How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
Causes For Gestational Diabetes
During pregnancy, the placenta produces various hormones to support your pregnancy. These hormones make your cells more impervious to insulin.
However, your pancreas reacts by producing sufficient extra insulin to overcome this resistance. However, sometimes your pancreas cannot keep up. At this point, a negligible amount of glucose gets into your cells. Although a lot of glucose stays in your bloodstream. This leads to gestational diabetes.
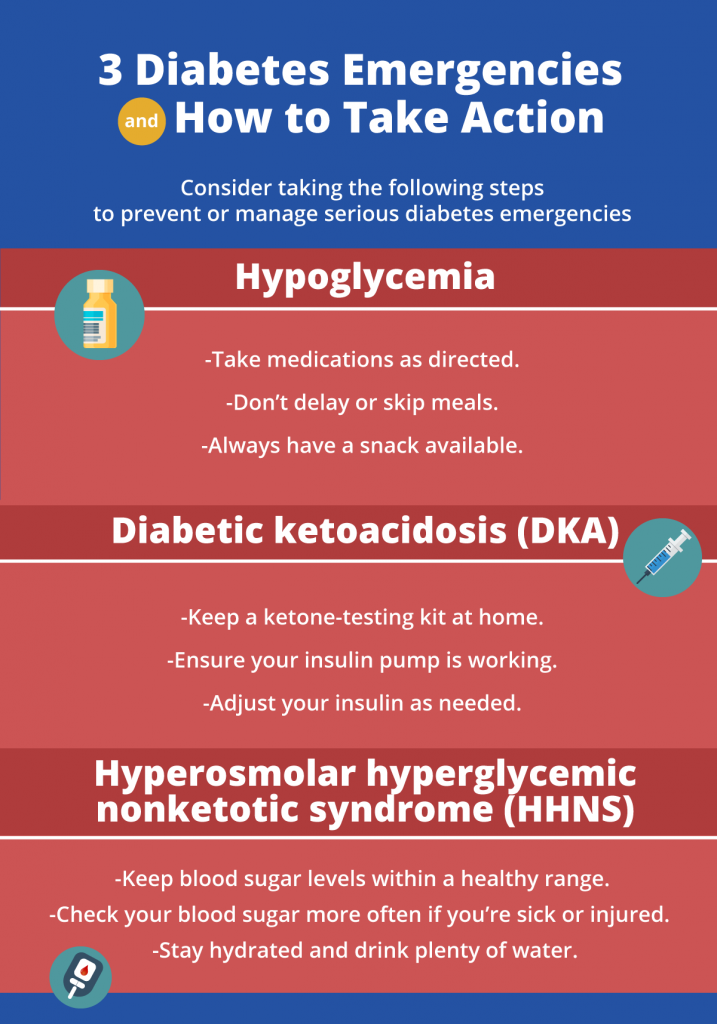
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetes-related ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed. If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
Recommended Reading: Is Nutrisystem Good For Type 2 Diabetes
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
What Diabetics Eat To Get Energy

Diabetics get their energy, or calories, from carbohydrate-rich foods with a low to moderate glycemic index 2. The glycemic index is a measure of how rapidly a food raises your blood sugar or glucose 2. Energy-rich foods for diabetics also have a significant amount of fiber, fat or protein which slows the digestion and absorption of the food.
Also Check: How Many Types Of Insulin Are There
Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
Differences Between Participants And Nonparticipants
There was no significant difference on the mean scores on the SFQ between participants and nonparticipants completing questionnaires. Nonparticipants, including nonresponders, did not differ significantly from participants on sex . Participants and nonparticipants did differ significantly from each other on age and HbA1c. Participants were older , participants had lower HbA1c values , and their latest HbA1c was measured more recently compared with nonparticipants. The mean age of nonparticipants was 43.6 years, mean HbA1c values were 8.6 , and HbA1c was measured 8 months previously .
Recommended Reading: Doctor To See For Diabetes
How Does Carbohydrate Affect Anyone With Type 2 Diabetes
For people with Type 2 diabetes who may be overweight or obese, reducing the calories you eat helps to lose weight. This can be done through different means including following a low carb diet or simply reducing the current amount of carbs you eat. People have successfully followed low carb diets to lose weight and manage their diabetes including lowering their HbA1c, cholesterol and blood pressure levels as well as reducing the amount of diabetes medications they take. If you are taking diabetes medications that put you at risk of hypos, checking your blood glucose levels regularly and speaking to your healthcare team to review your medications will help to reduce your risk of hypos when you restrict your carb intake.
