The Heart Brain And Blood Vessels
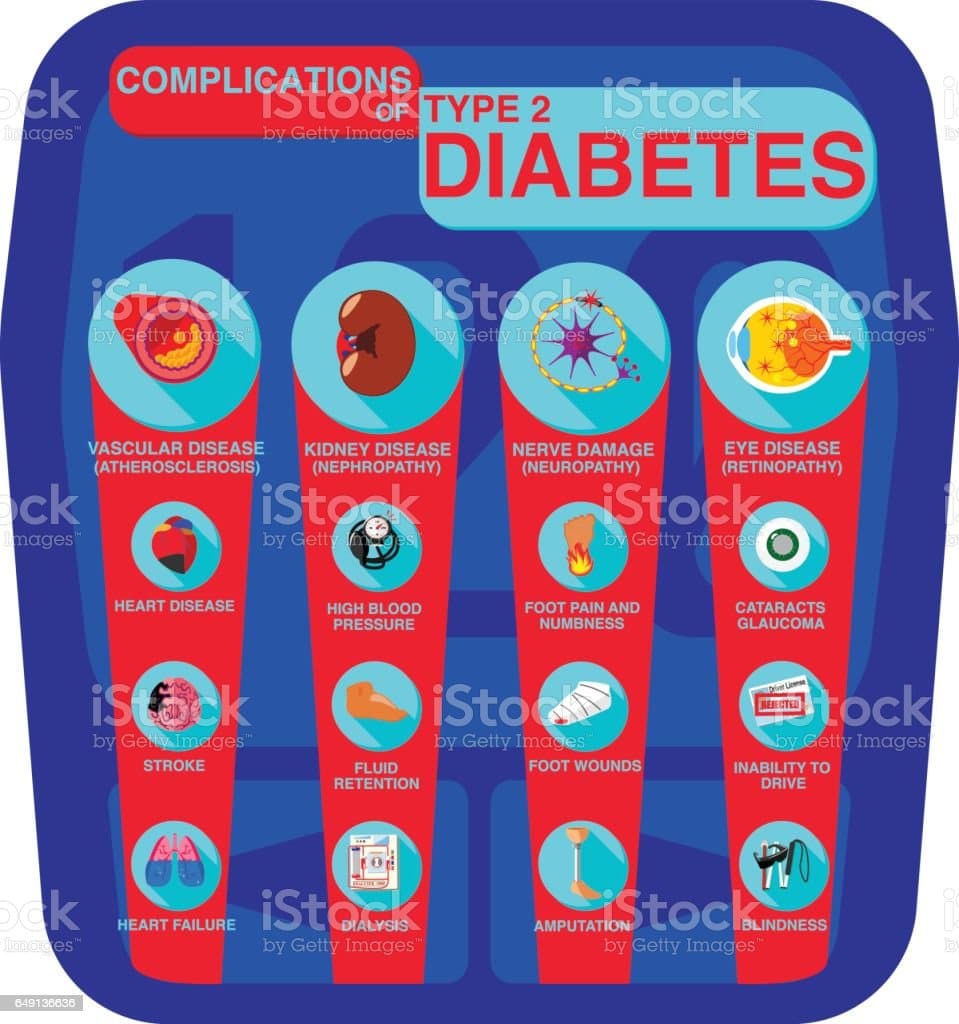
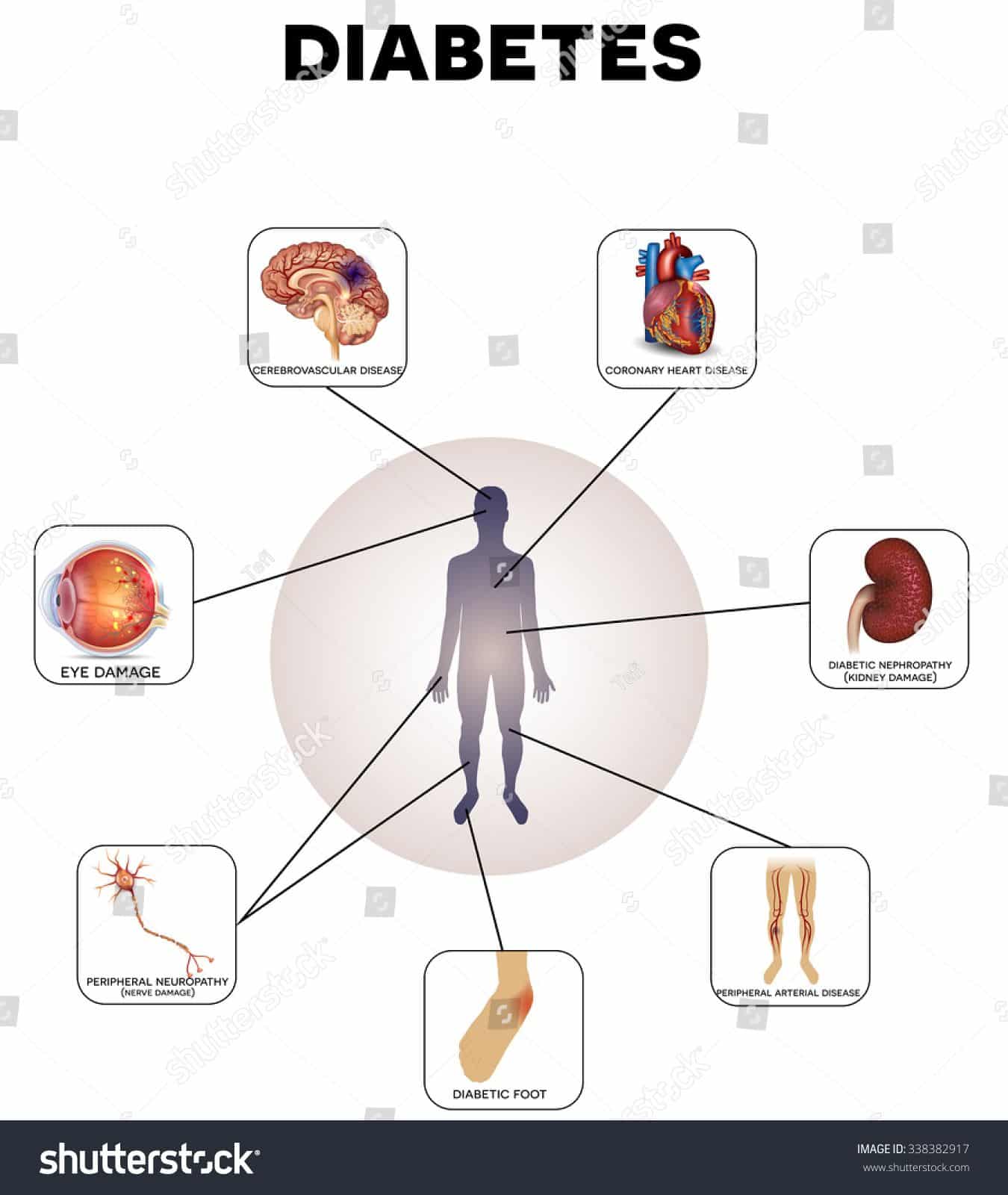
Type 2 diabetes can also affect the large blood vessels, causing plaque to eventually build up and potentially leading to a heart attack, stroke or vessel blockage in the legs .
To prevent heart disease and stroke as a result of diabetes, you should manage your diabetes well, but you should also make heart-healthy choices in other areas of your life: dont smoke, keep your blood pressure under control, and pay attention to your cholesterol.
It is important to have your cholesterol checked annually. Your doctor should check your blood pressure every office visit. Also at every office visit, the doctor should check the pulse in your feet to make sure there is proper circulation.
Type 2 diabetes comes with certain short- and long-term complications, but if you maintain good blood glucose control, you can avoid them.
Put The Brakes On Diabetes Complications
A healthy lifestyle is the key to preventing or delaying complications.
