Causes Of Gestational Diabetes
Pregnant women experience fluctuation of glucose levels because of the hormonal changes in the body, characteristic for pregnancy. There are hormones that prevent insulin normal functioning, which is breaking down the sugar from the blood . All this happens to ensure that the baby gets enough sugar to develop. At the same time, moms body need more insulin but there are none and this is what causes gestational diabetes.
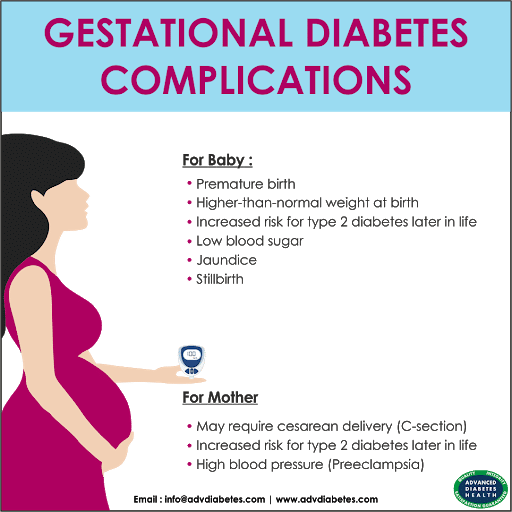
This condition must be treated, or it could harm both mom and unborn child. The first symptoms are tiredness, dizziness, sweating and increased hunger. It could cause preeclampsia and premature labor in pregnant women and lead to birth defects in the baby. The unborn child might have jaundice, low blood sugar or be overweight in that case.
- Among these risk factors, women with overweight, obesity and morbid obesity are related to an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus at a rate of two, four and eight times, respectively.
- Today, the interventions such as lifestyle changes, the use of metformin, glyburide, myo-inositol, insulin, diet and exercise activities are applied to prevent and treat the gestational diabetes mellitus.
- Some studies showed physical activity in pregnancy has these features, and also it is effective on insulin resistance.
Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
Imagine wanting to get pregnancy and bring discouraged from doing so. About 25 years ago, this was the case for many women with diabetes. Fortunately, with recent advances in diabetes management and careful planning, the chances of having a successful pregnancy are excellent!
Preconception Planning
If you have diabetes and are thinking about becoming pregnant, it is recommended that you start preparing about 6 months prior to conception. The most important thing to do before conception is to have your diabetes in good control and to learn how to continue managing your diabetes during pregnancy.
Once youve decided you want to become pregnant, you should make an appointment with your endocrinologist to review your health status and pregnancy plans. If you dont have an endocrinologist, your primary care provider can refer you to one.
In addition to an endocrinologist, there are other who can help you during your pregnancy: an obstetrician, of course but other members of your healthcare team my include a registered nurse and/or dietitian who focus on the management of diabetes and an ophthalmologist who will be sure your eyes stay healthy. While you will be the one in charge of your pregnancy, it is still necessary to have a medical team as well as loved ones to support you during this time.
The Joslin-Beth Israel Deaconess Pregnancy Program recommends the following goals and medical assessments before pregnancy:
If You Are Already Pregnant
Glucose Management in Pregnancy
What Happens If You Fail The 3 Hour Glucose Test
If you fail the 3-hour glucose test, you have impaired glucose tolerance and you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
A failing score is considered when you have 2 or more values in these ranges:
- Fasting > 95mg/dL
- 2 Hour > 155 mg/dL
- 3 Hour > 140 mg/dL
This is a very serious condition that requires very close monitoring of your blood sugar levels every single day.
If you dont, you are putting your own life and your babys life at risk.
You will meet with a nutritionist to learn how to improve your diet, and you will have to check your finger stick blood glucose 4 times a day for the remainder of the pregnancy.
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Medicare Pay For Diabetic Foot Care
What Are The Risks Factors Associated With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Although any woman can develop GDM during pregnancy, some of the factors that may increase the risk include the following:
-
Overweight or obesity
-
Family history of diabetes
-
Having given birth previously to an infant weighing greater than 9 pounds
-
Prediabetes, also known as impaired glucose tolerance
Although increased glucose in the urine is often included in the list of risk factors, it is not believed to be a reliable indicator for GDM.
