Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia
Some people dont have symptoms or dont notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge arent aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. Theyre then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
Role Of Epinephrine In Low Blood Sugar Levels
Low amounts of sugar in the blood also cause a release of the hormone epinephrine which is also called the fight or flight hormone. Epinephrine is released when the brain senses any danger or stressful situation the body is in. The release of this hormone causes symptoms of Hypoglycemia like being anxious, fast heartbeats, excessive sweating, and tingling sensation in the body. As the blood sugar level continues to drop it hinders the flow of glucose present in the blood.
If an appropriate amount of glucose does not reach the brain then it may cause the functioning of the brain to stop and appear in the form of seizures, unconsciousness, and feeling of disorientation along with blurred vision. In very rare conditions, if the blood sugar level drops and does not get treated on time then it may lead to the death of the patient or would make them stay in the coma.
Talk To Your Doctor Or Nurse
If you use insulin and your blood sugar is frequently or consistently low, ask your doctor or nurse if you:
- Are injecting your insulin the right way
- Need a different type of needle
- Should change how much insulin you take
- Should change the kind of insulin you take
Do not make any changes without talking to your doctor or nurse first.
Sometimes hypoglycemia can be due to accidently taking the wrong medicines. Check your medicines with your pharmacist.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetes Cause Vision Problems
Severe Low Blood Sugar
As your low blood sugar gets worse, you may experience more serious symptoms, including:
- Feeling weak.
- Having difficulty walking or seeing clearly.
- Acting strange or feeling confused.
- Having seizures.
Severe low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. Blood sugar this low may make you faint . Often, youll need someone to help you treat severe low blood sugar.
People with diabetes may experience low blood sugar as often as once or twice a week, even when managing their blood sugar closely. Knowing how to identify and treat it is important for your health. Learn how to treat low blood sugar.
How Can I Prevent Low Blood Sugar In The Morning
If you have diabetes, make sure you regularly check your glucose levels, especially before bed. If your blood sugar regularly dips while you sleep, consider using a continuous glucose monitoring device, which alerts you when your blood sugar goes too low or too high. Try to follow these guidelines for healthy glucose levels:
- before breakfast: 70130 mg/dL
- before lunch, dinner, or a snack: 70130 mg/dL
- two hours after meals: under 180 mg/dL
- bedtime: 90150 mg/dL
If you dont have diabetes but experience regular hypoglycemia, you may also want to periodically check your glucose levels. Try to keep your glucose level from dropping below 100 mg/dL throughout the day and before bed.
Whether or not you have diabetes, follow these tips to avoid waking up with low blood sugar:
- Eat balanced meals with healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats regularly throughout the day.
- Have a bedtime snack.
- If you drink alcohol, avoid excessive intake and have a snack with it.
- Avoid exercising too much at night.
For a bedtime snack, try these suggestions:
- 1 apple with 1 tablespoon of peanut butter
- 1 ounce of cheese and a small handful of whole-grain crackers
- one 8-ounce glass of milk
- 1/2 avocado spread on a piece of whole-grain toast
- handful of berries with a small handful of nuts and seeds
Also Check: Best Cold And Flu Medicine For Diabetes
Why Am I Having Lows
If you are experiencing low blood glucose and youre not sure why, bring a record of blood glucose, insulin, exercise, and food data to a health care provider. Together, you can review all your data to figure out the cause of the lows.
The more information you can give your health care provider, the better they can work with you to understand what’s causing the lows. Your provider may be able to help prevent low blood glucose by adjusting the timing of insulin dosing, exercise, and meals or snacks. Changing insulin doses or the types of food you eat may also do the trick.
Preventing A Low Blood Sugar Level
If you have diabetes, you can reduce your chance of getting a low blood sugar level if you:
- Check your blood sugar level regularly and be aware of the symptoms of a low blood sugar level so you can treat it quickly.
- Use a continuous glucose monitor or flash monitor to see how your blood sugar levels are changing. Ask your diabetes care team about getting a monitor if you do not already have one.
