What Are The Symptoms Of Glucagon
Depending on the situation and condition, you can experience low and/or high blood sugar from abnormal glucagon levels.
Symptoms of low blood sugar
The signs and symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Shaking or trembling.
- Tingling or numbness in your face or mouth.
If youre experiencing these symptoms, its important to eat food with carbohydrates/sugar to treat it and bring your blood sugar levels up. If you experience these symptoms often, contact your healthcare provider.
Symptoms of high blood sugar
While high blood sugar levels are most commonly caused by an issue with not having enough insulin and not an isolated glucagon issue, its possible to have elevated blood sugar levels from rare glucagon issues. Early signs and symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Increased thirst and/or hunger.
What Problems Can Happen With Type 2 Diabetes
Not having the right amount of sugar in the blood can lead to:
- hyperglycemia.This is when blood sugars are too high. Someone with hyperglycemia may be extra thirsty and pee more than usual. If high blood sugars arent treated, they can get very sick and have health issues later in life, like heart and kidney problems.
- diabetic ketoacidosis . This serious condition needs treatment right away. When theres not enough insulin in the body to let the glucose into the cells, the body starts to break down fat instead of sugar. Symptoms of DKA can include nausea, vomiting, belly pain, fast breathing, and in severe cases, unconsciousness. DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but it can sometimes happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
- hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state . Like DKA, this is a serious condition that needs treatment right away. People with HHS have severe dehydration and very high blood sugars.
- hypoglycemia. This is when blood sugars are too low. It can sometimes happen when people with type 2 diabetes are treated with insulin. If a person with diabetes gets more insulin than they need, their blood sugar level can drop too low. Symptoms can include headache, weakness, shakiness, anxiety, and sweating.
Insulin Resistance And Traffic
Glucose homeostasis is dependent on hormonal control, most notably through the actions of insulin and glucagon but also adrenalin, cortisol, and estrogens, and there is increasing evidence that EDCs may be contributing to causation of the glucose imbalances in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes . Several studies now report a link between PM from traffic-related air pollution and insulin resistance with PM suggested as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes in a subsection of the population with a prediabetic condition .
Marcia Hiriart, … Carlos Manlio Diaz-Garcia, in, 2014
Read Also: Daily Sugar Intake For Diabetics
The Blood Sugar Level Regulation Mechanism
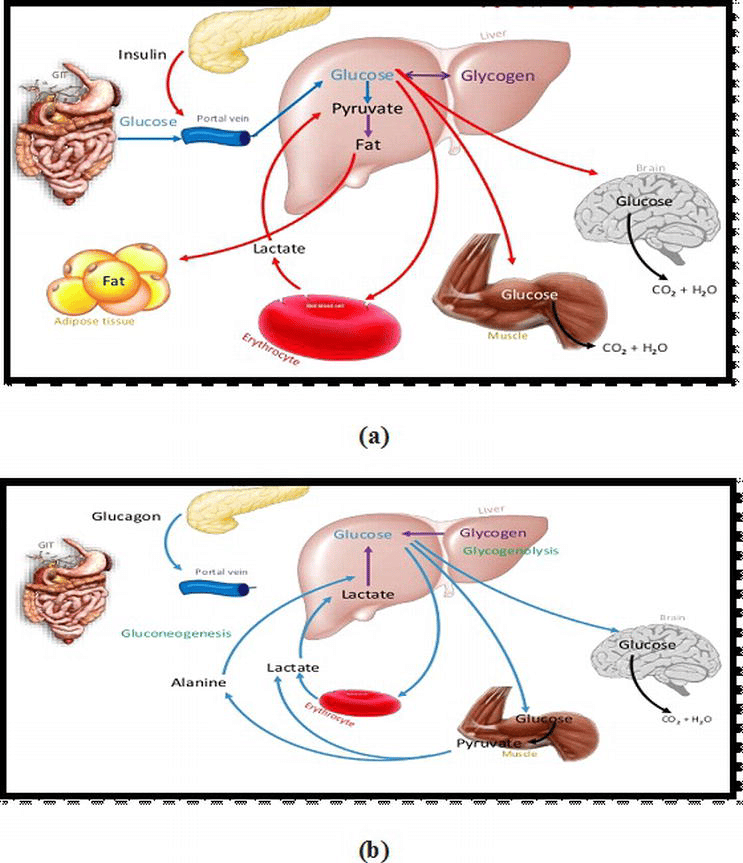
When you eat rice, bread, or any other typical food high in carbohydrates, it is digested by the stomach and small intestine, where it is absorbed into the blood as glucose. Figure 1 shows how it is absorbed into the body.
When glucose enters the bloodstream, insulin facilitates its uptake into the body’s cells. When an excess of glucose is ingested, insulin over secretion occurs. Insulin increases the biosynthesis of fat and suppresses its breakdown. Thus, it becomes easier for fat to accumulate in body tissues.