What Do Abnormal Glucose Test Results Mean
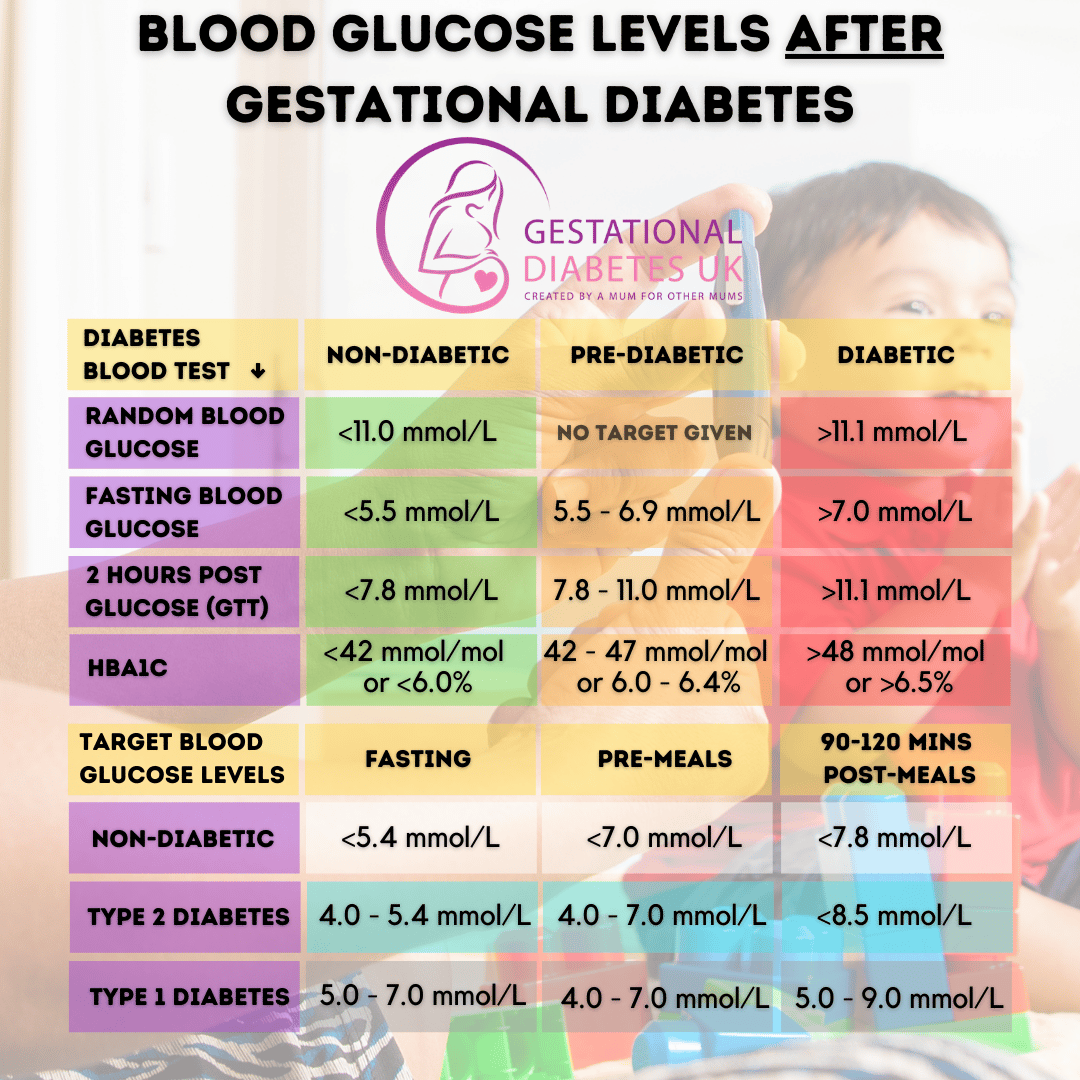
The results of your glucose test show how well your body breaks down sugar. If your glucose test results are higher than the standard limit, your body is not processing sugar properly, a sign of gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes usually occurs due to pregnancy-related hormonal changes. Its important that patients not blame themselves or feel guilty for results of the hormonal changes of pregnancy, this is precisely why we screen all patients for gestational diabetes, shares Dr. Juusela.
The good news is that for the most part, gestational diabetes can be successfully managed through diet, exercise and careful monitoring, Dr. Wool says. In cases where that is not enough, medications, such as insulin or metformin, can be used to help control blood sugar levels. In other words, you can have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby with this condition.
