Whats Considered A Normal Glucose Level
Your doctor will likely test your blood glucose levels as a screening test for diabetes during a standard yearly check-up. Additionally, many people track their glucose at home with an over-the-counter finger-prick test. When you check blood glucose , either at a doctors office or with a home finger stick glucose monitor, the results are in milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood.
One of the most common glucose measurements is fasting plasma glucose or fasting blood glucose , and its found by checking blood glucose levels after not having any calories at least eight hours before the test. According to the American Diabetes Association , people can be classified into three categories depending on their fasting plasma glucose levels: normal, prediabetes, and diabetes. To be considered normal, fasting glucose must be under 100 mg/dl.
Of note, CGM devices measure interstitial glucose levels compared to blood/plasma glucose levels measured in the FPG tests. While interstitial glucose and blood/plasma glucose levels correlate highly, they are not precisely the same, and diagnoses are not made from interstitial measurements.
Below is a summary overview of data about 24-hour glucose trends in nondiabetic individuals wearing CGM to gain a better understanding of whats normal.
How To Use A Glucose Meter
Glucometers are easy to use. Take the following steps to successfully test blood glucose:
People with type 2 diabetes normally need to test blood sugar concentrations at least once each day.
Those who need to take insulin, which includes all people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2, have to test their blood several times a day.
An accurate reading of the blood glucose level can help achieve good diabetes control.
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue, and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis . Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
Don’t Miss: Insulin Pump And Glucose Monitor In One
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a measurement that show how much glucose you have in your blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from food and drink. Your blood sugar levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who don’t have diabetes.
How Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring Help You Maintain Optimal Glucose Levels
It is not uncommon for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. We know that we want to prevent excessive spiking of glucose levels because studies show that high post-meal glucose spikes over 160 mg/dl are associated with higher cancer rates. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals.
Keeping your glucose levels constant is more complicated than just following a list of eat this, avoid that foods. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be quite dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food.
You May Like: Fruits For Type 1 Diabetes
What Do The Test Results Mean
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 3.6mmol/l and 6mmol/l, this means that your blood glucose level is normal.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is 7mmol/l or higher, this is likely to mean that you have diabetes. Diabetes is a long-term condition where the body is not able to control the amount of glucose in the blood.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 6.1mmol/l and 6.9mmols/l, you may have IFG.
What Should I Aim For
Effective management of diabetes is all about aiming for a careful balance between the foods you eat, how active you are and the medication you take for your diabetes. Because this is a delicate balance, it can be quite difficult to achieve the best possible blood glucose management all the time.
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individuals circumstances. While it is important to keep your blood glucose levels as close to the target range of target range between 4 to 6 mmol/L as possible to prevent complications, it is equally important to check with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator for the range of blood glucose levels that are right and safe for you. Therefore the following information should be treated only as a general guide.
Also Check: Is There A Genetic Test For Diabetes
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range.
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people.
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
Normal Sugar Level In Healthy Individuals
Blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels, can be normal, high, or low. The sugar levels are generally measured after 8 hours of eating.
A normal blood sugar range for a healthy adult after 8 hours of fasting is > 70 mg/dL. and < 100 mg/dL.
While a normal sugar level in a healthy person after 2 hours of eating is between 90 to 100 mg/dL.
Blood glucose levels change throughout the day. Major factors affecting such change in the blood glucose levels are as follows:
Summary
Recommended Reading: Can Diabetics Drink Sugar Free Energy Drinks
What If The Range Of Your Fasting Blood Sugar Levels Go Up 100 Mg/dl Chart Explained
The chart below will help you get an idea on what goes on in case of changing of fasting blood sugar levels up 100mg/dl and down 70 mg/dl.
When your fasting blood sugar level readings are between 100 and 125 mg/dl, then most probably you may have pre-diabetes.
That is a condition in which your body insulin function is impaired. You may know it also as impaired fasting blood glucose condition.
In case your fasting blood sugar levels figures are higher than 125 mg/dl, than most probably you may have diabetes. Further diagnostic exams will determine what type of diabetes you may have.
Remember: always will be a double check to fully determine if you have diabetes or not.
This means that youve to monitor your fasting blood sugar levels for one week, record the results for reference when consulting your doctor. Then, and only then you will know if you are diabetic or not.
Postprandial Or Reactive Hyperglycemia
This type of hyperglycemia occurs after eating .
During this type of hyperglycemia, your liver doesn’t stop sugar production, as it normally would directly after a meal, and stores glucose as glycogen.
If your blood glucose level 1-2 hours after eating is above 180mg/dL, that signals postprandial or reactive hyperglycemia.