Knowing How Much Carbs Is In You Food
If youre living with diabetes, and take insulin, youll need to take that into account when eating carbs. Learn about which foods contain carbohydrates, how to estimate carbohydrate portions and how to monitor their effect on blood glucose levels.
There are special courses available, such as the DAFNE course for people with Type 1 diabetes, which your diabetes healthcare team can tell you about.
Our downloadable PDF e-book, Carbs Count, provides an introduction to carbohydrate counting and insulin dose adjustment. It takes you through the essential information, with practical examples and exercises. You can .
Also Check: Is Simvastatin Used For Diabetes
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
Why Does Having Diabetes Cause Fatigue
Having diabetes changes your blood. Imagine someone without diabetes having blood that flows like water. Now imagine someone with diabetes having blood that flows like maple syrup. When the blood flows much thicker and slower, like syrup, it is harder for cells to flow through the bloodstream to provide energy and oxygen to parts of the body, including the brain.
Diabetes also causes inflammation, which sends messages to the brain that the body needs to take a rest in order to heal. When this happens, fatigue is going to be a problem.
One of the biggest reasons that diabetes causes fatigue is because of its complications. Organs such as the kidneys, eyes, heart, and the nerves can all be damaged because of diabetes. End stage renal disease, which is when the kidneys fail, can lead to low red blood cells. Low red blood cells, which is also known as anemia, can lead to fatigue. Studies have shown that people with diabetic complications such as nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney problems have increased levels of fatigue. The next section of this article discussed more things that can cause fatigue.
Read Also: What Is The Correct Reading For Diabetes
How Can I Beat/reduce Fatigue With Diabetes And Regain My Energy
There are many ways to reduce fatigue with diabetes and regain energy. The most important thing that you can do is to control your blood sugar. This limits complications and also provides your body with the fuel that it needs to operate. You can also eat smart and exercise. Exercise actually decreases fatigue up to 65%. By taking care of yourself, you can decrease fatigue and increase quality of life.
You shouldnt make any changes to your diet, insulin, or exercise regimen without talking to your doctor. First off, your doctor needs to be consulted and you need to talk with him about the following things:
- Can my fatigue be caused by another disease? This rules out all other reasons for your fatigue so you can focus on the main cause.
- Are any of the side effects from my medications causing the fatigue?
- Is it a good idea for me to start taking supplements such as Vitamin D, Vitamin B, Calcium, Chromium, Ginseng, Coenzymes, or Magnesium?
- Is my thyroid okay?
- What kind of exercises would be best for me?
- How can I better control my blood sugar to decrease fatigue?
- What is a healthy weight for me to be?
Eating too many carbohydrates can cause you to feel drowsy. You should also schedule an appointment to talk with your dietitian or nutritionist to discuss the following things:
- Would juicing be okay for me?
- Am I eating too many carbs?
- How can I improve my diet to decrease my fatigue?
Other things that you can do to decrease fatigue include:
What Does It Mean If Test Results Show I Have Protein In My Urine
This means your kidneys are allowing protein to be filtered through and now appear in your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The continued presence of protein in your urine is a sign of kidney damage.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Theres much you can do to prevent the development of diabetes . However, if you or your child or adolescent develop symptoms of diabetes, see your healthcare provider. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner steps can be taken to treat and control it. The better you are able to control your blood sugar level, the more likely you are to live a long, healthy life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/28/2021.
References
Read Also: Diet Plan For Diabetes Cancer Patient
How Your Body Makes Glucose
It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit. As you eat, food travels down your esophagus to your stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released.
It goes into your intestines where it’s absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to your cells.
Can Diabetes Cause Hair Loss
Yes, its possible for diabetes to cause hair loss. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to persistently high blood glucose levels. This, in turn, leads to blood vessel damage and restricted flow, and oxygen and nutrients cant get to the cells that need it including hair follicles. Stress can cause hormone level changes that affect hair growth. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your immune system attacks itself and can also cause a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
Read Also: Mens Diabetic Slip On Shoes
When To See A Doctor
Visit your GP as soon as possible if you experience the main symptoms of diabetes, which include:
- weight loss and loss of muscle bulk
- itching around the penis or vagina, or frequent episodes of thrush
- cuts or wounds that heal slowly
- blurred vision
Type 1 diabetes can develop quickly over weeks or even days.