If you do need medication, SingleCare can help you save on your prescriptions. The free search tool allows patients to compare prices at pharmacies nearby to be sure youre getting the best deal. Simply enter your medication and location to get started today.
Recommended Reading: What Diet Plan Is Best For Type 2 Diabetes
Also Check: Diet For Insulin Resistance To Lose Weight
Treatments For Gestational Diabetes
If you have gestational diabetes, the chances of having problems with your pregnancy can be reduced by controlling your blood sugar levels.
Youll be given a blood sugar testing kit so you can monitor the effects of treatment.
Blood sugar levels may be reduced by changing your diet and exercise routine. However, if these changes dont lower your blood sugar levels enough, you will need to take medicine as well. This may be tablets or insulin injections.
Youll also be more closely monitored during your pregnancy and birth to check for any potential problems.
If you have gestational diabetes, its best to give birth before 41 weeks. Induction of labour or a caesarean section may be recommended if labour does not start naturally by this time.
Earlier delivery may be recommended if there are concerns about your or your babys health or if your blood sugar levels have not been well controlled.
What Is Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which your blood sugar levels become high during pregnancy. It affects up to 10% of women who are pregnant in the U.S. each year. It affects pregnant women who havenât ever been diagnosed with diabetes.
There are two classes of gestational diabetes. Women with class A1 can manage it through diet and exercise. Those who have class A2 need to take insulin or other medications.
Gestational diabetes goes away after you give birth. But it can affect your babyâs health, and it raises your risk of getting type 2 diabetes later in life. You can take steps so you and your baby stay healthy.
Also Check: Insulin Pump For Type 2 Diabetes
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring your blood glucose levels is essential. It gives you a guide as to whether the changes you have made to your lifestyle are effective or whether further treatment is required.
A diabetes nurse educator can teach you how and when to measure your blood glucose levels. They will discuss the recommended blood glucose levels to aim for.
Your doctor or diabetes educator can help you register with the National Diabetes Services Scheme for discounted blood glucose strips. Regular contact with your diabetes educator or doctor is recommended.
Testing Your Blood Glucose Levels
If you are using continuous or flash glucose monitoring, the device will check your blood glucose levels throughout the day. Your care team should talk with you about when to do finger prick tests on top of this.
If you are using testing strips, your care team should talk with you about when to test your blood glucose levels during the day:
|
Diabetes type and treatment |
|
|---|---|
|
Women with type 1 diabetes |
|
|
Women with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes having 2 or more insulin injections a day |
|
|
Women with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes having any of the following:
|
|
Recommended Reading: Fastest Way To Get Rid Of Diabetes
Will Gestational Diabetes Affect My Baby
Your baby will probably be healthy, if you and your doctor manage your blood sugar while you have gestational diabetes.
Right after you give birth, doctors will check your newborn’s blood sugar level. If itâs low, they may need to get glucose through an IV until it comes back up to normal.
Gestational diabetes raises the chance that you will have a baby who is larger than normal. It’s also linked to jaundice, in which the skin looks yellowish. Jaundice generally fades quickly with treatment.
Although your child will be more likely than other kids to get type 2 diabetes later on, a healthy lifestyle can cut that risk.
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
Also Check: What Is Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
Blood Glucose Target Levels
You and your care team should agree ideal blood glucose levels that are right for you and are manageable without causing problems with hypoglycaemia.
If you are taking metformin, or you are on insulin, you should be advised to aim for the following target blood glucose levels, unless this leads to difficulties with hypoglycaemia:
-
fasting: below 5.3 mmol/litreand
-
1 hour after meals: below 7.8 mmol/litre.
If you are not able to test until 2 hours after a meal, the target glucose level at that time should be below 6.4 mmol/litre.
If you are on insulin, you should also be advised to keep your blood glucose above 4 mmol/litre, because of the risk of hypoglycaemia.
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Is Treated With
What Is The Glucose Challenge Screening Test
No preparation is required prior to the test. During the test, the mother is asked to drink a sweet liquid and then will have blood drawn one hour from having the drink, as blood glucose levels normally peak within one hour. No fasting is required prior to this test.
