PI 3-kinase.79
Clinical Syndromes Associated With Insulin Resistance
Type 2 diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome would be the most common clinical syndromes associated with insulin resistance. Others include hypertension, PCOS, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, certain forms of cancer and OSA,3 which some authors consider a component of the metabolic syndrome per se. There are also relatively common conditions where insulin resistance is a secondary phenomenon these include acute illness, hepatic cirrhosis, renal failure, pregnancy, hyperthyroidism, Cushings disease and Cushings syndrome as well as acromegaly and phaeochromocytoma which are less common.26 In many of these, the insulin resistance is due to increased production of counter-regulatory hormones.
However there are also a large number of generally rare disorders where insulin resistance is a major clinical feature.28,105 Though individually rare, these conditions may provide insight into the mechanisms of insulin resistance in other settings. Typically they are characterised by disturbances in organ systems where insulin action plays a critical role.
What Problems Can Happen With Type 2 Diabetes
Not having the right amount of sugar in the blood can lead to:
- hyperglycemia.This is when blood sugars are too high. Someone with hyperglycemia may be extra thirsty and pee more than usual. If high blood sugars arent treated, they can get very sick and have health issues later in life, like heart and kidney problems.
- diabetic ketoacidosis . This serious condition needs treatment right away. When theres not enough insulin in the body to let the glucose into the cells, the body starts to break down fat instead of sugar. Symptoms of DKA can include nausea, vomiting, belly pain, fast breathing, and in severe cases, unconsciousness. DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but it can sometimes happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
- hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state . Like DKA, this is a serious condition that needs treatment right away. People with HHS have severe dehydration and very high blood sugars.
- hypoglycemia. This is when blood sugars are too low. It can sometimes happen when people with type 2 diabetes are treated with insulin. If a person with diabetes gets more insulin than they need, their blood sugar level can drop too low. Symptoms can include headache, weakness, shakiness, anxiety, and sweating.
Don’t Miss: How To Fix Low Blood Sugar
What Will Insulin Be Like In The Future
Pharmaceutical companies are working on very long-acting versions of insulin that could last for a week. There is also an ultra-fast version of insulin under development that will act in less than 15 minutes.
Another group of researchers is looking at glucose responsive insulin , which would react to the needs of your body in real time. It would have nanosensors bound to the insulin so that when insulin is needed, it releases, and when it isnt, it stops, according to Dr. Hirsch.
Mechanisms Of Insulin Resistance
Physiologically, at the whole body level, the actions of insulin are influenced by the interplay of other hormones. Insulin, though the dominant hormone driving metabolic processes in the fed state, acts in concert with growth hormone and IGF-1 growth hormone is secreted in response to insulin, among other stimuli, preventing insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Other counter-regulatory hormones include glucagon, glucocorticoids and catecholamines. These hormones drive metabolic processes in the fasting state. Glucagon promotes glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis. The ratio of insulin to glucagons determines the degree of phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of the relevant enzymes.29 Catecholamines promote lipolysis and glycogenolysis glucocorticoids promote muscle catabolism, gluconeogenesis and lipolysis. Excess secretion of these hormones may contribute to insulin resistance in particular settings, but does not account for the vast majority of insulin resistant states.
Recommended Reading: Type 2 Diabetes Can It Be Reversed
How To Choose The Right Method For Injecting Insulin
Both syringes and insulin pens use a small needle to inject insulin into your body. There are pros and cons to each, and which one you ultimately end up with will depend on your lifestyle and your doctors advice.
Things to know about insulin syringes:
- They come in a few different sizes.
- Your doctor will tell you how much insulin you need per dose.
- You will usually draw the insulin into the syringe when you need it.
- Theyre not as discreet as an insulin pen.
Things to know about insulin pens:
- Some pens use cartridges that are manually inserted into the pen.
- Other pens are prefilled and thrown away after all the insulin is used.
- Needles in pens are often smaller than those in syringes.
- Not all types of insulin can be used with a pen.
- Pens can be more expensive than syringes and are sometimes not covered by insurance.
