Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes
Whether you had diabetes before you got pregnant or you developed diabetes during your pregnancy, you’ll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Tight control will help you avoid complications and long-term health problems for both you and your baby. You’re eating differently because your body needs more energy to help your baby grow and be healthy. And your changing hormones affect how your body makes and uses insulin. In the later parts of your pregnancy, you may become more insulin resistant, so blood sugar builds up to higher levels. How often should you check your blood sugar? Pre-existing diabetes: Before and after meals and before bedtime If you are pregnant and have type 1 diabetes, your doctor might sometimes ask you to check your blood sugar in the middle of the night, around 3 a.m. You should check your fasting urine ketones every day, too. For every type of diabetes, if you’re pregant you need to see your doctor at least once a month, perhaps as often as once a week.Continue reading > >
When Do You Have The Glucose Tests During Your Pregnancy
The glucose challenge test is usually performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy in women who are determined by their healthcare providers to be at low risk of gestational diabetes.If your healthcare provider has determined that you are at high risk of developing gestational diabetes, the provider may order the glucose challenge test for you earlier than the aforementioned range.If the result of the glucose challenge test comes back indicating a high level of glucose, your provider may order another testâcalled a glucose tolerance testâto more accurately diagnose your chance of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy.If the result of an early glucose challenge test comes back indicating a normal level of glucose in your blood, your provider may order an additional glucose challenge test between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Treated
If youre diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your treatment plan will depend on your blood sugar levels throughout the day.
In most cases, your doctor will advise you to test your blood sugar before and after meals, and manage your condition by eating a nutrient-rich diet and exercising regularly.
In some cases, they may also add insulin injections if needed. If your doctor encourages you to monitor your blood sugar levels, they may supply you with a special glucose-monitoring device.
They may also prescribe insulin injections for you until you give birth. Ask your doctor about properly timing your insulin injections in relation to your meals and exercise to avoid low blood sugar.
Your doctor can also tell you what to do if your blood sugar levels fall too low or are consistently higher than they should be.
A balanced diet is key to properly managing gestational diabetes. In particular, people with gestational diabetes should pay special attention to their carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake.
Eating regularly as often as every 2 hours can also help you manage your blood sugar levels.
Also Check: What Diabetic Testing Supplies Are Covered By Medicare
How Do I Prepare For My 1 Hour Glucose Test
You shouldnt make any drastic changes to prepare for the 1 hour glucose test.
In fact, its best that you follow your normal diet because its important to get an accurate representation of how your body handles sugar on a day to day basis.
Otherwise, try and get a good nights sleep the week before the test.