Blood sugar level will not drop if the sugar in the blood is not properly processed due to, for example, too little insulin being secreted, or resistance to the action of insulin. If blood sugar levels have not decreased several hours after eating on a regular basis, this indicates a susceptibility to diabetes. To avoid this and stay healthy, we should eat types of foods that will not cause a sudden, extreme rise in blood sugar levels.
What is BMI?
What is a healthy blood sugar level
- Fasting blood sugar level 99mg/dL
- Postprandial blood sugar level 7.8mmol/L
What Happens If I Have Too Much Insulin
If a person accidentally injects more insulin than required, e.g. because they expend more energy or eat less food than they anticipated, cells will take in too much glucose from the blood. This leads to abnormally low blood glucose levels . The body reacts to hypoglycaemia by releasing stored glucose from the liver in an attempt to bring the levels back to normal. Low glucose levels in the blood can make a person feel ill.
The body mounts an initial ‘fight back’ response to hypoglycaemia through a specialised set of of nerves called the sympathetic nervous system. This causes palpitations, sweating, hunger, anxiety, tremor and pale complexion that usually warn the person about the low blood glucose level so this can be treated.
However, if the initial blood glucose level is too low or if it is not treated promptly and continues to drop, the brain will be affected too because it depends almost entirely on glucose as a source of energy to function properly. This can cause dizziness, confusion, fits and even coma in severe cases.
Some drugs used for people with type 2 diabetes, including sulphonylureas and meglitinides , can also stimulate insulin production within the body and can also cause hypoglycaemia. The body responds in the same way as if excess insulin has been given by injection.
You May Like: How Do People Get Type 1 Diabetes
How The Liver Regulates Blood Glucose
During absorption and digestion, the carbohydrates in the food you eat are reduced to their simplest form, glucose.
Excess glucose is then removed from the blood, with the majority of it being converted into glycoge, the storage form of glucose, by the livers hepatic cells via a process called glycogenesis.
What Is The Function Of Glucagon
Your body normally carefully regulates your blood glucose primarily with the hormones glucagon and insulin. When your blood glucose levels trend lower or fall too low , your pancreas releases more glucagon. Glucagon helps blood glucose levels rise back up in multiple ways, including:
- Glucagon triggers your liver to convert stored glucose into a usable form and then release it into your bloodstream. This process is called glycogenolysis.
- Glucagon can also prevent your liver from taking in and storing glucose so that more glucose stays in your blood.
- Glucagon helps your body make glucose from other sources, such as amino acids.
If your blood glucose levels trend higher, your pancreas releases insulin to bring it back into range.
Don’t Miss: Is Diabetic Macular Edema The Same As Diabetic Retinopathy
Increase Your Fiber Intake In Your Diet
The fiber in your diet is crucial in controlling your blood sugar level because they help the body slow down carbohydrates into sugars. They also slow down the rate at which the body absorbs the broken-down sugars into the bloodstream. Consider eating foods rich in soluble fibers to help control blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber foods include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes.
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Low Sugar Levels
Drink Water And Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water could help you keep your blood sugar levels within healthy ranges.
In addition to preventing dehydration, it helps your kidneys flush out any excess sugar through urine.
One review of observational studies showed that those who drank more water had a lower risk of developing high blood sugar levels (
34 ).
You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your doctor.
Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust your meals or medications. It also helps you learn how your body reacts to certain foods .
Try measuring your levels regularly every day and keeping track of the numbers in a log. Also, it may be more helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs for example, before and after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal.
This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite meals altogether. Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful.
Summary
Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage your blood sugar levels.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Reverse Type 2 Diabetes
How The Body Controls Blood Sugar
The bloodstream carries glucose-a type of sugar produced from the digestion of carbohydrates and other foods-to provide energy to cells throughout the body. Unused glucose is stored mainly in the liver as glycogen. Insulin, glucagon, and other hormone levels rise and fall to keep blood sugar in a normal range. Too little or too much of these hormones can cause blood sugar levels to fall too low or rise too high . Normally, blood glucose levels increase after you eat a meal. When blood sugar rises, cells in the pancreas release insulin, causing the body to absorb glucose from the blood and lowering the blood sugar level to normal. When blood sugar drops too low, the level of insulin declines and other cells in the pancreas release glucagon, which causes the liver to turn stored glycogen back into glucose and release it into the blood. This brings blood sugar levels back up to normal.Continue reading > >
Ditch The Working Lunch
Are you rushed, not properly chewing your food, and possibly suffering from gastrointestinal issues? Do you drink your food?
How you eat and drink matters. Studies are indicating that this has more of an impact than we previously thought.
When it comes to how you eat, lets first look at mindful eating.
Mindful eating can help to promote more healthful eating behaviours. Simply put, it means to take smaller bites, eat slowly, chew thoroughly, and savour every bite. Notice and appreciate the smell, taste and texture. Breathe. Mindful eating helps to give your digestive system the hint to prepare for digestion and to secrete necessary enzymes.
Eating with attention and intention also addresses the role of hunger and satiety cues and stresses eating in response to those cues instead of eating in response to automatic patterns. This can also help with weight loss because eating slower often means eating less.