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Meals For Diabetics And High Cholesterol
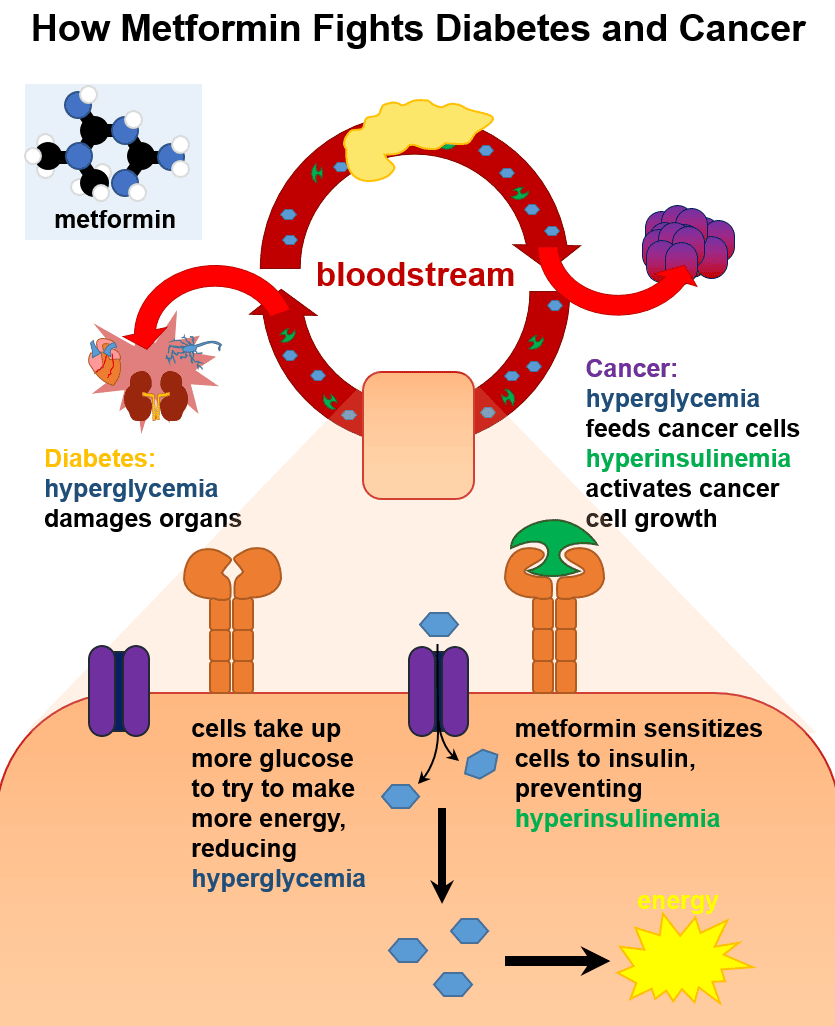
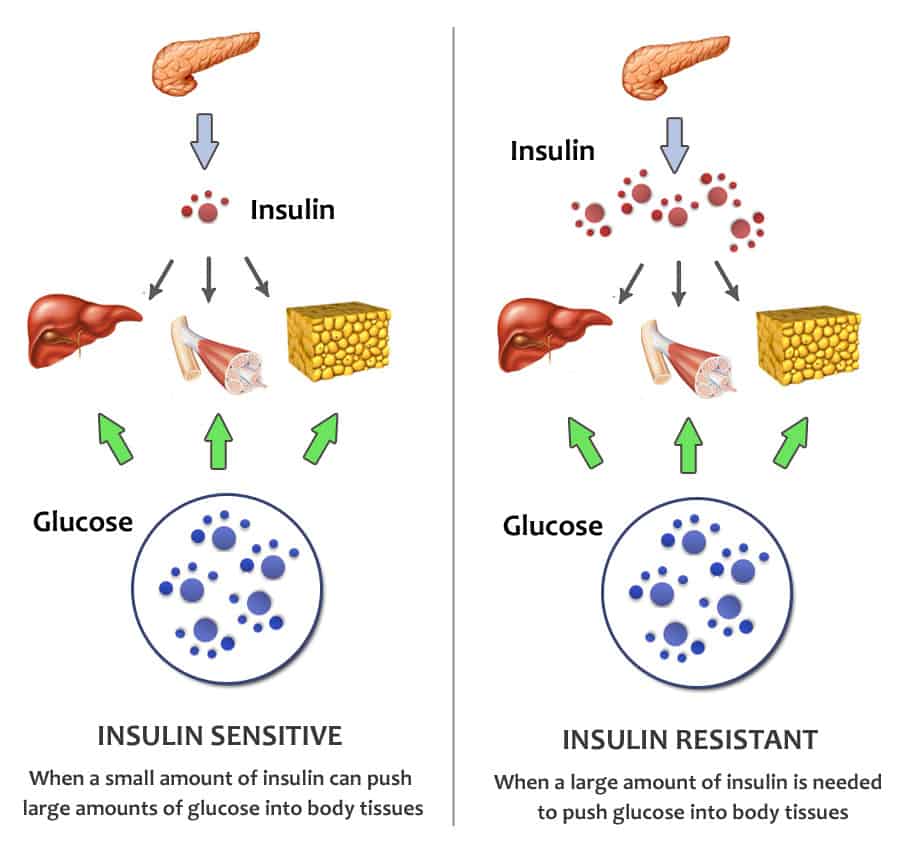
What Is Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, happens when cells in your muscles, fat and liver dont respond as they should to insulin, a hormone your pancreas makes thats essential for life and regulating blood glucose levels. Insulin resistance can be temporary or chronic and is treatable in some cases.