Encouraging news: People with diabetes are living longer, healthier lives with fewer complications. Whats the driving force? Greater awareness and better management of risk factors. Find out what you can do to prevent or delay diabetes health problems.
Weve come a long way in reducing the impact of diabetes on peoples lives. In the last 20 years, rates of several major complications have decreased among US adults with diabetes. The greatest declines were for two leading causes of death: heart attack and stroke. This is real progress.
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
Learn about the symptoms, causes, and treatments of type 2 diabetes.
Also Check: Non Insulin Injections For Type 2 Diabetes
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body cant use energy from food properly. Your pancreas produces insulin to help your cells use glucose . But over time your pancreas makes less insulin and the cells resist the insulin. This causes too much sugar to build up in your blood. High blood sugar levels from Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health problems including heart disease, stroke or death.
Hyperglycemia And Macrovascular Disease
Hyperglycemia, as measured by HbA1c, is a predictor of coronary heart disease risk. In a Finnish study that followed elderly men and women for up to 3.5 years, HbA1c> 7.9% were associated with a 21% incidence of CHD-related events and a 12% incidence of CHD mortality .28 In the Norfolk cohort of the European Prospective Investigation of Cancer and Nutrition , 82% of the excess mortality
Recommended Reading: Glucose Tolerance Test Normal Range Pregnancy
Can You Be Born With Diabetes Is It Genetic
You arent born with diabetes, but Type 1 diabetes usually appears in childhood. Prediabetes and diabetes develop slowly over time years. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.Scientists do believe that genetics may play a role or contribute to the development of Type 1 diabetes. Something in the environment or a virus may trigger its development. If you have a family history of Type 1 diabetes, you are at higher risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. If you have a family history of prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes, youre at increased risk of developing prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommend statins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
You May Like: Smart Blood Sugar 7-day Meal Plan
Healthy Eating For Type 2 Diabetes
A dietitian or your doctor will be able to advise you on what to eat to meet your nutritional needs and control your blood sugar. Your doctor should be able to refer you to a registered dietitian for personalised advice.
Eating healthy foods with a low glycaemic index can help to optimise your blood sugar levels. This includes wholegrain breads, minimally processed breakfast cereals like rolled or steel cut oats, legumes, fruit, pasta and dairy products.
Avoid high-carbohydrate, low-nutrient foods such as cakes, lollies and soft drinks, and eat a diet low in saturated fat.
You should eat at regular times of the day and may also need snacks. Try to match the amount of food you eat with the amount of activity you do, so that you dont put on weight.
If you are overweight or obese, losing even 5-10 per cent of your body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
No Matter Where You Are In Your Fight Heres Where You Need To Be
Whether youve been newly diagnosed, have been fighting against type 1 or type 2 diabetes for a while, or are helping a loved one, youve come to the right place. This is the start of gaining a deeper understanding of how you can live a healthier lifewith all the tools, health tips, and food ideas you need. Wherever youre at with your diabetes, know that you have options and that you dont have to be held back. You can still live your best life. All you have to do is take action and stick with it.
New to diabetes? Learn how diabetes is diagnosed.
Also Check: Best Lunch For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Cured
Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but people with the condition may be able to manage their type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and, if needed, diabetes medications to control blood sugar levels.
Its also emerging that some people who are overweight or obese can put their type 2 diabetes into remission by losing a substantial amount of weight, especially early in their diagnosis. Their blood sugar measurements return to healthy levels below the diabetes range. Its not a permanent solution, and diabetes could come back, so it needs to be maintained. However, many people were still in remission 2 years later. This should only be tried under the supervision of your doctor.
You May Like: High Blood Levels In Diabetes
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin. It helps your cells turn glucose, a type of sugar, from the food you eat into energy. People with type 2 diabetes make insulin, but their cells don’t use it as well as they should.
At first, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get glucose into your cells. But eventually, it can’t keep up, and the glucose builds up in your blood instead.