The test evaluates how your body processes sugar. A high level in your blood may indicate your body is not processing sugar effectively . If the results of this screen are positive, the woman may have the Glucose Tolerance Test performed. It is important to note that not all women who test positive for the Glucose Challenge Screening test are found to have diabetes upon further diagnosis.
You May Like: Menu For Someone With Diabetes
Don’t Miss: 1 Hour Glucose Test Instructions
Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes does not usually cause any symptoms.
Most cases are only discovered when your blood sugar levels are tested during screening for gestational diabetes.
Some women may develop symptoms if their blood sugar levels gets too high , such as:
- needing to pee more often than usual
But some of these symptoms are common during pregnancy and are not necessarily a sign of gestational diabetes. Speak to your midwife or doctor if youre worried about any symptoms youre experiencing.
How Is Diabetes During Pregnancy Managed
Special testing and monitoring of the baby may be needed for pregnant diabetics, especially those who are taking insulin. This is because of the increased risk for stillbirth. These tests may include:
-
Fetal movement counting. This means counting the number of movements or kicks in a certain period of time, and watching for a change in activity.
-
Ultrasound. This is an imaging test that uses sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasounds are used to view internal organs as they function, and to look at blood flow through blood vessels.
-
Nonstress testing. This is a test that measured the babys heart rate in response to movements.
-
Biophysical profile. This is a measure that combines tests such as the nonstress test and ultrasound to check the baby’s movements, heart rate, and amniotic fluid.
-
Doppler flow studies. This is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to measure blood flow.
Also Check: Can You Reverse Blindness From Diabetes
Blood Glucose Testing And Diagnosis
As a standard practice in our institution, all pregnant women without risk factors for GDM underwent a glucose challenge test at 2428 weeks of gestation. On the other hand, women with risk factors received a screening test at the initial visit and, if negative, were rescreened at 2832 weeks of gestation. Individuals with a GCT result of 140 mg/dL or higher would be scheduled for a diagnostic 100-g OGTT. The diagnosis of GDM was based on the Carpenter and Coustan criteria .
The management of women with GDM included dietary and lifestyle modifications as initial treatment. These women were evaluated for their levels of glycemic control throughout gestation by the measurement of fasting and 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose levels every 24 weeks. Insulin therapy, as determined and prescribed by an endocrinologist, was generally initiated when the FPG was 95 mg/dL and/or 2-hour postprandial glucose was 120 mg/dL. Factors that were also involved in the decision to initiate insulin treatment were the compliance of pregnant women with insulin injections, gestational age at which abnormally high FPG or 2-hour postprandial glucose was detected, and type , magnitude and number of hyperglycemic episodes.
After delivery, all women with a diagnosis of GDM were scheduled for a 75-g, 2-hour OGTT at 6 weeks postpartum.
05-Sep-2018 | Pennie Solorio
How Is Diabetes During Pregnancy Treated
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, your age, and your general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Treatment focuses on keeping blood glucose levels in the normal range, and may include:
-
A careful diet with low amounts of carbohydrate foods and drinks
-
Oral medicines for hypoglycemia
Read Also: Low Blood Sugar With Type 2 Diabetes
When Should I Measure My Blood Glucose
Throughout the rest of your pregnancy, you will need to measure your blood glucose levels at various points through the day, to check that they are within the limits you have been given at each of those times:
When you get up You need to measure your blood glucose levels each morning when you get up, before you have anything to eat or drink. This blood glucose level is called your fasting blood glucose level because you will have an empty stomach. You must not have eaten or drunk anything apart from water overnight, for at least eight hours.
Your team should have discussed this with you and agreed the ideal morning blood glucose level for you to aim for.
Before or after every meal You will probably be asked to measure your blood glucose level around the time of a meal. Some services measure before eating while others measure one or two hours after a meal .
Again, you will have discussed and agreed an ideal blood glucose level after meals with your diabetes team. These levels will be higher than your fasting blood glucose levels, as you will just have eaten.
If you are taking insulin to help to control your blood glucose levels, you may need to do a separate test before you go to bed, or even during the night, although this is unusual.
“When we did go out for a special meal or two, and I’d have a little bit of cheesecake or something, it really affected my sugar levels. But that would’ve been just twice in the whole pregnancy.” Gemma, mum of one
Diabetes Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Also Check: Diabetes 2 Meal Plan For A Week
Don’t Miss: What Organ Controls Blood Sugar
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels While Pregnant
It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels at home to check that management of gestational diabetes is keeping your blood glucose levels within the target range. Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator can show you how to check your blood glucose levels and help you understand your blood glucose patterns. This is to ensure appropriate treatment can be administered and changed as necessary.
