Setting Goals For A1c Levels
The target A1c level for people with diabetes is usually less than 7%. The higher the hemoglobin A1c, the higher your risk of having complications related to diabetes. Someone who has had untreated diabetes for a long time might have a level above 8%.
If you have diabetes and your level is above your target, your doctor may change your treatment plan to get your level down.
A combination of diet, exercise, and medication can bring your levels down.
People with diabetes should have an A1c test every 3 months to make sure their blood sugar is in their target range. If your diabetes is under good control, you may be able to wait longer between the blood tests. But experts recommend checking at least two times a year.
People with diseases affecting hemoglobin, such as anemia, may get misleading results with this test. Other things that can affect the results of the hemoglobin A1c include supplements such as vitamins C and E and high cholesterol levels. Kidney disease and liver disease may also affect the test.
Postprandial Glucose Levels May Be High Despite Normal Hba1c Levels
Abstract & Commentary
Synopsis: Postmeal glucose levels may be seriously elevated despite a normal fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c levels of less than 7%.
Bonora E, et al. Diabetes Care. 2001 24:2023-2029.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the plasma glucose excursions with meals, the relations between levels at different times of the day, and these findings with their relationship to the level of the HbA1c in noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetics.
The UK Prospective Diabetes study made their therapeutic decisions based on the fasting glucose levels possibly assuming that good control in the fasting state would be associated with good control throughout the day. Bonora and colleagues wanted to know how frequently diabetic patients experience broad glucose excursions with meals. How much does fasting plasma glucose influence subsequent glucose levels during the day? How strongly are plasma glucose levels during the day interrelated? And, finally, is the HbA1c influenced more strongly by the fasting or nonfasting glucose?
They assessed 3 groups of patients: 1) outpatients at their clinic 2) patients at home as well as 3) inpatients were examined. Subjects had plasma/blood glucose assessment before and 2-3 hours after breakfast, lunch, and dinner. HbA1c was measured in all the patients.
We do have the tools to control both the fasting and postprandial plasma/blood glucose levels and the current evidence favors our attempting to do so!
Normal Hemoglobin Hgb A1c And High Blood Sugar Means One Or All Of These:
Read Also: Symptoms Of Blood Sugar Spikes
What Is A Good A1c Level
Levels between 5.7 and 6.4 are considered prediabetes. For most people with diabetes, the general A1C goal is to have a level between 6.0 and 6.9. While it might sound like the ideal A1C target is under 6.0, for those with diabetes, this level can indicate low blood sugar levels, which can be just as dangerous as high blood sugar levels. If A1C results fall between 7.0 and 8.9, a doctor might suggest lifestyle changes or medications to help lower the levels to what is considered controlled. However, for some people, these levels might be appropriate, such as:
- Those with a limited life expectancy
- People with long-standing diabetes who have trouble reaching a lower goal
- Those with severe hypoglycemia or the inability to sense hypoglycemia
What Is A1c And A1c Test
A1C or hemoglobin A1C Is a protein that resides in red blood cells and carries oxygen to the rest of your body. Moreover, since glucose is in your blood, these hemoglobins affix themselves to the glucose and become Haemoglobin AIC or HbA1C. When your sugar level surges, it means you have higher levels of hemoglobin AIC in your blood.
So, what do the doctors do in this regard? Well, most of the GPs recommend such patients to take the A1C test. An A1C test is a sugar level test that, over the last 3 months, measures the level of blood sugar levels in your blood. If the AIC test comes higher, it means you have a higher level of glucose or sugar in your blood. Typically, the sugar level should be less than 5.7%.
Read Also: What Is The Least Expensive Long Acting Insulin
What Is A Hba1c Test
The hemoglobin A1c test measures the amount of blood sugar attached to your hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the part of your red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. It is an important blood test that gives a good indication of how well your diabetes is being controlled.
You can check these average blood sugar levels yourself, but youll have to buy a kit, whereas your healthcare professional will do it for free. Its different from a finger-prick test, which is a snapshot of your blood sugar levels at a particular time, on a particular day.
You find out your HbA1c level by getting a blood test by a doctor or nurse. Your healthcare team will arrange this for you, but chase it up with your GP if you havent had one for a few months.
Most people will have the test every three to six months. But you may need it more often if youre planning for a baby, your treatment has recently changed, or youre having problems managing your blood sugar levels.
And some people will need the test less often, usually later on during pregnancy. Or need a different test altogether, like with some types of anaemia. A fructosamine test can be used instead, but its very rare.
An HbA1c test is also used to diagnose diabetes, and to keep an eye on your levels if youre at risk of developing diabetes .
The test is sometimes called haemoglobin A1c or just A1c.
High Random Blood Glucose And Low Hba1c Can Be Caused By Many Reasons
If your Random blood glucose is in between 70 mg/dl and 140 mg/dl and your HbA1c is in between 4 % and 5.7 % then you need not worry as these are the normal ranges for Random blood glucose and HbA1c respectively. But if your levels are lesser or greater than the above values, then there may be some problem in your body.
Read Also: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
You Have High Triglyceride Levels
Your triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood, serving as an energy source for your body. Your body can convert energy it doesnât need to burn right away into triglycerides. It then uses them as an energy source between meals.