However, it’s not just people with diabetes who can develop hyperglycemia. Certain medications and illnesses can cause it, including beta blockers, steroids, and bulimia. This article will focus on hyperglycemia caused by diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Bydureon For Weight Loss In Non Diabetics
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
What Can You Do To Maintain Your Blood Glucose Levels
A good start in how to keep normal blood sugar is How can you decrease your blood sugar levels in this short article. Dont consume foods large in carbs and sugar such as buttered potatoes, fatty foods, sweet, and sweet desserts like cake with icing. Diet plan adjustment is a major step in your management of diabetes. Use a blood glucose log book with the date, time, and values of your or you and your medical professional to help you manage your type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes, and use a blood sugar home test set to get glucose test outcomes. In addition, log any modification in signs in time. The log book will equip you and your doctor to change treatments and actions to acquire the very best management of your diabetes.
Dont Miss: Intermittent Fasting And Alcohol
Also Check: Can Keto Diet Cause Diabetes
Alarming Facts About Diabetes
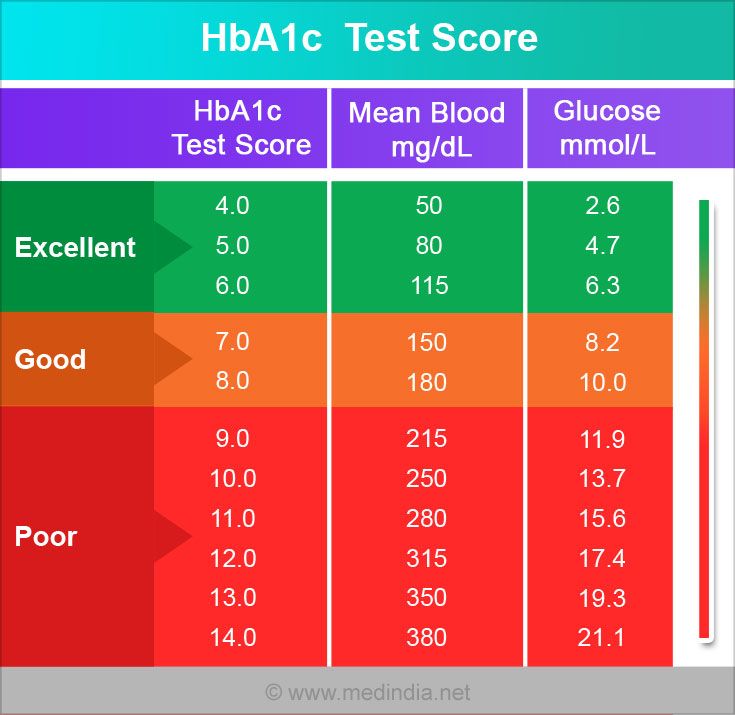
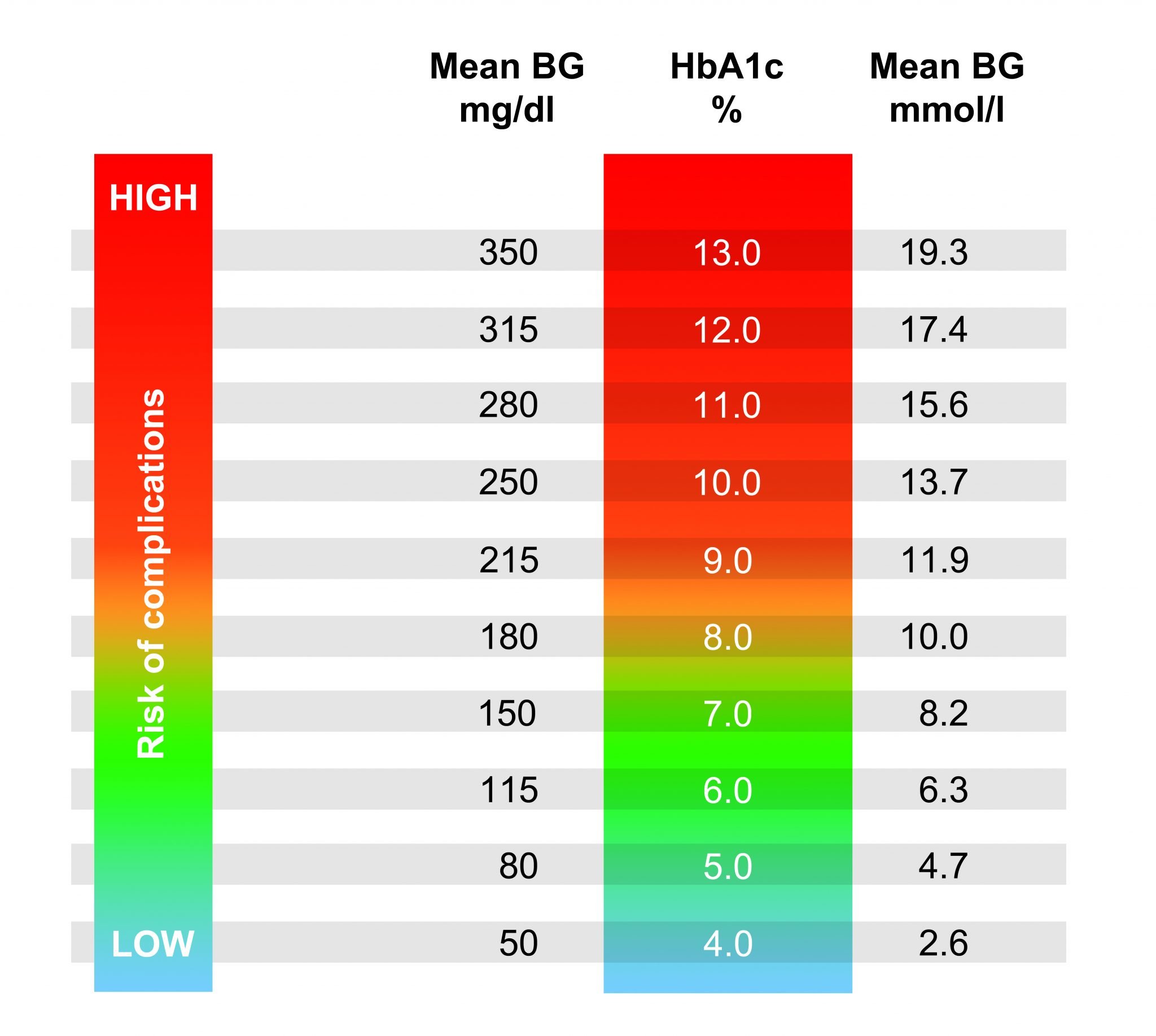
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1C is a lab test. It indicates an average blood glucose reading for the last 90 days. It is done when you find out you have diabetes, and every 3 months after that at clinic visits. A person without diabetes has a Hemoglobin A1C of less than 5.6%.