- Always carry a sugary snack or drink with you, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice or some sweets. If you have a glucagon injection kit, always keep it with you.
- Do not skip meals.
- Be careful when drinking alcohol. Do not drink large amounts, check your blood sugar level regularly, and eat a carbohydrate snack afterwards.
- Be careful when exercising eating a carbohydrate snack before exercise can help to reduce the risk of a hypo. If you take some types of diabetes medicine, your doctor may recommend you take a lower dose before or after doing intense exercise.
- Have a carbohydrate snack, such as toast, if your blood sugar level drops too low while you’re asleep .
If you keep getting a low blood sugar level, talk to your diabetes care team about things you can do to help prevent it.
Read Also: What Does It Mean If Your Glucose Levels Are High
What If I Don’t Get Any Signs That I Have Hypoglycaemia
Sometimes people are unable to recognise symptoms of hypoglycaemia and find it difficult to tell if their blood glucose might be low. This may be because a person has:
- had diabetes for a long time
- had too many recent episodes of hypoglycaemia
- not treated their hypoglycaemia correctly
- ignored early warning signs of hypoglycaemia.
The only way to know if blood glucose has gone too low is to check blood glucose levels more often. Sometimes people use a continuous glucose monitor to help them know where their glucose is trending.
It is possible to regain the ability to recognise symptoms of hypoglycaemia. Talk with your diabetes specialist or diabetes educator for advice and support.
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemic Episodes
The key to preventing hypoglycemic events is managing diabetes:
- Follow your healthcare providers instructions about food and exercise.
- Track your blood sugar regularly, including before and after meals, before and after exercise and before bed.
- Take all your medications exactly as prescribed.
- When you do have a hypoglycemic event, write it down. Include details such as the time, what you ate recently, whether you exercised, the symptoms and your glucose level.
Also Check: What Types Of Diabetes Are There
Do Not Drive With Low Blood Sugar
People will need to avoid driving while they have low blood sugar levels as it could be dangerous. People will need to wait until their levels return to within a normal range before driving.
If people start to experience symptoms of hypoglycemia while driving, they will need to safely stop the car and check their blood sugar levels.
People may find it helpful to store quick-acting carbohydrates, such as orange juice or glucose tablets, in their car if their levels drop while driving.
If people have hypoglycemia or diabetes, they can discuss an eating plan with a healthcare provider. Tips may include the following:
- eating snacks and small meals around every three hours throughout the day
- opting for a variety of foods, including protein, high-fat foods, and high-fiber foods
- limiting foods high in sugar
may help . These include:
Treatment For Severe Hypoglycaemia
In cases of severe hypoglycaemia the person cannot treat themselves, and needs the help of someone else. Call triple zero for an ambulance immediately.
If the person can’t swallow or follow instructions do not give them any treatment by mouth.
If you are trained in how to prepare and inject glucagon and feel comfortable injecting it, then this can be administered.
Ambulance paramedics have the resources to manage severe hypoglycaemia.
You May Like: Does Chromium Picolinate Help With Diabetes
Treatment For High Blood Sugar Levels
For those with high blood sugar levels, it is vital to keep track of your blood sugars at home on a daily basis. This can be done with a glucose meter. These test monitors are often provided to diabetic patients so that they can manage their blood sugar levels at home everyday. They are available to purchase online if you are non-diabetic but wish to check on your levels regularly for safety.
Diabetic patients can be prescribed medications to help with insulin levels when their blood sugar is high. Those with type 1 diabetes will be prescribed medication which needs to be taken several times daily. This type of diabetes has no cure but can be managed with the right medication.
Those with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes can treat their high blood sugar with a change in diet or exercise. A healthier balanced diet is usually advised and sometimes, insulin medication is also prescribed if the blood sugar level becomes abnormally higher than the high reading for diabetic patients.
