Diabetes And Brain Health
If you have diabetes, your doctor may screen you for depression or cognitive impairment. Older adults with diabetes are at higher risk for these conditions, compared with others their age who do not have diabetes. Having depression or cognitive impairment can make diabetes self-care challenging.
Your diabetes management plan will cover how to:
- Track your glucose levels. Very high glucose levels or very low glucose levels can be risky to your health. Your plan will show how often you should check your glucose and how often to get the A1C test. If you are managing your diabetes without taking insulin, you may not need to check your glucose as often.
- Make healthy food choices. The food you eat affects glucose levels, so its important to learn whats best for you to eat, how much, and when. If you are overweight, work with your health care team to come up with a plan to lose weight.
- Be active. Walking and other forms of daily exercise can help improve glucose levels in older people with diabetes. Set a goal to be more active most days of the week, and create a plan for being physically active that fits into your life and that you can follow. Your health care team can help.
- Take your medicines. You should take medicine as prescribed even when you feel good. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects or cannot afford your medicines. Also, let your doctor know if you have trouble taking your medicine or keeping track of your medication schedule.
What Are Consensus Recommendations For Clinicians Treating Older Adults With Or At Risk For Diabetes
Although several organizations have developed guidelines that pertain to older adults and/or those with significant comorbidity, lack of evidence makes it somewhat difficult to provide concrete guidance for clinicians. After review of the available evidence and consideration of issues that might influence treatment decisions in older adults with diabetes, the authors have developed recommendations in a number of areas. provides a framework for considering treatment goals for glycemia, blood pressure, and dyslipidemia. This framework is based on the work of Blaum et al. , in which health status, defined by the presence and number of comorbidities or impairments of functional status, leads to the identification of three major classes of older patients: 1) those who are relatively healthy, 2) those with complex medical histories where self-care may be difficult, and 3) those with a very significant comorbid illness and functional impairment. The three classes correspond with increasing levels of mortality risk . The observation that there are three major classes of older diabetic patients is supported by other research . The framework is an attempt to balance the expected time frame of benefit of interventions with anticipated life expectancy. provides additional consensus recommendations beyond goals of treatment of glycemia, blood pressure, and dyslipidemia.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Without treatment, type 2 diabetes appears to progress faster in young people than in adults.
Younger people also seem to have a higher risk of complications, such as kidney and eye disease, earlier in life.
There is also a greater risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels, which increase a persons risk of blood vessel disease.
Type 2 diabetes in children often occurs with obesity, which may contribute to these higher risks. Obesity affects the bodys ability to use insulin, leading to abnormal blood sugar levels.
Because of this, early detection of type 2 diabetes and attention to managing overweight and obesity in younger people are crucial.
This may include encouraging children to follow a healthful diet and get plenty of exercise.
The National Institute for Health Care and Excellence recommend testing children for diabetes if they:
- have a strong family history of type 2 diabetes
- have obesity
- are of Black or Asian family origin
- show evidence of insulin resistance, such as acanthosis nigricans
The outcomes for children with type 1 or type 2 diabetes improve greatly with early detection.
It is not currently possible to prevent type 1 diabetes, but type 2 diabetes is largely preventable.
The following steps can help prevent type 2 diabetes in childhood:
- Maintain a moderate weight: Overweight increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as it increases the chance of
Read Also: How To Lower Insulin Resistance
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
What Medicines Do I Need To Treat My Type 2 Diabetes

Along with following your diabetes care plan, you may need diabetes medicines, which may include pills or medicines you inject under your skin, such as insulin. Over time, you may need more than one diabetes medicine to manage your blood glucose. Even if you dont take insulin, you may need it at special times, such as during pregnancy or if you are in the hospital. You also may need medicines for high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or other conditions.
Learn more about medicines, insulin, and other diabetes treatments.
Also Check: Fasting For Type 1 Diabetes
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
If you have type 2 diabetes, your GP or diabetes care team will need to take a reading of your blood glucose level about every two to six months.
This will show how stable your glucose levels have been in the recent past and how well your treatment plan is working.
The HbA1c test is used to measure blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months.
HbA1c is a form of haemoglobin, the chemical that carries oxygen in red blood cells, which also has glucose attached to it.
A high HbA1c level means that your blood glucose level has been consistently high over recent weeks, and your diabetes treatment plan may need to be changed.
Your diabetes care team can help you set a target HbA1c level to aim for. This will usually be less than 53 mmol/mol or individualised as agreed with your diabetes team.
Read more about the HbA1c test
Is The Dash Diet Helpful For Type 2 Diabetes
The DASH diet, which stands for Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension, was designed to lower blood pressure.