|
Target Hgb A1C is 7.5% for all children and adults with diabetes. |
The chart below shows the Hemoglobin A1C result compared with the blood glucose number.
Recommended Reading: What Gauge Are Insulin Needles
What Is A Fasting Blood Sugar Or Fasting Glucose Level
A fasting blood sugar level is the result of a blood sample taken after a patient fasts for at least eight hours. A normal fasting blood sugar level for someone without diabetes is less than 100 mg/dL, or HbA1C below 5.7%. Prediabetes is a fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL, or HbA1C of 5.7%-6.4%. Diabetes is a fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL and above, or HbA1C of 6.5% or higher. Source:Continue reading > >
Why The Test Is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs of diabetes . More than likely, the doctor will order a fasting blood sugar test.
The blood glucose test is also used to monitor people who already have diabetes.
The test may also be done if you have:
- An increase in how often you need to urinate
- Recently gained a lot of weight
SCREENING FOR DIABETES
This test may also be used to screen a person for diabetes.
High blood sugar and diabetes may not cause symptoms in the early stages. A fasting blood sugar test is almost always done to screen for diabetes.
If you are over age 45, you should be tested every 3 years.
If you’re overweight and have any of the risk factors below, ask your health care provider about getting tested at an earlier age and more often:
- High blood sugar level on a previous test
- Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher, or unhealthy cholesterol levels
- History of heart disease
- Member of a high-risk ethnic group
- Woman who has been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary disease
- Close relative with diabetes
- Not physically active
Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Aflac Pay For Diabetes
If You Have An Acute Illness
Acute illnesses such as infections can affect your ability to control diabetes and can lead to serious diabetic complications, such as ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma and severe dehydration. Your health care provider will give you instructions about how to care for diabetes during acute illnesses, and you can learn to avoid acute complications through patient education.
Who Is Most At Risk For Developing Diabetes
The following categories of people are considered high-risk candidates for developing diabetes:
- Individuals who are overweight or obese
- Individuals who are 45 years of age or older
- Individuals with first-degree relatives with diabetes
- Individuals who are African-American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asia American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islanders,
- Women who developed diabetes while they were pregnant or gave birth to large babies
- Individuals with high blood pressure
- Individuals with high-density lipoprotein below 25 mg/dl or triglyceride levels at or above 250 mg/dl
- Individuals who have impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
- Individuals who are physically inactive engaging in exercise less than three times a week
- Individuals who have polycystic ovary syndrome, also called PCOS
- Individuals who have acanthosis nigricans dark, thick and velvety skin around your neck or armpits
In addition to testing the above individuals at high risk, the American Diabetes Association also recommends screening all individuals age 45 and older.
Dont Miss: Drinking Alcohol While Intermittent Fasting
Don’t Miss: Are Brussel Sprouts Good For Diabetics
Why Test Blood Sugar Levels
If you take certain medication, like insulin or sulphonylureas, checking your blood sugars is a vital part of living with diabetes. It can help you work out when you need to take more medication, when you need to eat something or for when you want to get up and move around more.
Routine checks can help you know when you might be starting to go too low or too high . Its a way of getting to know your body and how it works. It can help you and your healthcare team spot patterns too. Do you write your results down? You might find that helpful.
But importantly, it will help you stay healthy and prevent serious diabetes complications now and in the future. By complications, we mean serious problems in places like your feet and your eyes. This happens because too much sugar in the blood damages your blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow around your body. This can lead to very serious problems like sight loss and needing an amputation.
The higher your blood sugar levels are and the longer theyre high for, the more at risk you are.