Under normal circumstances, insulin functions in the following steps:
- Your body breaks down the food you eat into glucose , which is your bodys main source of energy.
- Glucose enters your bloodstream, which signals your pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps glucose in your blood enter your muscle, fat and liver cells so they can use it for energy or store it for later use.
- When glucose enters your cells and the levels in your bloodstream decrease, it signals your pancreas to stop producing insulin.
For several reasons, your muscle, fat and liver cells can respond inappropriately to insulin, which means they cant efficiently take up glucose from your blood or store it. This is insulin resistance. As a result, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to overcome your increasing blood glucose levels. This is called hyperinsulinemia.
As long as your pancreas can make enough insulin to overcome your cells weak response to insulin, your blood sugar levels will stay in a healthy range. If your cells become too resistant to insulin, it leads to elevated blood glucose levels , which, over time, leads to prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
Its The Area Under The Curve That Matters
Now I want to show you how to stabilise your blood sugars and reduce insulin levels across the day.
The diagram below shows how your blood glucose responds to the food you eat.
The amount your glucose rises is proportional to how many carbohydrates you eat. So, if your blood sugar rises more than 30 mg/dL after eating, you have probably overfilled your glucose fuel tanks in your liver and muscles. So next time, you may want to consider eating less of the food you just ate.
What goes up must come down! When your blood sugar comes crashing below what is normal for you, youll feel hungry. If your glucose goes way below average for you, youre more likely to make less than optimal food choices.
In contrast, the length of time your blood sugars will remain elevated after eating fatty meals is much longer, although they dont cause a significant spike. As a result, your blood sugars will stay above baseline for much longer.
You May Like: How Do You Get Type 1 Diabetes
What Severe Complications Can Occur Because Of Rationing Or Running Out Of Insulin
is an emergency condition that results if you dont have enough insulin to regulate your blood sugar. DKA causes your body to break down fat for energy in the absence of insulin. This leads to a dangerous accumulation of acids known as ketones in your blood that can cause your brain to swell and your body to go into shock.
Signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
-
Thirst or a very dry mouth
-
Frequent urination
-
High levels of ketones in your urine
-
Nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain
-
Difficulty breathing
-
A fruity or acetone odor on your breath
-
Confusion or acting drunk while sober
DKA is so common and can come on so quickly that it is the first sign of type 1 diabetes in 20% of cases, and the way many people with type 1 diabetes are first diagnosed with the condition. If you go into diabetic ketoacidosis, dont try to hide it or make light of it. Treat it as the emergency it is and get to a hospital as soon as possible to recover.
Ive had people tell me theyre tired of taking insulin, or that theyre rationing it due to cost. In type 1 diabetes, thats all it takes to end up in a life-threatening situation, says Dr. Zilbermint.
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to think about how they eat and how to control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, or helpless, or think that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your diabetes care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
Also Check: How Much Sugar Can A Diabetic Have In One Day
What Else Can I Do To Manage My Blood Glucose Levels
Food, sleep, and exercise are all of vital importance for regulating your blood sugar when you have diabetes.
Get enough sleep. Evidence shows that lack of sleep can lead to increased secretion of the hormone cortisol, which is inflammatory and can cause greater insulin resistance. Endocrinologist Al Powers MD of Vanderbilt University notes that when youre deprived of sleep or your sleep is disrupted, your glucose levels tend to go up, whether you have diabetes or not.
Exercise regularly. During exercise, insulin sensitivity is increased, and muscle cells use available insulin more efficiently. When your muscles contract during exercise, they also absorb glucose and use it for energy.
Follow an eating pattern that is healthful for you, as recommended by your doctor, such as the DASH diet or the Mediterranean diet. Both have been shown to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Colorful Fruits And Vegetables Can Help Lower Insulin
Fruits and vegetables are known for their healthy compounds, but they also provide health-boosting effects.
In particular, colorful fruits and vegetables contain antioxidant properties that protect your body from harmful inflammation that can occur inside the body.
Inflammation is one potential cause of insulin resistance. So, implementing fruits and vegetables into your daily diet can help you prevent inflammation and increase insulin sensitivity.
Aside from this, eating foods that contain plant compounds are linked to higher insulin sensitivity and thereby reduce insulin levels in the body.
However, when youre including fruit in your diet, stick to normal portion sizes and low glycemic fruits.
When it comes to vegetables, stick to non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli.