Sleep deprivation can increase cortisol levels, which can also affect your blood sugar levels.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
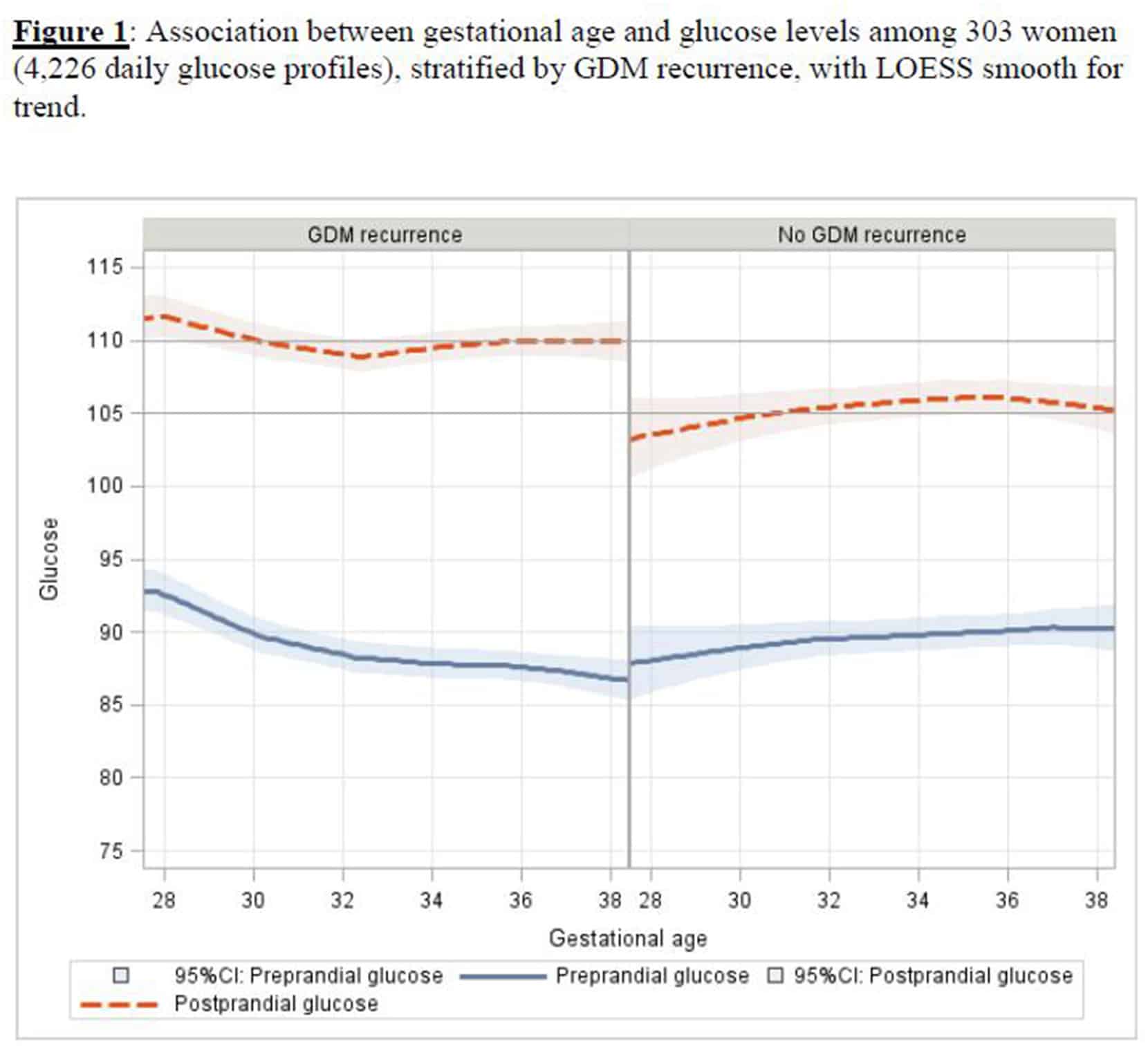
The American Diabetes Association encourages doctors to routinely screen pregnant women for signs of gestational diabetes. If you have no known history of diabetes and normal blood sugar levels at the beginning of your pregnancy, your doctor will likely screen you for gestational diabetes when youre 24 to 28 weeks pregnant.
Read Also: Can High Cholesterol Lead To Diabetes
Influence Of Lower Cutoff Values For 100
Department of Gynecology, Obstetrics and Mastology, Botucatu Medical School, So Paulo State University, So Paulo, Brazil. To evaluate data from patients with normal oral glucose tolerance test results and a normal or impaired glycemic profile to determine whether lower cutoff values for the OGTT and GP could identify pregnant women at risk for excessive fetal growth. We classified 701 pregnant women with positive screening for gestational diabetes mellitus into 2 categories normal 100-g OGTT and normal GP and normal 100-g OGTT and impaired GP-to evaluate the influence of lower cutoff points in a 100-g OGTT and GP for identification of pregnant women at excessive fetal growth risk. The OGTT is considered impaired if 2 or more values are above the normal range, and the GP is impaired if the fasting glucose level or at least 1 postprandial glucose value is above the normal range. To establish the criteria for the OGTT , we considered the mean , mean plus 1 SD , and mean plus 2 SD and for the GP, we considered the mean and mean plus 1 SD . Subsequently, the women were reclassified according to the new cutoff points for both tests . Consideration of values, in isolation or combination, yielded 6 new diagnostic criteria. Excessive fetal growth was the response variable for analysis of the new cutoff points. Odds ratios and their respective cContinue reading > >
Also Check: Does Insurance Cover Cgm For Type 2 Diabetes
A Rationale For Omitting Two
Get rights and content Objective: In making decisions regarding initiation of insulin therapy in gestational diabetes, most maternal-fetal obstetricians rely more on elevated fasting glucose values than on elevated 2-hour postprandial levels. We sought to determine whether the latter test is necessary. Study Design: From the patients with gestational diabetes mellitus managed over a 17-month period at Grady Memorial Hospital, we retrospectively analyzed data to determine whether normal fasting plasma glucose values predict elevated 2-hour postprandial values and whether the latter predict adverse outcome. Results: From 194 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus, 546 paired fasting and 2-hour postprandial glucose values were recorded. Fasting levels were normal in 467 in those, 2-hour levels were < 120 mg/dl in 83% and < 140 in fully 96%. In 131 women with all fasting plasma glucose values normal, the birth weights and the rates of cesarean delivery, shoulder dystocia, and macrosomia were similar, regardless of whether 2-hour postprandial glucose values were> 120. The actual cost of the 546 2-hour postprandial glucose tests was nearly $10,000. Conclusion: For metabolic surveillance in gestational diabetes mellitus, the 2-hour postprandial glucose test seems unnecessary, provided fasting plasma glucose values remain normal.Continue reading > >
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Diabetic Testing Supplies
How To Pass The 3 Hour Glucose Tolerance Test
Just like the 1 hour glucose test, there isnt any special way to ensure that you pass the 3 hour oral glucose tolerance test aka the ogtt.