Many people have type 2 diabetes for years without realising because the early symptoms tend to be general.
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
Recommended Reading: Is Coffee Healthy For Diabetics
Diabetes And Fatigue: Everything You Need To Know
Modified: Jun 4, 2020 by Nicole Justus, RN, BSN · This post may contain affiliate links ·
What exactly is fatigue? Is it just being tired after working a long week or not getting enough sleep?
The answer is no.
Fatigue is excessive tiredness that makes carrying out simple tasks difficult and interferes with one or more life functions. Sounds terrible, doesnt it? Well imagine having a chronic illness along with the fatigue. Diabetes and fatigue have a strong relationship, and it can make a persons life very difficult. The following article will discuss the relationship, along with ways to beat and reduce the risk of living with diabetes and fatigue.
What Diabetes Does To Your Body
Diabetes wreaks havoc on the way your blood glucose, or blood sugar affects your body. Blood glucose is your bodys source of energy for the cells in your muscles and tissues, but it only needs a certain amount.
How much you have is controlled by your bodys insulin, a hormone generated by your pancreas designed to regulate blood glucose levels. Diabetes lowers or eliminates the insulin in your body, causing a spike in blood glucose in your body and leading to a lot of complications.
Read Also: What Can Type 2 Diabetes Do To Your Body
Liver Energy Sensing: Ampk Reduces Liver Lipid Synthesis And Insulin Resistance
In summary, these data indicate that liver energy-sensing mechanisms involving the AMPK-ACC signaling axis and subsequent reductions in lipogenesis are important for mediating the chronic insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin and that these effects can be enhanced when used in combination with salicylate-based therapeutics such as salsalate. Further support for the importance of the liver AMPK-ACC signaling pathway in reducing lipogenesis and insulin resistance has also been established using small molecules that 1) directly activate AMPK 1 subunit containing heterotrimers and increase ACC phosphorylation , 2) mimic the effects of AMPK to inhibit ACC activity , or 3) starve ACC of substrate by blocking the production of acetyl-CoA through inhibition of ATP-citrate lyase . Whether these treatments are also effective for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and improving liver insulin sensitivity in humans remains to be established. Liver energy-sensing mechanisms may also be important for regulating the production of metformin-derived cytokines , such as GDF15, which suppresses appetite, thereby protecting the liver from nutrient excess in the face of metformin-induced reductions in mitochondrial function and thus linking energy demand with intake. Identification and characterization of other novel metokines may lead to new therapies for a multitude of disease ailments in which metformin has been shown to exert favorable effects.
What About The Quality Of Carbs
Evidence shows that the quality of the carbohydrates is more important to general health than the amount we eat. Quality of carbs has been assessed using glycaemic index , glycaemic load, fibre content and wholegrain among others. Generally, lower GI foods can be useful for managing blood glucose levels. More importantly for overall health, choosing foods that are high in fibre and wholegrains instead of refined carbs, such as white bread, is better for our heart health and reducing our risk of certain types of cancers. We also know that some specific carb-containing foods, such as fruits and vegetables, are associated with good health.
You May Like: When Do You Check Your Blood Sugar
Changes In Blood Sugar Levels
Diabetes affects the way the body regulates and uses blood sugar.
When a person eats, the body breaks down food into simple sugars, or glucose. Cells use insulin to absorb glucose from the blood and can then use this for energy.
In people with diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or the body does not use insulin effectively. This causes excess glucose in the blood.
Fatigue and weakness may result when the cells do not get enough glucose. Diabetes medications, such as insulin or metformin, help more of this sugar to move into the cells and prevent it from building to harmful levels in the blood.
A potential side effect of diabetes medications is low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia.
Low blood sugar can also cause fatigue, especially in people who have frequent episodes and do not get enough warning that their blood sugar levels are dropping. A person can still feel fatigued even after treatment for low blood sugar.
While not all of those symptoms account for feelings of fatigue directly, many of them may contribute to an overall feeling of being unwell. These persistent and uncomfortable sensations can have severe mental and physical effects that may lead to the development of fatigue.
Some of the symptoms of diabetes may also disrupt a persons sleep pattern. For example, a person with the condition can wake up several times every night to use the bathroom or get a drink. People with type 2 diabetes have a of developing a sleep disorder.