Read Also: What Happens If Your Glucose Is High
Physiology Of Insulin Secretion
Glucose is the principal stimulus for insulin secretion, though other macronutrients, hormones, humoral factors and neural input may modify this response. Insulin, together with its principal counter-regulatory hormone glucagon, regulates blood glucose concentrations.17 Pancreatic cells secrete 0.251.5 units of insulin per hour during the fasting state, sufficient to enable glucose insulin-dependent entry into cells. This level prevents uncontrolled hydrolysis of triglycerides and limits gluconeogenesis, thereby maintaining normal fasting blood glucose levels. Basal insulin secretion accounts for over 50% of total 24 hour insulin secretion. Following secretion of insulin into the portal venous system, 60% is subsequently removed by the liver so portal vein insulin concentrations reaching the liver approach triple that of the peripheral circulation. In healthy lean individuals circulating venous fasting insulin concentrations are about 315 mIU/L or 1890 pmol/L.17 Meal-related insulin secretion accounts for the remaining fraction of the total daily output.
How Does Insulin Resistance Affect My Body
The development of insulin resistance typically increases insulin production so your body can maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Elevated levels of insulin can result in weight gain, which, in turn, makes insulin resistance worse.
Hyperinsulinemia is also associated with the following conditions:
You dont have to have all four of these features to have metabolic syndrome.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar 160 After Eating
How Common Is Insulin Resistance
Since there arent any common tests to check for insulin resistance and there arent any symptoms until it turns into prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes, the best way to measure the prevalence of insulin resistance is through the number of prediabetes cases. More than 84 million adults in the United States have prediabetes. Thats about 1 out of every 3 adults.
Energy Creation And Distribution
The function of insulin is to help transform glucose into energy and distribute it throughout your body, including the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.
Without insulin, cells are starved for energy and must seek an alternative source. This can lead to life threatening complications.
Read Also: Cinnamon For Diabetes Type 2
Recover The Ability To Produce Insulin
Lars Krogvold explains:
We found that the insulin-producing cells still have the ability to produce insulin when they are stimulated in the lab.
But whats new is our additional discovery that the cells increased their ability to produce insulin after a few days outside the body.
Indeed, some became roughly as good at making insulin as cells from people without diabetes.
Some of the hormone-producing cells in the pancreas, the beta cells, produce insulin when they are stimulated by sugar.
Previous work has shown that you do not immediately lose your ability to produce insulin when you are first diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
What Happens To Insulin Between Meals
When you dont eat, your pancreas produces a little less insulin to let more energy flow into your blood. Just like Monicas closed-loop insulin pump, your basal insulin is slightly decreased for more energy to flow out of storage.
The reduction in insulin signals your liver to open the tap a little more and release energy from stored liver glycogen and adipose tissue into your bloodstream.
Later, as your liver starts to get depleted of glycogen and your blood sugars drop, ghrelin increases to prompt feelings of hunger so that you seek out food. When you eat, energy from fat and carbs gets stored in your liver and adipose tissue. The process then starts all over again!
You May Like: Are Brussel Sprouts Good For Diabetics
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
People who have type 2 diabetes have a hard time using glucose from food for energy.
After we eat, carbohydrates in food break down into glucose. When glucose enters the bloodstream, blood sugar levels go up. When it does, the pancreas sends insulin into the blood. Insulin helps open cells throughout the body to let glucose in, giving the cells the energy they need.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas makes insulin, but the cells dont respond to it as they should. This is called insulin resistance. When glucose cant get into cells, the blood sugar level rises. Then the pancreas works harder to make even more insulin. At first, the extra insulin keeps sugars in the normal range. But over time, the pancreas cant keep up, and the blood sugars stay high. When blood sugars stay high, the person may have type 2 diabetes.
Does Insulin Push Glucose Into Cells
When my wife Monica was diagnosed with Type-1 Diabetes 35 years ago, she was taught that insulin is like a key that unlocks insulin receptors that work as cell doors to allow glucose into the cell. It can then be transformed and utilised as energy.
Our understanding of the role of insulin has come a long way since then. We now know that we can use energy in food via non-insulin-mediated glucose uptake .
If your cells run low on fuel, the energy from your blood floats into the cells to be used. Glucose is translocated across the gradient from high glucose in your blood to lower glucose in your cells. So, if your cells are using energy, they essentially suck it in from the bloodstream.
GLUT1 is the insulin-independent glucose transporter that allows cells to use glucose without insulin. A little bit of exercise goes a long way to increasing GLUT1 activity! Meanwhile, GLUT4 is the insulin-dependent glucose transporter that helps glucose enter cells.
The 2011 study by Krakoff et al. titled Assessment of Non-insulin Mediated Glucose Uptake: Association with Body Fat and Glycemic Status showed that 83% of glucose uptake occurs through non-insulin mediated mechanisms like GLUT1 glucose transport. On average, your body clears 1.6 mg/kg of glucose per minute from your bloodstream without using any insulin. Thats more than 160 g of glucose per day for the average 70 kg man. So, if youre on a lower-carb diet, all the glucose you eat could be used without insulin!
You May Like: Watch That Measures Blood Sugar