Your best bet is to eat a well-balanced diet leading up to the test and minimize the consumption of simple carbs like cereal, white flour, juice, and soda.
Making these changes the night before or the week before is unlikely to make a big difference. You should make these changes months in advance.
Its also a good idea to try and maintain these habits postpartum as well. Unfortunately, 60% of women with gestational diabetes will develop Type 2 diabetes later in life.
What Is The Two
The two-hour glucose tolerance test is basically a shortened version of the three-hour tolerance test. If you get this test, you likely won’t do the screening test first, which is why the two-hour version is sometimes referred to as the “one-step” glucose tolerance test.
Overnight fast: Typically you’re instructed to eat a late meal the night before the test and then to eat or drink nothing after that, except for sips of water. The fasting period is usually 8 to 14 hours before the test, so you’ll want to schedule the test for first thing in the morning.
Here’s what to expect at the lab:
- First blood draw: When you arrive for the test, a blood sample is taken to measure your fasting blood glucose level.
- Sweet drink: Next, you’ll drink a very sweet drink, which usually contains 75 grams of glucose.
- Two more blood draws: Your blood will be drawn at one hour and two hours after the drink.
- Results: If any of your blood sugar readings are abnormal you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
This chart shows the levels that the American Diabetes Association considers abnormal at each interval of the two-hour glucose tolerance test :
| Interval | |
|---|---|
| 2 hours | 153 mg/dl or higher |
Also Check: Are Brussel Sprouts Good For Diabetics
How To Prepare 3 Hour Test
If your doctor would like to see additional testing, based on your results from the 1 hour test, you may be asked to have a 3 hour OGTT. It is important to follow all of the instructions very carefully, as it will affect the results of the test.
When you arrive at the office a sample or baseline glucose test will be run and used for comparing other glucose values. You will be asked to drink a sweet liquid containing a measured amount of glucose, it is best to drink it quickly. Then blood samples will be collected at timed intervals of 1,2, and 3 hours after you drink the glucose.
Here is the best method of preparation:
Glucose Screening Tests During Pregnancy
TWO-STEP TESTING During the first step, you will have a glucose screening test: You DO NOT need to prepare or change your diet in any way. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose. Your blood will be drawn 1 hour after you drink the glucose solution to check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose from the first step is too high, you will need to come back for a 3-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test: DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose, 100 grams . You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 3 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked. Allow at least 3 hours for this test. ONE-STEP TESTING You need to go to the lab one time for a 2-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test: DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose . You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 2 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked. Allow at least 2 hours for this test.Continue reading > >
Read Also: Should You Fast Before Glucose Test
Type 2 Diabetes Numbers Chart
Type 2 Diabetes diagnostic ranges. Fasting glucose More than 126 mg/dl or more than 7.0 mmol/l. 2 hours glucose level More than 200 mg/dl or more than 11.1 mmol/l . Blood Sugar Levels Chart. The above chart and the one below are exactly the same, in different formats. Category: Fasting value: Post prandial / aka post meal Minimum: Maximum: 2 hours after meal: Normal: 70.
What Are The Preparations Needed For Gtt
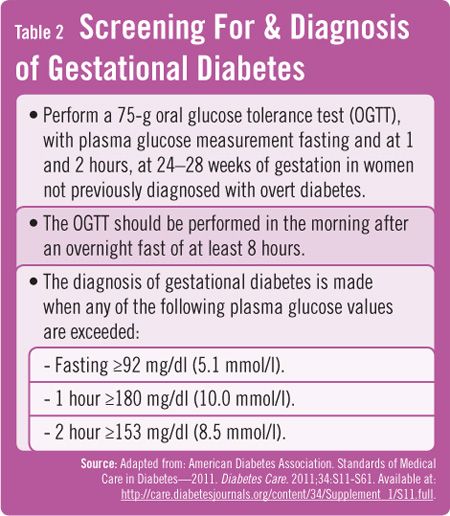
GTT is an elaborate blood test, that requires frequent testing and as the special requirements need for GTT are as follows
- Have a normal diet like any other day.