Like the Mediterranean diet, the DASH diet emphasizes plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, dried legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
It also includes fish, poultry, and low-fat dairy products. It limits red meat, sweets, and foods high in saturated fat, sodium, or added sugar.
According to published in 2017, the DASH diet can be a nutrient-rich and sustainable eating plan for people with type 2 diabetes. It can also help reduce:
- blood pressure
- seeds
- grains
They also include a wide variety of fruits and vegetables. Vegetarians typically eat eggs and dairy, but vegans dont.
One of six studies found that vegetarian diets were associated with lower levels of fasting blood sugar and long-term blood sugar management.
According to a 2018 review , eating more plant-based foods and fewer animal products could reduce the risk of insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes.
However, while it is possible to follow a vegetarian or vegan diet while meeting your nutritional needs with type 2 diabetes, not all vegetarian and vegan diets are created equal. Furthermore, just because a food is vegetarian or vegan doesnt mean that it contains beneficial nutrients.
Sometimes, when people try to follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, they dont eat enough protein or sources of vitamins and minerals.
Recommended Reading: When Are You Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
What You Can Do
Type 2 diabetes doesnât have to be a normal part of aging.
Some risk factors for the disease are things you canât change. They include if your mother had gestational diabetes during their pregnancy, if diabetes runs in your family, and if youâre African American, Asian American, Native American, or Latino.
But healthy habits can go a long ways to prevent diabetes, keep it under control, and even reverse it. Steps you can take include:
- Lose extra weight, especially if you carry a lot of belly fat.
- Move your body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity like walking every day, 5 days a week.
- Eat healthy. Cut back on sugar, salt, processed packaged foods, and saturated fats from meats. Load up on dark leafy vegetables, fresh fruit, whole grains, and lean protein.
- If you smoke, quit.
Show Sources
CDC: âNational Diabetes Statistics Report 2020,â âPrevent Type 2 Diabetes in Kids,â âPrevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults by Diabetes Type â United States, 2016.â
MedlinePlus: âDiabetes Type 2.â
The New England Journal of Medicine: âIncidence Trends of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes among Youths, 2002â2012.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. âRisk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes.â
Diabetes Care: âAn Inverse Relationship Between Age of Type 2 Diabetes Onset and Complication Risk and Mortality: The Impact of Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes,â âDiabetes and Aging: Unique Considerations and Goals of Care.â
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
First line treatment for type 2 diabetes typically includes a combination of diet modification with regular and appropriate exercise.
The NICE guidelines state that treatment for type 2 diabetes should take into account an individuals needs and preferences into account. People with diabetes should be given the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and work together with healthcare professionals.
The NICE guidelines encourage having high-fibre, low-glycemic-index carbohydrate in the diet. This allows a good amount of flexibility and it is possible to follow a range of diets, including lower-carb and low-calorie, whilst ensuring you get a good source of low-GI foods such as vegetables, beans and pulses.
Your health team should help you with setting recommendations for carbohydrate and alcohol intake that work for you.
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetes And Anxiety
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all. If you do have them, the symptoms develop slowly over several years. They might be so mild that you do not notice them. The symptoms can include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- Unexplained weight loss
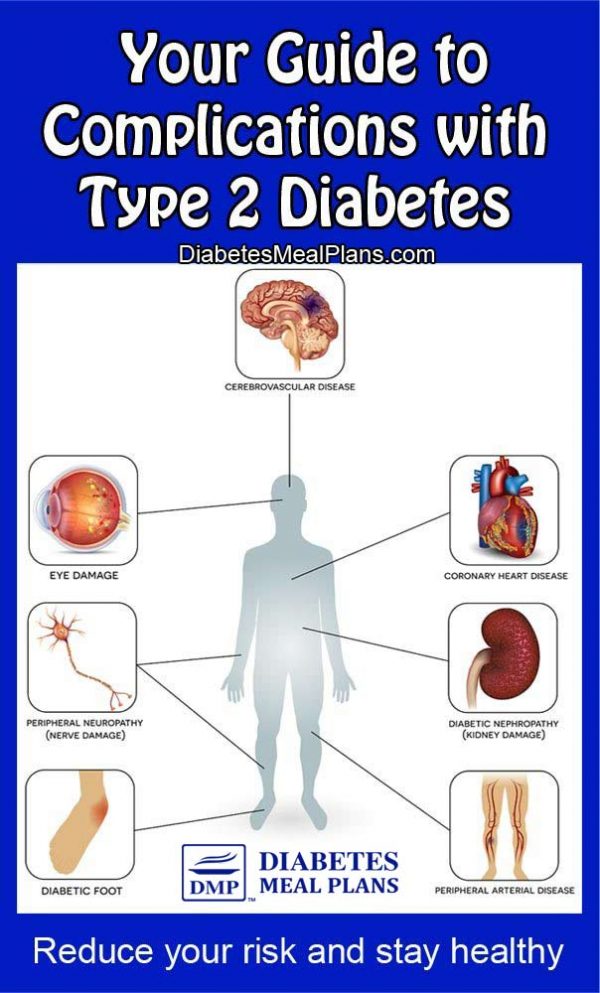
What Health Problems Can People With Diabetes Develop
Following a good diabetes care plan can help protect against many diabetes-related health problems. However, if not managed, diabetes can lead to problems such as
- heart disease and stroke
- gum disease and other dental problems
- sexual and bladder problems
Many people with type 2 diabetes also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . Losing weight if you are overweight or obese can improve NAFLD. Diabetes is also linked to other health problems such as sleep apnea, depression, some types of cancer, and dementia.