Usually, a combination of things causes type 2 diabetes. They might include:
Preeclampsia And Gestational Hypertension
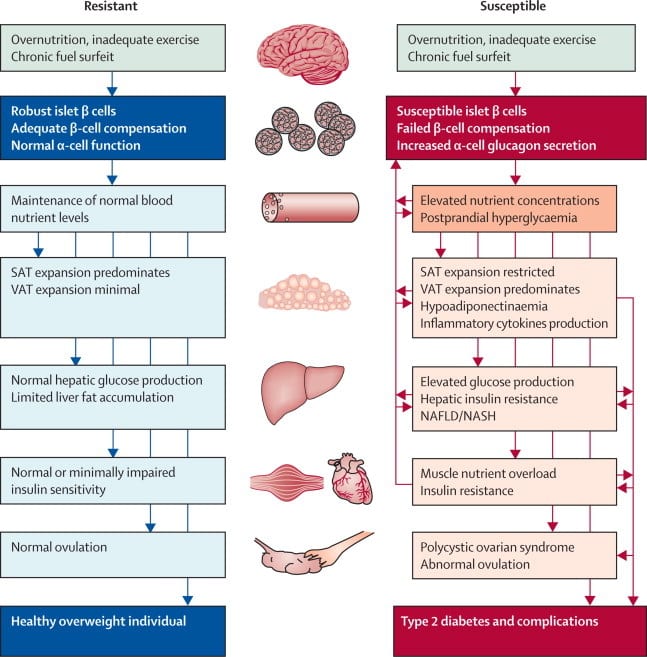
A population-based, retrospective cohort study of 1,010,068 pregnant women examined the association between preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy and the risk of developing diabetes post partum. Results showed the incidence rate of diabetes per 1000 person-years was 6.47 for women with preeclampsia and 5.26 for those with gestational hypertension, compared with 2.81 in women with neither condition. Risk was further elevated in women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension comorbid with gestational diabetes.
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus
How Does Diabetes Type 2 Occur
The primary cause of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is that the pancreas may produce enough insulin to transport sugar into the cells, however, the body refuses to use the insulin.
Insulin helps to unlock the cells of the body to allow the sugar to enter them so that the glucose is transformed into energy.
If there is more sugar in the body than is required, the insulin helps to store the sugar in the liver and releases it when the blood sugar level is low, or when the body needs more sugar, such as in between meals or during vigorous physical activity. Therefore, insulin helps to balance out the blood sugar level and keep it in a normal range. As blood sugar level increases, the pancreas secrete more insulin.
In diabetes type 2 since the body refuses to use the insulin produced, the insulin is unable to let the sugar enter the cells and transform into energy. The sugar level keeps increasing in the blood, and overtime hurts the eyes, heart, kidneys and nerves.
The insulin is not able to let the sugar enter the cells and transform into energy. The sugar keeps increasing in the blood and overtime hurts the eyes, heart, kidneys and nerves.
A secondary reason for diabetes mellitus type 2 is insufficient insulin production by the pancreas. A study done by a team of researchers at the Newcastle University shows that this occurs due to fat accumulation in the pancreas.
When the insulin production is not enough, blood sugar levels rise in the body causing diabetes mellitus type 2.
Occurrence In The United States
According to the CDC’s National Diabetes Statistics Report, the crude prevalence of diabetes in the adult US population is 14.7%. It was estimated that 11.3% of the adult population have actually been diagnosed, while 3.4% of adults have undiagnosed diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes rises with age, reaching 29.2% in persons aged 65 years or older. Data employed in the report were drawn from 2017-2020.
Prediabetes, as defined by the American Diabetes Association, is that state in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. It is presumed that most persons with prediabetes will subsequently progress to diabetes. The above-mentioned CDC report found the age-adjusted estimate for the prevalence of prediabetes in the adult US population to be 10.8%.
A study by Andes et al using a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey indicated that in the United States, prediabetes exists in approximately 1 out of 5 adolescents and 1 out of 4 young adults.
However, a study by Liu et al reported a higher incidence of prediabetes in young people, revealing that in the United States by 2018, approximately 28% of individuals between ages 12 and 19 years had the condition this was up from less than 12% in 1999. A greater prevalence of prediabetes was found in males in this group and in youth with overweight or obesity.