S For Treating A Person With Symptoms Keeping Them From Being Able To Treat Themselves
Dont hesitate to call 911. If someone is unconscious and glucagon is not available or someone does not know how to use it, call 911 immediately.
Do NOT:
- Inject insulin
- Provide food or fluids
Also Check: Best Yogurt For A Diabetic
Signs And Symptoms Of Low Blood Glucose
Each person’s reaction to low blood glucose is different. Learn your own signs and symptoms of when your blood glucose is low. Taking time to write these symptoms down may help you learn your own symptoms of when your blood glucose is low. From milder, more common indicators to most severe, signs and symptoms of low blood glucose include:
- Feeling shaky
- Color draining from the skin
- Feeling sleepy
- Feeling weak or having no energy
- Blurred/impaired vision
- Tingling or numbness in the lips, tongue, or cheeks
- Nightmares or crying out during sleep
The only sure way to know whether you are experiencing low blood glucose is to check your blood glucose levels, if possible. If you are experiencing symptoms and you are unable to check your blood glucose for any reason, treat the hypoglycemia.
A low blood glucose level triggers the release of epinephrine , the fight-or-flight hormone. Epinephrine is what can cause the symptoms of hypoglycemia such as thumping heart, sweating, tingling, and anxiety.
If the blood sugar glucose continues to drop, the brain does not get enough glucose and stops functioning as it should. This can lead to blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and drowsiness. If blood glucose stays low for too long, starving the brain of glucose, it may lead to seizures, coma, and very rarely death.
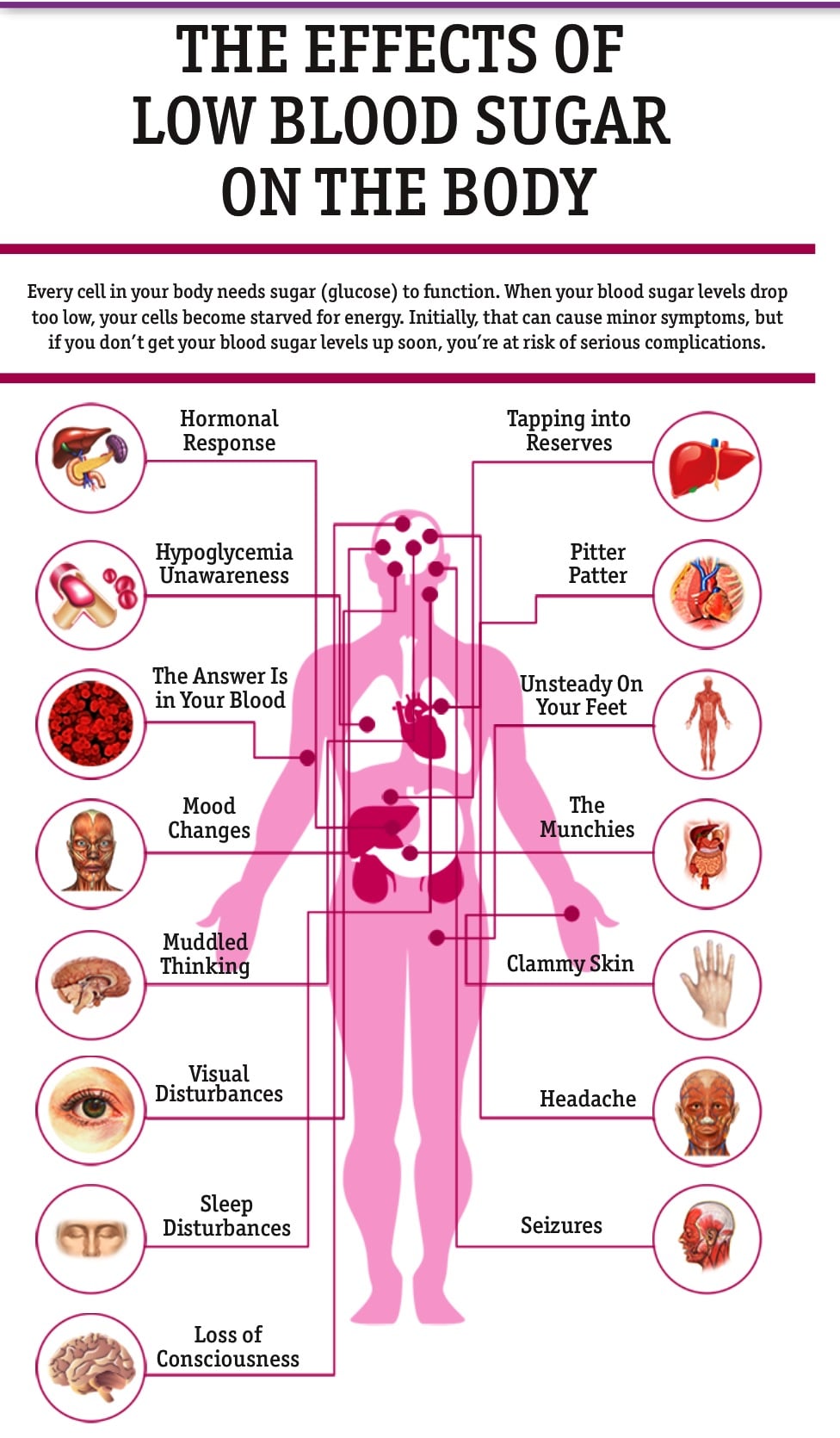
The Effects Of Low Blood Sugar On Your Body
Every cell in your body needs energy to function. The main source of energy might come as a surprise: Its sugar, also known as glucose. Blood sugar is essential to proper brain, heart, and digestive function. It even helps keep your skin and vision healthy.
When your blood sugar levels fall below the normal range, its called hypoglycemia. There are many identifiable symptoms of low blood sugar, but the only way to know if you have low blood sugar is by taking a blood glucose test.
Learn more about the symptoms of low blood sugar, as well as the long-term effects on the body.
