Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
If you have type 2 diabetes, your GP or diabetes care team will need to take a reading of your blood glucose level about every two to six months.
This will show how stable your glucose levels have been in the recent past and how well your treatment plan is working.
The HbA1c test is used to measure blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months.
HbA1c is a form of haemoglobin, the chemical that carries oxygen in red blood cells, which also has glucose attached to it.
A high HbA1c level means that your blood glucose level has been consistently high over recent weeks, and your diabetes treatment plan may need to be changed.
Your diabetes care team can help you set a target HbA1c level to aim for. This will usually be less than 53 mmol/mol or individualised as agreed with your diabetes team.
Read more about the HbA1c test
Your Sexual Function May Be Affected
Diabetes in both men and women can detract from intimacy. According to figures from Joslin Diabetes Center, more than 50 percent of men with type 2 diabetes experience erectile dysfunction about 30 percent of men whose diabetes is well controlled do. An erection requires good, healthy blood vessels, which get damaged in diabetes patients, says Dr. Cypess.
About 35 percent of women with diabetes may experience sexual dysfunction, including lack of desire, pain or discomfort, and inability to orgasm. High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels and nerves that make intercourse enjoyable, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
How To Prevent Complications Of Diabetes
Diabetes is unpredictable, but you can take steps to prevent complications. More than anything else, make sure your diabetes is well controlled. This includes taking diabetes medication as prescribed and never skipping a dose.
Also, learn how to recognize signs that your diabetes therapy isnt working, and then speak with your doctor before complications arise. These signs include increased hunger, increased urination, fatigue, blurry vision, and headaches.
- Lose weight.
- Eat a balanced, healthy diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean meats.
- Monitor your intake of carbohydrates and sugary foods.
- Manage your cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Check your blood sugar level frequently when sick.
- Get seven to nine hours of sleep.
- Don’t smoke.
- Get annual physicals, vaccines, and eye examinations.
- Drink alcohol in moderation.
- Manage stress .
Editor’s Picks
Also Check: How To Know If I Got Diabetes
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The following blood tests help your healthcare provider diagnose diabetes:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: checks your blood glucose level. This test is best done in the office in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This lab test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- Glycolated hemoglobin testing measures your average blood sugar levels over three months.
- Oral glucose tolerance testing checks your blood sugar levels before and after you drink a sugary beverage. The test evaluates how your body handles glucose.
| Type of test |
|---|
Preeclampsia And Gestational Hypertension
A population-based, retrospective cohort study of 1,010,068 pregnant women examined the association between preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy and the risk of developing diabetes post partum. Results showed the incidence rate of diabetes per 1000 person-years was 6.47 for women with preeclampsia and 5.26 for those with gestational hypertension, compared with 2.81 in women with neither condition. Risk was further elevated in women with preeclampsia or gestational hypertension comorbid with gestational diabetes.
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Glucose Range
Mental Health And Diabetes
Living with and managing either type 1 or type 2 diabetes can lead to stress, anxiety and depression. This can affect your blood glucose levels and how you manage your diabetes in general. Over time, this can affect your health.It is important to talk to your doctor if you are going through times of stress, depression or anxiety. Your doctor can refer you to a counsellor or psychologist by providing a diabetes mental health plan. This is Medicare rebated.Other help is available, including:
- online resources
Depression Distress And Burnout
The demands of managing type 1 diabetes are considerable. Diabetes burnout, diabetes distress and diabetes depression are very real problems you may experience. Its important that you dont ignore your emotional wellbeing. Diabetes NSW & ACT has developed several information sheets that will provide you with useful tips to avoid these complications:
- Building happiness and wellbeing
- Food and eating
- Diabetes-related stress and distress
Diabetes NSW & ACT offers a free Psychologist on Call service. Our Psychologist, is available for confidential phone discussions to help you develop strategies for managing your diabetes and get you back to a happy fulfilling life. If you would like to access this service, contact us on 1300 342 238 to make an appointment.