Read Also: What Causes Your Blood Sugar To Drop
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patients must be educated about the importance of blood glucose management to avoid complications associated with DM. Stress must be given on lifestyle management, including diet control and physical exercise. Self-monitoring of blood glucose is an important means for patients to take responsibility for their diabetes management. Regular estimation of glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and lipid levels is necessary.
Healthcare professionals should educate patients about the symptoms of hypoglycemia and required action .
Patients should be motivated to stop smoking. Emphasis is required on regular eye check-ups and foot care.
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Advancements in technology have given us another way to monitor glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring uses a tiny sensor inserted under your skin. You don’t need to prick your finger. Instead, the sensor measures your glucose and can display results anytime during the day or night. Ask your healthcare provider about continuous glucose monitors to see if this is an option for you.
Recommended Reading: When Is Insulin Needed For Type 2 Diabetes
Detection In Biological Fluids
Insulin is often measured in serum, plasma or blood in order to monitor therapy in people who are diabetic, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized persons or assist in a medicolegal investigation of suspicious death. Interpretation of the resulting insulin concentrations is complex, given the numerous types of insulin available, various routes of administration, the presence of anti-insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics and the ex vivo instability of the drug. Other potential confounding factors include the wide-ranging cross-reactivity of commercial insulin immunoassays for the biosynthetic insulin analogs, the use of high-dose intravenous insulin as an antidote to antihypertensive drug overdosage and postmortem redistribution of insulin within the body. The use of a chromatographic technique for insulin assay may be preferable to immunoassay in some circumstances, to avoid the issue of cross-reactivity affecting the quantitative result and also to assist identifying the specific type of insulin in the specimen.
General Characteristics Of Study Subjects
Overall, a total of 1,524 diabetic individuals were eligible in the study, 373 were recruited in Shanghai, 375 in Beijing, 376 in Guangzhou and 400 in Chengdu. Among them were 637 males and 887 females with a mean age of 63.3 years . The mean of time span between the diagnosis of T2DM and enrolment in the study was 8.7 years .
You May Like: Can You Buy Insulin Over The Counter At Walgreens
What Are The Side Effects Of Type 2 Diabetes
More frequent in male type 2 diabetic · Unilateral or asymmetrical bilateral Pain, wasting and weakness in proximal muscles of the lower limbs. Often associated with polynuropathy and weight loss. DD: Internal malignancy, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy.
What kind of pain does diabetic amyotrophy cause?
Diabetic amyotrophy is a nerve disorder complication of diabetes mellitus. It affects the thighs, hips, buttocks and legs, causing pain and muscle wasting. What is diabetic amyotrophy? What is diabetic amyotrophy like? What causes diabetic amyotrophy? How common is diabetic amyotrophy? How is diabetic amyotrophy diagnosed?
Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Teens
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But its not always because family members are related it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
- Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks
- Eating more fruits and vegetables
- Making favorite foods healthier
- Making physical activity more fun
Healthy changes become habits more easily when everyone makes them together. Find out how to take charge family style with these healthy tips.
Recommended Reading: I Am Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Prevention
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help you lower your risk of diabetes.
- Lose weight. Dropping just 7% to 10% of your weight can cut your risk of type 2 diabetes in half.
- Get active. Thirty minutes of brisk walking a day will cut your risk by almost a third.
- Eat right. Avoid highly processed carbs, sugary drinks, and trans and saturated fats. Limit red and processed meats.
- Quit smoking. Work with your doctor to keep from gaining weight after you quit, so you don’t create one problem by solving another.
How Do I Prevent Or Delay Complications
Theyre not inevitable. Keeping blood sugar, blood pressure and blood fats under control will hugely help to reduce your risk of developing complications. This means going to your diabetes health checks and finding out from your diabetes healthcare team how to look after yourself between appointments.You can prevent or delay the complications of diabetes. But you need to take action and its all about managing your diabetes well.
Also Check: Living With Diabetes And Celiac Disease