most common reasons for low blood sugar are some medications used to treat diabetes, such as insulin.
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas can no longer produce insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, or your body cant use it properly. Too much insulin or oral diabetic medication can lower the blood sugar level, leading to hypoglycemia.
However, contrary to popular belief, low blood sugar isnt exclusive to diabetes, though it is rare. It can also happen if your body makes more insulin than it should.
Another possible cause of low blood sugar is drinking too much alcohol, especially over long periods of time. This can interfere with the livers ability to create a buildup of glucose and then release it into your bloodstream when you need it.
Other causes include:
Also Check: What Diabetic Testing Supplies Are Covered By Medicare
Whats The Link Between Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is most common, by far, in people with diabetes. Treatment for the diseaseoften involves taking medication to increase insulin. Hypoglycemia can develop if things like food, exercise and diabetes medications are out of balance.
Common pitfalls for people with diabetes include:
- Being more active than usual.
- Drinking alcohol without eating.
- Eating late or skipping meals.
- Not balancing meals by including fat, protein and fiber.
- Not eating enough carbohydrates.
- Not timing insulin and carb intake correctly .
Also, if someone with diabetes uses the wrong insulin, takes too much or injects it incorrectly, that can cause hypoglycemia.
Digestive Endocrine And Circulatory Systems
After you eat, your digestive system breaks down carbohydrates and turns them into glucose. Essentially, glucose is your bodys fuel source.
As your sugar levels rise, your pancreas releases a hormone called insulin, which helps glucose get taken up and used by cells throughout your body. If you have insulin-dependent diabetes, you must take the right about of insulin to get the job done.
Any excess glucose goes to your liver for storage.
When you go a few hours without eating, blood sugar levels go down. If you have a healthy pancreas, it releases a hormone called glucagon to make up for the absence of food. This hormone tells your liver to process the stored sugars and release them into your bloodstream.
If everything works as it should, your blood sugar levels should remain in the normal range until your next meal.