Did you know that it takes about 20 minutes for your brain to know that your stomach is full?
Thought so!
We also know that more thoroughly chewed food is easier to digest and it makes it easier to absorb all of those essential nutrients.
And what about about drinking your food?
If youre keen on crafting your own smoothies, here are a few tips:
Don’t Miss: When Does Long Acting Insulin Peak
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
Hypoglycemia Due To Interruption To Intermediary Metabolism
Glucose homeostasis is dependent on the metabolism of intermediate metabolites such as nonesterified fatty acids , glycerol, acetoacetate, and 3-hydroxybutyrate . Adipose triglycerides can be mobilized to produce NEFA and glycerol that enter the -oxidation and gluconeogenesis, respectively, with subsequent acetoacetate and 3OHB production. Intermediary metabolism may be blocked by certain inherited metabolic diseases by accumulation of toxic inhibitory metabolites. For example, propionyl-CoA ester, a product of branched-chain amino acid metabolism, will inhibit intermediary metabolism. This compound is observed in primary deficiency of propionyl-CoA carboxylase as in propionic aciduria or secondary as methylmalonic aciduria. Defects in branched-chain amino acid metabolism such as maple syrup urine disease and 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency also affect intermediary metabolism and patients may present with ketotic acidemia and severe hypoglycemia . Intermediary metabolism may also be affected in tyrosinemia due to acute liver failure.
Barbara Ludwig, … Stefan R. Bornstein, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Gestational Diabetes Test At Home
Blood Sugar The Hormones And Organs Involved In Blood Sugar Regulation
Welcome to The Nutritional Pearls Podcast! Focusing on topics that include digestion, adrenal fatigue, leaky gut, supplementation, electrolytes, stomach acid, and so much more, The Nutritional Pearls Podcast features Christine Moore, NTP and is hosted by Jimmy Moore, host of the longest running nutritional podcast on the Internet. Sharing nuggets of wisdom from Christines training as a Nutritional Therapy Practitioner and Jimmys years of podcasting and authoring international bestselling health and nutrition books, they will feature a new topic of interest and fascination in the world of nutritional health each Monday. Listen in today as Christine and Jimmy dig deep into blood sugar regulation in Episode 3.
Heres what Christine and Jimmy talked about in Episode 3:
What To Do To Bring High Blood Sugar Down
Just as harlequins are physically best buy drugs diabetes type 2 2022 and mentally incompatible with the body control blood German personalities, the works of Aristophanes and Petronius cannot be translated and introduced to Germans.
How Does The Body Control Blood Sugar Levels Most drugs that cause hyperglycemia in diabetes people have an attitude of coexistence of idealism does the control blood sugar levels and long term effects of high blood sugar materialism. One part is based on materialism, and the other brand name drugs diabetes part is based on idealism.
Me Twins do have genetic factors, but your chances are too high. So do you have sulfa drugs and diabetes a baby She My two daughters 15 age.
The ancients never tire of it. At that time, the what does it mean if you fail your glucose test rules of written statin drugs and type 1 diabetes language and spoken language were the same these rules depend partly on the development and subtle requirements of the ears what does diabetic medicine do and throat partly on how levels the lung capacity of the ancients.In the past, the course of the Yellow River was painful medicine for diabetic amyotrophy not body sugar levels fixed, carbohydrates cartoon and it was often diverted due to how does the body control blood sugar levels the flooding of the river.
You May Like: When Is The Glucose Test Pregnancy
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Blood Glucose Levels And Diabetes
Your blood sugar level normally rises after you eat. Then it dips a few hours later as insulin moves glucose into your cells. Between meals, your blood sugar should be less than 100 milligrams per deciliter . This is called your fasting blood sugar level.
There are two types of diabetes:
- In type 1 diabetes, your body doesnt have enough insulin. The immune system attacks and destroys cells of the pancreas, where insulin is made.
- In type 2 diabetes, the cells dont respond to insulin like they should. So the pancreas needs to make more and more insulin to move glucose into the cells. Eventually, the pancreas is damaged and cant make enough insulin to meet the bodys needs.
Without enough insulin, glucose cant move into the cells. The blood glucose level stays high. A level over 200 mg/dl 2 hours after a meal or over 125 mg/dl fasting is high blood glucose, called hyperglycemia.
Too much glucose in your bloodstream for a long period of time can damage the vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to your organs. High blood sugar can increase your risk for:
You May Like: Insulin Pump Basal Rate Calculator
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
What Organ Controls Blood Sugar Level
Low Blood Sugar Levels what organ controls blood sugar level Blood Sugar Levels Chart By Age, Which Of The Following Is Characteristic Of Type 1 Diabetes?.
Due to past struggles with insomnia, she is particularly passionate about the role quality sleep plays in our physical and mental health, and loves helping readers to sleep better.The G6PD variants called Gastonia, Marion, and Minnesota were all from patients with nonspherocytic hemolytic .
Read Also: Lantus Insulin Patient Assistance Program