The NIH has found that A1C levels can be an indicator of your triglyceride count. If one is high, the other most likely is as well. This is especially true if your diet is high in added sugars.
What To Do About A High A1c
After a high hemoglobin A1C, you and your doctor can work together to lower your numbers and reduce your risks. Your doctor may recommend a three-pronged approach combining education, diet, and exercise. Also, you may need to lose weight if you are overweight.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you will need treatment with drugs. Many of those with type 2 diabetes will require drug therapy as well.
Also Check: What Number Is Too High For Diabetes
Low Hba1c May Also Increase Mortality
Increased mortality was also reported for HbA1c levels below the optimal range in diabetics. Some reported an increased risk for heart disease or death among nondiabetic subjects with HbA1c levels below 4.0% , 4.8% , 4.9% or 5.0% .
Some explanations for the low HbA1c and mortality relationship, include: being underweight or malnourished, inflammation, anemia, high alcohol consumption, liver disease and chronic kidney failure .
It appears that malnutrition, inflammation, and functional decline are characteristics shared by the populations that showed increased mortality and low HbA1c. Thus, frailty or decline may be the main confounding factor explaining the relationship between increased mortality risk and low HbA1c .
In one study, where HbA1c < 5% was associated with adverse outcomes in nondiabetic people, a link to inflammation and autoimmunity was suggested .
When Should Hba1c Levels Be Tested
Everyone with diabetes mellitus in the UK should be offered an HbA1c test at least once a year.
Some people may have an HbA1c test more often. This may be more likely if you have recently had your medication changed or your health team are otherwise wishing to monitor your diabetes control more than once a year.
| HbA1c |
|---|
Although HbA1c level alone does not predict diabetes complications, good control is known to lower the risk of complications
Also Check: Eating Too Much Sugar Diabetes
Is An Hba1c Test Suitable For Everyone
An HbA1c test wont tell you how high your blood sugar is. It also doesnt capture the hourly and daily changes in your blood sugar levels. But it can tell you if your blood sugar has been high for prolonged periods over the last 3 months. Some conditions can cause fluctuations in your HbA1c levels.
A doctor won’t use a single HbA1c result to diagnose diabetes. And there are situations where HbA1c shouldnt be used to diagnose diabetes. This includes if you:
- are pregnant or gave birth in the last 2 months
- have only been experiencing diabetes symptoms for 2 months like frequent urination or excessive thirst
- take medication that can affect your blood sugar levels like long-term steroid treatment and some antibiotics
- are currently acutely ill
- have pancreatic problems
- have end-stage kidney disease
- are HIV positive
If you have one of these conditions, it’s better to speak with your GP, who’ll most likely organise an oral glucose tolerance test instead. This test checks your glucose levels after you’ve fasted for 8 hours and then after you’ve had a sugary drink this shows how well your body handles glucose.
Some health conditions can make it more difficult to interpret your HbA1c results for example, if you’ve had a recent blood transfusion.
What Is The A1c Test Measuring

There can be several reasons for a spike in blood sugar levels, and itâs a good idea to know whatâs causing yours. But first, itâs essential to understand what A1C is and what the A1C test measures.
Any sugar that enters your bloodstream attaches itself to your hemoglobin on your red blood cells. The A1C test measures the amount of glucose âstuckâ to the hemoglobin, which provides a good proxy of how much average blood glucose was in your bloodstream over a two to three-month period.
A simple way to remember how to read the results is: the higher the percentage, the higher the risk of diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, under 5.7% is a regular A1C reading. A reading between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered a pre-diabetic range, while values above 6.4% indicate diabetes.
Before you start overanalyzing your results, remember that there are variables at play. For example, the U.S. National Library of Medicine found that adults without a history of diabetes often have A1C levels at 6% or greater. This means not every higher test result is cause for concern. Still, itâs worth checking with a doctor if you see consistently high values. High A1C levels lead to impaired fasting glucose, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Also Check: Contour Next One Blood Glucose Meter
What Is A1c And Why Is It Used
A1c estimates a persons average blood sugar levels over a 2 to 3-month span. It is the best measure we have of how well blood glucose is controlled and an indicator of diabetes management.
Though A1c doesnt provide day-to-day information, keeping A1c low has been proven to lower the risk of microvascular complications like kidney disease , vision loss , and nerve damage . The relationship between A1c and macrovascular complications like heart disease is harder to show in clinical trials, but having high blood sugar is a major risk factor for heart disease.
A1c is usually measured in a lab with routine blood work, or with a countertop machine in a doctors office using a fingerstick.
A1c measures the quantity of glycated hemoglobin, which refers to sugar attached to a red blood cell protein called hemoglobin. The number is reported as a percentage of the total hemoglobin in the blood. If a person consistently has higher blood glucose levels over time, A1c levels go up because more red blood cells are coated with sugar. The test is representative of a 2 to 3-month average because once a red blood cell becomes coated with sugar, the link is irreversible. It is only when the red blood cell is “recycled” that the sugar coating disappears.