Also Check: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
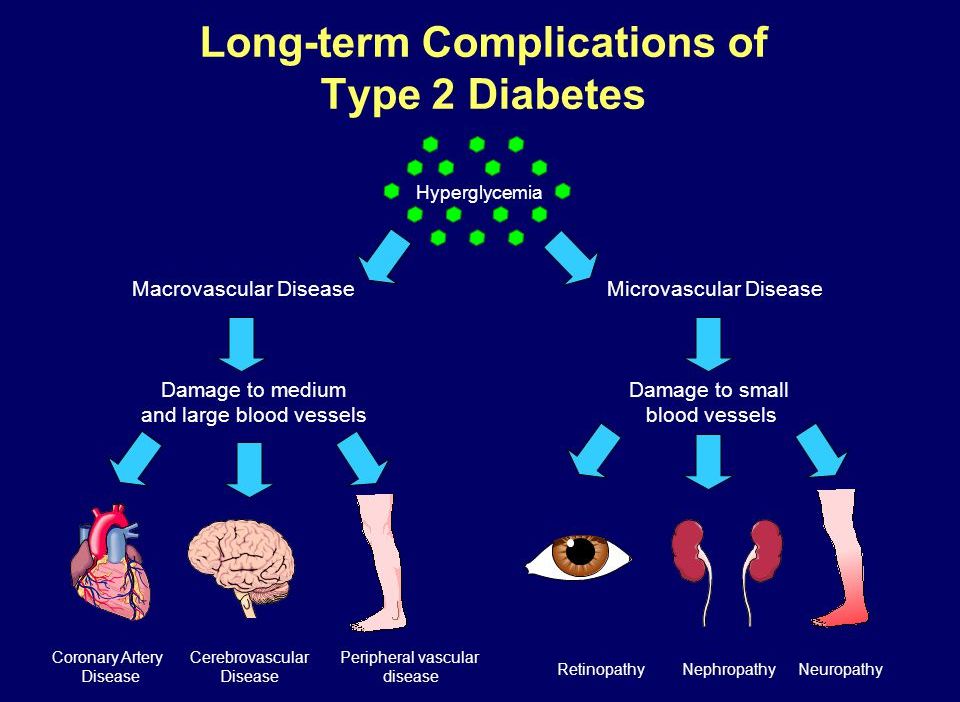
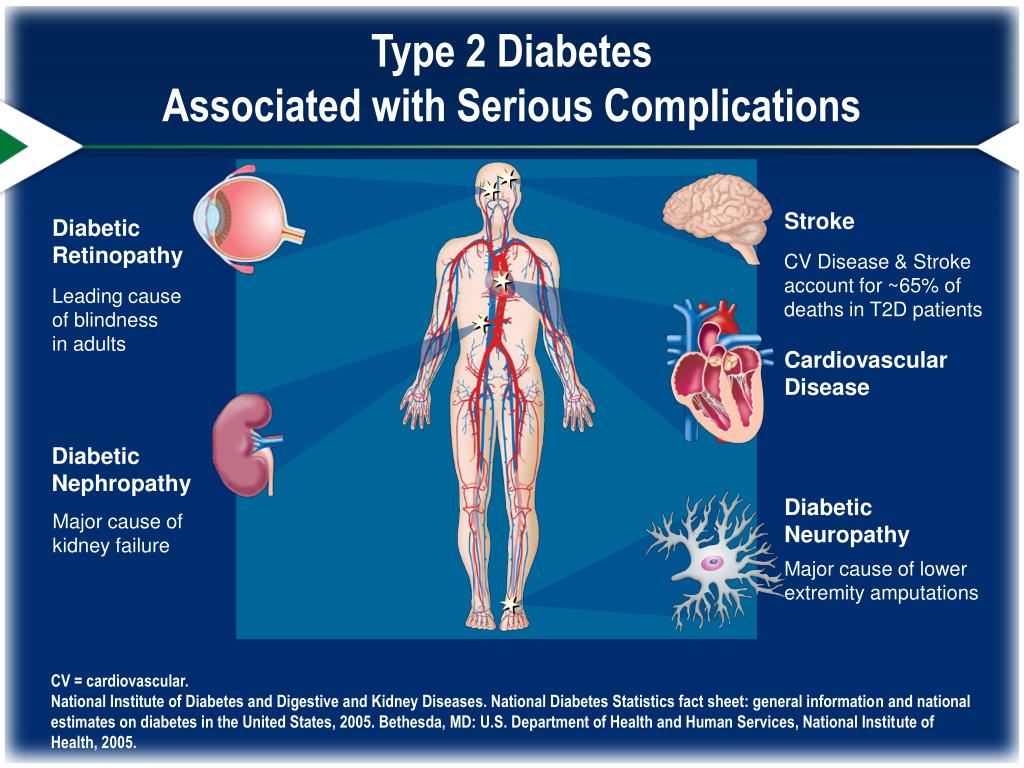
The Heart Brain And Blood Vessels
Type 2 diabetes can also affect the large blood vessels, causing plaque to eventually build up and potentially leading to a heart attack, stroke or vessel blockage in the legs .