Your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator will advise you on recommended blood glucose target levels and testing times.
If your blood glucose levels cannot be managed by healthy eating and physical activity alone, your doctor may suggest medication. Most diabetes tablets are not suitable for use during pregnancy, but insulin injections and/or a medication called metformin may be required to help manage your gestational diabetes.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Age Range
What Causes Gestational Diabetes
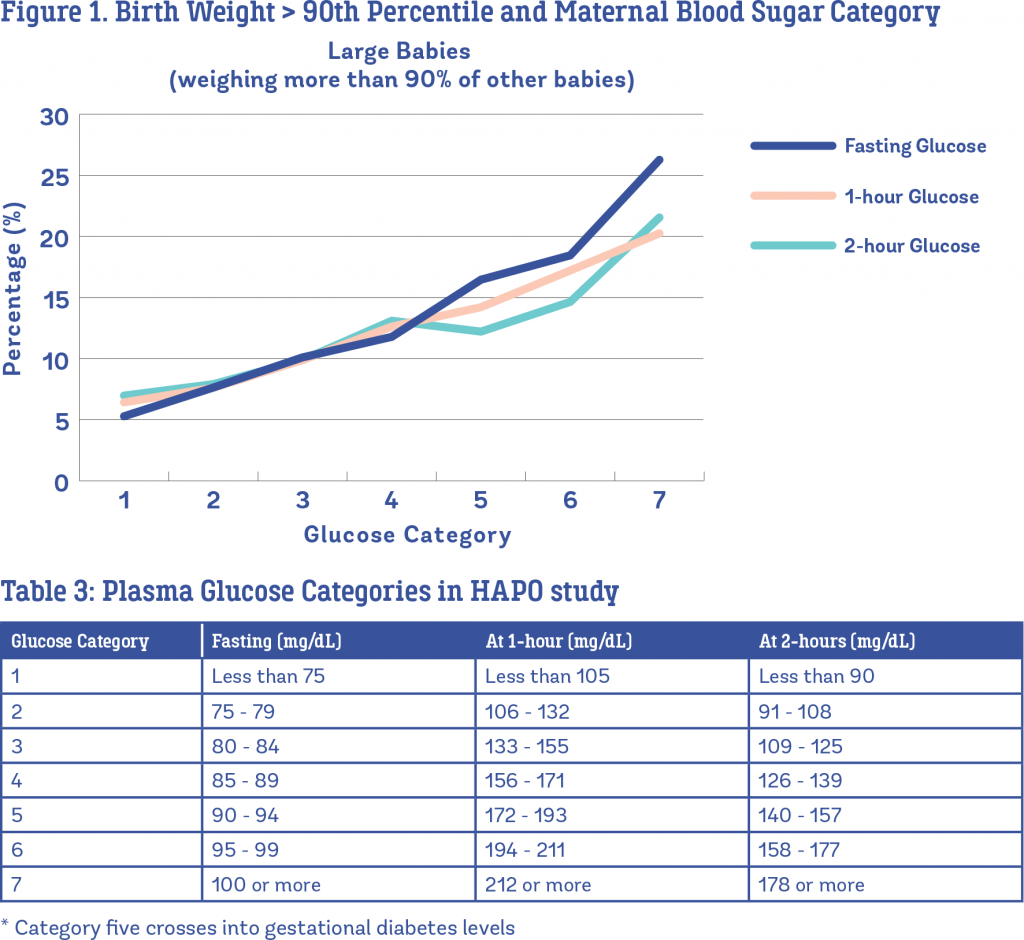
In pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that help the baby grow and develop. These hormones also block the action of the womanâs insulin. This is called insulin resistance. Because of this insulin resistance, the need for insulin in pregnancy is 2 to 3 times higher than normal. If you already have insulin resistance, then your body may not be able to cope with the extra demand for insulin production and the blood glucose levels will be higher resulting in gestational diabetes being diagnosed.
When the pregnancy is over and blood glucose levels usually return to normal and the gestational diabetes disappears, however this insulin resistance increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in later life.
Read Also: Best Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices 2021