What Tools Are Available If An A1c Test Is Not Accurate Or Sufficient
Besides A1c tests, the most common measures of blood sugar are the oral glucose tolerance test , CGM, and self-monitored blood glucose tests.
The OGTT is a diagnostic tool diabetes and prediabetes, assessing a persons response to consuming a fixed amount of sugar. After taking the sugar drink, blood sugar levels are measured two hours later. Below 140 mg/dl is considered normal, between 140 mg/dl and 200 mg/dl points to prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance, and above 200 mg/dl indicates diabetes. It is not useful for tracking diabetes management.
For those with established diabetes, CGM has the advantage of monitoring blood sugar levels consistently throughout the day , providing more detailed insight into time spent in-range, low blood sugars, and high blood sugars. Examples of CGM include:
-
Senseonics implantable Eversense CGM
If CGM is not available, taking frequent fingersticks with a blood glucose meter when waking up, before and after meals, and before bed can also indicate when blood sugar levels are going low, high, and staying in range.
Also Check: How Much Insulin In A Pen
Normal Fasting Glucose With High Hba1c
Jonathan’s fasting glucose: 85 mg/dl Jonathan’s high HbA1c reflects blood glucose fluctuations over the preceding 60-90 days and can be used to calculate an estimated average glucose with the following equation: Jonathan’s HbA1c therefore equates to an eAG of 145.59 mg/dl–yet his fasting glucose value is 85 mg/dl. This is a common situation: Normal fasting glucose, high HbA1c. It comes from high postprandial glucose values, high values after meals. It suggests that, despite having normal glucose while fasting, Jonathan experiences high postprandial glucose values after many or most of his meals. After a breakfast of oatmeal, for instance, he likely has a blood glucose of 150 mg/dl or greater. After breakfast cereal, blood glucose likely exceeds 180 mg/dl. With two slices of whole wheat bread, glucose likewise likely runs 150-180 mg/dl. The best measure of all is a postprandial glucose one hour after the completion of a meal, a measure you can easily obtain yourself with a home glucose meter. Second best: fasting glucose with HbA1c. Gain control over this phenomenon and you 1) reduce fasting blood sugar, 2) reduce expression of small LDL particles, and 3) lose weight.Continue reading > >
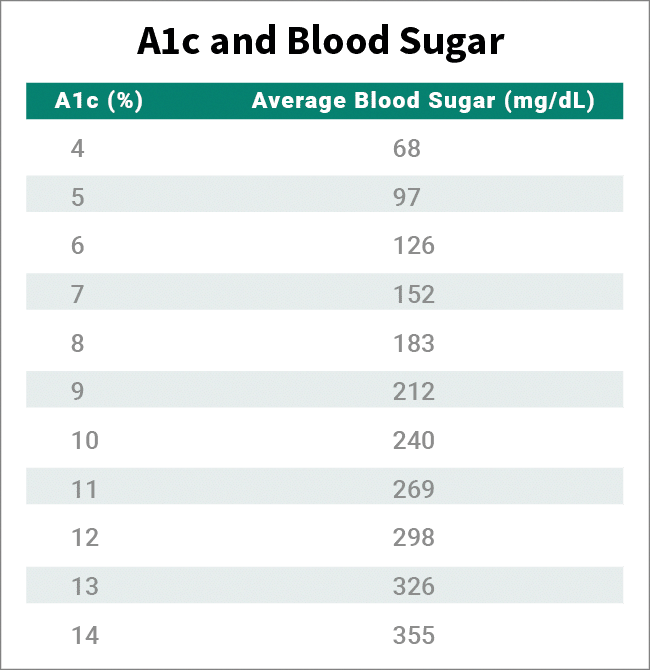
How Do Blood Glucose Levels Compare With Hba1c Readings
The table on the right shows how average blood sugar levels in mmol/L would be translated into HbA1c readings , and vice versa.
It is important to note that because blood glucose levels fluctuate constantly, literally on a minute by minute basis, regular blood glucose testing is required to understand how your levels are changing through the day and learning how different meals affect your glucose levels.
Read Also: What Happens When You Take Insulin
What Is It Used For
An A1C test may be used to screen for or diagnose:
- Type 2 diabetes. With type 2 diabetes your blood glucose gets too high because your body doesn’t make enough insulin to move blood sugar from your bloodstream into your cells, or because your cells stop responding to insulin.
- Prediabetes. Prediabetes means that your blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to diagnosed as diabetes. Lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating and exercise, may help delay or prevent prediabetes from becoming type 2 diabetes.
If you have diabetes or prediabetes, an A1C test can help monitor your condition and check how well you’ve been able to control your blood sugar levels.
What Is A High A1c
A1C results show the percent of glucose and hemoglobin bound together in your bloodstream. For example, a 5% A1C indicates five out of every 100 hemoglobins are glycated. The higher your A1C, the greater the risk of developing complications.
The A1C ranges for normal, prediabetes, and diabetes are:
- Normal: Less than 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Talk to your healthcare provider if your A1C is in the prediabetic range. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. A diet change, increased activity, and moderate weight loss can help improve blood sugar control to prevent diabetes.
Also Check: Fresh Figs And Diabetes 2