You can take steps to lower your chances of developing these diabetes-related health problems.
Also Check: Gestational Diabetes Diet Meal Plan
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood glucose levels with diet and exercise alone. Others may need diabetes pills or insulin injections, along with medicines to manage other conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Over time, a person with diabetes may need both lifestyle changes and medication.
Once youve been told you have diabetes, a health care team will work with you to create a diabetes management plan. Your plan will be based on your lifestyle, preferences, health goals, and other health conditions you have.
As part of your plan, your doctor may prescribe one or more medications. Other health care professionals may also be involved. For example, a diabetes educator may help you understand diabetes and provide support as you make lifestyle changes to manage your diabetes. A dietitian may help with meal planning. An exercise coach may help you become more physically active.
Development Of Type 2 Diabetes
The development of type 2 diabetes is thought to be a progression from normal blood sugars to pre-diabetes to a diagnosis of overt diabetes. These stages are defined by blood sugar levels.
The timeline to developing an elevated blood sugar depends on many environmental factors and also on how strong the gene traits are for diabetes. Ultimately, pre-diabetes and diabetes occur when the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance. Historically pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes has been diagnosed when individuals are older however, because of a wide-spread epidemic of obesity which causes insulin resistance, the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is occurring more frequently at younger and younger ages.
People born with the genetic traits for diabetes are considered to be pre-disposed. Genetically predisposed people may have normal blood sugar levels, but many will have other markers of insulin resistance such, as elevated triglycerides and hypertension. When environmental factors are introduced, such as weight gain, lack of physical activity, or pregnancy, they are likely to develop diabetes.
Some individuals with other types of diabetes may be misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes. Up to 10% of individuals who are initially diagnosed with type 2 diabetes may actually have an adult onset of type 1 diabetes also known as LADA or Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults.
Don’t Miss: Does Water And Baking Soda Help Diabetes
Symptoms And Risk Factors
It can take months or years for enough beta cells to be destroyed before symptoms of type 1 diabetes are noticed. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe.
Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions. Dont guessif you think you could have type 1 diabetes, see your doctor right away to get your blood sugar tested. Untreated diabetes can lead to very seriouseven fatalhealth problems.
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, though family history is known to play a part.
Tips To Keep Your Child Safe
Follow these tips to help keep your child safe and healthy at home and at school:
- Make sure that your child wears a medical ID bracelet or necklace at all times. This is especially important when they’re not with you.
- Give the school a detailed written plan for how to manage your childâs condition, including how to give insulin injections, meal and snack schedules, and a target blood sugar range. You can create this yourself or use a template called the Diabetes Medical Management Plan.
- Create a 504 or an Individualized Education Program. These documents take whatâs in your childâs diabetes medical plan and spell out the schoolâs responsibilities. They help keep your child safe and make sure they get the same education and opportunities as everyone else.
- Make sure your childâs school, coaches, friendsâ parents, and others know how to reach you and your childâs doctor in case of emergency.
- Teach your child, family, and anyone responsible for your child how to notice low blood sugar and what to do about it.
Try to keep calm when your child makes mistakes managing diabetes. You need your child to feel comfortable telling you when somethingâs wrong instead of trying to hide it.
You May Like: Is Paleo Diet Good For Diabetics
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Sometimes, there are no symptoms. It’s important to remember that not everyone with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes develops these warning signs, and not everyone who has these symptoms necessarily has type 2 diabetes.
But kids or teens who develop type 2 diabetes may:
- Need to pee a lot. The kidneys respond to high levels of glucose in the blood by flushing out the extra glucose in urine . Kids with high blood sugar levels need to pee more often and make more pee.
- Drink a lot of liquids. Because they’re peeing so often and losing so much fluid, they can become very thirsty and drink a lot in an attempt to keep the levels of body water normal.
- Feel tired often. This is because the body can’t use glucose for energy properly.
Read Also: What Gauge Are Insulin Needles