Insufficient blood sugar levels can cause a rapid heartbeat and heart palpitations. However, even if you have diabetes, you may not always have obvious symptoms of low blood sugar. This is a potentially dangerous condition called hypoglycemia unawareness. It happens when you experience low blood sugar so often that it changes your bodys response to it.
Normally, low blood sugar causes your body to release stress hormones, such as epinephrine. Epinephrine is responsible for those early warning signs, like hunger and shakiness.
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Treatment By Family Friends Or Co
Family, friends, and co-workers of those with hypoglycemia are often first to identify hypoglycemic episodes, and may offer help. Upon recognizing the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia in a diabetic, a blood sugar level should first be measured using a glucose meter. If blood glucose is below 70 mg/dL , treatment will depend on whether the person is conscious and can swallow safely. If the person is conscious and able to swallow, the family, friend, or co-worker can help the hypoglycemic consume 10-20 grams of a carbohydrate to raise blood glucose levels to a minimum of 70 mg/dL . Improvement in blood sugar level and symptoms is expected to occur in 1520 minutes, at which point blood sugar is measured again. If the repeat blood sugar level is not above 70 mg/dL , the hypoglycemic should consume another 10-20 grams of a carbohydrate and with remeasurement of blood sugar levels after 1520 minutes. Repeat until blood glucose levels have returned to normal levels, or call emergency services for further assistance.
If the person is unconscious, a glucagon kit may be used to treat severe hypoglycemia, which delivers glucagon either by injection into a muscle or through nasal inhalation. In the United States, glucacon kits are available by prescription for diabetic patients to carry in case of an episode of severe hypoglycemia. Emergency services should be called for further assistance.
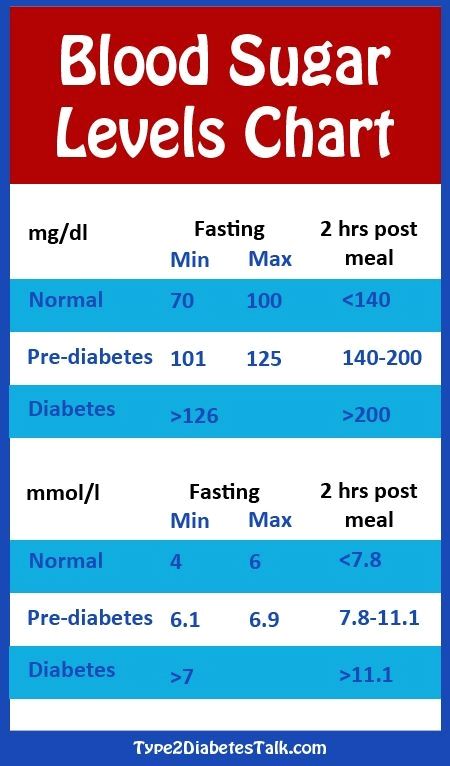
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
Normal blood glucose levels are from between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol per litre of blood when fasting, and up to 7.8 mmol per litre of blood two hours after a meal.
If you’re having your blood sugar levels tested, your doctor will perform something called a ‘glucose tolerance test‘ which involves two blood tests, one after fasting, and one after the consumption of a sugary drink.
Manage your blood sugar levels with GlucoBalance
You can also help manage your blood sugar levels with GlucoBalance, an advanced plant-based formula to protect against highs and lows of blood sugar, manage blood glucose and your blood sugar metabolism. Find out more here.
You May Like: Fruits For Type 1 Diabetes
Slurred Speech And Clumsiness
Your sugar-starved brain may change the way you sound. Slurred speech is a common symptom associated with blood sugar levels that drop below 40 mg/dL, according to University of Michigan Health Systems. Combined with clumsiness another sign of low blood sugar you may seem as though you’ve had a few too many cocktails, even if you haven’t touched a drop, according to the National Health Service.
For more on managing low blood sugar, check out Diabetes Daily’s article “How to Treat Lows Without Sabotaging Your Diet!“