To prevent heart disease and stroke as a result of diabetes, you should manage your diabetes well, but you should also make heart-healthy choices in other areas of your life: dont smoke, keep your blood pressure under control, and pay attention to your cholesterol.
It is important to have your cholesterol checked annually. Your doctor should check your blood pressure every office visit. Also at every office visit, the doctor should check the pulse in your feet to make sure there is proper circulation.
Type 2 diabetes comes with certain short- and long-term complications, but if you maintain good blood glucose control, you can avoid them.
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Medications for type 2 diabetes, like most other medications, can cause side-effects in some people. You can find out more about diabetes medications and their side-effects from our separate leaflet called Type 2 Diabetes Treatment.
However, one important side-effect which can affect people taking insulin and/or certain diabetes tablets is hypoglycaemia . This occurs when the level of glucose becomes too low, usually under 4 mmol/L. Not all tablet medicines used for diabetes can cause a hypo – for example, metformin does not cause this.
A hypo may occur if you have too much diabetes medication, have delayed or missed a meal or snack, or have taken part in unplanned exercise or physical activity. You can find out more about the symptoms and treatments of hypos from our separate leaflet called Hypoglycaemia .
Until about 20 years ago, the medication options for treatment of type 2 diabetes were fairly limited. Insulin, along with a group of medicines called the sulfonylureas, can cause hypos . In the last 20 years, as newer medication has been developed, many people do not need to take sulfonylureas. In fact, more and more people never need to take insulin as newer agents offer more options for type 2 diabetes treatment.
Note: hypoglycaemia cannot occur if you are treated with diet alone.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes And Sleep
You Can Be More Likely To Get Depression
Rates of depression are two to three times higher in people with diabetes than in those without the disease, says Dr. King. Scientists suspect that diabetes can contribute to depression and that depression can contribute to diabetes riska two-way street. Feeling depression-like symptoms are also a silent sign you have diabetes.
Your Memory And Mental Sharpness Can Suffer
Numerous studies suggest a link between type 2 diabetes and an increased risk of cognitive issues, including dementia. One study published in 2013 in the Journal of Diabetes Investigation found that people with diabetes were up to 73 percent more likely to develop dementia than those who didnt have diabetes. Diabetes can also damage blood vessels in the brain, which can affect blood flow and nutrient delivery to cells and contribute to a condition known as vascular dementia.
Don’t Miss: When Are You Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
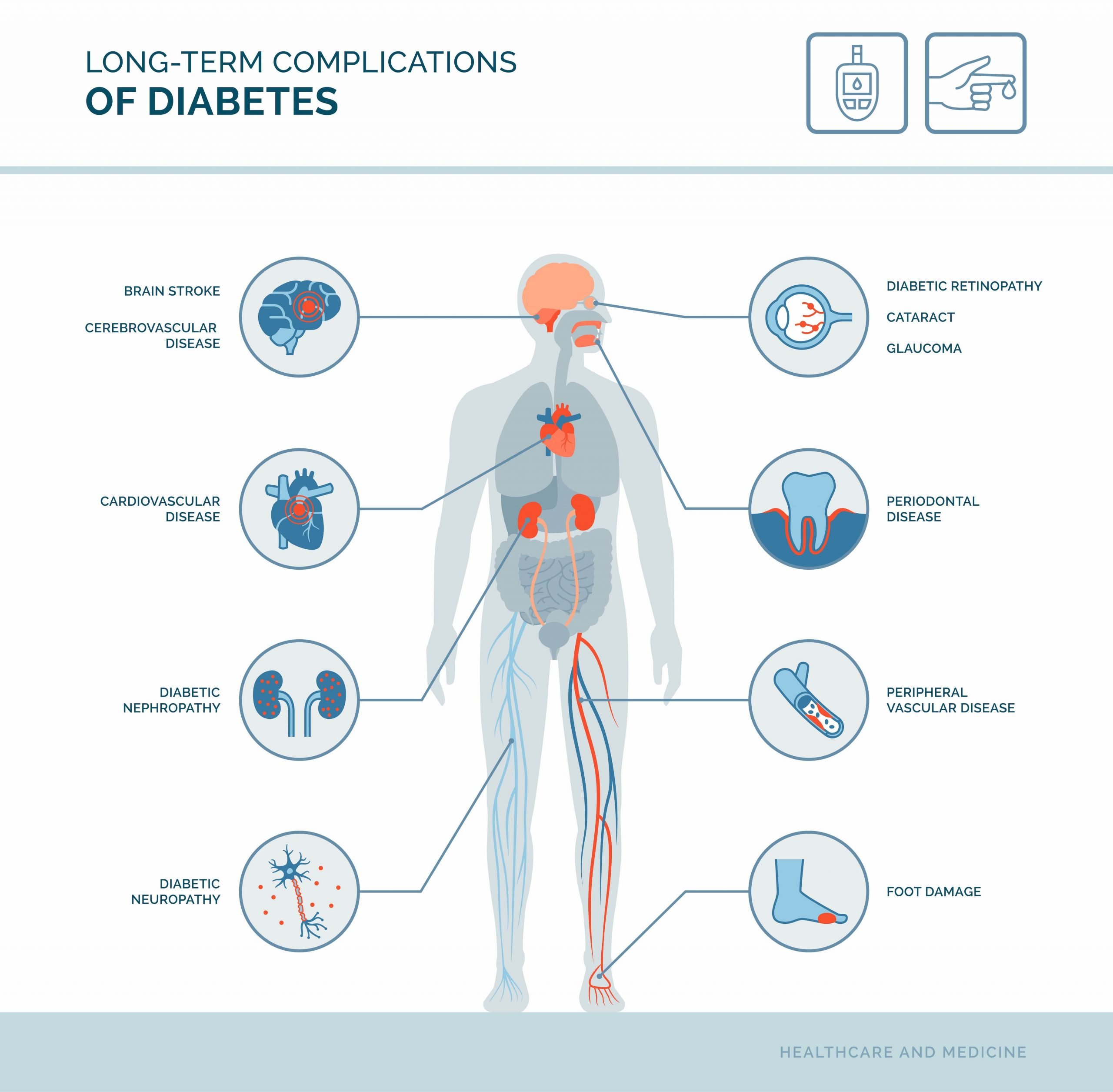
Diabetes And Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease includes blood vessel disease, heart attack and stroke. It’s the leading cause of death in Australia.
The risk of cardiovascular disease is greater for people with diabetes, who often have increased cholesterol and blood pressure levels. Smoking, having a family history of cardiovascular disease and being inactive also increase your risk.To reduce your risk and pick up any problems early:
- Have your blood pressure checked at least every six months, or more often if you have high blood pressure or are taking medication to lower your blood pressure.
- Have your HbA1c checked at least every year, or three- to six-monthly if recommended.
- Have your cholesterol checked at least every year. Further pathology tests such as an electrocardiogram or exercise stress test may also be recommended by your doctor.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible, but not too low. To do this, you will need to control your blood sugar. You will need to check it regularly.
You may be able to control your type 2 diabetes with weight loss, exercise, and healthy eating habits. But you may also need to take medicine or insulin.
Treatment may include some or all of these:
Recommended Reading: Which Type Of Diabetes Is Genetic
Put The Brakes On Diabetes Complications
A healthy lifestyle is the key to preventing or delaying complications.
Encouraging news: People with diabetes are living longer, healthier lives with fewer complications. Whats the driving force? Greater awareness and better management of risk factors. Find out what you can do to prevent or delay diabetes health problems.
Weve come a long way in reducing the impact of diabetes on peoples lives. In the last 20 years, rates of several major complications have decreased among US adults with diabetes. The greatest declines were for two leading causes of death: heart attack and stroke. This is real progress.
You Can Get More Cavities And Gum Infections
People with diabetes dont have as much saliva, which can lead to dry mouth and a greater risk of cavities and gum disease, says George L. King, research director at Joslin Diabetes Center, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and author of The Diabetes Reset. And you need normal blood sugar to maintain proper oral health, says Dr. Cypess. Its very important for people with diabetes to have regular evaluations of their teeth and gums, or else they could lose them. People with diabetes need to be more vigilant about brushing, flossing, and seeing a dentist than a person ordinarily would be.
Also Check: Can Someone With Type 1 Diabetes Join The Military
Your Heart Has To Work Overtime
According to Diabetes Canada, people with diabetes are likely to develop heart disease 15 years earlier than people without diabetes A cluster of issues is in play: Blood vessels in diabetics are more vulnerable to wear-and-tear from other risks like smoking, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
Fortunately, many of the same good lifestyle habits can help prevent both diabetes and heart disease. Even if youve heard them before, these big ones bear repeating: Stop smoking, lose weight if you need to, maintain healthy blood pressure and blood fats/cholesterol, get physical activity, and keep blood glucose levels in check.
Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Teens
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But its not always because family members are related it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
- Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks
- Eating more fruits and vegetables
- Making favorite foods healthier
- Making physical activity more fun
Healthy changes become habits more easily when everyone makes them together. Find out how to take charge family style with these healthy tips.