- Inform the doctor about the varied prescription drugs you are taking, as certain drugs like corticosteroids, diuretics and anti- depressants can cause false results.
- Fasting is required for 8 to 10 hours prior to the test and only water is allowed during this period.
- You might want to avoid using the washroom prior to testing as urine samples might be needed
- On the morning of the test do not smoke or have coffee or caffeine based product.
- The GTT is not to be done on a sick person
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Farxiga Lower Blood Sugar
How Effective Are Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
An OGTT can be used to effectively diagnose various types of diabetes, including prediabetes.
Its useful for confirming a diagnosis after an abnormal HbA1c test result. An A1C test is often part of routine blood tests, but its less sensitive than an OGTT. Because of this, an OGTT can help with making an official diagnosis.
This can alter the results, potentially leading to a misdiagnosis.
An OGTT is also time consuming. You may need to take off from work or school. Theres currently no alternative for the test, according to 2018 research.
An OGTT is considered to be a safe test.
Be sure to eat a meal the night before. This may help reduce discomfort caused by fasting.
For some people, drinking the concentrated glucose solution causes side effects such as:
Additional side effects, such as diarrhea and heart palpitations, are more likely to affect people whove had bariatric surgery.
Other OGTT risks are the same as getting your blood drawn for any reason:
- skin irritation from adhesive on a bandage
If you have any concerns, talk with a doctor before taking the test.
You May Like: Risk Factors Of Diabetes Mellitus
What Not To Eat The Night Before A Glucose Test
Here is a list of foods not to eat before your glucose test.
If your glucose challenge test is tomorrow, it is a good idea to avoid high glycemic foods for at least 8 hours before the glucose test.
These foods include
- Breakfast cereal
All of these will spike your glucose levels high.
Instead, go for whole grains that contain complex carbohydrates, such as steel-cut oats, brown rice, sweet potatoes, and leafy green vegetables.
Read Also: Ways To Reduce Type 2 Diabetes
What About Glucose Tolerance Testing During Pregnancy
As mentioned previously, the glucose tolerance test is used for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes . It may be used if there are equivocal fasting or random blood glucose results, or to screen for gestational diabetes in pregnant women between 24 to 28 weeks of gestation who are not known to have diabetes.
The test may also be used in the postpartum period to detect diabetes in women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Women who had gestational diabetes do not always develop diabetes later in life, but they should undergo diabetes screening at least every three years throughout their life.
Also Check: Diet For Diabetics With Heart Disease
Glucose Tolerance Test Results
Itâs worth knowing that approximately 66 percent of pregnant women who take the glucose tolerance test end up not being diagnosed with gestational diabetes. So, just because your provider has ordered a glucose tolerance test during your pregnancy doesnât automatically mean you have gestational diabetes.So, what do the results of the glucose tolerance test indicate? Four blood samples are drawn during a glucose tolerance test. If just one of the four results is higher than normal, your provider may recommend that you make subtle changes to your current pregnancy diet. The provider may have you take another glucose tolerance test after youâve made those changes to check if the results have improved.If more than one of the results is higher than normal, your provider may determine that you have gestational diabetes. The following figures indicate higher than normal blood sugar levels:
-
Fasting blood sample: Higher than 95 mg/dL
-
1-hour blood sample: Higher than 180 mg/dL
-
2-hour blood sample: Higher than 155 mg/dL
-
3-hour blood sample: Higher than 140 mg/dL .
If itâs determined that you have gestational diabetes, your healthcare provider can help guide you in making changes to help manage it. Eating a healthy diet, exercising during your pregnancy, and taking medication prescribed by your provider have been shown to help control blood sugar and to help keep you and your baby healthy.
You May Like: Tooth Removal For Diabetic Patient
What Happens If You Fail The 3 Hour Glucose Test
If you fail the 3-hour glucose test, you have impaired glucose tolerance and you will be diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
A failing score is considered when you have 2 or more values in these ranges:
- Fasting > 95mg/dL
- 2 Hour > 155 mg/dL
- 3 Hour > 140 mg/dL
This is a very serious condition that requires very close monitoring of your blood sugar levels every single day.
If you dont, you are putting your own life and your babys life at risk.
You will meet with a nutritionist to learn how to improve your diet, and you will have to check your finger stick blood glucose 4 times a day for the remainder of the pregnancy.