Also Check: Once Weekly Shot For Type 2 Diabetes
Signs And Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be so mild that you don’t notice them. About 8 million people who have it don’t know it. Symptoms include:
- Being very thirsty
- Weight loss without trying
- Getting more infections
If you have dark rashes around your neck or armpits, see your doctor. These are called acanthosis nigricans, and they can be signs that your body is becoming resistant to insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis And Tests
Your doctor can test your blood for signs of type 2 diabetes. Usually, theyâll test you on 2 days to confirm the diagnosis. But if your blood glucose is very high or you have many symptoms, one test may be all you need.
- A1c. It’s like an average of your blood glucose over the past 2 or 3 months.
- Fasting plasma glucose. This is also known as a fasting blood sugar test. It measures your blood sugar on an empty stomach. You won’t be able to eat or drink anything except water for 8 hours before the test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test . This checks your blood glucose before and 2 hours after you drink something sweet to see how your body handles the sugar.
Don’t Miss: Medicine From Canada For Diabetes
Diabetes Sick Day Rules
If you need to take insulin to control your diabetes, you should have received instructions about looking after yourself when you’re ill known as your “sick day rules”.
Contact your diabetes care team or GP for advice if you haven’t received these.
The advice you’re given will be specific to you, but some general measures that your sick day rules may include could be to:
- keep taking your insulin it’s very important not to stop treatment when you’re ill your treatment plan may state whether you need to temporarily increase your dose
- test your blood glucose level more often than usual most people are advised to check the level at least four times a day
- keep yourself well hydrated make sure you drink plenty of sugar-free drinks
- keep eating eat solid food if you feel well enough to, or liquid carbohydrates such as milk, soup and yoghurt if this is easier
- check your ketone levels if your blood glucose level is high
Seek advice from your diabetes care team or GP if your blood glucose or ketone level remains high after taking insulin, if:
- you’re not sure whether to make any changes to your treatment
- you develop symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
- you have any other concerns
Who Develops Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as maturity-onset, or non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Type 2 diabetes develops mainly in people older than the age of 40 . Over 462 million people are living with diabetes in the world, which is estimated to be 1 in 11 of the world’s adult population. It is estimated that by 2030, that figure will have risen to 540 million people. Type 2 diabetes is now becoming far more common in children and in young people.
The number of people with type 2 diabetes is increasing in the UK, as it is more common in people who are overweight or obese. It also tends to run in families. Type 2 diabetes is around five times more common in South Asian and African-Caribbean people . It is estimated that there are around 750,000 people in the UK with type 2 diabetes who have not yet been diagnosed with the condition.
Recommended Reading: Is 6.2 A1c Diabetes
Monitoring Your Own Blood Glucose
If you have type 2 diabetes, as well as having your blood glucose level checked by a healthcare professional every two to six months, you may be advised to monitor your own blood glucose levels at home.
Even if you have a healthy diet and are taking tablets or using insulin therapy, exercise, illness and stress can affect your blood glucose levels.
Other factors that may affect your blood glucose levels include drinking alcohol, taking other medicines and, for women, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
A blood glucose meter is a small device that measures the concentration of glucose in your blood. It can be useful for detecting high blood glucose or low blood glucose .
If blood glucose monitoring is recommended, you should be trained in how to use a blood glucose meter and what you should do if the reading is too high or too low.
Blood glucose meters aren’t currently available for free on the NHS but, in some cases, blood monitoring strips may be. Ask a member of your diabetes care team if you’re unsure.
Read about diabetic eye screening.
Keep Your Blood Pressure Down
It is very important to have your blood pressure checked regularly. The combination of high blood pressure and diabetes is a particularly high risk factor for complications. Even mildly raised blood pressure should be treated if you have type 2 diabetes. Medication, often with two or even three different medicines, may be needed to keep your blood pressure down but remember weight loss and exercise can really help with this too.
Also Check: How To Fill Out Fmla Paperwork For Diabetes
Gum Disease And Other Mouth Problems
High blood glucose levels can increase glucose in the saliva and cause harmful bacteria to grow in the mouth. These bacteria a person to develop mouth problems such as plaque, tooth decay, and gum disease.
Here are some symptoms of gum disease and other mouth problems that diabetes can cause:
- dark spots or holes in the teeth
- persistent pain in the mouth, jaw, or face
- loose teeth
- frequent bad taste in the mouth
- persistent bad breath that does not go away after brushing teeth